UNIT 6:EXTRACTING A TRIAL BALANCE
Key unit competence: To be able to extract a trial balance
Introductory activity 4
Observe the images below and answer the questions:
a) Make a comparison between the above three images
b) What would happen if the content of the right side of the image2 is increased without increasing the content of its left side?
5.1 Meaning, purpose and limitations of Trial Balance
Activity 5.1
a) What does the book keeper do after balancing off ledger account?
b) How does he/she proceed?
5.1.1 Meaning of trial balance
A trial balance is simply a list of account balances. It can also be defined as
a statement of debit and credit totals of balances extracted from the various
accounts in the ledger with a view to test the arithmetic accuracy of books. It
may also be defined as a table in which all the ledger accounts are listed with
their corresponding balances with the purpose of controlling at the end of the
month the general equality of all the recordings in the journal and their posting
too the ledger accounts..
5.1.2 Purpose of trial balance
i) It gives the balances of all the accounts of the ledger. The balance of any
account can be found from the trial balance without going through the
pages of the ledger;
ii) It is the check on the accuracy of posting. If the trial balance agrees, it
proves:
a. that both the aspects of each transaction are recorded;
b. That the books are arithmetically accurate.
iii) It facilitates the preparation of profit and loss account ant the balance
sheet.
iv) Important conclusion can be delivered by comparing the balances of two
or more than two years with the help of trial balances of those years.
Though agreement of the trial balance is not an absolute proof of the accuracy
of the books, disagreement is an obvious fact that an error has been committed.
You will see on the unit on error correction that there exist errors that do not
affect the trial balance. When such errors are made, the trial balance can stillbalance despite those errors
5.1.3 Limitations of the trial balance
Agreement of the trial balance is not a sound proof that the book keeping has
been carried out perfectly. There are certain book-keeping errors that do not
affect the agreement of the trial balance. This limits the scope of a trial balance
as a financial statement.
The following are the important limitations of the trial balance:
– The trial balance can be prepared only in those concerns where double
entry system of book keeping is adopted. This system is too costly.
– A trial balance is not a conclusive proof of the arithmetical accuracy of
the books of account. If the trial balance agrees, it doesn’t mean that
now there are absolutely no errors in books. On the other hand, some
errors are not disclosed by the trial balance.
– If a trial balance is wrong, the subsequent preparation of trading, profit
and long account and the balance sheet will not affect the true pictureof the concern
Application activity 5.1
a) What is the trial balance?
b) What is its content?
c) What is the main purpose of preparing the trial balance?
d) How can you know that an error is committed when preparing the
trial balance?
e) What are the limitations of the trial balance?f) How would correct trial balance be?
5.2 Preparation of the trial balance
Activity 5.2
a) What does the book keeper do after balancing off ledger account?
b) How does he/she proceed?
As mentioned above, a trial balance is a list of debit and credit balances extracted
from the ledger and aimed at checking the accuracy of the accounting process.
Accounts with net debit balances i.e. before closing the account, the total on
the debit side was more than the total on the credit side. Meaning balance
carried down is on the credit side and balance brought down on the debit
side, will appear on the debit side of the trial balance. Likewise accounts with
net credit balances will appear on the credit side of the trial balance. Ideally,
all asset accounts (except bank in case of bank overdraft or debtors in case
of advance received), expenses accounts and drawings account are expected
to have debit balances. If you get credit balances on these accounts, it might
mean that your working was wrong. Similarly, all liability accounts, revenue or
income account, capital account and reserve accounts are expected to have
credit balances. If you get a debit balance on any of these accounts, then it is
an indication that you are wrong.
In the trial balance, asset account balances are recorded in the debit column
while the accounts for liabilities and capital are recorded in the credit column.
The nominal accounts which relate to expenses and losses are recorded in the
debit column of the trial balance, but those that relate to items of income and
revenue are recorded in the credit column of the trial balance.
