SECTION 3. FACILITATION OF PROCEDURES IN CLINICAL SETTING
This step is concerned with the “learning by doing” in the clinical setting where the
student is required to perform different procedures assigned under the supervision
of the clinical mentor/Clinical class teacher.3.1 Task assignment
Following the weekly plan at hand, the Clinical facilitator will assign tasks, demonstrate
(know how transfer) and coach the student thereby providing guidance and clear
instructions for the adaptation of the demonstrated procedure. Task assignment
follows the main steps as indicated below:3.2 Preparing the student in clinical setting
– Prepare all tools, materials, and eventually the client (visual aids in a real
work situation)– Welcome the student in a friendly manner and arouse his/her interest
(motivation)– Present him/her with the needed materials, equipment and explain how they
function– Ask questions to check prior knowledge
– Explain the safety and hygiene regulations
– Place him/her in a good position to observe well
– Explain the significance of the task to perform (why it is needed)
– Explain the learning outcome to the students
3.3 Clinical preparation checklist
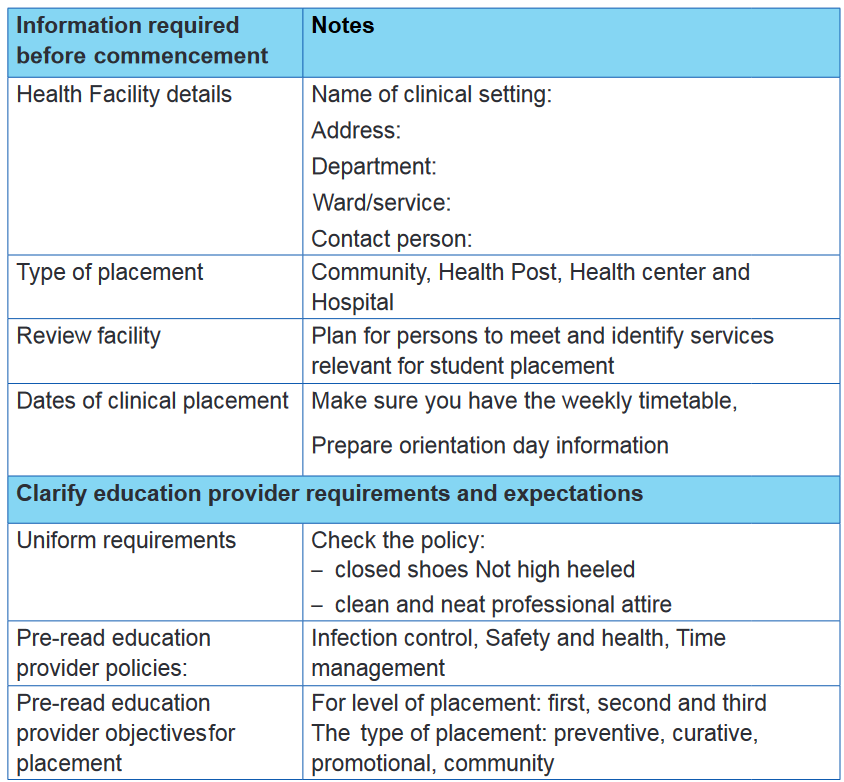
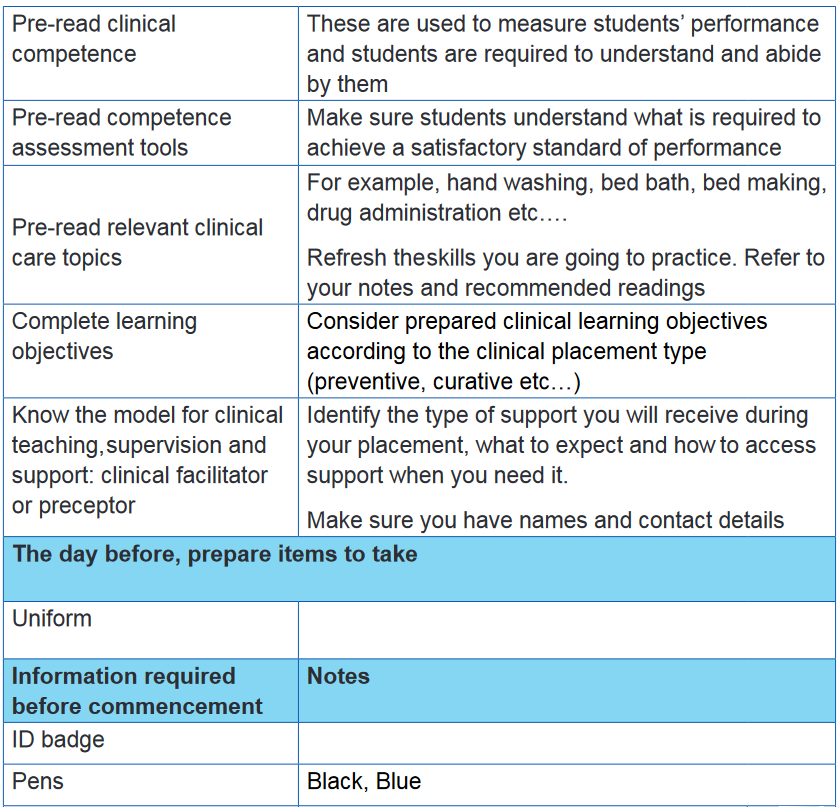

3.4 Demonstrating and explaining
The Clinical facilitator demonstrates how to do the assigned procedure /task (the
process and where to pay more attention when needed) what to use, how to use
tools, materials and equipment as well as how the system and equipment work.Specifically:
– The Clinical facilitator explains exactly WHAT is being done, HOW it is being
done it and WHY the procedure is done in this way and not in any other way– Before the student’s exercise, the complete procedure to be learned is
demonstrated by the clinical facilitator at a normal speed– After this, the complete procedure is demonstrated slowly in partial steps/
actions– The student is asked to watch the procedure carefully and to ask questions
if necessary– The student and the clinical teacher /mentor should ensure that each work
step is explained and supported verbally3.5 Adaptation
3.5.1 Imitation (Return demonstration or try-out-performance by the
student)– Under continuous observation of the Clinical facilitator, the student imitates
the procedure and takes care of the single work steps– The Clinical facilitator corrects the performance if it is not conforming to the
procedure process– The Clinical facilitator ensures demonstration of the procedure, respecting
health and safety guidelines– He/she makes no criticism or negative judgment but gives constructive
corrections– During the course of demonstration and learning, a little praise is helpful to
motivate learning– After repeating all work steps, the student should be asked to explain every
single step. Verbal support during the exercise renders the learning process
more effective and improves the retention of information– Finally, first the learners and then the Clinical facilitator should repeat the
3.5.2 Mastering by practicing
complete demonstration once again as comprehensively as possible. In
this way the requisite standards of quality and quantity are mastered by the
student once more before they go on to the unsupervised exercises
– The student practices to acquire the necessary skills directly during
implementation of procedures in the real clinical setting– The student develops a sense of the pace of work, becomes more confidentand secure in handling the equipment and materials, then begins to look
autonomous during practice with less physical effort but more efficient– The Clinical facilitator must remain in the vicinity during the phase of practice– She/ he must regularly check that the student performs the activities correctlyto avoid errors. Such errors may be difficult to reverse and even if possible, a
