UNIT 1: SELECTED NURSING THEORIES
Key Unit Competence:
Integrate the principles of nursing theories in the current nursing practiceIntroductory activity 1
Picture:
Look at the scenario represented by the image below carefully, and attempt to
answer the asked questions.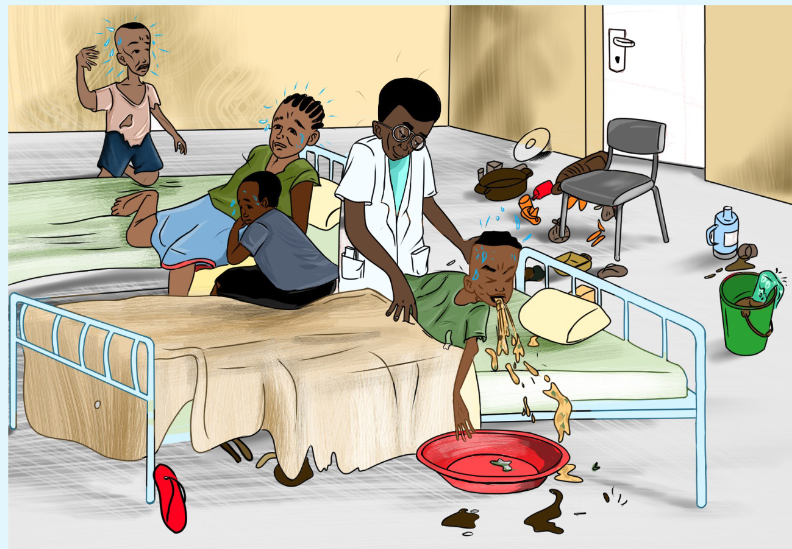
1) In which situation are the people in this Picture?
2) Which kind of issues can you find from this image?
3) Suggest what would happen when the identified issues from the image
are not solved?
4) Think about how patients were helped before modern nursing?
1.1. Historical Overview of NursingLearning activity 1.1
As you have learned in other subject, each science has its own history. Using
the following links: https://brainkart.com/article/Evolution-of-Nursing_35445/;
or using the Library books (fundamentals of nursing) search on Nursing
Evolution.Identify main periods of nursing evolution and what happened in each period
1.1.1. Concepts definition.
Different people have defined nursing in different ways. However, Nursing
is defined as a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of
individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover
optimal health and quality of life. The nurse is a caregiver or someone who has
been formally trained and educated to tend to the sick and infirm.According to ICN, “Nursing encompasses autonomous and collaborative care of
individuals of all ages, families, groups and communities, sick or well and in all
settings. Nursing includes the promotion of health, prevention of illness, and the
care of ill, disabled and dying people. Advocacy, promotion of a safe environment,
research, participation in shaping health policy and in patient and health systems
management, and education are also key nursing roles.The primary responsibility
of a nurse is to provide nursing care for patients, family and community. In addition,
the nurse plays an important role that include patient advocator, teacher/educator,
leader, collaborator, caregiver, communicator, counsellor, and researcher.Patient: Is someone who is waiting for or undergoing medical treatment and care.
The word “patient” comes from a Latin word meaning “to suffer” or “to bear”.
Traditionally, the person receiving health care has been called a patient. The
connotation commonly attached to the word is one of dependenceClient: A client is a person who engages the advice or services of another who is
qualified to provide this service. The term client presents the receivers of health
care as collaborators in the care, that is, as people who are also responsible
for their own health.
Health: WHO (1947) World Health Organization– definition of health
“a state of complete physical, mental, spiritual and social well- being, not merely
the absence of disease or infirmity”Illness: is referred as the condition in which an individual functions at optimal levels.
It means engaging in attitudes and behavior that enhance the quality of life and
maximize personal potential.Health-illness continuum: Wellness is a dynamic process that is ever
changinCaring: includes assistive, supportive and facilitative acts toward or for
another individual or group with evident or anticipated needs. Caring serves to
ameliorate or to improve human conditions or life ways. Caring is essential to
human development, growth and survival.Caring: includes assistive, supportive and facilitative acts toward or for another
individual or group with evident or anticipated needs. Caring serves to
ameliorate or to improve human conditions or life ways. Caring is essential to
human development, growth and survival.1.1.2. Evolution of nursing
In the times before nursing became an official profession, patient care was
commonly provided to sick people by family, friends, clansmen, or fellow tribe
members. Nursing began as a helping profession, often undertaken by nuns and
military personnel during wartime. Until recent history, nursing was considered
a woman’s profession. Although the origins of nursing predate the mid-19th
century, the history of professional nursing traditionally begins with Florence
Nightingale. The nursing profession has a rich history that spans centuries of
evolving health care for patients, families, and communities. At present, the World
Health Organization (WHO) considers nurses as the backbone of the health care
industry. However, nursing had to undergo a long period of development before
it became the occupation, we are now familiar with. Evolution of nursing can be
divided into three periods of time in history, Early Christian age, Middle age, and
the dawn of modern Nursing.a) Early Christian age
Health care started to become more organized during the early Christian age.
Christianity believed that one should render services of love to humanity without
any reward. It was equal to one’s sincere love to gods. The temples were more
like health spas rather than hospitals in religious institutions governed by priests
and nursing was done by women in temples or home. The caregivers had no
formal training in therapeutic modalities and volunteered their time to nurse the sick.
Deaconesses’ women, with some educational background, were assigned by the
church to take care of ill persons. The Deaconess Phoebe is considered by some
historians to be the first “visiting nurse” because of the home care services she
offered around A.D. 50. This principle was integrated later in nursing and helped to
improve the status of nursing.b) Middle age
Monks and nuns devoted their life to the care and services of the poor and sick.
