UNIT 3: BUSINESS IDEAS AND OPPORTUNITIES



3.1.1. Definition
A business refers to any economic activity that involves the production, selling of goods and services, covering risks with the aim of getting profits.
A business idea is a thought about the possibility of a business. It can also be defined as a thought that an entrepreneur may come up with as a result of scanning the environment with the purpose to develop a business activity. Examples of business ideas in Rwanda include Real estates, clothing and textiles, food processing,
E-Commerce, internet and computer services, food delivery services, photography and videography, horticulture business. Business ideas are internal to the entrepreneur because they originate from the entrepreneur’s mind. Ideas are not visible, but they can be shared through discussions.
Generating a good business idea is the first step towards transforming the entrepreneur’s desire and creativity into a real business. Generating viable business ideas is an innovative and creative process. Not everyone can have a viable business idea. One can have so many business ideas but all of them may not be turned into real businesses simply because there are no matching business opportunities.
Business Opportunity is an identified situation that can be turned into a real and profitable business activity. Business opportunities are situations or circumstances that create a good environment to implement a business idea. Business ideas and business opportunities are complementary for one to succeed.
When business ideas meet opportunities, then there is a high chance to turn them into real business activities “Ceteris paribus”
. Contrary, when a business opportunity arises but there is no business idea, that opportunity is lost. However, to some people in some instances business opportunities may trigger business ideas.
3.1.2. Characteristics of a viable business idea
In the previous definitions, it has been indicated that “not all business ideas can be turned into real business activities” This is to mean that “All business ideas can’t be viable”
. A viable business idea will be characterized by the following:
•Available market demand (number of willing buyers / customers)
• Simplicity to turn it into real business
• Accessibility of factors of production (Land, Labour, Capital, entrepreneur, Time, etc.)
• Favorable government policy
• Conducive social & cultural factors
• Availability of required technology
• Value creating (Is the intended business product going to add any advantage to the already existing products?) • Availability of required funds, etc.
3.1.3. Sources of viable business ideas and opportunities
Before you start a business, you must decide on the business you are to engage in. you must have a business idea. The question is where to get the idea from? Some people may copy businesses they see other people doing while others come up with unique business ideas. Business ideas may be:
• Completely new business ideas
• Modified business ideas (improving upon an existing idea - Franchises) or
• Using differently an existing business idea Any of the above business ideas may be developed from any of the following sources:
a) Personal skills and experiences:
You can generate a business idea based on what you can do with the skills you possess. What do other people normally ask you to help them do
b) Changes in the business world:
Most of the new changes may not yet be fully exploited and thus present opportunities. As an entrepreneur, you need to monitor changes in various business aspects to come up with possible business ideas.
c) Filling gaps in existing business:
If you realize that there are some unmet customer’s needs, then it is your opportunity to provide the missing product hence filling in the gap within the existing business model.
d) Visiting and learning from other businesses and entrepreneurs: By visiting other businesses and entrepreneurs, you may identify the needs of that business that you can meet or simply learn from them on how things are done
e) Attending trade shows and exhibitions:
Trade shows and exhibitions provide opportunities to study customers’ behavior, identify needed products, identify suppliers etc.
f) Interviewing different people:
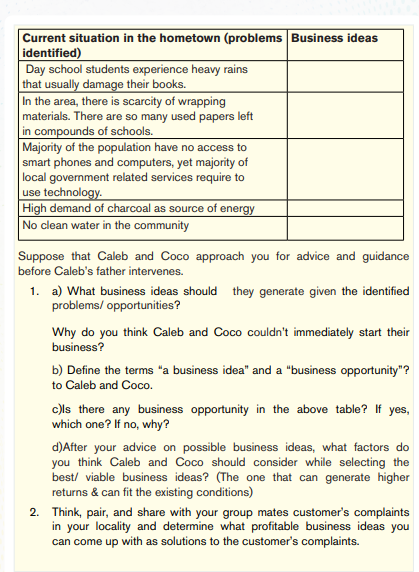
Through interviews, one can discover people’s problems, needs, complaints etc. Societal problems are the best sources of business ideas & opportunities. If in a certain area, day school students struggle with rain on their heads & back, providing affordable waterproof jackets, bags and boots; This will be an ideal business.
g) Information from the media:
Through radio, newsletters, TV and internet one can understand business trends and environment, know what is scarce, what is on demand, what is on fashion and much more information, Etc.
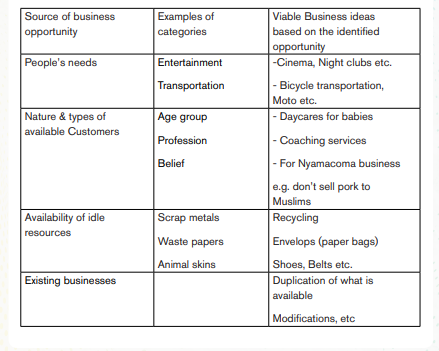
On the other hand, business opportunities can also be as a result from:
h) People’s needs
i) Nature & types of available customers
j) Availability of idle resources
k) Existing businesses, etc.