lot of harm will have been caused– To achieve the learning success and mastery there is need to repeat theexercises again– Stay near to the student to answer any questions and observe how she/heperforms3.5.3 Closing the session– Ensure respect of the standards– Clean the learning space
– Clean and replace used resources in the right place or place them where they
are supposed to be
– Ensure safety and security measures
– Ensure lifetime of resources for future re-use
– Record and report what has been done
– Close the session and agree on the way forward
– Provide constructive feedback
– Provide assignment if necessary
– Encourage students to have individual development plansConsidering that the Clinical teaching and learning is an effective way of transferringtechnical skills and preparing for the labor market and further learning. With the
help of the Clinical facilitator, the effective adaptation requires the student to be
integrated in the Clinical setting team and to build relationship with the Clinical
facilitator and coworkers.For this reason, not only the student has to adapt him/herself to the proceduresassigned to be performed as directed and demonstrated by the Clinical facilitator,
but also to the working conditions including:
– Observing the conditions of clinical setting learning agreement– Behaving in a courteous and professional manner– Obeying all rules and regulations
– Not wasting, damaging or injuring the property, goods or business of the
institution
– Working towards achieving the competencies according to the training plan
– Undertaking training and assessment as required under the training plan
– Keeping the training records and produce it when requiredNB:
– Students with disabilities and others with special need education should
benefit from appropriate facilitation and supervision throughout their learning– An overview of the clinical setting/site health and safety protocols, including
fire and evacuation procedures should be done3.6 Application and transposition3.6.1 MentoringMentoring is providing continual guidance and empowering a student to advance
towards a desired goal. It is a process that leads a student to self-reliance or
confidence. Therefore, for a student to build autonomous capacity, the clinical
facilitator creates situations and conditions where a student applies the same skills
in a different context. In such case, the clinical facilitator will play a role of a mentor.The level of supervision and support that is expected from the clinical facilitator
includes regular checks on how you are progressing throughout the shift, group
debriefingsessions and one-on-one time for specific skill assessments.The clinical facilitator provides clinical teaching with opportunity of acquisition
and demonstration of skills covered in theory. There are key skills that a clinical
facilitator is required to have in order to assist the student attain confidence and
competence in provision of quality mentoring and health care. These skills include:
– Clinical proficiency and capacity to make decisions
– Willingness to mentor students on site
– Capacity and desire to motivate the student to perform well
– Familiarity with and ability to use clinical standards
– Ability to facilitate a case discussion3.6.2 Roles of the clinical facilitatorThe clinical facilitator is a person who provides clinical teaching with opportunity of
acquisition and demonstration of skills covered in theory.The level of supervision and support that is expected from the clinical facilitator
includes regular checks on how students are progressing throughout the shift,
group debriefing sessions and one-on-one time for specific skill assessments for
