UNIT 7 LEADERSHIP, GOVERNANCE AND MANAGEMENT
Key Unit Competence:
To be able to criticize and improve different leadership stylesIntroductory activity
1. Observe the pictures above and identify different ways of leading.
2. Examine the characteristics of a good leader and challenges
facing them.
7.1. Concept and styles of leadership
Learning activity 7.1
1. Discuss the meaning of leadership that you know.
2. In groups discuss the characteristics of a good leader, a good
manager and a good governor.
7.1.1. Concept of leadership
Meaning of leadership: Leadership refers to the ability to influence followers
positively. It can also be defined as the ability to organize and supervise others
with the purpose of achieving goals. Leadership is the process whereby an
individual influences a group of individuals to achieve a common goal or to
accomplish a mission. Leadership is defined as a social relationship between
two or more persons who depend on each other to attain certain mutual goals ina group situation.
Leadership is inspiring others to pursue a vision within the goals set, so that it
becomes a shared effort, a shared vision, and a shared success. Leadership
involves:
• Establishing a clear vision, sharing that vision with others so that they will
follow willingly.
• Providing the information, knowledge and methods to fulfill that vision, and
coordinating and balancing the conflicting situations.
• Leadership is a process of social influence, which means influencing
people around you as a leader and maximizing their efforts towards the
achievement of a goal.
7.1.2. The leadership styles
Leadership styles refer to a leaders’ characteristic behaviors when directing,
leading, motivating, guiding, and managing groups of people. Great leaders can
inspire political movements and social change. They can also motivate others
to perform, create, and innovate. They refer to classification of a person while
leading a group. All leaders do not possess same attitude or same perspective
and the same ability to lead. Thus, all of the leaders do not get the things done
in the same manner. Their leadership style varies. The leadership style varies
with the kind of people the leader interacts and deals with. A perfect/standard
leadership style is one which assists a leader in getting the best out of the people
who follow him.a) The authoritarian/autocratic leadership:
It is the type of leadership where the leader keeps strict, close control over followers
by keeping close regulation of policies and procedures given to followers. There
is direct supervision in order to maintain a successful leadership environment.
Followers are expected to be productive, and therefore authoritarian leaders
endeavor to keep close supervision, because of their belief that for anything to
be done it requires consistent supervision and follow up. Authoritarian leadership
style often follows the vision of those that are in control even when the decisions
are not agreed upon by every individual.b) Paternalistic leadership:
This is a leadership style where the leader works by acting as a father figure, he
takes care of the followers as a parent. In this style of leadership, the leader has
complete concern for his followers or workers, creates a relationship of trust and
loyalty with followers. A team spirit is created and people work interdependently;they treat each other like family within the organization
c) Democratic leadership:
Democratic leadership style involves the leader sharing the decision-making
process with his followers. The followers have a sense of belonging, ownership
and responsibility; this also promotes the interests of the group members by
practicing social equality. One of the main characteristics of this leadership is
discussion, debate, sharing of ideas and encouragement of people to feel goodabout their involvement. It requires guidance and control by a specific leader.
d) Laissez-faire leadership:
This leadership style is where all the leaders and workers have the right and
power to make decisions. Laissez-faire leaders allow followers to have complete
freedom to make decisions concerning the completion of work and the running
of the community. There is a high degree of independence and self-rule, while
at the same time offering guidance and support when requested. The leader
guides with freedom, the followers are provided with all materials necessary toaccomplish their goals.
e) Transformational Leadership:
This is the leadership style where the leader is not limited by his or her followers’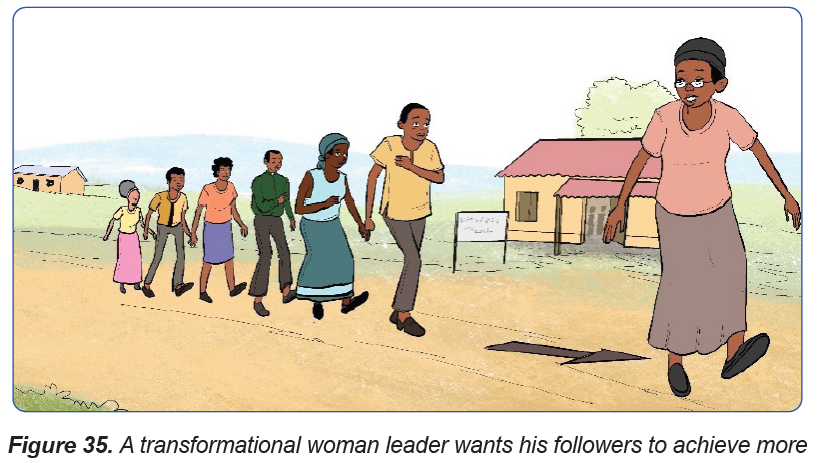
perception, ideas or innovations. The main objective is to work to change or
transform his or her followers’ needs and to redirect their thinking. Leaders that
follow the transformation style of leading challenge and inspire their followers
with a sense of purpose and excitement. They also create a vision of what they
aspire to be and communicate this idea to others.
