UNIT 8: RETIREMENT, OCCUPATION HAZARD BENEFIT AND DISMISSAL COMPENSATION
Key unit competence: Ability to compute retirement, occupation hazardbenefits and dismissal compensation
Introductory activity
A Case study
RSSB provides the pension monthly to their retirees, hazard etc. many people
around in Rwanda agreed that the Rwanda Social Security Board is operating
timely for paying the right amount of pension, proper accountability for the
contributions paid by employer for the amount withhold employees. RSSBprovides medical insurance to their retirees and family dependency.
There is a high positive and significance relationship between RSSB services
and socioeconomic development of retirees in Rwanda
RSSB should implement schemes to rural areas in Rwanda by initiating
development projects such as cheaper houses, surveyed plots for sale to thesociety.
The Government of Rwanda has set objectives of reducing poverty and
promoting the welfare of people due to retirement and income decrease as
follows: “in line with the vision to make
Rwanda, a country of development and better life for all; considering the
importance of protection of social risks as a major component of inclusive
social economic development and to improve social protection system and
provide adequate protection against the adverse consequences of various life
cycle events and risks”.
From the passage above answer the following questions:
Q1. When was the Rwanda Social Security Board (RSSB) established?
Q2. Enumerate the branches currently managed by Rwanda Social SecurityBoard (RSSB).
8.1. Introduction to Rwanda Social Security Board (RSSB)
Activity 8.1
Analyze the photos below and answer the questions that follow.
Question: Observe the picture above then state the main responsibilities of
Rwanda Social Security Board (RSSB)
1. Rwanda Social Security Board (RSSB)
Rwanda Social Security Board (RSSB) was established by the law No.45/2010
of 14th/12/2010 that determines its mission, organization and functioning. This
institution was established after the merger of Social Security Fund of Rwanda
(SSFR) with La Rwandaise d’Assurance Maladies (RAMA). The above Law was
modified and completed by the law No 04/2015 of 11th/03/2015 and gave
RSSB the responsibility to manage Community Based Health Insurance (CBHI).
The mandate of the institution is to administer social security in the country.
The branches currently managed are: pensions, occupational hazard insurance,
medical insurance, Community-Based Health Insurance (CBHI) and maternity
leave benefits insurance. RSSB as a financial institution is supervised by
the National Bank of Rwanda according to the banking law N°55/2007 of
30th/11/2007 whereas its activities are overseen by the Ministry of Finance and
Economic Planning.
• Mission of Rwanda Social Security Board (RSSB)
The mission of RSSB is to manage and promote social security in Rwanda
• Vision of Rwanda social security board (RSSB)
RSSB envisions a comprehensive social security system that addresses allsocial security needs.
2. Rwanda Social Security Board (RSSB) Corporate Values
The Corporate Values of RSSB are:
• Integrity
• Collaboration
• Accountability
• Respect• Excellent
3. The main responsibilities of RSSB
The main responsibilities of RSSB are:
• To manage and promote pension, medical insurance, occupational
hazards insurance; maternity leave insurance, contributions before
retirement and other necessary schemes;
• To register employers, employees, beneficiaries and self-insured
persons in various schemes managed by RSSB;
• To collect and manage contributions as provided by laws;
• To receive and manage donations;
• To pay benefits for or to beneficiaries;
• To make investments in accordance with laws;
• To contribute to the elaboration of social security policy;
• To advise the Government on matters relating to social security;
• To establish relations and collaborate with other regional or international
institutions with similar mission;
• To continue providing medical care for retirees who have monthlypension benefits.