During the middle age, hospitals in large Byzantine cities were staffed primarily by
paid male assistants and male nurses. These hospitals were established primarily
as charity houses, medical practices in Western Europe remained basically
unchanged until the 11th and 12th centuries, when formal medical education for
physicians was required in a university setting and nursing become differentiated
from medicine and surgery. Although there were not enough physicians to care for
all the sick, other care-givers were not required to receive any formal training. The
dominant caregivers in the Byzantine setting were men; however, this was not true
in the rural parts of the Eastern Roman Empire and in the West. In these societies,
nursing was viewed as a natural nurturing job for women.When taking a sight at nursing in the Middle Ages, there were numerous
advancements and innovations that were implemented within the nursing industry
during these years, helping to form some of the roots of modern nursing. Hospitals
functioned in innumerable ways, housing lepers and refugees among the typical
sick and injured patients. It was due to this that a nurse’s role within the hospital
involved a wider range of duties than may be seen today.c) Modern Nursing:
The dawn of modern Nursing is a very different field than it was before the world
wars, and even before the Crimean War. The history of modern nursing originates
from the pioneering work of Florence Nightingale. Through innovative nursing care
and influence, Nightingale laid the foundation for nursing as an official profession.
Nightingale, who belonged to a wealthy British family, chose not to lead the leisurely
life of a typical upper-class lady during the Victorian era. Instead, she devoted her life
to providing nursing services to sick persons, even if it was not considered a proper
occupation for women in her social class during that period. Miss. Nightingale was
the first to mention Holism (Treating the whole patient) in Nursing. Nightingale was
the founder of modern nursing. In 1860, Nightingale also opened the first nursing
school, called the Nightingale School for Nurses, which began to regulate how
nurses learned and practiced. Not only did this ensure nurses had an educational
foundation of knowledge and techniques, but it helped ensure a standard of care
for patients, as well.Because of the work Nightingale did for modern nursing, the oath taken by nurses
when they graduate is called the “Nightingale Pledge.” The field of health care is
also more diversified, so nurses can choose what area they would like to practice,
and tailor their education to that field. A nurse may choose paediatrics, emergency,
hospice, cardiology, or a number of other areas, and focus his or her efforts on
the care of patients in that area. In the modern nursing field, nurses have a higher
reputation, as well. They are no longer seen as simply assistants to physicians
who do the things physicians won’t do. Instead, nursing is a strong field of its own,
and nurses have a wide range of duties and responsibilities. Nurses earn respect
for themselves among health care professionals because of the education and
experience required to be a nurse.In Rwanda, training of nurses began during the colonial era, many of the nursing
schools were opened by religious institutions such as Catholics, Protestants
and Adventists, some being public and private. During 1980s, education was
restructured and the secondary program was fixed to 6 years; the nursing program
was integrated in secondary education. In 1994, the Genocide against the Tutsi
has seriously affected all sectors of life especially nursing. After the 1994 Genocide
against the Tutsi, the Government of Rwandan invested in training nurses at various
levels, and many public and private nursing and midwifery schools were opened.
Today, with the support from the Government of Rwanda, Nursing and Midwifery
professions are becoming a pillar and cornerstone of Rwandan Health system.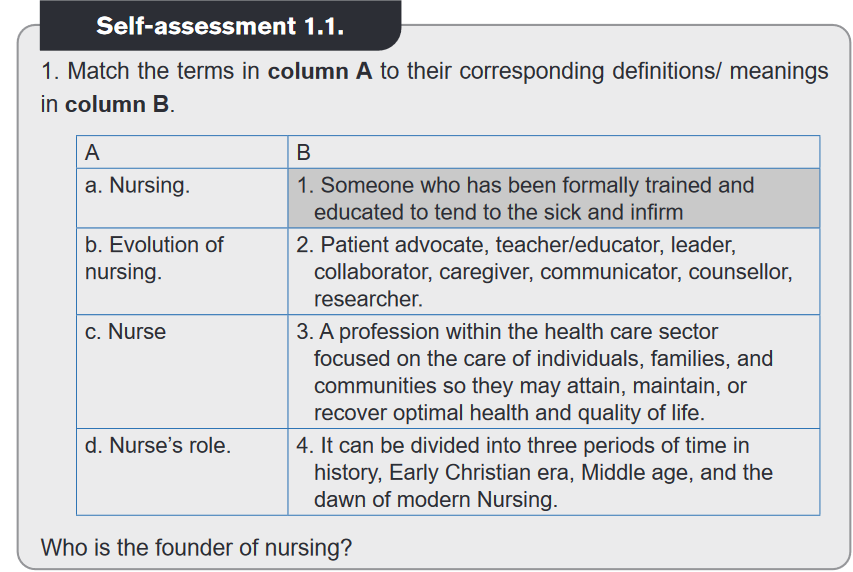

A: With a crush car in accident where there are two survived person (Mrs M and Mrs
T),
B: the survived persons moved to the hospital, both Mrs M and Mrs T is transported
on stretcher,
C: Mrs M was well cared for by a nurse removing dirty clothes, washing her, moving
her from stretch to well make bed
D: There a doctor examining the Mrs M (greetings, ask what happen, how is she
feeling, where she has pain, the patient reply that nothing is ok she feel pain
everywhere, the doctor reassures the patients “do not worry you are in good hand
everything will be ok, let us do x-ray investigation to see if there is no fracture.
E: Mrs T sitting in the wheelchair, with many lacerations on both arms and one leg,
being drowsy, no body care about her.Observe the images and answer the following questions
Between the two persons, which one have received good care and why?
