Unit 8: Business
Key Unit Competence: To use language learnt in the context ofBusiness.
Introductory activity: Observe the picture below and guess whatthey relate to.
You will develop these skills
• Use ‘if’, ‘unless’, ‘need to’, ‘be able to’, ‘have to’, ‘must’.
• Use the third conditional.• List the vocabulary of entrepreneurship, costs, production, marketing.
Quick checkHave you ever thought about how important businesses are in Rwanda?
When you complete your education, you will want to get a job.
Many of you will be employed in businesses and you will need to
understand aspects of business such as production, profits, costsand management.
The business world is very important in any country. It provides
people with goods and services that they want to buy. Businesses
also provide jobs, for which people get paid. The more businesses
there are in a country and the more people have jobs, the more
people there are earning wages; these people can buy the goodsand services that they desire.
Entrepreneurship
Read about entrepreneurs

People do not always choose to work in the informal sector. Sometimes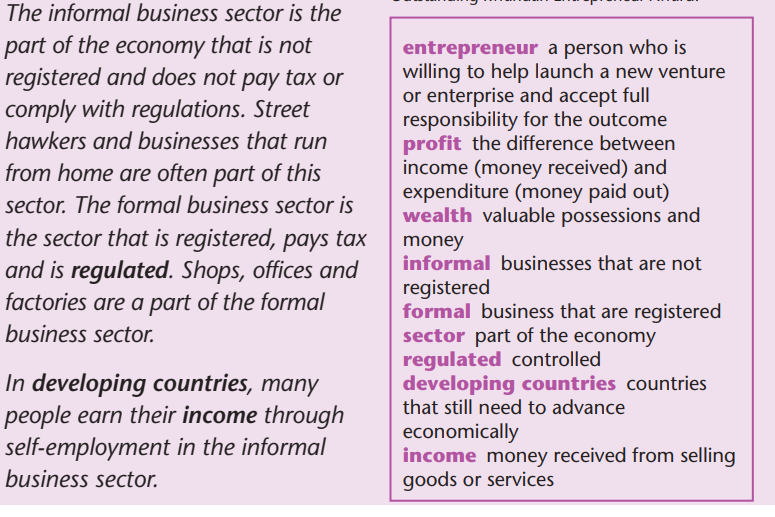
their earning opportunities are scarce. They may be unable to find a job
in the formal business sector. They may only be able to work a few hoursa day through temporary employment for low wages.
To be an entrepreneur, you need to be an innovator. You must be willing
to take risks. You should also be able to lead and manage people. You
must be a good communicator. Unless you take risks, you will not keep
ahead of the market. If you cannot communicate, you will not persuadepeople to buy your product, or to be productive if they work for you.
Entrepreneurs must deal with a large number of challenges that
employees do not have to think about, and in return entrepreneurs expect
to make a profit. Entrepreneurs see an opportunity and, at their ownfinancial risk, set up a business to make the most of that opportunity

Activity 1: Comprehension
After reading the case study above, answer the following questions.
1. Why did Eugene start his own furniture company?
2. What were the disadvantages?
3. What would have happened if Eugene became ill?4. Why do you think Eugene used other people’s wood to start with?
Grammar focus
Conditional clauses
A conditional clause is one that states that an action can only take place if a
certain condition is fulfilled. Conditional clauses make use of ‘if’, ‘unless’,
‘need to’, ‘be able to’, ‘have to’ and ‘must’.
Example:
• If I find her address, I’ll send her an invitation. (I cannot send the invitation if
I do not find the address.)
In the text about entrepreneurs, the following two sentences contain examples
of conditional clauses:
• Unless you take risks, you will not keep ahead of the market.• If you cannot communicate, you will not persuade people.
Activity 2: Complete conditional clauses
Fill in the space with a word that will complete the conditional clause.
1. ______ you come this way, the principal will see you now.
2. I will be back tomorrow ______ my car breaks down.
3. ______ I were a rich man, I would buy a new house.
4. I __________ use my bike to take the produce to market.5. If you want to go to university, you _______ pass your exams.
Read about the characteristics of an entrepreneur
Entrepreneurs are very special people because they have the courage and
willpower to try to start a business. They are not afraid of failure. There
are certain characteristic that entrepreneurs need to possess.
• They need to be disciplined. Entrepreneurs are focused on making their
enterprises work. Successful entrepreneurs are disciplined enough to
take steps every day towards achieving their objectives.
• They need to be confident. The entrepreneur does not ask questions
about whether they can succeed or whether they are worthy of
success. They have confidence in everything they do.
• They need to be open-minded. Entrepreneurs realise that every event
and situation is a business opportunity. They have the ability to look ateverything around them and focus it toward their goals.
• They need to be self-starters. Entrepreneurs know that if something
needs to be done, they should start it themselves. They are proactive,
not waiting for someone to give them permission.
• They need to be competitive. Many companies are formed because an
entrepreneur knows that they can do a job better than someone else can.
• They need to be determined. Entrepreneurs are not put off by their
defeats. They are determined to make all their efforts succeed, so willtry and try again until they succeed.

