UNIT 1: INITIATION TO ENTREPRENEURSHIP
Key unit competence: To be able to analyze entrepreneurial stages for the success of a business.

Introductory activity
After completing S.3 national exams, Umuhoza thought of starting a small project that will help her get money for school fees at advanced level, using the knowledge of entrepreneurship she learnt in the three years and her great appetite for mandazi. she asked herself what project she could start! she talked to a nearby small business owner who inspired her to start a small bakery project because it required limited capital, Umuhoza was happy and liked the idea, her mother also taught her how to make bread, she decided to start that small project with personal savings accumulated from pocket money while at school. Before starting this project, she first researched about the most marketable bakery product and found out that cakes and chapattis are marketable than bread. she also discovered that the whole village had one supplier of these items and in many shops, such items were lacking. Because she had little money, she prepared a budget focusing on sources of revenue and projected expenditure. Amidst all these challenges, Umuhoza was able to start and operate her bakery project within the trading centre. she named her business Hoza Bakery Supplies. she is now able to borrow loans from the village co-operative bank, pay tuition (school fees), support her family, and offer jobs to her friends using the profits generated. she has a plan of extending her project to Kigali by opening a branch.
Questions.
a)
What skills do you think Umuhoza acquired from O’level entrepreneurship that motivated her to start her bakery project?
b)
What inspired Umuhoza to start her own business?
c)
What did it take Umuhoza to start a bakery project?
d)
Is Umuhoza an entrepreneur? If yes, explain?
e)
How will the above project solve community problems?From the above passage, we can conclude that being an entrepreneur takes an extra effort and all
the activities undertaken by entrepreneurs such as Umuhoza to start production is called ‘entrepreneurship’.
1.1. Meaning of entrepreneurship, an entrepreneur, Intrapreneur and manager
Activity 1.1
Using your knowledge of entrepreneurship obtained in O’level and research made from internet or libraries distinguish between the following terms, entrepreneur, entrepreneurship, Intrapreneur and manager.1.1.1. Meaning of an entrepreneur
The word entrepreneur is derived from a French word “Entreprendre” meaning to undertake. It is used to mean a person who takes the risk of starting a new organization or introducing a new idea, product or service to the society.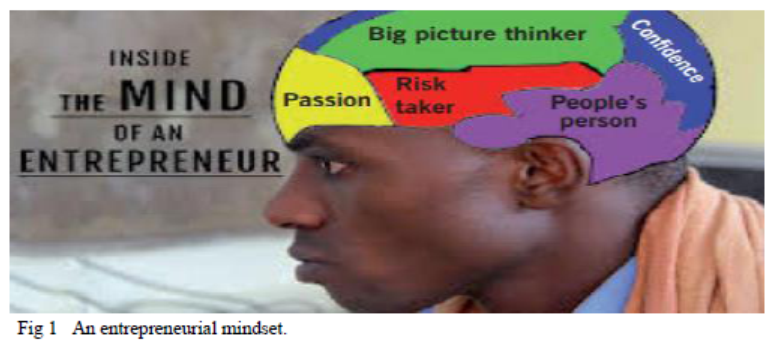
According to J.B. Say, “An entrepreneur is an economic agent who unites all means of production; land, labor and capital which are used to produce goods and services.
By selling commodities in a goods market, he/she pays rent to land, wages/salary to labor and interest to capital and remains with a profit.
According to Richard Schumpeter, “An entrepreneur is an individual who introduces something new in the economy; a method of production not yet tested by experience in the branch of manufacturing, a product which is new in the market from a new or old source of raw materials using new or existing methods of production.”
The entire definitions highlight: bearing of risks, combining factors of production, innovation and introduction of new methods and products, and bringing about economic change as a function of entrepreneur.Therefore. An entrepreneur is a person who has the ability to see and evaluate business opportunities, gathers necessary resources and uses them to initiate and manage the identified business; takes risks in the business with the aim of making profits.

NB: Any person who assumes risks of any business and owns that business enterprise with an aim of making profits is an entrepreneur irrespective of the size and mode of operation of the business.
1.1.2. Meaning of entrepreneurship

Different scholars have defined entrepreneurship as below:
Arthur H. Cole in his book, Business Enterprise in its social setting; defines entrepreneurship as “the purposeful activity of an individual or a group of associated individuals undertaking to initiate, maintain and increase profits by production or distribution of economic goods and services”.
Higgins in his book, The Economic Development defines entrepreneurship as “the function of foreseeing investment and production opportunities, organising an enterprise to undertake new production process, rising capital, hiring labour, arranging the supply of raw materials, finding sites, introducing new techniques, discovering new resources or raw materials, and selecting top managers for the day-to-day operations of the enterprise.
Grey Watson: defines entrepreneurship as “the process through which individuals identify opportunities, allocate resource and create value”.
From the above definitions, it can be observed that entrepreneurship.
- Involves the ability of a person to identify business opportunities.
- It involves mental attitude of risk taking, resource organisation and exploitation.
- It involves one or more individuals.
- It involves creativity, being innovative, initiative
Therefore, entrepreneurship is the process of identifying business opportunities from a locality, organising necessary resources, and using them to start an enterprise to produce goods and services, market them while covering risks with the aim of making profits.
Entrepreneurship is also a way of thinking and acting that focuses on identifying opportunities, apply action with analysis, and is driven by a passionate individual or team.1.1.3. Intrapreneur

