UNIT 1 SOCIAL COHESION
Key Unit Competence:
The student should be able to make decisions that promote social cohesionin practical situations.
Introductory Activity 1
Mugabo was born in the village of Masaka to business parents. His father
was a shop keeper and his mother a small scale milk seller. One day, when
he was coming from school, he saw a young girl called Keza who was
crying…… When Mugabo asked her why she was crying, Keza replied that
she was hungry. Mugabo decided to take her to his mother so that she could
get what to eat. When the two arrived, his mother served them with milk and
Keza was very happy. From that day, they became great friends.
How can you term or name this kind of positive and humanistic value?
Discuss the importance of Citizenship Education to both students and theentire Rwandan community basing on this afore-mentioned social behavior.
Learning Activity 1.1
Using internet and/or other reference books, carry out research and write
the meaning of Citizenship Education and its objectives. Afterwards, shareyour findings in pairs with one of your classmates.
1.1. The concept of Citizenship Education and its objectives
1.1.1. The Citizenship Education
Citizenship comes from two Latin words, ‘Civis’ (citizen), and ‘Civitas’ (city) which
is equivalent to the Greek word of ‘Polis’. In that sense, citizens are members
or inhabitants of a city, or a state, they form a political community and can be
differentiated from foreign citizens.
The term citizenship is often used interchangeably with nationality, but it refers
to the legal relationship between an individual and a state, in which the state
recognizes and guarantees the individual’s rights. ‘Legal’ is used to mean formal
status, with prior registration, recognition, and publication by civil status services.
As regards the concept of Citizenship Education most often named “civic
education” in different countries and organizations, it can be defined as educating
children, from early childhood, to become clear-thinking and enlightened citizens
who participate in decision making concerning society.
Citizenship education is also defined as the approach of facilitating civic/
democratic competence development by providing the background knowledge
necessary to create an ongoing stream of new citizens participating and engaging
with the creation of a civilized society. Therefore, in order to secure the future
of a society, citizens must train younger generations in civic engagement and
participation.
Objectives of Citizenship Education
Citizenship Education in Associate Nursing Program has the following objectives:
• Equip the learners with required knowledge, skills, attitudes and values
which enable them be accountable, committed, responsible and patriotic
citizens;
• Teaches learners the theories, principles, values and procedures on which
dependents the qualities of a good and patriotic citizen.
• Promote the ethical, humanistic, and moral values that characterize
Rwandan society.
• Show awareness of cultural aspects affecting or likely to affect society.
• Play a central role in uniting people, the preservation of culture and
conservation of social identities.
• Develop attitudes and values relevant to peace and tolerance, justice,
respect for others and for human rights, solidarity and democracy,
patriotism, hard work, commitment, resilience and dignity.
• Get a deeper understanding of global issues and challenges and therefore
appreciate the need for national, regional and international cooperation insolving these challenges for the good of the human race.
Application Activities 1.1.
1. Explain the concept of citizenship Education
2. Discuss the objectives of citizenship Education
1.2. Importance of Citizenship Education
Learning activity 1.2.
In group of 4 or 5 learners Use internet and other reference books, conduct
a research and write the importance of learning Citizenship Education. Write
it down and then present it to the whole class.
It is of great importance to study Citizenship Education for different reasons.
First of all, Citizenship education gives learners the knowledge and skills which
help them become informed and responsible citizens who are willing and able
to take responsibility for themselves and their communities and contribute to the
political process. Therefore, Citizenship Education helps learners become active
citizens once they understand their role within society and how they can go about
improving it.
Citizenship Education also helps learners to develop self-confidence and a
sense of agency, and successfully deal with life changes and challenges such as
bullying and discrimination.
Moreover, Citizenship Education enables learners to make a positive
contribution by developing the knowledge and experience needed to claim their
rights and understand their responsibilities. As a result, it prepares them for the
challenges and opportunities of adult and working life.
For schools and other educational organizations, Citizenship Education helps to
produce motivated and responsible learners, who relate positively to each other,
to staff and to the surrounding community.
For society, it helps to create an active and responsible citizenry, willing to
participate in the life of the nation and the wider world and play its part in thedemocratic process.
Application activities 1.2.
Explain why it is very important to learn Citizenship Education.
1.3. Concept and factors of social cohesion
Learning activity 1.3.
In Rwanda, after the 1994 genocide against the Tutsi, cohesion among the
people of Rwanda was negatively affected. Today, Rwandans have rebuilt
this social cohesion. Discuss with your friend and come up with the definition
of the term of social cohesion and the factors that have contributed to itspromotion in Rwanda and indicate how.
