UNIT 10 FINANCIAL SCAMS
Key Unit Competence:
To be able to protect oneself against financial scams and identity fraud.
Introductory activity
1. Explain difffferent ways in which people are conned of their money
by fraudsters or criminals worldwide.
2. Describe ways people can use to protect themselves from such
people.
10.1. Concept and types of financial scam in the world today
and identity fraud
Learning activity 10.1
Answer the following questions.
1. Research and find out examples of financial scams that are on
the rise in the country since the introduction of mobile and online
banking.
2. Visit a bank near your school. Ask a resource person at the bank
the following questions:
a). Have they witnessed cases of financial scams at the bank?
b). What methods were used by fraudsters to steal money from
innocent people?
c). How can individuals protect themselves from fraudsters?
Financial scams are deceptive schemes used by fraudsters to rob people and
business organisations off their money. Fraudsters are also called financial
scammers. Financial scams do not involve documentation since most of the
information they provide is falsified. Financial scams are treated as serious
crimes and a violation of civil law. Financial scamming is also called white collar
crime because of the non-violent means used to rob victims off their money.
In the world, there are numerous financial fraudsters who have robbed people and
organisations of billions of dollars’ worth of money. Financial scams characterise
every economy in the world today. World governments are increasingly concerned
about the catastrophic effects of fraudulent activities carried out by numerous
financial scammers and fraudsters.
In terms of types, financial scams have been characterised according to the
methods or ways used by scammers. Some of the common types of financial
scams include the following:
1) Advance fee scams
Scammers communicate with their target victims informing them that they have
won prize money from a lottery, sweepstake or other competitions in which the
target victims did not participate. They inform their intended victims that they
need to pay some advance fees to a specified account before the prize money is
released. Once the money is deposited in the specified account, the prize money
is not released. The scammers then vanish by switching off their communicationchannels. The victims end up losing their money to the scammers.
Alternatively, scammers call their target victims and trick them into entering a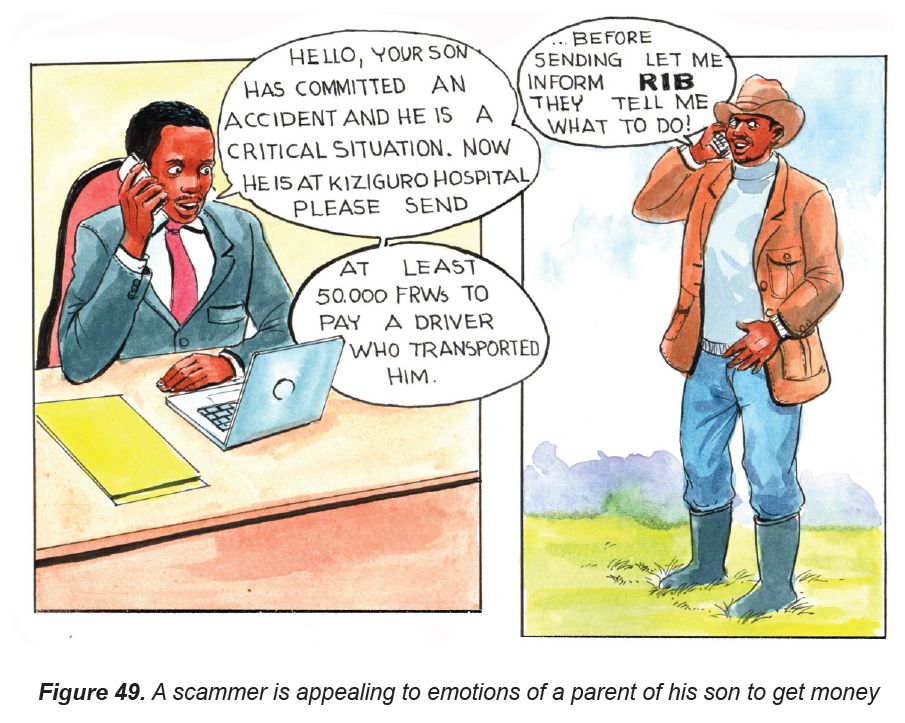
non-existent lottery or sweepstake competition. They are lured into buying fake
lottery, sweepstake or gambling competition tickets. The victims are then informed
that they have won huge sums of money in the lottery or sweepstake competition
they entered. The victims will then be told that they need to pay a prize fee to a
specific account before the money is released to them. Once the prize fee paid,
scammers switch off communication, having conned the victims
2) Investment scams
Scammers use investment scams to con people who want to invest their money
in highly profitable ventures. Some of the investment scams that scammers use
to con their victims are:
a) Ponzi investment scams or pyramid schemes
Scammers establish fake companies to target wealthy investors. These
companies trick their victims by offering very high rates of return on investors’
money in the form of share capital. The victims invest in buying shares in fake
companies and become ‘shareholders’. The scheme collapses when money
from new investors is not enough to pay the original initial investors. The new and
initial investors lose their money once the scheme collapses. Investors are also
tricked into marketing schemes that appear to be real, for example, marketing
of products. Investors are promised large profits based on the number of people
they recruit in the marketing scheme. Profits are not based on the actual sale of
products but rather the number of recruits.