1.2.1. Definition of nursing Theory
Nursing theory is “an organized framework of concepts and purposes designed
to guide the practice of nursing”. It expresses the values and beliefs of nursing
discipline, creating a structure to organize knowledge and illuminate nursing
practice. Nursing theories help us to describe, explain, or predict caring practices.
Briefly nursing theory give us directions of how-to best care for our patients. The first
nursing theories appeared in the late 1800s when a strong emphasis was placed on
nursing education. Nursing theories are developed to explain and describe nursing
care, guide nursing practice and provide a foundation for clinical decision making.
Examples: During care to any patient, you must ensure that the patient has good
hygiene, his surroundings are clean, has fresh air in room, room is warm, has
light, and patient has taken food. This instruction/framework requesting the good
environment of the patient is an example of Theory. The nursing theory to be used
in caring the patients in mental health services will not be the same as the one to
be used in Emergence service1.2.2. Purpose of nursing theories
They provide a foundational knowledge of care concepts that enable those in the
profession to explain what they do for patients and the reasons for their actions.
It helps nurse’s articulate evidence that justifies the methodologies behind their
practice.Self-assessment 1.2.
Answer these questions
1) What do you understand by the term ‘’Nursing theory?
2) Do you think nursing theories are important? Justify your answer.1.3. Major Concepts of Nursing Theory
Learning activity 1.3.
Rwanda as a developing country is building strongly health sector for wellbeing
of its population as it is its precious resources, as an associated nurse your
contribution will require to understand the set of ideas or concepts that provide
the structure for how nursing discipline should function. Read the Page 40
in the book “Kozier and ERB’s Fundamental of nursing concepts, process
and practice fourth Australian Edition”; on “Metaparadigm for nursing” and
in three to four sentences, summarize what you have read in the book.1.3.1. Concept of nursing theory.
A concept, is like ideas, are abstract impressions organized into symbols of reality.
It describes objects, properties, events and relationships among them. Nursing
concept is a fundamental nursing perception also called the metaparadigms of
nursing. They provide the framework for understanding nursing practice.1.3.2. Element of Concepts of Nursing Theory
There are four major concepts of nursing theory which are frequently interrelated
and fundamental to nursing theory: person, environment, health, and nursing.
They are collectively referred to a metaparadigm for nursing.a) Person
Is referred to Client or Human Beings. Person is the recipient of nursing care and
may include individuals, patients, groups, families, and communities.b) Health
The degree of wellness or wellbeing that the person experiences. It may have
different meanings for each patient, the clinical setting, and the health care provider.c) Nursing
The nurse’s attributes, characteristics, and actions provide care on behalf of or
in conjunction with the client. There are numerous definitions of nursing, though
nursing scholars may have difficulty agreeing on its exact definition.d) Environment:
Environment is defined as the internal and external surroundings that affect the
client. It includes all positive or negative conditions that affect the patient, the
physical environment, such as families, friends, and significant others, and the
setting for where they go for their healthcare.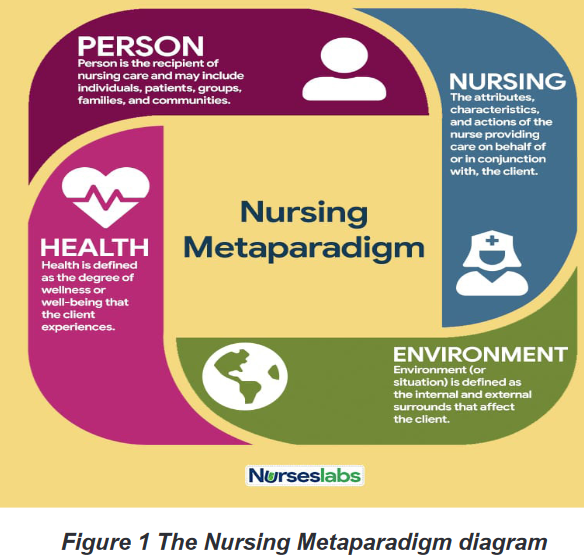
1.4. Selected Nursing theorists
1.4.1. Florence NightingaleLearning activity 1.4.1.
Observe the images below and respond to the questions that follow:
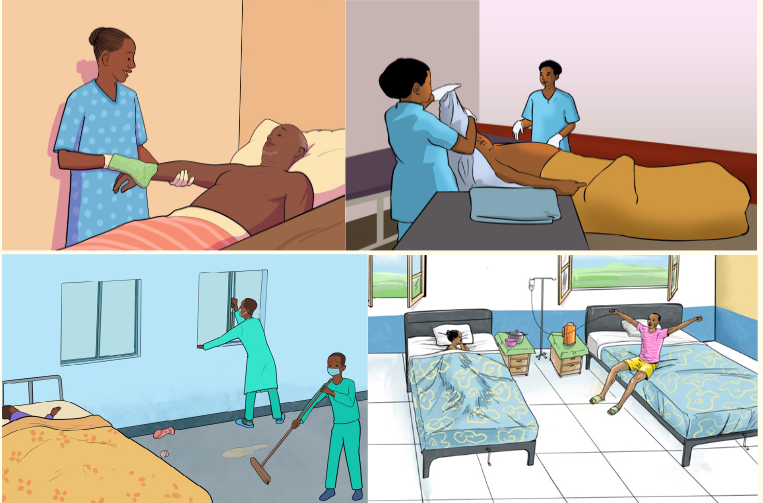

1) Observe the first three images and describe activities that are being
done,
2) What do you think would happen if these activities are not performed?