1.3.1. The Concept of social cohesion
Social cohesion is similar to unity. When members of different groups work together
harmoniously, this means that there is a good relationship among them. This
good relationship acts as a bond linking people together for better growth.
This bond among members of a group or society can be termed as cohesion.
The overall good relationship that makes people in a group or society to work
together and relate well with one another is called social cohesion.
Social cohesion balances individual rights against those of the society and
appreciates that a good relationship enables people to respect each other’s
values. Therefore, it works towards the well-being of all its members.
For example, it fights exclusions and marginalization and creates a sense of
belonging. It also offers members of the group or the society the opportunity for
upward mobility. This promotes peace and unity and results in both individual andnational development.
1.3.2 Factors for social cohesion
In each society, there are many things that can contribute to the promotion of
social cohesion. These can be referred to as factors of social cohesion. In
Rwanda, the factors of social cohesion include society norms’ respect, positive
values, the respect of human rights, religious tolerance, promotion of national
and humanistic values, active listening, and empathy and active bystandership.
a) The Society norms’ Respect
Norms can be defined as rules or expectations that define the appropriate
behavior within the society, for example, how students behave in class, how to
live with neighbors, how to behave in public, etc. Norms can be prescriptive when
they encourage positive behavior, for example “be honest” or proscriptive when
they discourage negative behavior, for example “do not cheat”. Failure to follow
these norms may lead to a consequence such as being rejected in the society.
However, norms change according to environment or situation and may change
overtime.
b) Strengthening Positive values
Suppose you are travelling home from school. On the way, an old woman gets
into the bus and finds all seats occupied. You are the only young person in that
bus. How would you react to this situation?
In the situation above, your conscience is likely to push you into standing for the
old woman to sit down. This is because you may feel obliged to show respect
for the elderly. This is a positive value. Indeed, positive values are like a compass
direction: they help point the way to critical and logical thinking.
i. We often demonstrate positive values in different ways. For example, by
solving problems that affect others, helping those in need, having a sense
of responsibility in what we do, being honest or even being caring for
others. All these positive values contribute to social cohesion. The Humanrights’ Respect.
In your discussion, you may have observed that as much as you are required
to work hard in your studies, there is some time spared for breakfast, lunch
and games? This is because each person is entitled to basic needs such as
food, clothing and shelter. As a child, you are also entitled to play. Similarly, your
parents send you to school because you have right to education.
Human rights point to us how tolerate with others. When a person’s human rights
are respected, that person is likely to live in peace with others. Up holding human
rights also helps us to respect and appreciate others. This creates an enablingatmosphere for personal as well as national development.
c) The Religious Tolerance
Though each religion has its own religious teachings and practices, such as
different dress codes, worship of different supreme beings, etc. the values
promoted by the different religions are mostly the same. For example, Buddhism,
Judaism, Islam and Christianity have different religious teachings but they all
encourage the religious values of love for fellow human beings, honesty in dealing
with others, showing care and concern for the needy and living a righteous life.
These values, and others, are drawn from the teachings of each religion. These
religious values make a person embrace others and desire to live harmoniously
with them. This translates to social cohesion hence unity which promotes selfgrowth
and national development.
1.3.3. Promoting National and humanistic values
There are values that are promoted by the government and those which are
expected from all of us as human beings. They include:
a) Resilience
Resilience is the ability of a person or society to recover quickly from difficult situations.
A good example here is the History of Rwanda. Though faced with the unfortunate
happening of the genocide against the Tutsi in 1994 where many Tutsi were
murdered, the country has sprung back to the path of national development,
economic growth and national healing and reconciliation. As a result, the people
of Rwanda now live in peace.
Indeed, Rwanda is today known to be one of the most peaceful countries in the
world. This has happened due to the strong spirit of resilience among the Rwanda
people and leadership. Resilience is thus an important national value in Rwandawhich promotes social cohesion.