(Sources: The Little Book of Big Scams (Third Edition) (2014) pages 1-40, and The
Little Black Book on Scams (2012), pages 4 –30)
b) Pump and dump stock scam
This is where the price of stocks in a specific company are promoted based on
false and misleading information. The stock prices rise to high levels on the stock
exchange markets. This overvalues the actual price of the stocks in the market.
Promoters sell their stock at an overvalued price and stop promoting the stock.
The stock prices then fall to low levels. Investors end up losing the value of their
capital.
c) Offshore investment scams
Financial scammers promote non-existent offshore investments. These are
investments made in fake foreign companies and sold to investors. The scammers
benefit from high rates of return and avoid paying government taxes. These fake
companies will then vanish making it impossible for investors to trace or recover
their money in the foreign company.
d) Foreign exchange (forex) scams
Scammers lure investors into trading in foreign currencies in a forex market.
An unsuspecting investor is lured into wiring money to an offshore account as
a requirement before being accepted to trade in foreign currencies. Financial
scammers then disappear with the investor’s money.
e) Purchase of precious minerals scams
Financial scammers target victims promising them a sale of precious minerals,
for example, diamonds. They persuade their victims that the sale of precious
minerals is a lifetime opportunity to grow wealthy. The unsuspecting victims then
buy these precious minerals only to realize later that they are not worth the money
invested. By this time, the financial scammers have vanished.
f) Door- to- door sale scams
Door-to-door sales scammers use this method to scam their target victims by
selling them poor quality products at high prices. Such scammers pretend to sell
or promote goods of very high quality. Financial scammers carry out a survey
in advance to obtain personal details of their intended victims. They use this
information to scam their victims. They also con people out of their household
goods.
g) Dating and romance scams
Many people, especially the young, use online dating websites and applications
such as Facebook in search of companions. Financial scammers take advantage
of these online dating sites to scam innocent people. Scammers use fictitious
names to conceal their identities and target people. They play with the emotions
of the target victims by establishing close relationships. They also send the
victims gifts, personal photos and greeting cards. Scammers then ask for
personal information which may be used to scam a victim. After the victims have
sent information or money, the scammers vanish and block their communicationchannels.
h) Banking and online payment scams
Internet and mobile banking are the latest business technologies in today’s
electronic age. Electronic commerce (e-commerce) is revolutionizing the way
people do business across the globe. Financial scammers have encroached on
the new banking technologies to steal money. There are three main categories of
banking and online payment scams. They include the following:
i) Phishing
Scammers email their victims pretending they are from the victims’ banks. They
inform the victim that they want to rectify a problem that has occurred in the
victims’ accounts. They ask their victims to give them their bank account details
such as account name and number. If the victims respond, scammers use the
details to send information electronically to manipulate personal identification
details such as passwords and fraudulently transact business on the victims’
behalf.
j) Vishing
This is similar to phishing. However, instead of emailing, scammers call the victims
purporting to be working for a bank, police unit or fraud investigation agency. They
inform their intended victims that they need their bank account details such as
account name and number, passwords or debit/credit card details. They inform
victims that their accounts are at risk and that they are likely to lose their money.