Florence Nightingale, “the mother of modern nursing”. Florence Nightingale
(1820-1910) was a British nurse, best known as the founder of modern nursing and
“The Lady with the Lamp” because she would visit soldiers at night with a small
lantern in her hand. Her experiences as a nurse during the Crimean War were
foundational in her views about sanitation. Florence Nightingale is the first nurse
theorist well known for developing the environmental theory. Her theory focused on
the environment. She linked health with five environmental factors.In Florence Nightingale’s Environmental Theory, she identified five (5) environmental
factors: fresh air, pure water, efficient drainage, cleanliness or sanitation, and light
or direct sunlight.a) Pure fresh air
“To keep the air he breathes as pure as the external air without chilling him.”b) Pure water
“Well water of a very impure kind is used for domestic purposes. And when
the epidemic disease shows itself, persons using such water are almost sure to
suffer.”c) Effective drainage
“All the while the sewer may be nothing but a laboratory from which epidemic disease
and ill health are being installed into the house.”d) Cleanliness
“The greater part of nursing consists in preserving cleanliness.”e) Light (especially direct sunlight)
“The usefulness of light in treating disease is very important.Deficiencies in these five factors produced lack of health or illness.
In addition to the above factors, Nightingale also stressed the importance of
keeping the patient warm, maintaining a noise-free environment, and attending to
the patient’s diet in terms of assessing intake, timeliness of the food, and its effect
on the person. Her general concepts about ventilation, cleanliness, quiet, warmth,
and diet remain integral parts of nursing and health care today. “To facilitate “the
body’s reparative processes” by manipulating client’s environment”External influences can prevent, suppress or contribute to disease or death
– Nightingale’s concepts• Person/ client
– Patient who is acted on by nurse
– The recipient of nursing care
– Affected by environment
– Has vital reparative powers to deal with disease• Environment
– The major concepts for health are ventilation, warmth, light, diet,
cleanliness, and absence of noise. Although the environment has social,
emotional, and physical aspects, Nightingale emphasized the physical
aspects.
– Internal and external environment were both important to the progress of
the patient’s health.
– The importance of fresh air and ventilation and an environment free of
odors and waste, she knew that properly prepared food and clean water
were also necessary.• Health
– Being well and using one’s powers to the fullest extent.
– Maintaining well-being by using a person’s powers
– Nightingale saw health as an absence of disease
– Health is maintained through prevention of disease via environmental
health factors. Maintained by control of environment and taking care of
the body, health was achieved.• Nursing
– Provision of optimal conditions to enhance the person’s reparative
processes and prevent the reparative process from being interrupted.
– Provided fresh air, warmth, cleanliness, good diet, quiet to facilitate
person’s reparative process
– Facilitates a patient’s reparative process by ensuring the best possible
environment
– Influences the environment to affect healthFlorence Nightingale (1860) defined nursing as: “the act of utilizing the
environment of the patient to assist him in his recovery. Nightingale considered a
clean, well-ventilated, and quiet environment essential for recovery. What nursing
has to do is to put the patient in the best condition for nature to act upon him.
Application of Florence Nightingale theory in nursing education and practice:
The environmental theory of Florence Nightingale is the basis of nursing practice
today. Nurses use the environmental aspects of Nightingale’s theory (ventilation,
warmth, quiet, diet, and cleanliness) in their daily practice to care for patients with
different conditions to assist them in recovery. In addition, Nightingale’s principles
of nurse training provided a universal template for early nurse training schools and
is still evident in today’s nursing programs across the world.Self-assessment 1.4.1.
Read this cases study and criticize according to nightingale theory.
1) In hospital X, where Miss MUKAMANA, associated nurse went for
clinical placement; there was a very small general ward, overcrowded
by patients, with closed windows and small open door in corner. There
were also 3nurses, 4 students; the patient’s belongings were on floor
under bed. With Miss MUKAMANA’s observations, she saw one nurse
feeding the patient A, Nurse MAHORO together with nurse KANYANA
after doing patient B wound dressing and administrating painkiller they
moved him outside for Sunlight exposure as the patients was recovering
and prepared to be discharged. Miss MUKAMANA was very surprise to
see nurses doing all these interventions and her supervisor told her
that it is very good, “Nurses have to care for and respond to all patient’s
Needs.2) Florence Nightingale was known as
a) Nurse who changed nursing forever.
b) Nurse responsible for the end of Crimean war.
c) Lady with the lamp.
d) Mother of nursing.
e) c & d3) The Theory of Florence nightingale focus on the clean environment.