b) The Benevolence activities
Benevolence is the actor quality of being kind to others. A benevolent person i s kind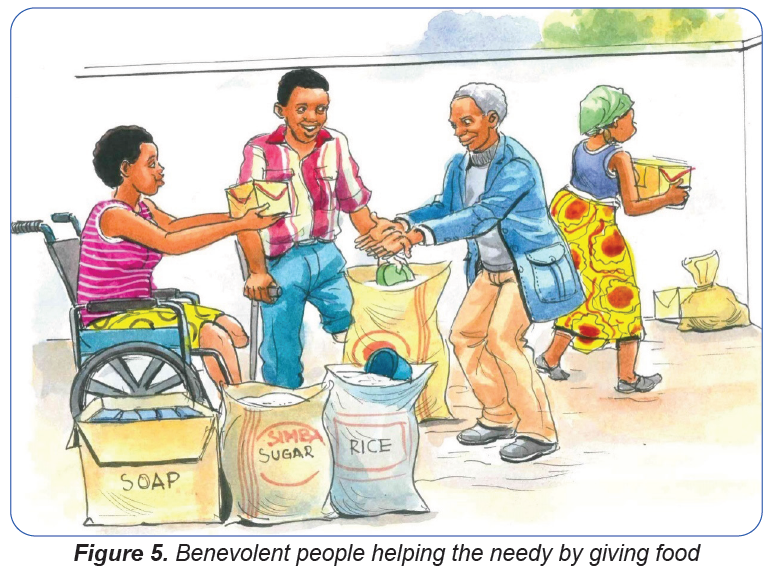
and helpful to others. He/she strives to meet the needs of others without expecting
anything in return. People who help others without asking for any compensation or
favor, their actions can be termed as benevolence. No doubt their actions bring you
closer to them. In the same way, benevolence helps people in the society to become
brotherly and to live in harmony. This promotes social cohesion.
c) Repentance
Repentance is the act of expressing sincere regret about one’s wrong doing or
sin. It is mostly done when asking for forgiveness. It can be done in church,
to a friend or to anyone whom you have wronged. Repentance sets you free
and restores your human dignity. It takes away feelings of bitterness between or
among people in the society. This restores good relations thus promoting social
cohesion.
d) Forgiveness
Forgiveness is the action or process of forgiving or being forgiven. When you
are forgiven, you feel free to relate with the person who forgave you. When you
forgive, you release yourself from bitterness and therefore you can embrace
those who had wronged you. This fosters good relationship among members of
the society there by fostering social cohesion.
is good to note that we forgive others not because they deserve forgiveness but
because we deserve peace.
e) Promoting unity and Reconciliation
Reconciliation is the act or process of restoring friendly relations between two
or more people or groups of people. This means that the people had enmity
between them or a feeling of bitterness towards each other. Reconciliation helps
to drive away the feelings of hatred and bitterness and replaces them with love
and friendliness.
f) Consensus-building
Consensus building is the process of coming up with a conclusion agreeable to
all parties after many opinions have been given. Consensus building involves
considering the input of every member of the group and collectively crafting an
outcome that best meets the needs of the group with the least opposition from a
majority of the members.
During consensus building, people must work together. This promotes cooperation
among the members of the group. This cooperation cultivates a good working
relationship which promotes peace and unity in the group.
Also, different ideas are suggested then analyzed critically so as to come up with
the best decision. This builds up the skills of critical thinking and problem solving.
These help members to make decisions that are informed, most appropriate for
their circumstances and which are acceptable to all. This builds commitment
from all members hence leading to oneness that promotes social cohesion.
g) Active listening and Empathy
Active listening is the ability to listen attentively and not just hearing. It is important
to practice active listening because it assists in identifying a problem, identifying the
cause of the problem and finding a solution to a problem. It also allows others to
express their opinion freely and frankly.
In active listening, one must show interest in the subject matter, try to understand
the speaker and respond only when necessary without interrupting the speaker: the
result of active listening in social cohesion..
Empathy refers to the to understand and share the ability feelings of others. This
is especially when the people you are empathizing with are going through difficult
times. This makes the person feel valued and cared for even when little help has
been given to them. As a result, they get close to those showing empathy. Thisresults in friendly relations and therefore social cohesion.
h) Inclusiveness
Inclusiveness is the act of involving all interested parties in a matter and listening
to the views of each one of them. It is important to involve all members of the
society, regardless of their social status, in making decisions on issues that affect
them. When this happens, every person feels appreciated.
They also feel that their opinions matter and that they are important members of
the group. This promotes trust and mutual respect among all the members there
by promoting good relations among them. This results in social cohesion.
Inclusiveness should be embraced in education, at the work place and in the
activities that a society engages in. This results in a more harmonious society
and thus a peaceful and united nation.
Inclusion is not simply physical presence. It is about intentionally planning for the
success of everyone. This can be done at the workplace, in school, in the village
as well as at the national level.
i) Active bystandership
Bystandership refers to the act of watching without extending any help as a victim
goes through a bad situation. In active bystandership, the person witnessing
what is happening intervenes in a way to solve the problem of the victim. He/she
is active and not just passive. Though he/she may not actually offer a workable
solution, his/ her intervention shows the victim that someone is concerned about
what he/she is going through. This makes it easy for the victim to reach out
to those helping him/ her in a bid to get a workable solution. At the end, good
relations are established thus fostering social cohesion.