The victims may respond by giving out their account details. Scammers then use
the details to access funds from victim accounts and transfer them to another or
other accounts. The victims may lose their money through this method.
k) Card skimming
Scammers steal information from credit cards and ATM cards during a
legitimate transaction. They use skimming devices to store information on
a magnetic strip. This information is used to access victims’ accounts and
steal money from them.
l) Card fraud
Scammers use stolen credit or debit cards to make unauthorized transactions
from the victims’ accounts. They can also use information from unsuspecting
victims to make fake cards. The fake cards are then used to make transactions
and steal money from a victim.
m) Online shopping scams
E-commerce involves buying and selling of goods and services online. Many
online businesses are legitimate. However, financial scammers use e-commerce
to con unsuspecting shoppers. They use the following financial scams.
i. Online-classified scams
Financial scammers create online-classified websites that provide an opportunity
for would-be sellers and buyers of online goods to transact business. Scammers
also use genuine websites pretending to be genuine sellers or buyers of goods
to con unsuspecting members of the public. Thus, they create an opportunity to
scam their victims, for example, by giving out bouncing cheques.
ii. Online auction scams
Financial scammers take advantage of websites that auction products online.
They send messages to their targets claiming that they are winners in an auction
for a specified product. They ask for advance payment as commitment to buy the
product. The excited victim promptly pays the advance payment. After receiving
the advance payment, the financial scammers vanish from the auction sites. The
victims end up losing their money.
iii. Fake retailer’s scams
Financial scammers create fake retailer websites. They ask unsuspecting buyers
to pay for items through online money transfers. Once the victims pay, the
scammers vanish and never communicate again.
6) Job and employment scams
With the high rates of unemployment, financial scammers promise unemployed
people’s job placements with high salaries. This scam is promoted by
advertisements on fake websites or the use of the Short Message Service
(SMS). The scammers lure their victims to pay a certain amount of money to
a specified account for processing of documentation and a commission fee.
Once unsuspecting victims have paid the money, the websites are closed and
scammers cut-off all communication.
7) Charity scams
Scammers create fake websites where they target victims of charity scams. They
are most prevalent when there are national disasters in certain countries. Victims
are requested to make donations to assist the people affected by the disaster.
Once the victims deposit money in the scammers’ account, the scammers
disappear and the websites are closed down.
Concerning identity fraud, this one is the unauthorized use of another person’s
identity to deceive or defraud someone else. Identify fraudsters use other people’s
personal details to operate bank accounts, order goods and services, take over
bank accounts, use mobile phone contacts and obtain personal identification
documents to commit crimes.
The victims, whose identities are used, may receive loan statements, service
bills, invoices or statement of accounts for transactions they did not carry out.
Identity fraud is a growing problem in the world today. Most of the organised
crimes witnessed such as illegal immigration, drug trafficking, money laundering,
terrorism and human trafficking are linked to identity fraud. These are types of
identity fraud:
– Identity theft
This is the fraudulent use of another person’s identity or information to commit
fraud without his or her knowledge. Imposters (identity fraudsters) create new
accounts and obtain new debit or credit cards using the personal details of the
victims. The new card that carries similar information to an original one is used to
transact illegal transactions. The Internet is used to facilitate fraudulent activities
of identity thieves.