State environmental factors it focused on.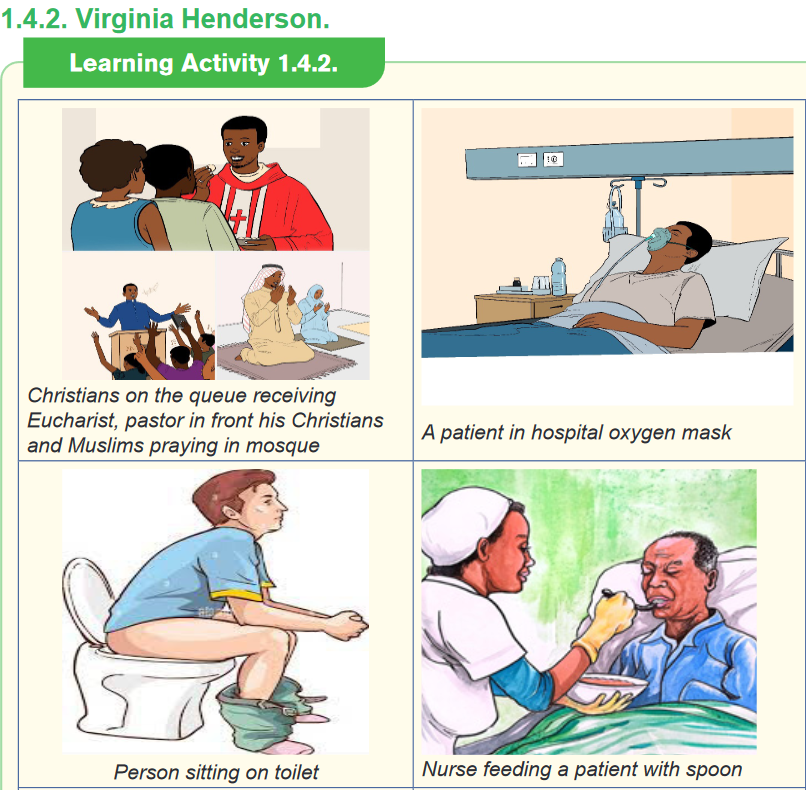
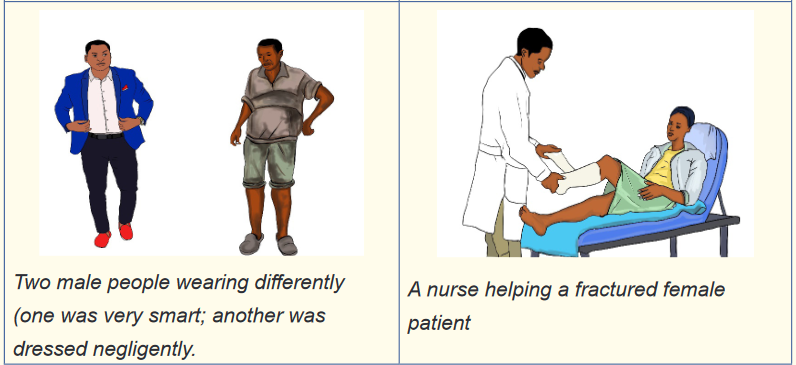
) Observe the different boxes of images and describe how you see the
personnel on the images.
2) Do you think what you have observed are important in our life? Justify
your answer.
Virginia Avenel Henderson (November 30, 1897 – March 19, 1996) was a
nurse, theorist, and author known for her Need Theory. According to Henderson,
individuals have basic needs that are components of health. Virginia Henderson
consider Person, health, nursing and environmental as:
– Person:Individual have basic needs that are component of health and require
assisstance to achieve health and independence or a peacefuldeath– Heath :Balance in all aspect of human life.
– Nursing: Unique function of the nurse is to assist the individual, sick or well,
in the perfomance of those activities contributing to health or or its recovery
that he would perfome unaided , if he has the necessary strenght , will or
knowledge.In such way as to help him to gain independence as rapid as
possible.– Environment: Maintaining a supportive environment conductive for health.
The 14 components of Virginia Henderson need theory show a holistic nursing
approach covering the physiological, psychological, spiritual, and social needs.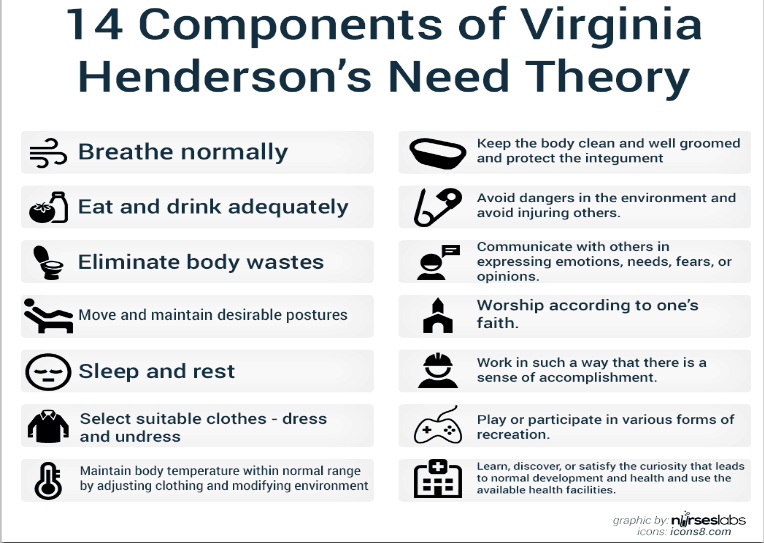
Application of Virginia Henderson theory in nursing education and practice:
Today the nurses use Henderson’s needs theory in their routine practice to set
patient’s goals based on 14 components of Henderson ‘s theory. To utilize this in
the nursing practice, the nurse would see whether the client has all of these basic
needs. If not, then, a problem exists. The nursing diagnosis must be then formulated
and the nurse must assist the client to meet all these 14 fundamental needs.Henderson’s Needs Theory is used in different nursing schools to help the students
learning how to assess the basic needs of a patient, understanding the significance
of theory and determine the situation in which it can be used to assist the patients
regaining independence.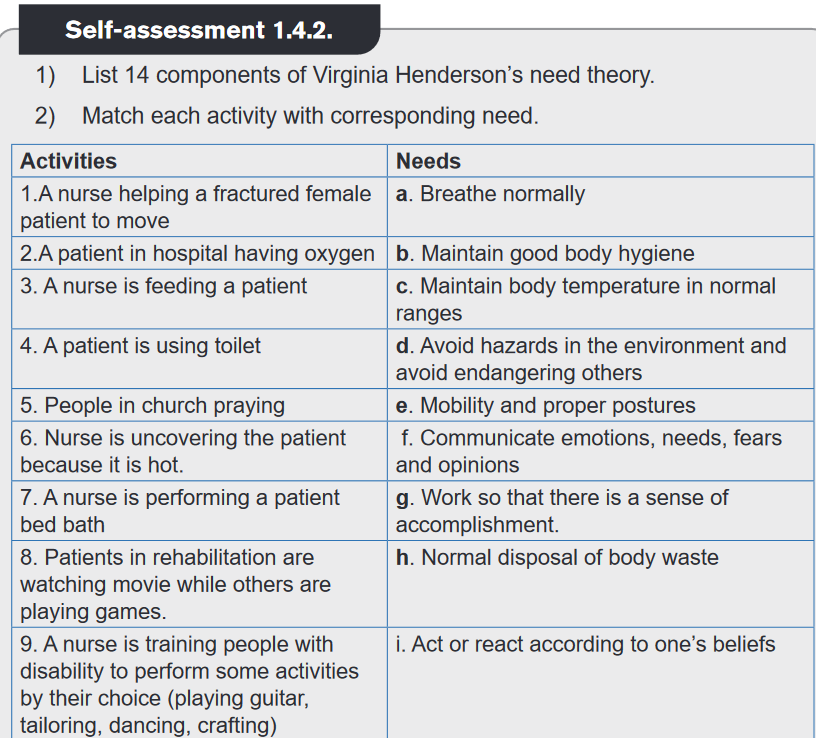
1.4.3. Hildegard Peplau
Learning Activity 1.4.3.