The following are the steps to active bystandership:
– Notice what is happening around you;
– Interpret whether it is an emergency that needs intervention or help;
– Imagine yourself in the situation of the person in need of help (empathize);
– Intervene in the situation.
This can be done by:
• Interrupting yourself the harmful situation;
• Interrupting and disrupting the people involved;
• Involving others around you;
• Calling the police or the administration.
When intervening, remember to:
• Approach every one as a friend;
• Avoid being controversial or antagonistic;
• Avoid using violence;
• Be as honest and direct as possible;• Keep yourself safe.
Application activities 1.3
1. Define the concept of social cohesion.
2. Outline five religious values that enable tolerance in Rwanda
3. Identify and explain different national and humanistic values
4. Explain ways in which your school is inclusive. How does this promote
social cohesion in the school?
5. Imagine you found your friend copying homework from your classmate.
Describe different ways in which you can practice active bystandership inthis situation.
1.4. Challenges to social cohesion
Learning activity 1.4
Think of a situation where you tried expressing your opinion on something
and you were silenced. What reason was given for your being silenced?
How did you feel? Let your friends analyze how you reacted to the situation
and to which extent this act constitutes a challenge to the social cohesion.
1.4.1. Regionalism
It makes an individual to avoid others and do things on his/her region. This
limits cooperation with other members of the society and thus can hinder social
cohesion.
Regionlism can also be used to refer to a social theory that advocates for freedom
of action for region over collective or state control. Whenever this is practiced, it
makes people to be self-centered. They have no regard or empathy for others.
A society that encourages regionalism practices individualism is likely to embrace
bystandership as well. This is because no one cares for the other. This is ahindrance to national unity and social cohesion.
1.4.2. Discrimination and exclusionism
The act of treating someone differently from others and in an unjustified way is
referred to as discrimination. Discrimination can happen due to differences in
social status, sex, age, tribe, nationality or skin color. The person discriminated
against feels unwanted. This reduces the person’s ability and motivation to relate
well with those discriminating against him/ her. As a result, the person may pull
himself/herself out of the group and adopt individualistic tendencies.
Any form of discrimination is bad. For example, gender discrimination in the
workplace hinders good relations between men and women in the workplace.
This eventually spills over to the entire society, creating social barriers between
males and females. Discrimination hinders social cohesion and national cohesion.
As Sharron Angle said, “There is a plan and a purpose, a value to every life no
matter its location, gender or disability.” Embrace everyone!
1.4.3. Social injustice
When you try to express your feelings on a certain matter and someone silences
you, arguing that you are not right, or that you should keep quiet and this
amounts to social injustice. Social injustice is the unfair treatment of people who are
considered marginalized in one way or another. This could be because they have
traits or characteristics that are different from those of the majority or because
they are considered less privileged. For this reason, they are considered unequal
to other society members.
Social injustice involves a collection of shared unjust experiences. This means
that it affects a group of people. This group is mostly seen as inferior and therefore
expected to remain silent regarding what they feel or think to the advantage of a
dominant group. This makes interaction between the two groups hard there by
hindering social cohesion.
Examples of groups of people who can be considered marginalized and therefore
be victims of social injustice include women, people living with HIV and AIDS,
disabled people and the poor. We should make every effort to embrace inclusivenesswhen dealing with these people.
Application activities 1.4
1. What dangers would arise if a country adopted the regionalism as a
national decision?
2. Identify any aspects of discrimination that you have witnessed in your
community and suggest possible ways of curbing it.
3. Identify Possible ways of curbing discrimination4. Explain what ways of overcoming challenges to social cohesion
1.5. End Unit Assessment
End Unit Assessment
1. Define the term of Citizenship Education and account for its
importance.
2. Identify and explain two factors of social cohesion in the
Rwandan society.
3. Account for three objectives of Citizenship Education.
4. Discuss the different measures that the government has put in
place to promote reconciliation among people living in different
place in Rwanda.
5. Explain the benefits of repentance.
6. Explain the ways in which the people of Rwanda have shown
resilience.
7. How does upholding of human rights promote social cohesion?
8. Explain ways in which your school is inclusive. How does this
promote social cohesion in the school?
9. Suggest possible ways of overcoming different challenges tosocial cohesion.