f) Bureaucratic Leadership
This style of leadership follows rules very strictly and ensures that their people
follow procedures precisely. Bureaucratic leadership is also useful for managing
employees who perform routine tasks. This style is much less effective in teams
and organizations that rely on flexibility, creativity or innovation. Bureaucratic
leaders are like autocratic leaders in that they expect their team members
to follow the rules and procedures precisely as written. The bureaucratic
style focuses on fixed duties within a hierarchy where each employee has a set
list of responsibilities, and there is little need for collaboration and creativity. This
leadership style is most effective in highly regulated industries or departments,such as finance, health care or government.
g) Charismatic Leadership:
Charismatic leadership is a type of leadership style that resembles transformational
leadership; both types of leaders inspire and motivate their team members.
The difference lies in their intent. Transformational leaders want to transform
their teams and organizations, while leaders who rely on charisma often focus onthemselves and their own ambitions, and they may not want to change anything.
h) Servant Leadership:
Servant leadership is a style of leadership leads simply by meeting the needs of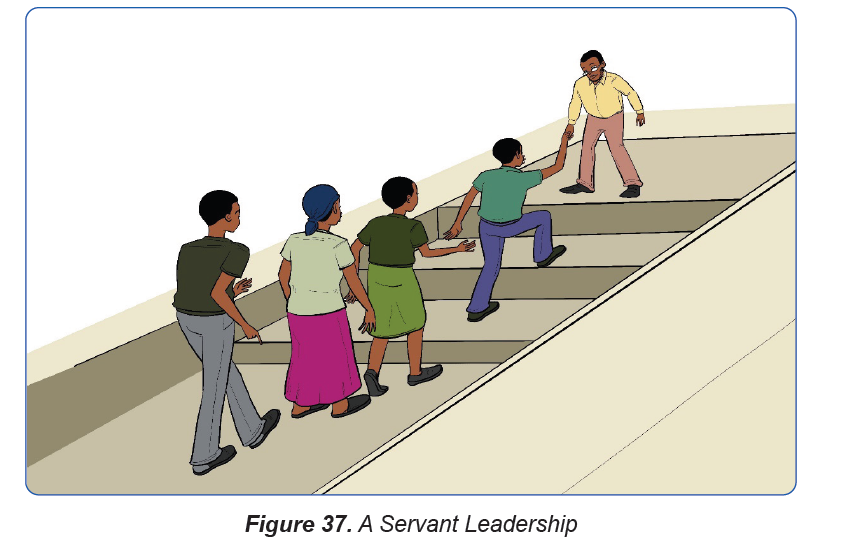
the people or community. In this leadership the person isn’t formally recognised
as a leader. These people often lead by example. They have high integrity and
lead with generosity. This way of leadership creates a positive culture, and it canlead to high morale among the people or community.
i) Transactional Leadership:
Transactional leadership is a style of leadership in which leaders create structures
where it is clear what is required of their workers, and the rewards that they get
for following orders. Punishments are not always mentioned, but they are also
well understood. These leaders look to keep things the same.
j) Situational Leadership
Situational leadership is where the leader must adjust his style to fit the
development level of the followers he/she is trying to influence. With situational
leadership, it is up to the leader to change his style, not the follower to adapt to
the leader’s style. The style may change continually to meet the needs of othersin the organization based on the situation.
Application activity 7.1
1. What do you understand by leadership?
2. From the various types of leadership you have learnt, which one
appeals to you the most?
Give reasons for your answer.
7.2. Characteristics of a good leader and challenges facing
leaders
Learning activity 7.2
Case study: Kaneza was appointed to be a leader of the health Centre.
After three years he became the leader of hospital because he was
competent.
Discuss the possible reasons that led to the promotion of Mr Kanezaas characteristics of a good leader
7.2.1. Characteristics of a good leader
Leading other people or an activity a strong set of leadership qualities to help
positively interact with employees, team members, and clients and other people
in surrounding environment. Behavioral theories suggest that leadership skills
aren’t ingrained and can be taught people can obtain good leadership qualities
through teaching and learning these skills over time while some others suggest
that some leadership skills are hereditary.
The following are some of the characteristics of a good leader:
• Honest: This is being truthful, sincere, having integrity in every action.