When constructing a trial balance therefore, place assets (e.g. motor vehicles,
stock, cash in hand and at bank, debtors, etc.); expenses (e.g. salaries and
wages, rent and rates, discounts allowed, etc.), in the debit column and liabilities
(e.g. creditors, bank overdraft, unpaid salaries, etc.), revenues or incomes (e.g.
sales, discounts received, rent received, etc.), in the credit column.
The following is the procedure to prepare the trial balance:
• Before you start off with the trial balance, you need to make sure that
every ledger account is balanced off;
• Prepare a worksheet. The column headers should be for the account
name and the corresponding columns for debit and credit balances;
• For every ledger account, transfer to the trial balance worksheet the
account name along with account balance in appropriate debit or credit
column
• Add up the amounts of the debit column and the credit column. Ideally,
the totals should be the same.
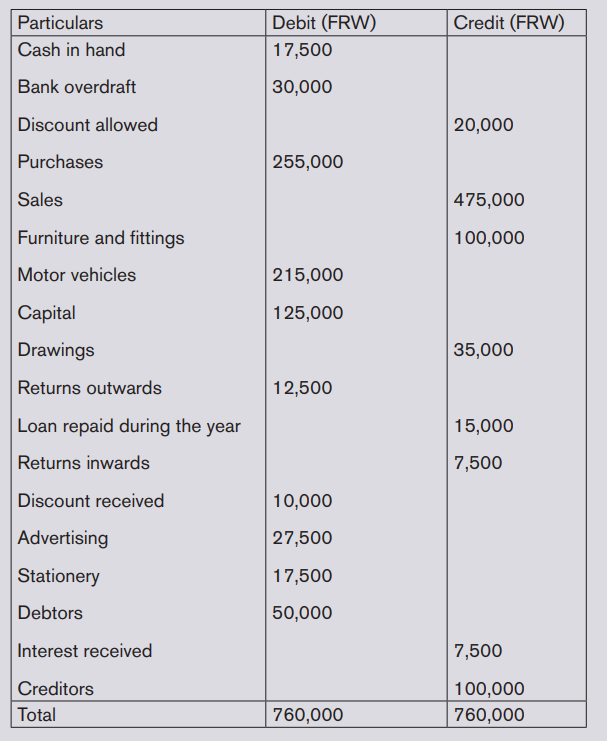
Illustration 1
Referring to the application activity 4.5 above, prepare AKANYANA Ltd’s trialbalance knowing that the closing ledger balances are the following:
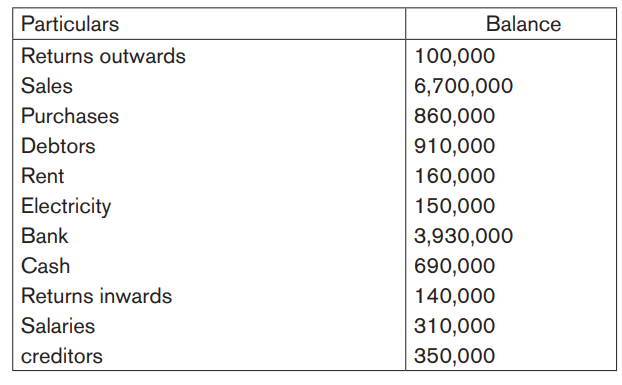
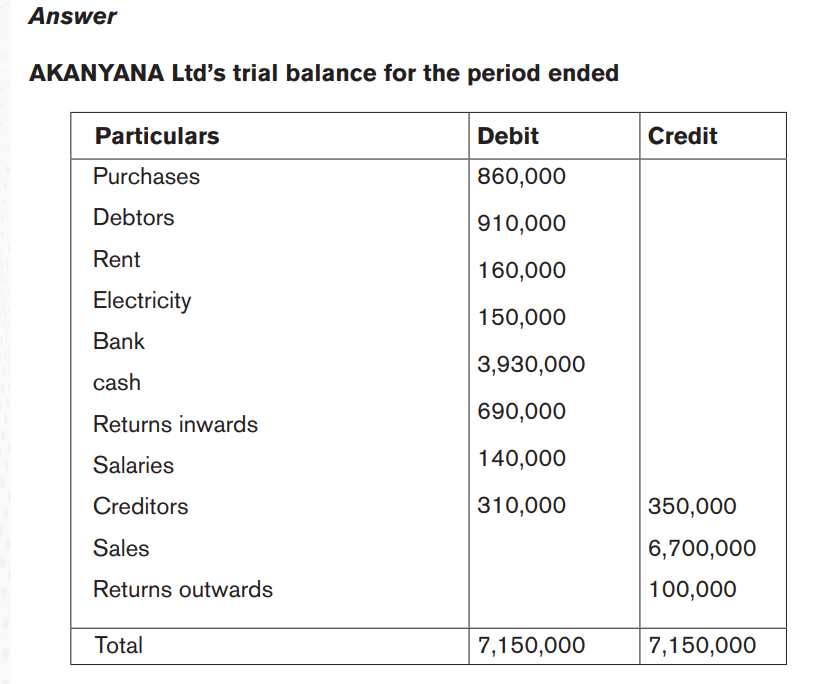
Illustration 2
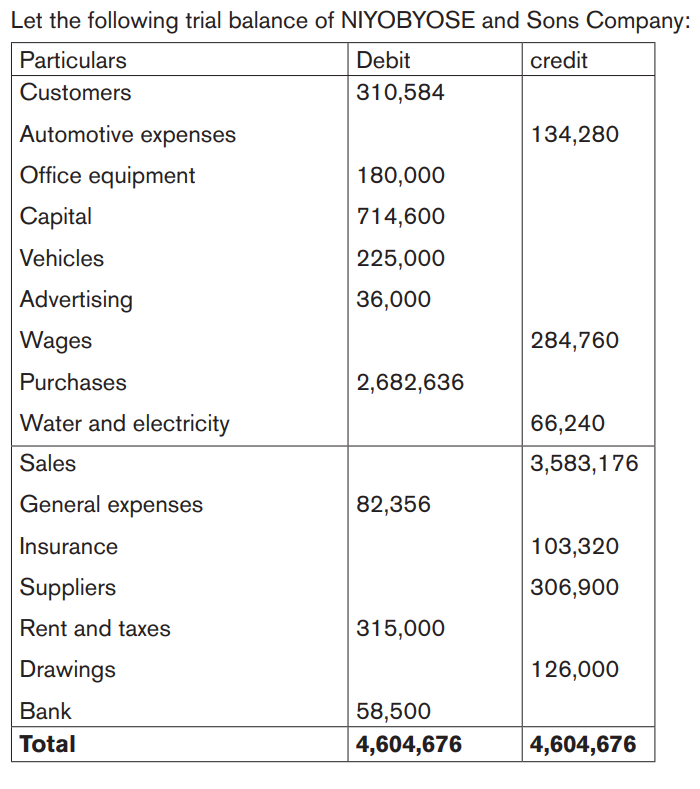
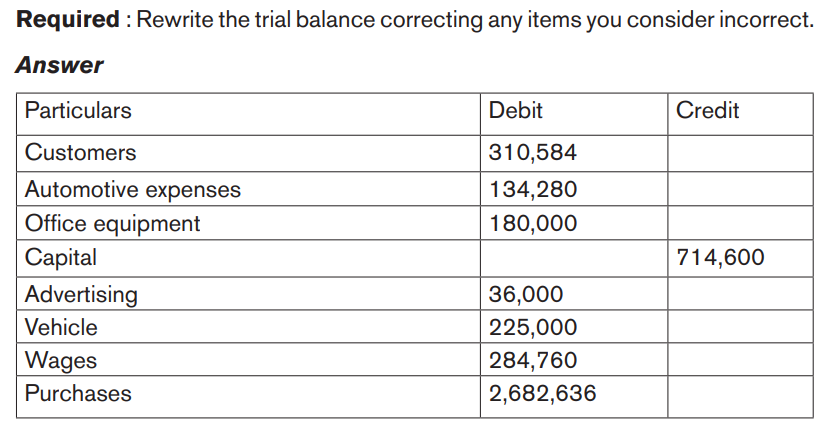
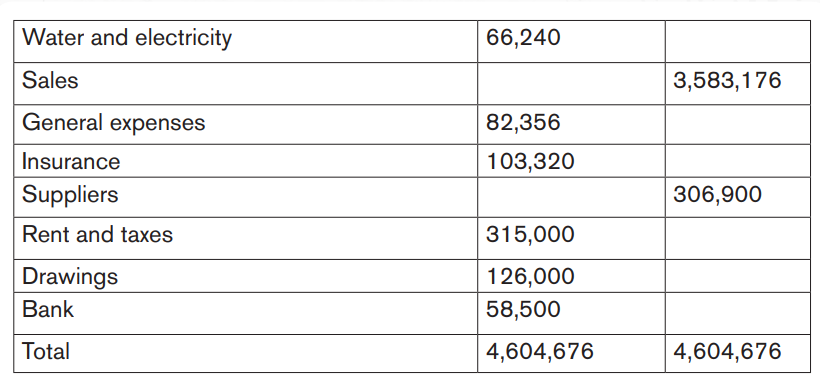
Application activity 5.2
a) How account balances are listed in the trial balance?