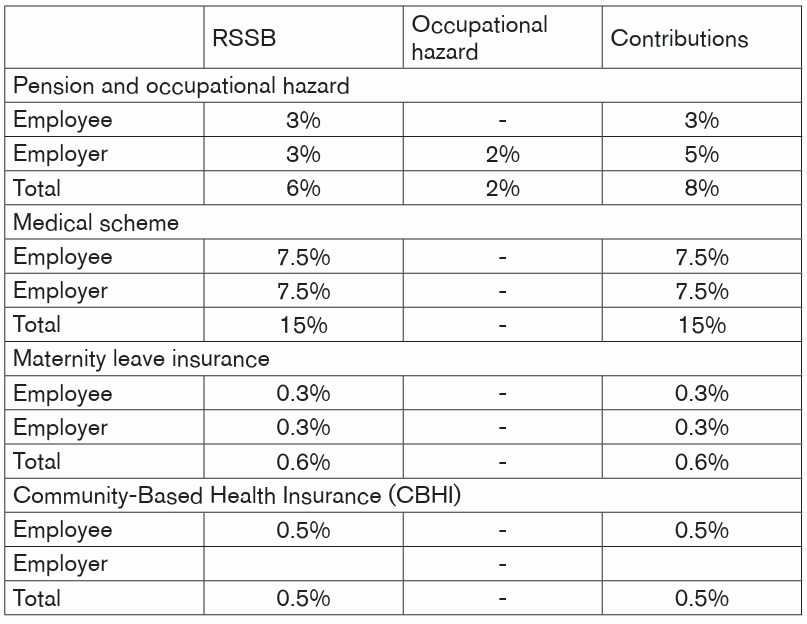
4. The contributions rate of Rwanda Social Security Board (RSSB)
branches
The main branches of Rwanda Social Security Board (RSSB) are: pension,
occupational hazard, medical insurance and maternity leave.
• The contributions pension and occupational hazards are 8% of the
employee’s remunerations (employee’s gross salary minus transport
allowances, retirement benefits and other allowances with refund
character),
• Contributions for medical branch are 15% of the employee’s basic salary
• Contributions for maternity leave benefits are 0.6% of the employee’s
remunerations (employee’s gross salary minus transport allowances,
retirement benefits and other allowances with refund character)
• Contributions for Community-Based Health Insurance in Rwanda are
0.5% of employees net salary.
Except the contributions for occupational hazard and CBHI, all those contributionsare paid by both employee and employer as shown in the table below:
Application activity 8.1
Q1. Enumerate Rwanda Social Security Board (RSSB)Corporate Values
Q2. What is the mission of RSSB?Q3. State the main branches of RSSB
8.2. Pension scheme
Activity 8.2
Case study:
Observe the picture above and answer the following questions.
Q1. Who must register for RSSB Contributions?Q2. When should people register?
8.2.1. Definition of pension scheme
Pension scheme: pension scheme is a scheme of social security which help
workers who become old and incapable of working for a salary or become invalid
and incapable of living by working. The scheme helps also the survivors of the
deceased worker. The social security benefits offered under pension’s scheme
are: old age benefits, invalidity benefits, anticipated benefits and survivors’benefits.
8.2.2. Benefits offered in pension scheme
1. Old age pension- (Eligibility conditions & requirements)
Eligibility conditions
• To be at least sixty (60) years old or to be of the age provided for by legally
recognized specific statutes; example: having attained at least 65 years of age
• To have contributed to the pension scheme for at least fifteen (15) years;• To have ceased to perform any remuneration activity.
Note:
If the member of the pension scheme reaches the retirement age without having
contributed for fifteen (15) years, he/she shall receive a lump-sum retirement allowance.
Requirements for applying for retirement benefits:
• Fill out the application form from RSSB Branch
• Birth certificate issued by the Registry Office
• Life certificate
• Copy of Identification card
• His /Her own Bank account Number opened in Rwanda
• Service testimonial from the last employer for the person who was still in service• 2 Passport photos
Note:
A person who is outside Rwanda may submit his/her application form duly
signed and stamped by Rwandan Embassy or Consulate either electronically
or by post. For a person who is unable to go to the office of social security
administration due to physical or mental disability; the application form is
submitted by his/her representative with a written proxy signed and stamped
by the competent authority of his/her residence. For a person who is in a
correctional or rehabilitation center, the administration of the center signs andstamp the written proxy of application for pension benefits.
2. The anticipated/early retirement pension benefits (Eligibility
and Requirements)
Eligibility conditions:
If an insured person becomes prematurely incapable to work and is certified so
by a commission composed of recognized medical doctors established by the
Minister in charge of health upon request by the employer or employee, he/she
is entitled to early retirement.
He/she must also have contributed for at least fifteen (15) years and haveceased to perform any remunerated activity.
Note:
An insured that is eligible for early retirement pension benefits; but who did notcontribute 15 years; he/she shall receive a lump-sum pension allowance.