1) Follow the nurse-patient conversation between patient KARAKE (Mr. K)
and nurse UWIMANA and respond to these questions.
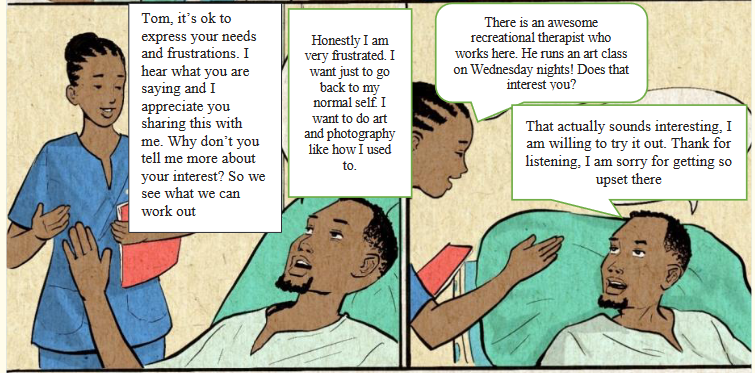
a) In which emotional status is patient Tom Karake?
b) Why patients Tom Karake feels unhappy?
c) What is Nurse UWIMANA doing?
d) How nurse UWIMANA arrived to calm down KARAKE?
e) How the conversation ended up?
2) Do you think it is good to have someone who could understand you?
Explain your answer.
Hildegard Elizabeth Peplau (September 1, 1909 – March 17, 1999) was an American
nurse. She became the first publisher of nursing theory since Florence Nightingale.
Hildegard Peplau’s interpersonal relations theory emphasized the nurse –client
relationship as the foundation of nursing practice. Peplau frequently acknowledged
the importance of patients’ experiences of nursing care. Peplau’s theoretical work on
the nurse patient relationship continues to be essential to nursing practice. Peplau
developed the four levels of anxiety (mild, moderate, severe, and panic levels) that
are the standards nurses use in assessing anxiety. Peplau believed that nurses
play an important role in helping clients reduce their anxiety and in converting it
into constructive action. Large institutions are educating their workforce on the
importance of having a relationship, a connection with those with whom the nurse
interacts and to whom he or she provides care. How Peplau’s theory view person,
health, nursing and environmental?• Person: An organism that strives in its own way to reduce tension generated
by needs or organism that lives in an unstable balance of a given system.• Health: symbolizes movement of the personality and other ongoing human
Fundamental of Nursing | Associate Nursing Program | Senior 4 21
processes that directs the person towards creative, constructive, productive
and community living.
• Nursing is defined as an interpersonal, therapeutic process that takes place
when professionals, specifically educated to be nurses, engage to recognize
and respond to people who are in need of health services though therapeutic
relationships cooperatively
• Environmental: Peplau does not directly address society environment, she
encourages the nurse to consider the patient’s culture and mores when the
patient adjusts to hospital routine. Forces outside the organism and in the
context of the socially –approved way of living, from which vital human social
process are derived such as norms, customs and believedApplication of Hildegard Peplau theory in nursing education and practice:
Peplau came out with four levels of anxiety (mild, moderate, severe and panic levels).
These levels are used by nurses as standards in the anxiety assessment. Peplau
trusted that nurses have a major role in assisting clients minimize their anxiety
and transform it into productive deed. Peplau’s theory continues to be necessary
in nursing practice particularly on the nurse-patient relationship. Nursing schools,
hospitals are educating their students/workers the necessity of relationship; how
important it is to interact with those that they provide care.Self-assessment 1.4.3.
Answer the following questions:
1) Which of the following best describe Peplau’s theory?
a) Putting patients’ needs ahead of your own
b) Providing excellent clinical skills to improve patient’s health status
c) Use excellent interpersonal skills to help patients improve their
health status
d) Self-protection though avoidance of a relationship with the patient2) Peplau viewed nursing intervention as those that:
a) Support the implementation of doctor orders.
b) Direct the wants and desires of the patients
c) Are soundly based on nurse knowledge?
d) Assist patients in gaining interpersonal and intellectual competencies
grown through the nurse –patient relationship.1.4.4. Dorothea Orem
Learning Activity 1.4.4.
1) Observe the images below and list the activities observed on each image.