progression. This includes to:– Participate in identification of learning needs of the nursing students– Set goals with the students in collaboration with the institution and in line with
the curriculum.– Provide patient care in accordance with established evidence- based nursingpractice standards– Fulfill nursing duties according to hospital and training institution’s policies
and procedures– Facilitate the student’s professional socialization into the new role by building
their practice.– Provide the student with feedback on his / her progress, based on clinical
facilitator’s observation of clinical performance, achievement of clinical
competencies and patient care documentation.– Participate in educational activities of the institution to promote continuous
learning and professional growth of nursing students.– Promote safe, effective and qualitative client care– Know the strengths and weaknesses of the student, find experiences to
address the weaknesses and capitalize on the strengths– Create a non-threatening environment to make integration and transition less,
stressful for the students.– Outline the requirements and expectations of both the clinical facilitator and
students– The mentor is expected to notify the Course Faculty immediately when theperformance of the student is in question3.6.3 Mentoring TipsStudents should be assigned a clinical facilitator who also acts as a mentor. The
clinical facilitator may assign other employees the role of a mentor because the
student is going to be spending time in different departments of the institutions. A
mentor is an experienced person who trains, guides and advises someone to help
them learn something new.The type of clinical supervision and support that you will experience may differ
depending o health care environment where students are placed. Here are some
examples and explanations of the types of clinical support, and where you may
experience that model of supervision.3.6.4 Procedure to reduce risk of training dropoutAccording to Clinical placement syllabus/and education system each end of term,
there is a midterm clinical setting assessment which will be graded to show the
student’s performance progress. The marks will not be considered at the end of
the term but it will be recorded. At the end of every term there will be clinical setting
comprehensive assessment for all students organized in which the general situation
of progress of the student is assessed. If the conclusion is that the student shows
difficulties and risks to repeat the class/program; the herewith described procedure
must be applied.The procedure aims to fast intervene and define effective measures. This should
happen as early as possible in the first term of the year. A discussion based on
careful professional assessment is the right way to do this.3.6.5 CoachingCoaching is an ongoing professional learning relationship in which a clinical
facilitator with appropriate competences inspire students (by challenging them) to
maximize their professional potentials through initial and follow up conversation
aiming to support them to learn from within rather than teaching them. It builds on a
shared understanding on effective teaching, learning and leadership.As students get in deep of application or develop autonomous capacity, the clinical
facilitator shifts from the mentoring to the coaching role. Through the conversation,
the clinical facilitator helps students to be able to find solutions to the problems and
challenges they encounter in the clinical setting.The student should be able to use the professional language and quality standards,
as well as methods, procedures, equipment, and materials in a professional manner
(professional competence).