Being untrue and deceptive in behaviour will not inspire trust.
• Competent: To be competent means to be capable, fit, suitably skilled and
well qualified. A leader’s actions should be based on reason and moral
principles. A good leader does not make decisions based on emotional
desires or feelings.
• Forward-looking: Setting goals and having a vision of the future is a good
sign of good leadership. Effective leaders envision what they want and how
to get it.
• Inspiring: Another characteristic of a good leader is inspirational. A leader
displays confidence in his actions. By showing endurance in mental,
physical, and spiritual stamina, you will inspire others to reach for new
heights. Take charge when necessary
• Intelligent: When a leader reads, studies and seeks challenging
assignments, he or she improves their knowledge. This is very beneficial
when leading others.
• Fair-minded: A leader who shows fair treatment to all people and does not
have prejudice will treat people and give justice fairly. A good characteristic
of leadership is when a leader shows and displays empathy by being
sensitive to the feelings, values, interests, and wellbeing of others.
• Broad and open-minded: This means a leader is open to hearing and
considering different points of view.
• Courageous: Have the perseverance to accomplish a goal, regardless
of the seemingly insurmountable obstacles. A good leader displays a
confident calmness when under stress
• Straightforward: Use sound judgment to make good decisions at the right
time. A good leader considers all points of view and makes positive and
workable decisions.
• Imaginative: A good leader uses his natural gift of being creative and uses
his imagination to drive the community towards the goals set.
• Problem solver: A good leader should be able to quickly and creatively,
while following protocol, solve any problems that arise.
• Communication: Good communication skills are one of the leadership
attributes that are absolutely important in leadership positions. Good
leaders ensure that horizontal and vertical communication are effective and
efficient.
• Integrity: Integrity is doing the right thing, even when no one is watching.
Without integrity, no real success if possible. A leader cannot expect
his or her followers to be honest when he or she lacks this tremendous
value: Integrity. Honest and great leaders succeed when they stick to their
word, live by their core values, lead by example, and follow-through.
• Accountability: A good leader takes little more than his share of the blame
and little less than his share of the credit.” Strong and good leaders are
accountable for the team’s results, good or bad. They hold themselves
and their employees accountable for their actions, which creates a sense
of responsibility among the team. Being accountable and leading by
example is one of the quickest ways leaders can become good leaders
are by building trust with their team. Being responsible for the actions
and behaviors of those around you is essential to developing leadership
qualities, like accountability.
• Empathy: Truly great leaders have enough open-mindedness to understand
their followers’ motivations, hopes, dreams, and problems so that they can
forge a deep personal connection with them.
• Humility: “Pride makes us artificial and humility makes us real.” Being
humble and vulnerable with their team members will make a leader much
more relatable and effective.
• Resilience: The true grit of a good leader is not how they perform during
good times, but how they roll up their sleeves and produce when times get
difficult. Great leaders with positive attitudes lead by example and rally their
team no matter the circumstances. It’s this inherent positivity that helps
react to situations with a calm, collected manner and focus on solutions
rather than on problems.
• Vision: True leaders inspire loyalty, enthusiasm, and commitment,
help remind everyone of the big picture and challenge people to outdo
themselves. Every great leader has had to develop the leadership attributes
of vision and foresight; it wasn’t gifted to them. Sharing this vision and
compelling others to act is a secret trait of successful leaders.
• Influence: Some leaders believe that when they attain a certain level of
leadership status and those leadership qualities we have talked about
are owed to them. This is not the case. Leadership and influence are not
interchangeable, and respect has to be earned, not given.
• Positivity: Leaders inspire their team not based on their own goals or
outcomes, but on their exhibited behavior, life outlook, and attitude in any
given situation. It’s often said that employees and direct reports exhibit the
behavior of their managers and good leaders need to lead by example at
all times while mirroring how they want their team to act. Positivity isn’t one
of those leadership qualities that should be over looked and deemed not
important. Being positive during stressful or unfortunate situations is a sign
of strength.
• Confidence: To be an effective leader, you need to roll up your sleeves
and take charge. This includes being confident enough to lead, knowing
that your plans and vision are not only viable for the team but the absolute
best decision possible. Being confident in every situation is one of the
leadership qualities that you must develop. Truly great leaders are able tobe confident during any situation even if they feel fear or uncomfortable.
7.2.2. Challenges facing leaders
Executive secretary is a leader in the sense that he is supposed to enforce
law that maintains healthy and wealthy in the society. Refusal paying health
insurance is unacceptable. Most leaders experience challenges that hinder them
from exercising their leadership efficiently. The following are some of the other
challenges faced by leaders.