b) What are the main ledger accounts with debit balances?
c) What are the main ledger accounts with credit balances?
d) What does credit balance of bank account mean?
e) The following are balances in the books of ISHEJA Plc for the period
ended 31st March 2010: FRW
• Bank overdraft………...24,160
• Sales…………………...131,340
• Commission income…..13,670
• Debtors…………………41,300
• Postage and stationery... 6,000
• Repairs to buildings…. 6,200
• Heating……………….….2,130
• Purchases……………..112,100
• Cash in hand…………. 1,100
• Creditors…………… 26,950
• Premises………………269,000
• Owner drawings…… 7,150
Required: find out its capital and prepare the trial balance for theperiod ended
End of unit assessment
1. The following items were extracted from MUHIRE’S ledger account
for the year ending on 31st December 2014:
Required: Calculate the level of the owner’s capital and then prepare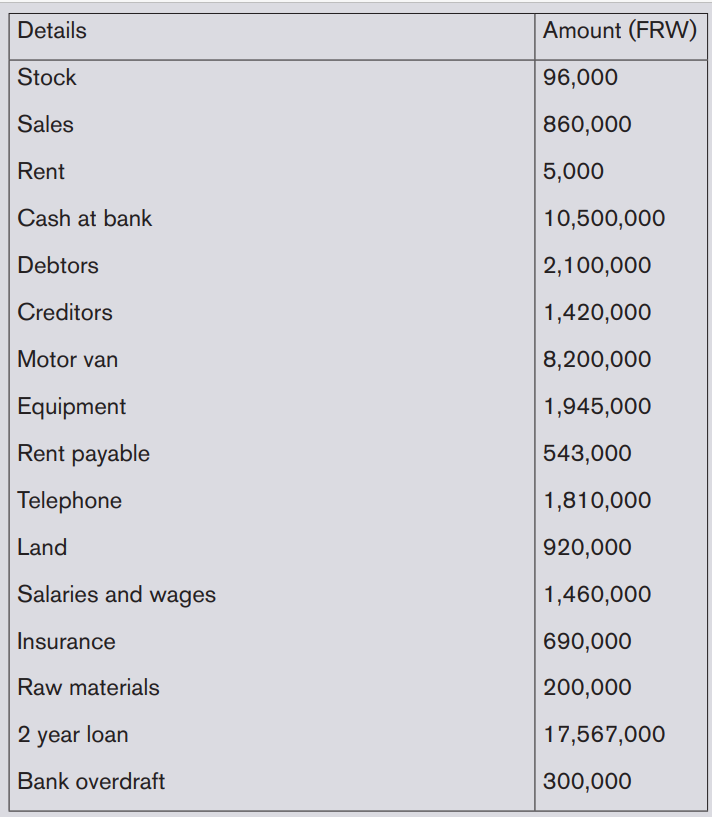
the trial balance for the period ended.
2. Rewrite the following trial balance correcting any items youconsider to be incorrect