An Intrapreneur is a person within a large corporation/enterprise who takes direct responsibility for turning an idea into a profitable finished product or service through assertive risk taking and innovation. Great ideas and products can result from letting your employees think, experiment, and try using new technology and production techniques. This is different in each company but what is important is to embrace the idea of engaging employees, and to choose a system for applying that vision in a way that fits your company culture.
Intrapreneurs are usually employees within a company who are assigned a special idea or project and are instructed to develop the project like an entrepreneur would.
Example: If an employee working in Airtel Company Rwanda suggests and introduces the use of Airtel cash for its customers to access funds on their bank accounts i.e. can withdraw and deposit money using Airtel cash then such an employee is an Intrapreneur and has to be paid for such
inventions by Airtel Company in Rwanda.
1.1.4. Meaning of Manager
A manager is a person who organizes resources, allocates tasks, oversees and controls business operations so as to achieve the organizational goals, mission and vision.
1.1.4. Entrepreneur vs Manager
The term entrepreneur is often used synonymously with Manager, yet these are conceptually different. It is true that an entrepreneur is a manager of his own enterprise but not all managers are entrepreneurs.Difference between an entrepreneur and a manager
Kharim is a graduate who recently graduated from UR college of science and technology with a degree in Computer Programming. He has developed an application that he believes will make him earn a living. He performed very well and was called by prominent telecommunication company for a job, he accepted and worked for one month and after he thought to leave that Company so as to start his own project of designing new software. He wants to challenge himself and work the way he wants without answering to a boss. He is using a small inheritance to fund the start-up alongside contributions from his grandparents. As an entrepreneur, Kharim is not only starting a business, but is risking his personal wealth to establish it.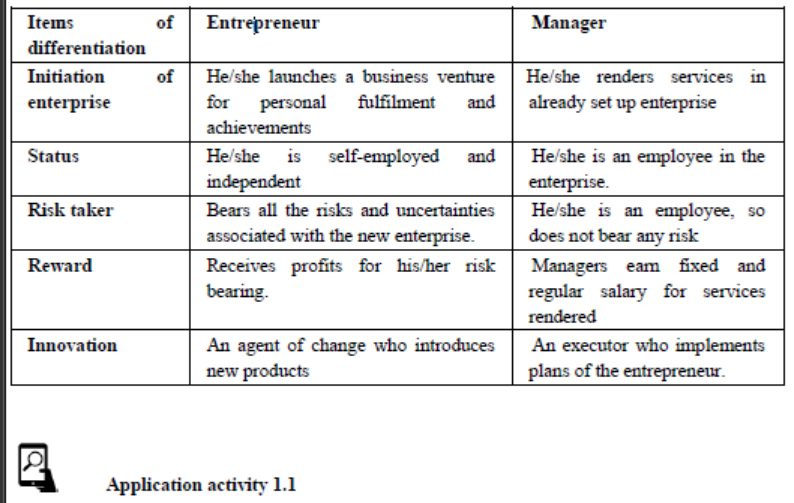
Kharim is also trying to convince some friends from school to form an entrepreneurial team with him. Kharim has a friend who majored in Web designing and another in marketing. He is hoping they may come along with him and bring their skills. He is building the right team so that they can co-operate and achieve more together than they would individually.
Kharim hopes that his entrepreneurial gamble will pay off as well as the gambles of other well-known entrepreneurs.
Questions:
1. What lessons can be learnt from Kharim’s experience?
2. Briefly explain the relationship between an entrepreneur and entrepreneurship.1.2. Qualities/characteristics of an entrepreneur
i) Do you have a role model that inspires you to join business? YES/NO?
ii) State and describe characteristics your role model possesses.
Qualities or characteristics of a successful Entrepreneur
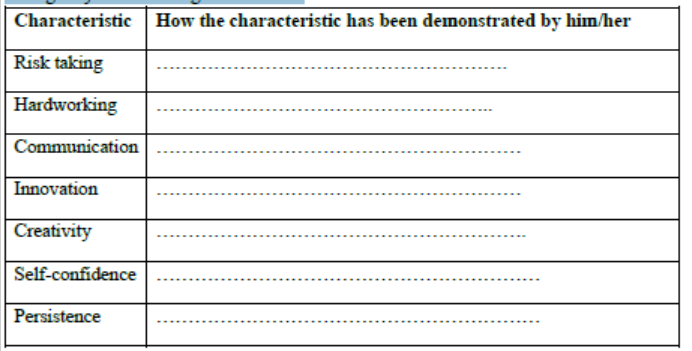
▪Hard working: This involves using extra effort to do whatever one is doing. It involves working extra or additional hours, days and nights. A hard-working person commits more time, more energy and more resources to achieve the desired objective. Commitment and hardworking are essential to success in business.
▪Creative and Innovative: Creativity involves using ideas to come up with new products. For a person to be successful in life, S/he must be creative by doing new things or doing old things differently. Being innovative helps a person find new business ideas, improve existing business activities, and find solutions to difficult problems. All these help an entrepreneur to become successful.
The relationship between Creativity and Innovation is like the relationship between recycling and upcycling. One brings new idea, new product while others improve what is existing.
▪Risk taking: Entrepreneurs are risk takers. They risk starting a business. This is not to mean that they are reckless people. Good entrepreneurs assess the risks related to their business before they take them. They do not take every risk; they only take moderate risks that they will be able to manage.
▪Decision making skills: A successful entrepreneur makes intelligent, right and informed decisions on various issues, follows the decisions made, and accepts their results.
▪Persistence and Perseverance: Starting and growing a business requires a lot of determination and a “never-give-up” attitude. It is said that winners never quit and quitters never win. Entrepreneurs never give up, irrespective of all problems and setbacks met in the business. They put in as much efforts as possible to ensure business success.
▪Opportunity seeking: A good entrepreneur is able to spot opportunities even where other people are not able to see any. Ability to see opportunities also helps the entrepreneur to take advantage of other opportunities like identifying the best employees, taking advantage of cheap loans from commercial banks, raw materials, etc… he/she sees society’s challenges or problems as basis for business creation or expansion.
▪Seek information: good entrepreneurs are always on the lookout for information related to their businesses to make good decisions. Good decisions are based on right and updated information. For example, for a manufacturing business, the entrepreneur seeks information about suppliers of new machinery, new industries entering competition, potential customers, new government policies, etc. All this information is helpful in making informed and profitable decisions.
▪Self-confidence: An entrepreneur should have a strong belief in his/her abilities. He/she should be confident that he/she will achieve what s/he sets himself to achieve. If a person is not confident of himself/herself, he/she cannot be a good entrepreneur.
▪Financial Discipline: A good entrepreneur has excellent money management skills. He/she does not spend business money on unplanned activities or things.
▪Goal setting and planning: good entrepreneurs set goals and strive for achieving them. The goals set should be SMART that is to say specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time frame/ bound.
▪Commitment: An entrepreneur will succeed in business if he/she is committed to the business and to fulfilling obligations; for example, he/she should spend a lot of time in the business and make sure that customers are served properly, they are given very good services and when he/she makes a promise, he/she has to fulfill it.
▪Persuasive and good at networking: Persuasiveness is the ability to convince others and change their thinking. Networking involves meeting other people involved in the same kind of work, to share information and support each other. A good entrepreneur will always get time to meet and share ideas with people who matter to the business such as suppliers, competitors who can give him/her good advice, etc. A good entrepreneur will not be an ‘island’ but will always be networking.
▪Controlling/monitoring: An entrepreneur ensures that results match with plans. Monitoring business activities helps him/her to know whether the business is succeeding or failing. By doing this he/she decides on what to do if the business is not achieving desired results.