• Leading without being an example. Leadership requires that a leader
has a good and admirable life background in and out of office. This can be
very challenging when one wants to do and live according to one’s desires
and yet the leader needs to set a good example.
• A leader may face the challenge of lack of funding and other resources,
opposition from forces in the community, and interpersonal problems
within the community. Social, economic, and political activities may affect
the community, for example regarding differences in human rights beliefs.
When world powers decide that homosexuality for instance is a human
right, then a leader of a conservative African country will have the challenge
of implementing this in his/her community.
• There is a challenge of motivating people and keeping them from staying in
the same place too long especially when they feel like they are doing well.
Leaders also have to motivate themselves, and to be enthusiastic about
what they are doing.
• Leaders in most cases are faced with public criticism, especially from those
they lead. This may arise because of finances, the politics of the country or
community, or the morale of the people.
• Natural disasters and crises may occur and yet a leader has to find a way of
controlling the situation. A Police Commander in cases of a tragic situation
like murder or a road accident will have to deal with the bereaved families,
the logistics of workers at the site among others. These are different from
crises in that in a crisis, something important seems to be happening, and
the situation needs to be controlled.
• One of the greatest challenges of leadership is facing your own personal
issues, and making sure they don’t prevent you from exercising leadership.
For example, challenges and issues from one’s home environment, like
family problems.
• Leaders also face the challenge of effective communication. This is difficult
especially because a leader has a group of people with different personalities
and their own challenges. Communication has to reach each individual in
the way the leader intended, but sometimes this doesn’t happen.
• The loss of passion and intensity that can come with familiarity and long
service. Think of a situation where a president rules a country for more than
thirty years. He or she may lose the passion of good leadership
• Non-cooperation from the community or people being led. This happens
when people in the community do not participate in the general leadership
and community goals.
Application Activity 7.2.
1. After listing characteristics of a good student, search and find other
characteristics of a good leader.
2. Suggest the causes of challenges to leaders.
7.3. Concept and functions of management and characteristics
of a good manager.
Learning Activities 7.3.
Mr Kwizera is a manager of a pharmacy that deals in selling medicine
in Rwanda. He delivers a service to different patients in the area
and people appreciate good service they receive. Basing on yourexperience, suggest the role and responsibilities of Mr Kwizera.
7.3.1. Concept of management
Management is the ability to coordinate or direct, leading to production of results,
it involves identifying the mission, objectives and procedures required to meet a
particular goal or objective. It involves planning, organizing, coordinating and
controlling activities of others. It also involves the ability to delegate and follow
up on goals being set. So managers practice management by delegating duties
and ensuring that they are done. It is the skill of knowing what is to be done
and seeing that it is done in the best possible way. Management must have
people, a positive attitude towards work and good communication. It consists of
six functions.
Functions of management: There are six major functions of management
• Planning: The manager creates a detailed action plan aimed at some
organizational goals. Planning is an ongoing step and can be highly
specialized based on community or organizational and team goals. It is up
to the manager to recognize which goals need to be planned within his or
her individual area
• Organising: Organizing is done by delegating authority, assigning work,
and providing direction so that the team works without any problems.
Organizing involves designating tasks and responsibilities to employees
with the specific skills required to fulfill the tasks.
• Leading: In this step, the manager spends time connecting with employees
on an interpersonal level. It involves communicating, motivating, inspiring,
and encouraging the community towards a higher level of productivity.
• Controlling: the manager evaluates the results against the goals. If a goal
is not being met, the manager must also take any necessary corrective
actions to continue to work towards that goal.
• Staffing: This involves hiring the right people for the right jobs to achieve
the objectives of the organization. Staffing involves recruitment, training’
performance appraisals, promotions and transfers.
• Coordinating: It is important to coordinate the organizing, planning and
staffing activities of the company and ensure all activities work well together
for the good of the organization. Coordinating involves communication,
supervision and direction by management.
7.3.2. Characteristics of a good manager
Learning activity 7.3.2
Case Study 1: Kagabo is a sales manager of a company that sells Hand
sanitizer in Rwanda. This company is new in the country. Kagabo has
a good plan on how to launch it. He has gathered all the resources
necessary and hired enough staff to have the product in the market. To
begin with, Kagabo has planned a launching ceremony and after that
he intends to give each member of his team a role to play in distributing
the medicine product. He plans to hold weekly meetings to discuss the
challenges his team might be facing and deliberate on how to tackle
them.