been subjected to prescribed screening achieved break-even sales faster than those businesses that had undergone purposeful searches. Below are some factors to consider when deciding what business opportunity to pursue.
• Identified market need or gap; the nature of the identified need or challenge in the market or customer need will influence an entrepreneur’s choice of a business idea. A person is likely to choose an opportunity which he/she thinks will solve the identified market needs.
• Growing market: most people want to avoid the hustles of starting a new business. So, they will choose ideas or opportunities that are easy for them to start their businesses while others may choose ideas that give them a chance to be creative.
• Low funding requirements: The amount of funding required to implement a business opportunity may influence one’s choice of a business idea. Most people will choose opportunities that do not involve a lot of funding in relation to profits.
• Vision or goals: The choice of a business opportunity will greatly depend on the vision or goals of the entrepreneur. These could be short term or long-term goals.
• High profit margins: Of course, on every entrepreneur’s mind is profit. The profit margin expected from the opportunity will greatly influence one’s choice.
• Not easily copied: Every entrepreneur of course wants to protect their ideas, protect intellectual property and develop a brand reputation. So entrepreneurs are likely to choose ideas/ opportunities that cannot be easily duplicated in the market at least in the short run.
• Inheritance: Inheritance is the practice of passing on properties, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. Most people would prefer continuing in the line of family business than going for new business opportunities.
• Discovery vs Purposeful: Some entrepreneurs absolutely believe that choosing viable business ideas must be through a purposeful search for opportunities while others believe that a viable business idea is something that had been readily available and overlooked but now discovered accidentally. Businesses established on accidentally discovered venture ideas and which had not been
subjected to prescribed screening achieved break-even sales faster than those businesses that had undergone purposeful searches.

3.3.1. How to evaluate a business idea
After getting a business idea, it is important to analyze it and be sure it is profitable and worth to be implemented. The following factors should be taken into consideration while evaluating your business idea:
• Is the business legal?
• What are the entry barriers?
• What problem is going to be solved?
• Are there potential customers?
• How big is the market?
• What are the requirements to start?
• What is your Unique Selling Proposition (USP)?
• What is your exit strategy?
• Is the idea profitable?
• What is the expected Return On Investment (ROI)? Etc.
1.3.2. Evaluating business ideas using SWOT analysis
To set meaningful business, entrepreneurs should first look at what would be the business strength and weaknesses, then opportunities and threats to the business. This will help them to evaluate different business opportunities and then arrive at a decision of what to do in business. There are two approaches to internal and external analysis for business opportunities.
Inside out approach: Entrepreneurs evaluate themselves first in terms of skills, experience and abilities and then try to find how they can apply them in the business world and create a product for the market.
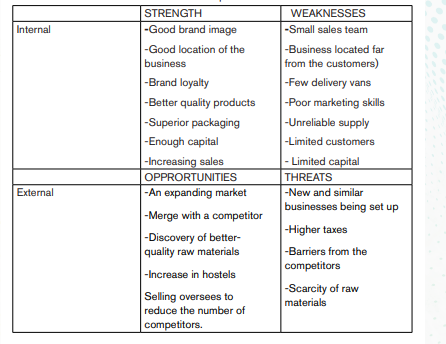
Outside in approach: Entrepreneurs study the environment in terms of market needs, availability of resources and other external factors and then relate the identified gaps and opportunities to themselves.
-S- Strengths: They increase the chances of success of the business opportunities
-W- Weaknesses: These are likely to frustrate chances of success.