Activity 3: Describe an entrepreneur, using the third conditional
1. Reread the eight characteristics of an entrepreneur above.
2. Using ‘if’, ‘unless’, ‘need to’, ‘be able to’, ‘have to’ or ‘must’ clauses, make a
sentence about each characteristic and write it in your exercise book. For
example: If an entrepreneur is not disciplined, he or she will not be able toorganise a business properly.
Activity 4: Discuss the characteristics of an entrepreneur
1. Read the following case study and discuss which entrepreneurial
characteristics would have been most important for Josianne.
2. List the characteristics in order of importance.3. Compare your list with the rest of the class.

The costs of a business
Being in business is about making a profit. The entrepreneur needs
to sell his or her goods for the right price – enough to cover all thecosts, but not so much that the customer won’t buy.
Read about the costs of running a business
Businesses aim to produce goods that they sell at a higher price than it
cost them to produce. They do this in order to make a profit. If the cost of
producing goods is greater that the amount received from selling the
goods, the business is running at a loss. Profit is an incentive for
entrepreneurs. The entrepreneur can reinvest the profit in the business ortake it out for personal use.
Before deciding on the selling price for goods, a business must carefully
work out its costs. Some of these costs are fixed, while others are variable
costs. We add these together to get the cost of production. The costs of
production can also be divided into material costs and selling costs.
Material costs are the costs of tools, materials and shipping. Selling costsare the costs of marketing and distribution.
Fixed costs + Variable costs = Cost of production (Total costs)
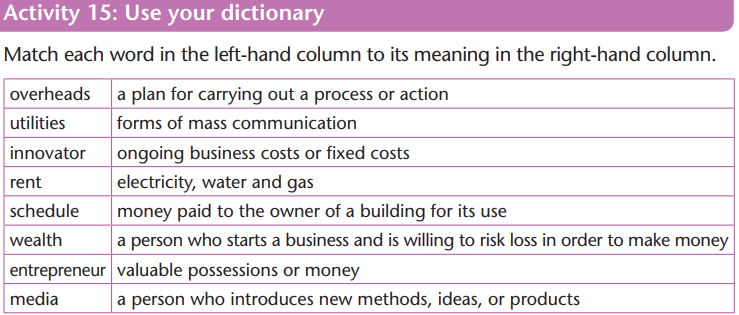
Fixed costs are costs that must be paid regardless of how much is
produced and sold. Examples of these are rent, monthly salaries, loan
repayments and utilities (electricity, water and telephone). Fixed costs are
also known as overheads.
Variable costs are costs which change according to how much is
produced. Examples of these are materials used in production and hourlywages.