Case study 2: NDIZEYE is a part time manager of a company that sales
medicines. He coordinates the sales of the company products from the
main office in Kigali mainly by communicating on phone. He has not met
any of his team members: however, he makes follow up on the amount
of money made on a monthly basis. Any member of his staff who does
not deliver is dismissed without notice and immediately replaced. After
reading carefully two case studies above, identify who is a good manager
and justify your answer.
The following are some characteristics of a good manager.
• Leadership: Good managers should be able to lead the employees they
manage, they should have emotional stability, self-assurance, enthusiasm
and be energetic and engaged. They do not get frustrated and overwhelmed
with stress. Enthusiasm means the manager is interested in the work that
is being done.
• Communication: Good managers must be able to communicate and listen
effectively. They take the time to listen to what employees and customers
have to say and are able to communicate that they understood what was
said and act accordingly. Good managers are also aware of non-verbal
communication, through the gestures and expressions of their employees.
• Good managers are good planners; they are organized, and they have
knowledge of what needs to be done and when it needs to be done. They
know and understand the goals of the business and what the employees
need to do to achieve that goal. They plan the steps involved in achieving
that goal and communicate the steps to the employees.
• Identify and solve problems: A good manager is able to identify and
solve problems and also take responsibility for problems that arise and findethical solutions.
• Self-Motivation is a quality of an effective manager. This is the ability to
see one’s self getting the job done especially when they are faced with
many challenges. A good manager should also be able to motivate others.
• Integrity: A good manager expresses integrity in and outside of the work
environment.
• Dependability and reliability: A good manager is both dependable and
reliable. Employees will find it easy to fulfill their tasks sufficiently and relate
to a manager who displays this character
• Optimism and confidence are traits of a good manager. Being able to
have and express a positive attitude inspires and motivates others.
• Calmness: This means that a manager ought to be able remain calm even
in the most difficult and disastrous situation.
• Being flexible: This is required because situations and circumstances are
always changing, therefore a leader is required to have the ability to adapt
to any situation.
• A good manager has to be knowledgeable and open to learning more
about the environment and the industry.
• Being able to delegate; a good manager should know that tasks need to be
delegated. Not everything can be done by one or two individuals, therefore
successful accomplishment of tasks requires a manager to assign various
duties to suitable people.
• Another good characteristic of a good manager is that of being a mediator.
Managing will require the manager to solve and mediate in conflicts in the
workplace.
• Team Player: Are you part of a team? You need to be able to function as
part of a team if you want to succeed as an effective manager. Make sure
that you are willing to work with others, and that you will hold up your end.
• A good manager ought to respect and value others and be able to combine
respect with collaboration and create an excellent team spirit among the
workers. You should also be able to work well with others, and understand
different personal.
Principles of management according to Henri Fayol.
Henry Fayol, also known as the ‘father of modern management theory’ gave a
new perception of the concept of management. He introduced a general theory
that can be applied to all levels of management. The Fayol theory is practiced by
the managers to organize and regulate the internal activities of an organization.
He concentrated on accomplishing managerial efficiency.
The fourteen principles of management created by Henri Fayol are the
following:
1. Division of Work
Henry Fayol’s first principle for management states that staff perform better at
work when they are assigned jobs according to their specialties. Hence, the
division of work into smaller elements then becomes paramount. Therefore,
specialization is important as staff perform specific tasks not only at a single
time but as a routine duty also. Efficiency and effectiveness of work are better
achieved if one staff member is doing one thing at a time and another doing
a different thing, but all leading to the same collective goal, at the same time.
Henri believed that assigning clear work and tasks in the workforce amongst the
worker will enhance the quality of the product. Similarly, he also concluded that
the division of work improves the productivity, efficiency, accuracy and speed of
the workers.
2. Authority and Responsibility
This principle suggests the need for managers to have authority in order to
command subordinates to perform jobs while being accountable for their
actions. These are the two key aspects of management. Authority facilitates
the management to work efficiently, and responsibility makes them responsible
for the work done under their guidance or leadership. The formality is in the
organizational expectations for the manager (his responsibilities), whereas the
informality (the authority) can be linked to the manager’s freedom to command,
instruct, appoint, direct, and ensure that his or her responsibilities are performed
successfully.
3. Discipline
This principle advocates for clearly-defined rules and regulations aimed at
achieving good employee discipline and obedience. Fayol must have observed
the natural human tendencies to lawlessness. He perceived the level of
organizational disorder that may erupt if employees are not strictly guided by
rules, norms, and regulations from management. Without discipline, nothing can
be accomplished. It is the core value for any project or any management. Good
performance and sensible interrelation make the management job easy and
comprehensive. Employee’s good behaviors also helps them smoothly build and
progress in their professional careers.