2) When observing those images who do you think maybe in need of such
kind of care provided as mentioned by the images?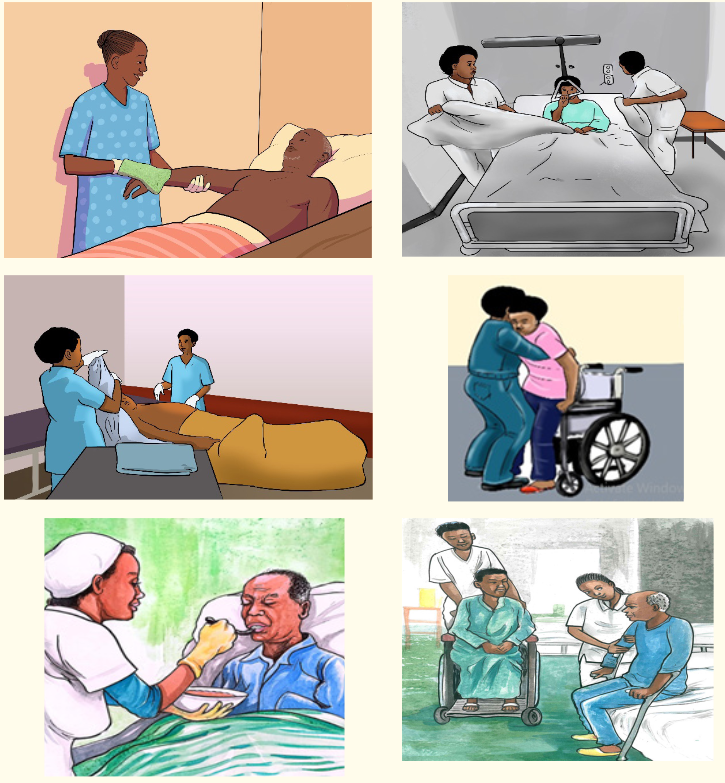

Dorothea Elizabeth Orem (June 15, 1914 – June 22, 2007), born in Baltimore,
Maryland, was a nursing theorist and creator of the self-care deficit nursing
theory, also known as the Orem model of nursing. The theory of self-care, which
focuses on the performance or practice of activities that individuals perform on
their own behalf. Those might be actions to maintain one’s life and life functioning,
develop oneself or correct a health deviation or condition. Orem’s theory provides
a comprehensive basis for nursing practice. It has utility for professional nursing
in the areas of nursing practice, nursing education, and administration. A nurse
assists the patient or family in self-care matters to identify and describe health and
health-related results. Collecting evidence in evaluating results achieved against
results specified in the nursing system design.Theorist Orem Dorothea define Person, Health, Nursing, and environmental as
follow:
• Person: Humans (Men, Women and children) cared for either singly or as
social units and are the of nurses and others who provide direct care• Health: is being structurally and functionally whole or sound.
• Nursing: is an art thought which the practitioner of nursing gives specialized
assistance to persons with disabilities or incapability which makes more than
ordinary assistance necessary to meet needs for self-care.• Environmental: The environment as physical, chemical and biological
features, it includes the family, culture, and community.Application of Dorothea Orem theory in nursing education and practice:
Orem’s theory gives a complete foundation for nursing practice. It has useful
information in nursing practice, education and administration. A nurse helps the
patient or family members in self-care to know and express health and health
related results. Students nurse are educated Orem’s theory to integrate it in their
daily practice during clinical practice. It helps in evaluating the goals set.Self-assessment 1.4.4.
1) Which of the following theories was developed by Dorothea Orem?
a) Developed the self-care deficit theory, which explains what nursing
care is required when people cannot care for themselves
b) Developed the adaptation model, inspired by the strength and
resiliency of children; relates to the choices people make as they
adapt to illness and wellness
c) Developed the caring theory, which focuses on nursing as an
interpersonal process
d) Developed the culture care diversity and universality theory2) Respond by TRUE or FALSE to the following statement
According to Dorothea Orem, Self-care refers to the practice of activities
that individuals initiate and perform on their own behalf in maintaining
life, health and well-being.1.4.5. Jean Watson
Learning activity 1.4.5.
Read careful the following scenario showing jean Watson theory and respond
to the questions.KALISA, a 39-year-old truck driver is admitted to the hospital following an accident
which caused the burn on front of his chest, is feeling much pain, appears very
tense with tears in his eyes, and was rushed immediately to the hospital. The nurse
at the hospital received him, holding his hands, with a soft voice, have a seat,
you are so nervous, feeling too much pain, what happened to you?’’ I am ready
to listen to you,’’. KALISA responded that he got an accident which caused him
to get burned. The nurse in caring voice, oh my God, let me do my best to make
you more comfortably and I am hopeful that you’ll feel better. The nurse started
giving him painkillers, antibiotics, and a rapid infusion of lactated ringers. After one
hour, KALISA started feeling better, very happy, laughing and thank the nurse for his
interest and support.’’ I felt lost’’ stated KALISA. Now I know that somebody is beside
me and has comforted me.
1) How Mr KALISA was helped by the Nurse?
2) What do you think have helped Mr KALISA to feel better and happy?
Jean Watson (June 10, 1940 – present) is an American nurse theorist and nursing
professor known for her “Theory of Human Caring” humans cannot be treated
as objects and that humans cannot be separated from self, other, nature, and
the larger workforce.” The human being is defined as “…a valued person in and
of him or herself to be cared for, respected, nurtured, understood and assisted;
in general, a philosophical view of a person as a fully functional integrated self.