Requirements for applying to early retirement pension benefits (how to apply)
• Fill out the application form at RSSB branch birth certificate issued by
the Registry Office
• Life certificate
• Copy of identification card
• Medical certificate of professional inaptitude issued by a legal medical
• Condition certificate of your working capacity issued by the employer
• 2 Passport photos• His /Her own Bank account number opened in Rwanda
3. Invalidity pension/Non occupational disability benefits(Eligibility & requirements)
Eligibility conditions:
• To have contributed for at least three (3) years;
• To have contributed up to six (6) months within a period of twelve (12)
months before the date on which his/her disability is certified by a
medical doctor;
• To have ceased to perform any remuneration activity;
• If, upon his/her request or upon the employer’s request, the disability
is certified by a recognized medical doctor and confirmed by medicalofficer for the public entity in charge of pension scheme.
Note:
If the disability results from a hazard, the member shall be eligible for disability
pension, provided he/she is a member at the time of hazard. Where the insured
person is already partially disabled and his/her disability subsequently develops
to the point where he/she can no longer perform any remunerated activity, he/she shall be deemed to be disabled.
Requirements
• Fill the application form at RSSB Branch
• Birth certificate issued by the Registry Office
• Life certificate
• Certificate of your working capacity issued by the employer
• Medical certificate of professional inaptitude issued by a doctor
approved by the Government
• Bank account number• 2 passport photos
4. Survivors’ pension
Eligibility conditions:
• The surviving spouse who did not divorce the deceased
• The legitimate orphans single, non – employed and under eighteen
(18) years of age or twenty-five (25) years of age if still studying. If
they suffer from physical or mental disability certified by a recognized
medical doctor which renders them unable to perform a remunerated
activity shall receive pension benefits until they die• The deceased’s biological or adoptive parent of the deceased.
Requirements
• Fill the application for at RSSB Branch
• Birth certificate of the insured person if the person had not yet received
old age pension
• Death certificate issued by an Officer of the Registry Office or by an
approved doctor who confirmed the death
• Marriage certificate
• Birth certificates for the deceased’s surviving children
• Certificate of legal recognition of natural children
• Certificate of guardianship issued by competent tribunal in case of the
absence or death of both the parents of the surviving children
• Certificate of school attendance issued by the Heads of schools for the
children who are still at school from age of 18 to 25 years
• Certificate of invalidity issued by medical authority for children who are invalid
• Certificate of bachelorhood or spinsterhood for the insured person who died single
• Life certificates of the beneficiaries and 2 passport photos
• Legal document for adoptive parents• Copy of identification card of the applicant
Application activity 8.2
Q1. Explain the contributors to RSSB.
Q2. Why does RSSB not provide pension benefits to close relatives (sisters,
brothers etc...) in case the contributor dies without leaving any child, spouse or parentQ3. What are the rates of the pension scheme?
8.3. Retirement benefit calculations

Activity 8.3
Scenario:
In most countries especially in Rwanda, standards of living and healthcare
advancements are allowing people to live longer. While this should be
celebrated, the implications for the financial systems, designed to meet
retirement needs but already in many nations, must be considered. As part
of the Rwanda Economic Forum Retirement Investment Systems Reform
project of retired person for continuous living without any problem of shortage
money for financing their daily expenses with employees who goes the age
of retirement.
From the Scenario above answer the following questions:
Q1. Mugisha has just reached age 60, and has contributed for 19 years.
His salary has been FRW 100,000 per month for the last 5 years. Find hisretirement benefits
8.3.1. Retirement benefit calculations
What are the retirement contributions?
Enrolling for pension benefits is compulsory for the following individuals:
• All employees governed by the Law regulating labour in Rwanda
regardless of nationality, type of contract, duration of the contract or
the number of wages;
• Employees governed by the General Statutes for public service and
civil servants governed by special statutes;
• Political appointees;
• Employees of international organizations, national non-governmental
organizations, international non-governmental organizations, faith-based
organizations and employees of Embassies accredited to Rwanda.
N.B: Employees working for an enterprise operating in Rwanda but seconded
to work for the same enterprise in another country shall remain subjected to
pension scheme applicable in Rwanda provided the duration of work does not
exceed twelve (12) months.
Employees working for an enterprise operating abroad but seconded to work for
the same enterprise in Rwanda remain subject to the pension scheme to which they
are affiliated provided the duration of work does not exceed twelve (12) months.