4. Unity of Command
This means an employee should have only one boss and follow his command. If
an employee has to follow more than one boss, there begins a conflict of interest
and can create confusion. This principle states that employees should receive
orders from and report directly to one boss only. This means that workers are
required to be accountable to one immediate boss or superior only. Orders and
directives emanate from one source and no two persons give instructions to an
employee at the same time to avoid conflict.
5. Unity of Direction
This principle proposes that there should be only one plan, one objective, and one
head for each of the plans. Whoever is engaged in the same activity should have
a unified goal. This means all the person working in a company or organization
should have one goal and motive which will make the work easier and achieve
the set goal easily.
6. Subordination of Individual Interest
The interests of the organization supersede every other interest of staff,
individuals, or groups. Imperatively, employees must sacrifice all their personal
interests for the good of the organization. In other words, organizations should
not tolerate any staff that is not committed to the organization’s objectives and
goals. This implies that a company or organization should work unitedly towards
the interest of a company rather than personal interest.
7. Remuneration-
Payment of staff salaries should be as deserved. The salary should be reasonable
to both staff and management and neither party should be short-changed. The
salary of every staff member must be justifiable. A supervisor should receive
more pay than line staff. Thus, whosever management appoints to be supervisor
takes more than the subordinates by virtue of his or her responsibilities. This
plays an important role in motivating the workers of a company.
8. Centralization
This principle suggests that decision-making should be centralized. This
means that decision-making and dishing-out of orders should come from the
top management (central) to the middle management, where the decisions are
converted into strategies and are interpreted for the line staff who execute them
(decentralization). In any company, the management or any authority responsible
for the decision-making process should be neutral. However, this depends on the
size of an organization. Henri Fayol stressed on the point that there should be a
balance between the hierarchy and division of power
9. Scalar Chain
This principle is a product of the formal system of organization. It is also known as
the hierarchy principle. It asserts that communication in the organization should
be vertical only. It insists that a single uninterrupted chain of authority should
exist in organizations. Horizontal communication is only allowed when the need
arises and must be permitted by the manager. Fayol on this principle highlights
that the hierarchy steps should be from the top to the lowest.
10. Order
This is another formal organizational control system which has been interpreted
in different ways. Some see it as the rule of giving every material its right position
in the organization and others think that it means assigning the right job to the
right employee (Rodrigues, 2001). A company should maintain a well-defined
work order to have a favourable work culture. The positive atmosphere in the
workplace will boost more positive productivity.
11. Equity
Another word for equity is fairness. Henri Fayol suggested that manager should be
fair to their staff. But the fairness required, probably, is such that must make staff
to comply with principle of subordination of individual interests to organizational
interests. Such organizations make staff feel at home, share a portion of profits
with staff, communicate with staff, remain open to staff, share staff feelings, and
identify with staff personal/family challenges. . All employees should be treated
equally and respectfully. It’s the responsibility of a manager that no employees
face discrimination.
12. Stability
In this principle, Fayol expresses the need to recruit the right staff and train them
on the job with a hope to retain them for long. The basis of this principle is the
belief that such staff with a secured tenure will put back into the organization the
knowledge and experience which they may have garnered while working for the
organization. An employee delivers the best if they feel secure in their job. It is
the duty of the management to offer job security to their employees.
13. Initiative
A good manager must be one who can be creative to initiate new ideas and
also be able to implement them. Fayol was direct to managers at this point.
He understood the importance of good ideas to the growth and success of
organizations. The management should support and encourage the employees
to take initiatives in an organization. It will help them to increase their interest and
make then worth.
14. Esprit de Corps
It is the responsibility of the management to motivate their employees and be
supportive of each other regularly. Developing trust and mutual understanding
will lead to a positive outcome and work environment. This is a French phrase
which means enthusiasm and devotion among a group of people. Fayol is of the
view that organizations should enforce and also maintain high morale and unity
among their staff. Thus, understanding, love for each other, unity, peace, and
common determination is paramount to their success.