Activity 5: Calculate profit and loss
Work out the following:
1. A farmer is selling trays of fruit and wants to make a profit of RWF 10. The
cost price of the product is RWF 15.What must the selling price be?
2. What would happen if the farmer sold his trays of fruit for RWF 9?
3. If the farmer sold the fruit for RWF 9, would he be able to stay in business forvery long? Write your answer using an ‘if’ clause.
Activity 6: Write an essay explaining production costs
One of your friends wants to start a small business. Write a short composition of
about a page, explaining what production costs are, and why it is important tobe able to calculate them.
Drawing up a business plan
Before starting a new business, an entrepreneur must compile a
business plan. A business plan is a formal statement of business
goals and how the entrepreneur plans to reach these goals. The
plan may also contain background information about theorganisation or team attempting to reach these goals.
Read about business plans
A business plan contains a description of who runs the business, the
market (people who will buy the product or service) and the competition
(other businesses offering similar products or services). There is also a
financial management section explaining how the business will make aprofit and pay off debt.
If an entrepreneur wants people to invest in his/her new business, or
wants to borrow money from a bank, then he/she needs to have a
business plan. The investors or bank will read the business plan verycarefully before deciding whether or not to loan money.
Activity 7: Summarise a business plan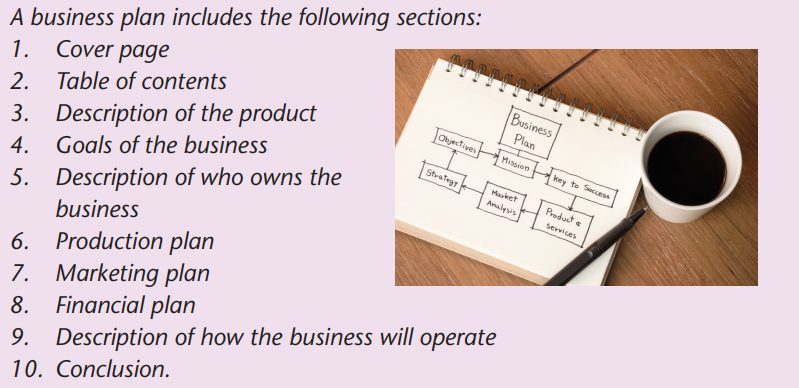
Write a summary of the contents of a business plan, explaining why each part isimportant.
Describing production
Read about the production process
Producers make the goods and provide the services that people buy or
use. Without production, there would be very little in the shops for you to
buy! Production is the process by which inputs (raw materials and semi-finishedproducts) are made into finished goods that can be bought.
An example of a semi-finished product is a roll of cotton cloth used by a
clothing factory. The cloth has already been spun from cotton thread in a
cloth manufacturing factory. The clothing factory buys the cloth and
makes clothes that are sold in a shop. The clothing factory also usesbuttons and belts that are produced in other factories.
The different suppliers of raw materials and semi-finished products that
are needed for production are known as the supply chain. Once the
finished goods have been made, they must be packaged and distributed
to shops, where they can be sold. The different types of distributors that
make goods available for consumers to buy are known as the distributionchain. These include factory outlets, warehouses, wholesalers and shops.
Consumers and producers need each other. Consumers need producers to
make the goods and services that they buy and use. Producers need
consumers to buy the goods and services they want to sell. All businesses
produce something: a hairdresser produces hair cuts, a farmer producesagricultural produce

Activity 8: Describe the production process of a baker
In your group, discuss the production process of a baker producing bread.
1. What time do you think he or she had to get up and start baking bread if
you are to have fresh bread for breakfast?
2. What ingredients does the baker have to buy and how does the supply chain
work?
3. Make a timeline of the steps involved in getting fresh bread into the shops
each day.
4. Compare your timeline with the rest of the class.
5. Write four sentences beginning with ‘if’ to explain what will happen if the
baker does not manage the production process. For example: If the bakerdoes not get up early, the bread will be late getting to the shops.
Describing marketing
Read about marketing
Marketing includes branding and advertising. Branding means appearing
in the media, sponsoring local events and making sure people remember
the business’s name. Some businesses design powerful logos that people
will recognise. For example, fast food chains and petrol stations have
logos that can be recognised from a distance. This helps with marketingbecause people can identify the brand.
To advertise a product, a firm needs to make use of the media. The media
is any form of mass communication and it includes both print and online
advertising.There are many different types of media that can be used in
advertising such as:
• Print advertising, such as newspapers, magazines and flyers.
• Outdoor advertising, such as billboards and events.
• Broadcast advertising, such as the TV, radio or Internet.
• Covert advertising, which is when an actor uses a product in a movie.
• Celebrity advertising, which is when a famous celebrity uses a productin public.