– Phishing
Fraudsters create fake bank websites that look like genuine websites of known
banks. The fraudsters then send emails to bank customers and lure them to the
fake bank websites where they provide personal details. With such information,
they access the customers’ bank accounts to withdraw money without their
knowledge. This type of identity fraud usually affects customers who use online
banking.
– Hacking
Fraudsters may hack into the website of a financial institution and access
details of customers’ e-banking transactions. They steal the password or PIN
to access the bank’s computerised software system. They may then lure the
bank’s customers into fake websites that look similar to the bank’s real websites.
The fraudsters then use such information to steal money from the unsuspecting
customers’ accounts.
Fraudsters use personal information stolen from innocent people to process
licenses, identity cards and passports to carry out fraudulent business transactions.
– ATMs and credit cards skimming
The credit and ATM cards’ information are captured or copied using electronic
means when customers are carrying out genuine transactions. Fraudsters can
steal vital information by looking over the shoulder of a customer when he or sheis performing business transactions.
Application activity 10.1
1. Identify other types of online financial scams prevalent in the world.
2. Discuss how people lose their money to financial scammers
through the seven types of financial scams identified above.
3. Explain reasons why people in Rwanda are vulnerable to the types
of financial scams identified in question (1) above
10.2. Impact of financial scams on individuals and families
Learning activity 10.2.
Carry out a survey on the impact of financial scams on individuals
and families in Rwanda
Some of the major impacts of financial scams on individuals and their
families include the following:
Financial loss
Financial loss harms individuals and their families. Many people lose large sums
of money to scammers. As a result, victims find it difficult to fulfill their financial
obligations, as they may be bankrupt. They have trouble providing for their basic
needs such as food, clothing, shelter and health. Some of the affected persons
may be too old to start building wealth afresh.
Loss of employment
If individuals affected by financial scams are self-employed and experience
bankruptcy, their businesses may close down. Similarly, if the organisations
where individuals are employed are victims of financial scams, it also leads to
loss of employment. This happens when the organisations become bankrupt and
are forced to close down or lay off workers. Their families also suffer as there is
no money to satisfy their needs.
Mental health problems
Victims who are scammed by fraudsters become shocked, anxious, embarrassed,
worried, upset and angry. This may lead to depression among individuals and
family members. A prolonged period of depression results in health problems that
make it difficult for them to carry out their day-to-day activities.
Psychological, sociological and emotional problems
Victims blame themselves for being scammed. They feel ashamed and
embarrassed to report incidences of financial fraud to their spouses, close friends,
family members and colleagues because they fear being criticized. There is a
tendency for relationships to break down between the affected victims and their
friends, relatives and family members.
A large number of victims lose their self-esteem because of feelings of guilt,
embarrassment and shame. Some victims suffer in silence and may develop
undesirable temperamental behaviour. Other victims may resort to substance use
and abuse or attempt suicide. Victims who are in business develop an extreme
fear of transacting business or trusting people. Victims of online dating scamsdevelop a fear of other potential partners.
Application activities 10.2
Carry out a survey on the impact of financial scams on individuals
and families in Rwanda.
10.3. Steps to take when you are a victim of financial scams
Learning activity 10.3
With the help of your teacher, visit the nearest bank or mobile banking
customer service agent. Ask the relevant person to provide you with
information on what to do to avoid being a victim of financial scam.
They are some steps you can take when you are a victim of financial scams. In
fact, it is not easy for victims of financial scams and identity fraud to recover from
the impact of such fraudulent schemes. There are steps that one should take if
scammed by fraudsters. The steps to be taken include the following:
The first step a victim should take to is report to the respective authorities. Detailed
information should be provided about how one has been scammed. This will help
to prevent and warn others of such scams. For fake online scams, one shouldreport to the genuine online websites.