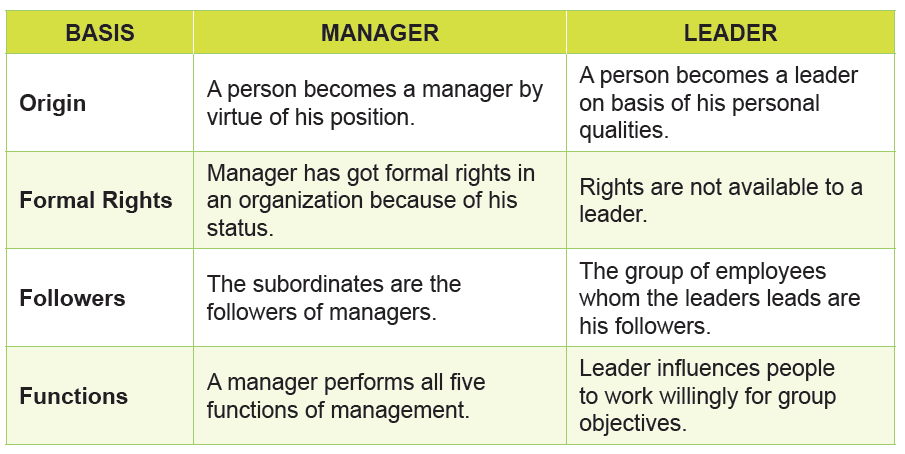
Relationship between leadership and Management
Leadership doesn’t require any managerial position to act as a leader. On the
other hand, a manager can be a true manager only if he has got the traits of
leader in him. By virtue of his position, manager has to provide leadership to
his or her group. A manager has to perform all five functions to achieve goals,
i.e., Planning, Organizing, Staffing, Directing, and Controlling. Leadership is a part
of these functions. Leadership as a general term is not related to managership.
A person can be a leader by virtue of qualities in him. For example: leader of a
club, class, welfare association, social organization, etc. Therefore, it seems to
be true to say that “All managers are leaders, but all leaders are not managers.”
A leader is one who influences the behavior and work of others in group efforts
towards achievement of specified goals in a given situation. On the other hand,
manager can be a true manager only if he or she has got traits of leader in him.
Manager at all levels are expected to be the leaders of work groups so that
subordinates willingly carry instructions and accept their guidance.Table: Comparative Leader and Manager
Application activity 7.3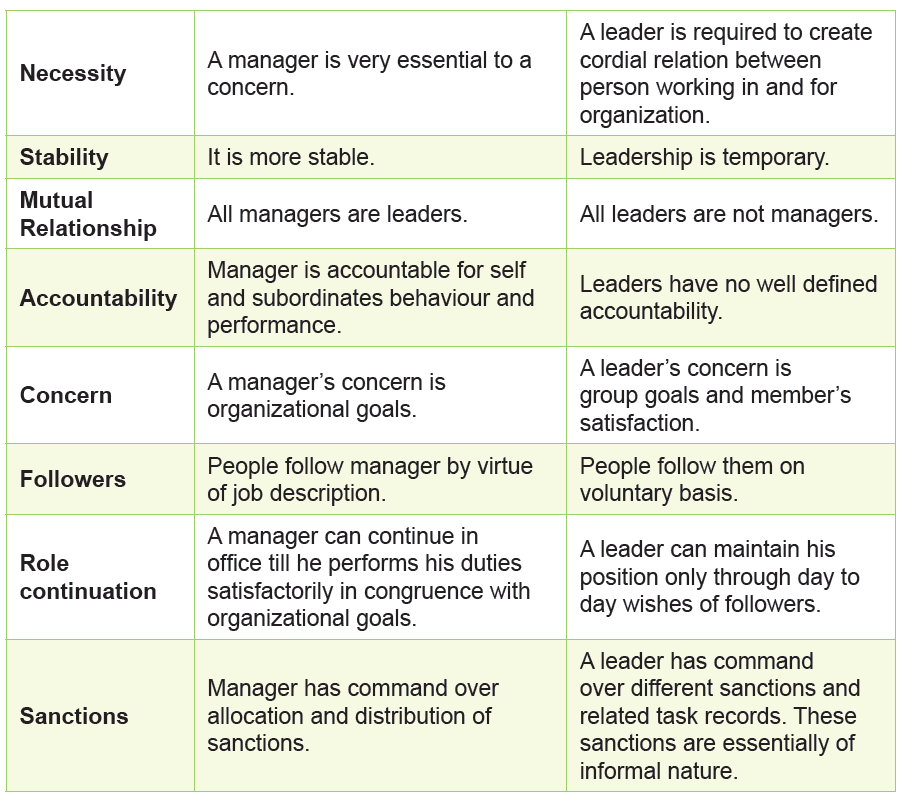
Discuss the importance of managerial functions in any organization.
7.4 Governance
Learning activity 7.4
As a future associate nurse, how do you expect to do in your career
that can contribute to the good governance of the country.
7.4.1. Notion
Governance is the ability to have rule or authority over people, controlling
resources and commanding government activity. For example: taxation and
providing social services, being responsible for provision of security of people
and property.
7.4.2 Types of government
Democratic Governance
This is where the leaders in the different institutions; political, economic or private
sectors, ensure that the institutions work as they are supposed to and helps the
people they are supposed to help. This form of governance aims to not only
reform the institutions but also help them find better and more efficient ways of
dealing with the challenges affecting them.