And this shall apply subject to international conventions ratified by Rwanda.
The contribution rates are 3% of gross salary of employee minus transport
allowances, paid by the employer and 3% by the employee.
Declaration and remittance of contribution to mandatory pension scheme are
made on monthly basis; not later than the 15th day of the month following the
month to which the contributions relate.
What are the retirement benefits?
Retirement Benefits:
If you have 15 years of service, then your pension will be 30% of your higher
average salary in the last 5 years. If you have more than 15 years of service, then
you earn an additional 2% for each additional year.
For example:
√ 32% for 16 years
√ 34% for 17 years
√ 36% for 18 years, etc.
If you have less than 15 years’ service, then you will receive a lump sum
settlement.
Pension or lump sum settlement benefits are payable from age 60 (or thepension age fixed by particular statutory arrangements).
Examples:
Retirement Benefits Example (more than 15 years’ contributions):
Mugisha has just reached age 60, and has contributed for 19 years. His salary
has been FRW 100,000 per month for the last 5 years. His benefits are therefore:
38% x FRW 100,000 = FRW 38, 000 per month pension for the rest of his life
Retirement Benefits Example (less than 15 years’ contributions):
Kagabo has just reached age 60, and has contributed towards the pension
scheme for a period of 9 years. His monthly salary was FRW 85,000 per month
during the last 5 years. His benefits are therefore:
Lump Sum Settlement = FRW 85,000 x 9 = FRW 765,000
There is no pension payable in this case as Kagabo has not contributed for 15years.
8.3.2. Survivor benefit
What benefits are paid in case of death?
In the event of death, your eligible survivor will be entitled to either a survivor’smonthly pension or a survivor’s lump sum settlement.
A. Survivor’s pension
A survivor’s pension is payable when you die in retirement (normal, early or
invalidity) and you fulfil the required conditions for receiving a pension.
Who are your eligible survivors?
– The surviving spouse who did not divorce the deceased
– The children who are unmarried, not working for a salary and are either
the deceased’s legitimate children, legally adopted or those born outside
wedlock but recognized as his or hers by law. They must be aged less
than 18 years old, or less than 25 years old if still in full time education and
without age limit if they are disabled and cannot work for a salary.
– The deceased’s own or adopted parents i.e., if he or she left no wife orhusband or children.
How is the survivors’ pension calculated?
Survivors’ pensions are calculated in percentages based on the pension whichthe deceased was receiving or was eligible to receive at the time of death.
The percentages are:
• 50% of the old age pension for the widow
• 25% for each child (where the other remaining parent is still alive)
• 50% for each child (where both parents are now deceased)
• 25% for each direct or adopted parent when the deceased leaves nowife, husband or children
For example:
If Mugisha had a pension of FRW 38,000 when he died, what will be the
survivor’s pension be for his wife and son?
• His wife would receive FRW 38,000 x 50% = FRW 19,000 per month
• His son would receive FRW 38,000 x 25% = FRW 9,500 per month
• If Mugisha’s wife dies, his son would receive FRW 38,000 x 50% =
FRW 19,000 per month
• If Mugisha leaves no wife or children, the direct or adopted parents
would receive FRW 38,000 x 25% = FRW 9,500 per month
Please note that the total amount of pension for the survivors cannot exceed
100% of the amount the deceased was entitled to get.
• The wife would have been entitled to 50% pension
Thus, if Mugisha had a wife and 4 children, the following pension would be
payable:
• 4 children would have been entitled to 25% x 4 = 100% pension
• Total pension = 50% + 100% = 150% (but this needs to be capped
at 100%)
• The revised pension is therefore prorated for the wife, and becomes:
FRW 38, 000 x = FRW 12, 666
• The revised pension is therefore prorated for each child, and becomes:
38,000 FRW x = FRW 6, 333
B. Survivor’s Lump Sum
This is payable when a pension to the member was not previously payable (as
the criteria had not been met – i.e. less than 15 years’ service).
How are the survivors’ Lump Sum calculated?
The survivor will receive a lump sum equal to the pension to which the beneficiary
was entitled if they had completed 15 years of insurance multiplied by thenumber of 6-month periods they actually completed.