1. a) Discuss the various qualities an entrepreneur should possess.
b) Choose two best entrepreneurs in the world today that act as your role models: one male and one female.
(i) …………………………………………………………..
(ii) …………………………………………………………2. Explain briefly how the above entrepreneurs have demonstrated the following characteristics basing on your knowledge about them.
1.3. Stages of entrepreneurship process.
Looking at fully developed businesses with tangible products in your home area.
e.g., Inyange industries. What stages do you think the above business went through to get to where it is today?The stages of entrepreneurship development

At this stage an entrepreneur generates ideas, recognizes opportunities, determines the feasibility
of ideas, markets, and ventures and other prior information.


Here an entrepreneur starts and operates business and utilizes resources to achieve its goals and objectives.
Harvesting:

Here an entrepreneur decides on the venture’s future (growth, development, or demise).
Gap-filling questions
1.…………...an entrepreneur decides on the venture’s future (growth, development or demise).
2.…………… here an entrepreneur plans the business, identifies needed resources through developing a business plan.
3.……… an entrepreneur starts and operates business and utilizes resources to achieve its goals and objectives.
4.………. acquires needed resources for the venture startup including financial, material, and human and technology.
Draw a new product design that uses recycled materials and solves customer’s need. Explain what problem it solves and what innovation it possesses.
1) Joanna is a senior 4 student and wants to start a small business project in her holidays. Imagine a situation where she comes to you for advice. How would you advise her to apply the five stages of the entrepreneurship process to start a successful business?
2) Come up with a business opportunity by analysing a need in your community, your own skills or passion and available resources.