Economic and Financial Governance
Economic and financial governance is where leaders are involved in promoting
economic growth and reducing poverty in any institution. This can be done by
finding ways for sustainable development, implementing economic policies
that are transparent, predictable and credible, and ensuring proper financial
management.
E-Governance or information technology governance
This is the assessment on information technology and communication and the
impact it has on government practices, and how the government relates with the
society. It has an indirect influence on relations between governments and their
citizens, strengthening the participation and involvement of citizens in political
choices so that their rights and duties are better understood and respected.
The goals of e-governance is to ensure profitability in businesses dealing with
information technology and that dangers that could arise are taken care of before
they do
Corporate Governance
Corporate governance deals with moral principles, values and practices that
work to bring a balance between economic and social goals of different people,
institutions and the society as a whole and the individual and common goals.
The main emphasis of corporate governance is ensuring the best interest of the
parties involved is upheld.
Land governance/Environmental governance
Land governance or environmental governance is concerned with issues of
land ownership and tenure. It deals mostly with the policies, processes and
institutions which are directly involved in the access to, use of and control over
land. It also looks at how these policies are implemented and enforced and the
people involved. It is involved in finding ways to sustain land development and
reduction of poverty.
Public governance:
Public governance can be said to be the power relationship between the
government and its citizens. It can occur through the government working with
community organisations to provide services to the citizens and through the
government ensuring there is proper competition for goods and services in a
market that is regulated by the government.
Private governance:
Private governance occurs when nongovernmental entities or private societies
or institutions make policies that have a major effect on the quality of life and
opportunities of the citizens of a country.
Non-profit governance:
Non-profit governance works in ensuring that an institution achieves its social
mission while still making sure the institution or organization is viable. Public trust
and accountability is important to the survival of an organization, so it needs to
achieve its mission in a way that is respected by those it serves and the society
in which it is located.
Functions of governance
• Determining the objectives of the organization: These are expressed
through the organization’s vision and mission statements and implemented
through its strategic plan.
• Determining the ethics of the organization: This means to define what
aspects of behaviour are really important. Ethics are based on morals and
values. They help to set the rules or standards that govern the conduct
of people within the organization. The set of behaviour normally is set by
the people heading the organization and passed down to the rest of the
members.
• Creating the culture of the organization: This looks at the way people
interact with each other. The leaders of the organization decide on the
culture they want and influence this decision through the people they
appoint to top positions.
• Ensuring compliance by the organization: This means ensuring the
members of the organization comply with its regulatory, statutory and legal
obligations and also work towards achieving the organization’s objectives.
• Designing and implementing the governance framework for the
organization: The governing body is accountable for the performance of
the organization, and retains overall responsibility for the organization it
governs.
• Ensuring accountability by management: To ensure the efficient
governance of the organization, various responsibilities need to be delegated
to people within the organization’s management. There is a governance
framework that defines the principles, structures, enabling factors and
interfaces through which the organization’s operational arrangements will
operate, which is what ensures accountability.
Application activity 7.4
Discuss any four types of governments that are used in your
community.
7.5. Relationship between leadership, management and
governance
Learning activity 7.5
Discuss the relationship between leadership, management andgovernance
Governance can be said to be representing the owners or people who represent
a firm, company or any institution and the will of these people.
These owners will then appoint the management personnel whose mandate is to
manage the organization. These managers must have some leadership qualities
for them to be accepted by the governing body as managers. This therefore
shows a relationship between management, governance and leadership.
One of the functions of governance is to determine the objectives of the
organisation, its vision and how this can be made the organisation’s policy.
Management, on the other hand, is about making decisions for implementing the
policies set by the governing body of the organisation. The leadership qualities of
the managers brought on board is what will determine how well the policies are
implemented or not and how well the rest of the staff in the organisation take up
the vision.
Management comes second to the governing body of any organisation. This
means there has to be an organisation that needs managers. The managers
are bound to exist only if they agree to the wishes of the governing body. The
qualities of a leader that exist in the manager and how acceptable they are to the
governing body are also what ensure an individual stays in management in the
organization.
There are different types of governance and different types of leadership styles.
The governing body, based on what type it is, may chose management individuals
with specific leadership styles that suit their wants.
Application activity 7.4
Show the relationship between leadership, management and
governance
7.6. End Unit Assessment
End Unit Assessment
1. Define leadership?
2. Discuss leadership styles applied by leaders in your community?
3. Differentiate the characteristics of a good leader and a good
manager?
4. Suggest the causes of challenges to leaders
5. What do you think is importance of electing leaders indemocracy?