For example:
Rukundo contributed for 4 years (which is 8 complete 6-month periods). If he
had contributed for 15 years then he would have received a 30% of salary
pension.
Each child will receive half of the widow’s lump sum as long as the total for
all the children’s lump- sum benefits do not exceed the double of the widow’s
lump-sum.
Lump Sum payment to the wife = 30% x FRW50,000 x 8 (6-month periods)
= FRW120,000 Lump sum payment per child = FRW 120,000 x 50% =
FRW60,000
Total lump sum payments = FRW 120,000 + (FRW 60,000 x 4) = FRW360,000
If Rukundo leaves no wife or children, his direct or adopted parent will have alump sum that is equal to 50% x FRW 120,000 = FRW 60,000 for each parent.
NB: Pension benefit are paid monthly
Application activity 8.3
Q1. Who are eligible for Survivor’s pension?Q2. How is the survivors’ pension calculated?
8.4. Occupation hazard computations

Activity 8.4
Case study
In Rwanda, RSSB is facilitates personnel affected by accidents and covers
employee health, safety and welfare at the workplaces. Hospitals as the
largest group in health care industry in Rwanda, hazards are faced to the
employees at the time doing with major hazards categorized as chemical,
biological, physical, ergonomic and psychosocial risks. Although Rwanda
demonstrates rapid economic growth, amount person saves practically have
not been fully enough for financing if an employee is affected by an accident.
For this reason, the employer needs to assess risks for health staff, contribute
for planning of health services and enhance regulations. Which provides more
consistency in decision process and gives an appropriate final rank of hazard
types. On conclusion of the hazard control hierarchy, measures are overtaken
for the hazards and areas open for improvement are presented so that the
employer makes sure that all employees are registered in RSSB in order to
fight against the level of inability to meet hospitalization cost.
From the passage above answer the following questions:
Q1. What are occupational hazards?
Q2. What is the contribution of occupational hazards?Q3. Outline the the benefits for occupational hazards scheme.
8.4.1. Occupational hazards
1. Definition of Occupational hazards
An occupational hazard is a scheme under RSSB which provides assistance to
employees and employers in the risk of illnesses or accidents in the workplace. The
benefits covered by RSSB under occupational hazard scheme are: medical care,
daily sickness allowances, incapacity social security benefits and survivors’ benefits.
Meaning that, in case of occupational accident or disease, an employee
who has suffered from it while his/her employer has contributed for him/ her
in a social security body in Rwanda, he/she is entitled to compensation inaccordance with Laws governing social security in Rwanda.
2. What is the contribution of occupational hazards?
A contribution of 2% of salary is paid on behalf of mandatory members byemployers. There is no employee contribution towards this benefit.
3. What are the benefits of occupational hazards?
On satisfying the criteria to make a claim, the benefits cover you for:
• Free medical care
• Daily sickness allowances
• Incapacity social security benefits
• Incapacity lump sum benefits• Survivors’ benefits
4. Categories of benefits
• The temporary incapacity benefit is: 75% of average daily earnings in
the last 3 months payable until full recovery or certificate of permanent
incapacity for a maximum of 180 days.
• The permanent incapacity benefit is: a pension of 85% of average
monthly earnings in the last 3 months payable.
• Partial permanent incapacity benefit: is given according to the degree
of incapacity in proportion to the pension the beneficiary would get if
they had been permanently incapacitated.
– If the degree of the incapacity is at least 15%
- the percentage of full pension according to the degree of incapacity.
– If the degree of the incapacity is less than 15% - then a lump sum payment
equal to 3 years’ pension according to the degree of incapacity is awardedto the beneficiary.
5. How are survivors’ allowances calculated?
The survivor’s allowances are fixed percentages of salary, as follows:
– 30% for the widow or widower
– 15% for each child of the father or mother (with the other remaining parent
surviving)
– 20% for each child of father and mother (with both parents deceased)
– 10% for each direct or adopted parent. An accident befalling a worker
at the occasion of a crime or an offence committed by the worker or anintentional fault on his or her part is not covered by RSSB.
6. How do I make a claim?
• Inform your employer and area labour inspector directly, as soon as possible.
• Give precisions relating to circumstances i.e., place of accident, eye
witnesses, third party responsible for the accident. As soon as all
information is received, the employer will fill the accident declaration(A1) in 6 copies.