– Throughout clinical setting learning process, the clinical facilitator must
highlight that:
• The quality work should be organized carefully and consciously
• Attention is paid to the economic and ecological aspects
• The professional work techniques, learning, information, and communication
strategies are applied in an objective-oriented way
• Thinking and acting in processes and networks is needed– The coach facilitates the student to consciously shape his/her relationships
with her/ himself, in the team and with customers and deal constructively with
challenges in communication and conflict situations– Let it be known that students reflect on their thinking and acting on their
own. They are flexible about changes, learn from the limits of resilience and
develop their personality. They are willing to perform, maintain good working
posture and continue to train for lifelong learning– Guide the student in time management and setting procedures priorities
(e.g. to stay focused when assigned a procedure, to take the initiative to find
additional work, to record procedures, to know how to say NO, etc.).– Involves the student in the activities of the institution (formal and informal) so
that they develop a sense of belonging3.7 Supervision and interaction with the studentFrom the first day a student gets in the clinical setting, the clinical facilitator will
play the supervision role of all the activities that a student will be involved in. That
is why the clinical facilitator as In-house supervisor will play a central role in the
success of the student minimizing dropout and irregularities risks by meeting his/
her expectations and achieving outcomes, providing quality training with good
general clinical setting conditions; gender responsive environment and effective
clinical setting relationships, as well as increasing the student feelings about how
supported he/she is in the clinical setting.As the clinical setting supervisor, the clinical facilitator is responsible for:
– On-site training for the student– Answering any questions that the student may have regarding hers/ his
training, assigned procedure or other aspects of his/her work– Informing the student of clinical setting expectations, safety procedures,
codes of conduct, working hour’s information, etc.– Ensuring that the student is not harassed or bullied at the clinical setting
To be an effective clinical setting supervisor the clinical facilitator will:– Provide a safe and supportive clinical setting environment– Integrate learning procedures into work activities based on the training plan– Manage safety and production risks during facilitation– Act as a role model– Collaborate with the school clinical placement teacher regularly to ensure
effective training delivery and assessment, practices and to review progress
according to the training plan– Promote independence and self-direction in learning– Motivate the student and manage the learning needs– Provide regular feedback, encouragement, monitor progress and maintain
records– Help the student to develop problem solving and general employability skillsReminder:
– Giving regular feedback on performance is a big role of a clinical facilitator,
feedback should be balanced, emphasizing the positive but also giving
suggestions for improvement. The positive feedback can build the students’
confidence and make them feel good about themselves.– “Negative” feedback should state what was not done correctly but should
suggest ways to improve as well. This is also known as constructive
feedback and can help students further develop their skills and knowledge
for student to do better.3.7.1 The Clinical setting comprehensive assessments
To evaluate the student performance and make improvement/corrective measures,
the student will be assessed on the four dimensions of competence (professional,
methodological, social and self) throughout the clinical setting and as the work
progresses:– Formative assessment: The institutional day-to-day activities, as the clinical
facilitator is more of a technician than a trainer; the formative assessments
will mostly be through observation and oral questioning.– In addition to the day-to-day formative assessments, the clinical facilitator
will conduct comprehensive formative assessments. She/he must sit at
least once in a term with the student and share observations with the student
regarding the strength, weakness and the way forward. Comprehensive
formative assessments are non-scored checks on performance criteria at
the end of each learning procedure. The purpose of this type of assessment
is to prepare a student for the summative assessment and is done once a
term in the Clinical setting.The clinical setting comprehensive summative assessments are scored
checks on up-to-date acquisition of all competencies at each end of term under
the responsibility of the Clinical facilitator and school clinical teacher. A 40 minutes’
practical schedule for each student at the designated site.
– If scores are too low, the risk mitigation procedure may be initiated regarding
career guidance for orientation into a suitable combination.