Most victims blame themselves for being scammed. However, we should not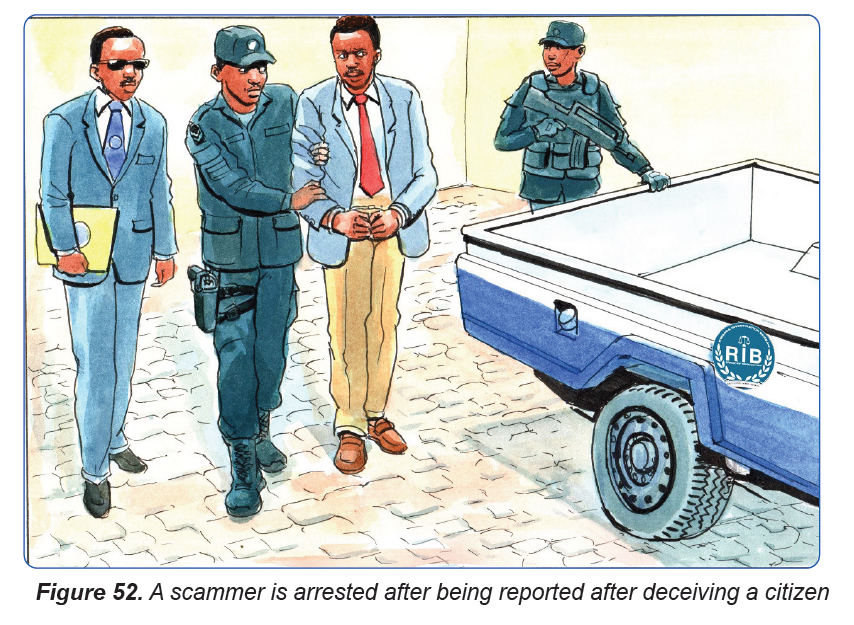
blame ourselves. Victims should accept the reality and stop brooding over it. One
should recover as quickly as possible in order to lead a normal life.
Care should be taken not to fall victim of financial scams. You should always be
extra careful and cautious of people who might be attempting to lure you into
financial scams.
If you realise that you are being scammed, stop contact immediately with
the scammers. You should not respond to further communication from the
scammers and contact the relevant authorities. You should educate yourself
comprehensively about financial literacy and knowledge of financial scams and
identify frauds. Knowledge prepares you to protect yourself from future possible
scams and frauds. If the financial scam involves your banking transactions,
report immediately to the bank. Cancel all other pending transactions. Get new
ATM and credit or debit cards and change your PIN number.
Be on the lookout for possible scams such as miracle cures, fake weight-loss
pills, deceptive lotteries, fake charities, gambling or sweepstake tickets and
pyramid schemes.
Never provide personal identification details or information to suspicious people.
If one calls or emails asking for personal information, always confirm with the
relevant agencies that the caller is genuine.
Application activity 10.2
Design a poster educating the public about measures they can take to
avoid being victims of financial scams and identity fraud do to avoid
being a victim of financial scam.
10.4. Methods of protecting oneself from financial scams and
identity fraud.
Learning activity
Supposing your friend receives a short message service (SMS) or
email from an unknown number and has the following message:
You have won Rwf 250,000 in the National Lottery Draw. Call
+255012345 for further details on how to get your cash prize.
How would you treat such a text message or email?
Supposing your friend is excited and would like to call that number
to enquire how they can get the prize money, what recommendations
would you give him or her?
Supposing your friend called the number and was asked to send
Rwf 20,000 for processing the prize money and they sent the money,
suggest ways in which you will assist him or her.
You should do a thorough investigation of investment companies that offer huge
returns on invested capital. You should check whether the company is real,
registered and licensed to do business.
Do not rush to invest in shares or stocks of companies which unprecedentedly
rise one day. You may lose your investment if the stock or share prices of these
companies tumble to very low levels.
If you operate an e-banking account and receive suspicious emails, you should
not open them. They may contain a virus which corrupts files in your computer.
You should always update your anti-virus or have the latest anti-virus for your
computer. Remember to change your email password regularly.