• The doctor should fill in the medical certificate of the first-hand state of
the injury sustained (A2).
• Ask the doctor to give RSSB a medical certificate of the prolongation of
incapacity of injuries every 30 days. This prolongation must not exceed
150 days.
• You must equally inform your employer to give the RSSB a receipt of
payment/non-payment.
• At the end of the treatment, ask your doctor to fill the certificate of
healing and consolidation of injuries (A5).• Keep careful the bills for medical treatment or food given by the hospital.
Application activity 8.4
Q1. Discuss about how survivors’ allowance for occupation hazard are
calculatedQ2. Outline the categories of benefits according to the occupation hazard
8.5. Dismissal compensation (terminal benefits)

Activity 8.5
Scenario
KARERA Company ltd is a company registered with RDB. 10 years ago,
it hired employee following employment law. During this week, KARERA
Company ltd has gone bankrupted for technical reason.
Employer has decided to cancel all employment contracts.
From the Scenario above answer the following questions:
Q1. What is terminal benefits?
5. Terms used
– Terminal benefits
Terminal benefits can be expressed as benefit given to an employee upon
the ending of the employment relationship as a result of economic reasons,
technological transfer or sickness– Definition of dismissal
Dismissal is a process where an employee’s employment contract is terminated
after an employer expels him from work. In short, the employee’s services will
no longer be required by the employer. This can be due to a number of reasons
such as theft, incompetence, decline in business, incapacitation of the employeedue to medical ground, etc.
6. Why dismissed employees should receive their terminal benefits
Under Law n° 66/2018 of 30/08/2018 regulating labour in Rwanda, chapter
II: employment contract, apprenticeship and internship contracts, Section 2:
Termination of employment contract and dismissal of employee, article 31 it
is provided that any employee is entitle of terminal benefits for termination of
employment contract as a result of economic reasons, technological transfer or
sickness.
Without prejudice to other provisions of this Law, the termination of employment
contract due to economic reasons, technological transfer or sickness for an
employee having served for at least twelve (12) consecutive months entails theemployee’s right to terminal benefits.
7. Terminal benefits for termination of employment contract as a
result of economic reasons, technological transfer or sickness
Apart from clauses of the collective agreement or individual employment contract more
favorable to the employee, terminal benefit can in no way be less than:
• Two (2) times the average monthly salary for the employee having less
than five (5) years of service with the same enterprise;
• Three (3) times the average monthly salary for the employee having
between five (5) and ten (10) years of service with the same enterprise;
• Four (4) times the average monthly salary for the employee having
between ten (10) and fifteen (15) years of service with the same
enterprise;
• Five (5) times the average monthly salary for the employee having
between fifteen (15) and twenty (20) years of service with the same
enterprise;
• Six (6) times the average monthly salary for the employee having
between twenty (20) and twenty-five (25) years of service with the
same enterprise;
• Seven (7) times the average monthly salary for the employee having
over twenty-five (25) years of service with the same enterprise.
The average monthly salary is obtained by dividing by twelve (12) the total
salary the employee has received for the last twelve (12) months exclusive of
allowances allocated to the employee to enable him/her to perform his/her
duties.
The terminal benefits must be paid within seven (7) working days of the dismissal
of the employee.
The terminal benefits provided for under this Article are also allocated to an
employee whose employment contract is terminated after six (6) months due to
sickness in case he/she is unable to resume a work.
Illustration:
Q1. Mahoro is an employee in KEZA Maize Ltd company since year 2000
with an annual average salary of FRW 5,400,000. In 2022, he has received a
dismissal notice due to the economic issues of the company.
Required: Calculate Mahoro’s dismissal compensation.
Answer
Number of years= (Ending time - Starting Time) + 1
From 2000 to 2022: 23 years
From 0 to 5: 2 times monthly salary
From 5 to 10: 3 times monthly salary
From 10 to 15: 4 times monthly salary
From 15 to 20: 5 times monthly salary
From 20 to 25: 6 times monthly salary
Monthly average salary: = FRW 450,000Dismissal compensation: FRW 450,000 x 6 = FRW 2,700,000
Application activity 8.5
Q1. Kagiraneza is an employee in MUSANZE cement LTD company from
year 2004 with an annual average salary of FRW 6,600,000. For the year
2022, he has received a dismissal notice due to the economic issues of the
company.