Nursing is concerned with promoting health, preventing illness, caring for the sick,and restoring health.” It focuses on health promotion, as well as the treatment of
diseases. Watson’s Theory of Human Caring is found in the 10 Caritas Processes: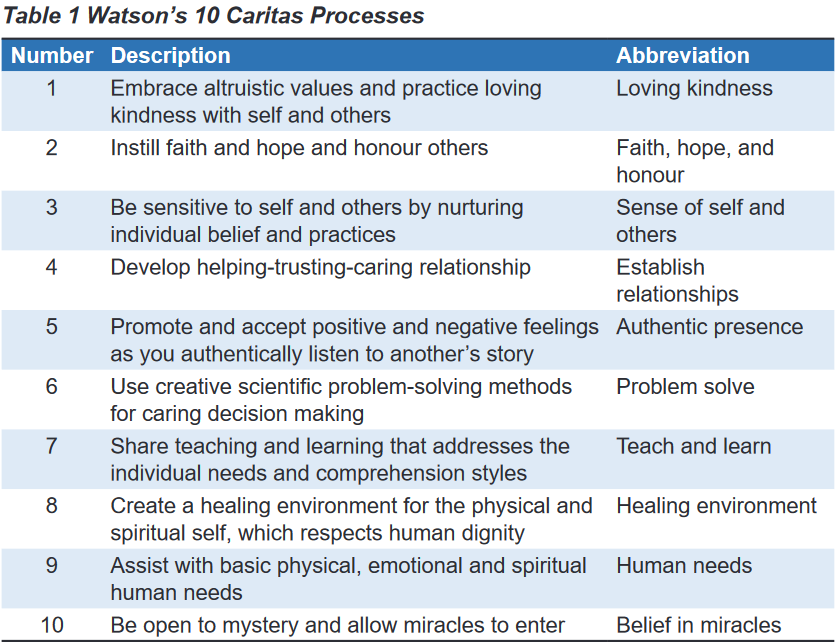
Watson’s theory has been validated in outpatient, inpatient, and community health
clinical settings and with various populations, including recent applications with
attention to patient care essentials and simulating care. Watson’s theory calls upon
nurses to go beyond procedures, tasks, and techniques used in practice settings,
coined as the trim of nursing. Watson’s writings focus on educating graduate
nursing students and providing them with ontological, ethical, and epistemological
bases for their practice, along with research directions. Watson’s caring framework
has been taught in numerous baccalaureate nursing schools.Jean Watson’s metaparadigm
• Person: Human being is a valued person to be cared for, respected, nurtured
understood, and assisted, in general a philosophical view of a person as fully
functional integrated self.• Health: Is the unit and harmony with the mind, body, and soul, health is
associated with the degree of congruence between the self as perceived and
the self and the self as experienced.• Nursing: Is a human science of persons and human health-illness experiences
that are mediated by professional, personal, scientific, esthetic and ethical
human care transactions.• Environment: Society provides the values that determine how one should
behave and what goals s one should strive towards.Application of Jean Watson theory in nursing education and practice:
Watson’s theory is used in all health facilities today (hospitals, health centers,
community settings) whereby nurses involved in the care of inpatients and
outpatients using human caring theory to promoting patient health, preventing
illness as well as the treatment of diseases. In nursing education, students are
educated human caring theory which provide them with ethical, and knowledge
base for their practice.Self-assessment 1.4.5.
1) Which of the following is the theory of Jean Watson?
b) Environmental theory
c) Human Caring
d) Need Theory
e) Self-care deficit2) The following are Caritas Processes. Except.
a) Be open to mystery and allow miracles to enter.
b) Develop helping-trusting-caring relationships.
c) Share teaching and learning that addresses the individual needs and
comprehension styles.
d) Impose your personal beliefs about wellness on others.End unit assessment 1
1) Mrs. UWIMANA is brought to the hospital after sustaining an accident, he is
bleeding and has multiple wounds on her both legs, and clothes were torn
into pieces. She also states that she is dizzy and feeling too much pain, full
of anxiety. The nurse at the hospital immediately received her putting her on
flat bed in clean environment with fresh air and light and start giving her the
medications to calm the pain and fluids to replace fluid loss due to bleeding.
The nurse fails to stop bleeding and call the doctor to help him, the doctor
come and UWIMANA was treated well and become stable. At discharge
time, UWIMANA states that she is very poor and does not have the money to
pay for the service provided. The nurse went to social service in the hospital
to request for social support for Mrs UWIMANA to pay the hospital and find
new clothes. The nurse also told UWIMANA to not worry about her life,
saying that everything will be ok, he started instructing her how to continue
the self-care at home, respecting the hygiene and eating balanced diet.
a) Based on the scenario above, what is nursing?
b) What are the nurse’s roles stated in the scenario?
c) Enumerate the theorists the nurse in scenario referred to, when
giving care to Mrs. UWIMANA and why?2) List the three periods of nursing evolution
3) Match the theorist in column A to their definition of Nursing as one
element of metaparadigm in column B.
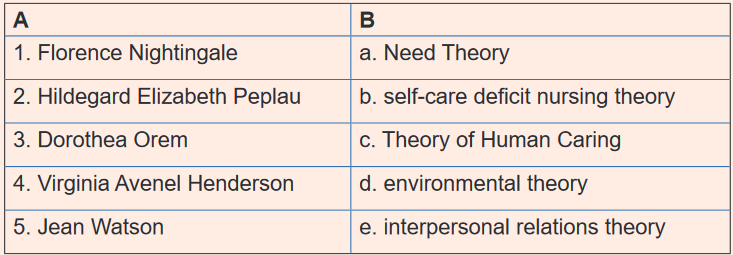
4) Match the following theorists in column A to their corresponding theories
in column B.