Do not be lured into wiring money into an offshore account or assist a stranger
to buy foreign currencies. Always buy foreign currencies from a reputable foreign
exchange dealer. Scammers may lure an innocent person into money laundering
schemes.
Do not give your personal details or photographs to strangers you meet online.
Neither should you send money to them.
Your personal identification documents should be kept secure. If such documents
are stolen or misplaced, report immediately to the relevant authorities.
If you are withdrawing money from an ATM machine, be conscious of people
around you. You should shield your transactions in the ATM keypad from those
who may be checking your transactions over your shoulder.
After making transactions, safely keep your personal identification documents.
Do not leave behind your receipts, mini statements or balance enquiries. If your
card is retained in the ATM machine, report immediately to your bank or the
issuing company.
Do not buy goods online from unfamiliar websites. Always buy goods from
genuine websites. When accessing social media sites such as Facebook
and Twitter using public computers, ensure you log out after you arethrough. Before doing anything online, stop, think and click.
Application activity 10.4
1. Describe measures you would use to ensure you do not fall victim
to online identity theft on social media networks such as Facebook,
WhatsApp, Instagram or Twitter.
10.5 End Unit Assessment
End unit assessment
1. Distinguish the meaning of the terms financial fraud and identity
theft.
2. Identity financial scams and identity frauds most common in
Rwanda.
3. Explain common types of identity theft found in the digital world
today.
4. Discuss reasons why victims of financial scams and identity
frauds rarely report incidents to state security agents or their
relatives.
5. Examine reasons why security agents in your country may not
fully contain the activities of financial scams and identity frauds.
6. State reasons why pyramid schemes usually go on for a very
long time before being uncovered.
7. Suggest steps that can be used in helping victims of financial
scams and identity fraud to recover quickly.
8. Assess strategies one may use to protect oneself against
financial scams and identity fraud.
9. Describe how you would help someone if you witnessed an act
of identify fraud happening.
10. is it possible to recognise persuasive messages of scamming
intent in the current era of sophisticated information andcommunication technology?
REFERENCES
DECETY, J. Dissecting the neural mechanisms mediating empathy. Emotion Review.
2011; 3(1): 92-108. doi:10.1177/1754073910374662
HUGHES, Cr. (2006). Education for Global Citizenship: A Guide for Schools.
London, UK: Oxfam Education.
MINEDUC, REB. (2016). Rwanda General studies and communication skills
Learner’s book, Kigali
MINEDUC, REB. (2016). Rwanda General studies and communication skills
Teacher’s Guide, Kigali
MINEDUC, REB. (2021). Rwanda National curriculum for Citizenship, Kigali
REBLIN, M.& Uchino, B.N. Social and emotional support and its implication for
health. CurrOpin Psychiatry. 2008;21(2):201‐205.
doi:10.1097/YCO.0b013e3282f3ad89
Republic of Rwanda, Ministry of Gender and Family Promotion. (2010).
“National gender policy”, Kigali.
SENYONGA, M. (2000). Reflections in General Paper: A Comprehensive Guide.
Kampala, Uganda: Fountain Publishers.
SHAMAY-TSOORY SG, Aharon-Peretz J, Perry D. Two systems for empathy: A double
dissociation between emotional and cognitive empathy in inferior frontal
gyrus versus ventromedial prefrontal lesions.Brain. 2009;132(PT3): 617-627.
doi:10.1093/brain/awn279
SHUAYB, M. (2012). Rethinking Education for Social Cohesion: International Case
Studies. Basingstoke, UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
TIMOTHY, Dallen J. (2011). Cultural Heritage and Tourism. Bristol, UK: Channel
View Publications.
UWANZIGA Nzamwita, J. (2015). Manners in Rwanda: Basic knowledge of
Rwandan Culture, Customs and Kinyarwanda Language. Kigali, Rwanda:
New Times.
VIVANTE, B. (1999). Women’s Roles in Ancient Civilizations: A Reference Guide.Westport, USA: Greenwood Press.