Required: Calculate the Kagiraneza’s dismissal compensation.
Q2. How do you determine the terminal benefits for termination of employment
contract as a result of economic reasons, technological transfer or sicknessgiven the employee office tenure?
Skills Lab 8
Via internet search or visit of resource person from RSSB, students write
a note on the following:
• Retirement of employees
• Occupation hazard profits of employees
• Dismissal compensation benefits for employees according toRwanda Labor Law.
End of unit assessment 8
Q1. Fabien Fashaho has been employed by the company for 32 years. He
has respectively attained 68 years and wishes to retire ended 2019 from
employment.
Five years preceding the admissibility to the pension he received the
following salaries:
• 5th year (2015): FRW 480,000
• 4th year (2016): FRW 540,000
• 3th year (2017): FRW 600,000
• 2nd year (2018): FRW 660,000• 1st year (2019): FRW 720,000
Advise him on the benefits and amounts he is entitled to.
Q2. Amahoro employs Innocent and pays him a basic salary of FRW
57,000 and a cash allowance of FRW 2,000 for transport and FRW 3,000
for airtime related to calls on behalf of the business.
Required: Find the contribution of RSSB Pension for Innocent
Q3. What are RSSB contributions?
Q4. Who collects RSSB contributions?
Q5. After the work accident, AMANI, ALICE, and MUGISHA were seriously
hurt. AMANI was hospitalized during 30 days. ALICE’s incapacity was
total and that of MUGISHA, less than his colleague was evaluated to 20%.
Each of them received the following monthly wages during the three (3)
months preceding their accident:
July: FRW 340,000; August: FRW 230,000; September: FRW 450,000.Required: Show the amounts each of them is entitled to.
REFERENCES
ICPAR. (2019). Taxation. London: BPP LEARNING MEDIA LTD.
ICPAR. (2020). Company Law. Kigali: Institute of Certified Public Accountants
of Rwanda.
Miller, R., & Jentz, G. (2008). Business Law Today: The Essentials. Thomson
West: 674: Cengage Advantage Books.
Mustard Seed Corporate Center. (2016, March 28). Advantages and
disadvantages of a manual vs computerized payroll system. Quezon City,
Pinyahan, Phillipines.
Parliament of the Republic of Rwanda. (2015, March 28). Law No. 06/2015 of
28/03/2015 relating to investment promotion and facilitation. Official Gazette
No. Special of 27/05/2015, pp. 02-36.
Parliament of the Republic of Rwanda. (2018, March 13). Law No. 16/2018
of 13/04/2018 establishing taxes on income. Official Gazette No. 16 of
16/04/2018, pp. 48-134.
Parliament of the Republic of Rwanda. (2018, August 30). Law No. 66/2018
of 30/08/2018 regulating labour in Rwanda. Official Gazette No. Special of
06/09/2018, pp. 02-104.
Parliament of the Republic of Rwanda. (2020, October 07). No. 017/2020 of
07/10/2020 Law establishing the general statute governing public servants.
Official Gazette No. Special of 08/10/2020.
Parliament of the Republic of Rwanda. (2020, December 11). Ministerial Order
No.003/20/10/TC of 11/12/2020 establishing general rules on transfer pricing.
Official Gazette No. 40 of 14/12/2020, pp. 02-55.
Parliament of the Republic of Rwanda. (2021, February 05). No. 007/2021
of 05/02/2021 Law governing companies. Official Gazette No. 04 ter of
08/02/2021.
Rich, S., Jones, P. J., Heitger, L. D., & Mowen, M. M. (2010). Cornestones of
Financial & Managerial Accounting. Ohio: South-Western Cengage Learning.
RRA. (2019). RRA Tax Handbook, 2nd Edition. Kigali: Rwanda Revenue
Authority.
RRA. (2022, March 30). rra.gov.rw/index.php?id=32. Retrieved from rra.gov.
rw: http://www.rra.gov.rw
RSSB. (2018). Understanding Social Security, Edition 2018. Kigali: Rwanda
Social Security Board.
Rwanda Prime Minister’s Office. (2020, September 30). Oder No. 105/03
of 30/09/2020 related to the community-based health insurance schemecontributions. Official Gazette No. Special of 01/10/2020, pp. 03-20.