Activity 9: Design a poster for a product
With your group, choose a product and design a large poster to advertise it. You
will need a large sheet of card, pencils, coloured pencils, glue, scissors and old
magazines. Here are some tips to help you with your design:
1. Use a large piece of paper or cardboard.
2. Design your poster before you make it – plan where each element will go on
the page.
3. Use bright colours and preferably one large picture that will attract attention
from a distance.
4. Use very few words, but include all the necessary information that will make
people want to buy your product.
5. Use large letters for the main points that you are trying to get across.6. Use a fun design, but keep the poster easy to read.
Grammar focus
The third conditional clause
We can use third conditional clauses to talk about conditions that are impossible
because they are in the past and we cannot change at all. impossible because
they are in the past and we cannot change what has happenedat all. This
conditional case refers back to regrets, sorrows, wished for but non achievedsituations.
Here, we use Past perfect in the if-clause and the Conditional perfect in the Main
clause.
Examples:
• She would have become a teacher if she had gone to university.
• If I had paid more attention in class, I would have understood the lesson.
The third conditional can also be expressed by removing IF and invert the
auxiliairy HAD with its subject. Thus, the equivalent sentence always starts with
HAD.
Activity 10: Use third conditional clauses
Complete the following sentences in the third conditional by using ‘if’ clauses:
1. ___________ , I would have gone to the party.
2. ____________ , we could have had a picnic.
3. ____________ , I would have known it was going to rain.
4. ____________ , she would have said hello.
5. They _____________ accepted your ideas _________ you had explained more
clearly.Describing a business
Businesses can be very small or very large. Many entrepreneurs
start a small business due to a crisis in their personal lives, like
losing their job or failing at school. Sometimes, these small
businesses grow into huge groups, like the Virgin Group of
Companies, started by Richard Branson.Read about a successful entrepreneur
Sir Richard Branson is an English businessman and investor. He is best
known as the founder of Virgin Group, which comprises more than 400companies. He was born in 1950, in Surrey, England.
Richard Branson struggled in school and dropped out at age 16; it wasthis decision that lead to the creation of Virgin Records.
From his entrepreneurial success with Virgin Records, he went on to create
more companies. He is now a billionaire. One of the interesting companies
in the Virgin Group is Virgin Galactic, a space-tourism company. Branson
is also known for his adventurous spirit and sporting achievements,including crossing oceans in a hot air balloon.

Activity 12: Talk about a Rwandan business
1. Research and find out about a business in Rwanda. This can be in your own
community or elsewhere.
2. Write a report of your findings to share with the rest of the class. Make useof the conditional wherever possible.
Recounting the development of a business
In this unit, we have learned about entrepreneurs and the world of
business. We have discovered that entrepreneurs have a very
important role to play in our economy. They take risks, which are
not always successful. Not all new businesses are successful. Hereare the stories of some entrepreneurs
Read about a business that succeeded
His business continued to grow and today Daniel has a team of ten ‘Mr
Fixits’ working with him. He no longer works from home; he has an office
and has registered as a private company. Over time, Daniel began to
make a name for himself as the local ‘Mr Fixit’ and had more work thanhe could handle.
He hired someone to help him. Sometimes, he feels sad that he now has a
lot of paperwork to do and cannot spend so much time doing the thinghe loves – fixing things.
Read about a business that failed
When Seth left school, he found it difficult to get a job. His father
suggested that Seth join him in his successful grocery store. All went well
for the first year. Seth learned about the business and his father kept tightcontrol of expenditure.

Activity 13: Discuss the success and failure of businesses
In your pairs, take turns to recount the experiences of Daniel and Seth. Why doyou think the one business succeeded while the other one failed?
Corporate social responsibility is about improving the living
conditions of local communities and being as eco-friendly as
possible. For example, the ICT firm, Dell, once came up with plan
to sell more PCs by informing its customers that the company
would plant a certain number of trees for each unit bought. The
firm knew that trees are crucial in absorbing the greenhouse gasesthat pollute the air and cause global warming.

Activity 14: Talk about CSR in your district
1. In your groups, suggest CSR projects that would improve the lives of people
in your community.
2. Propose CSR projects that would help to protect the environment.3. Report your findings to the rest of the class.
Vocabulary, spelling and pronunciation
Assessment
1. Define the meanings of the following terms.
a) production
b) marketing
c) business plan (3 marks)
2. Write three sentences about business using either ‘if’, ‘unless’,
‘need to’, ‘be able to’, ‘have to’ or ‘must’ sentences. (3 marks)
3. Complete the following sentences:
a) If you ________ spent more time on the project, you _________
have made fewer mistakes.
b) If I __________ seen him in the office, I __________ have
told him to call you. (4 marks)
4. Briefly explain why we need entrepreneurs in Rwanda. (5 marks)
5. Discuss how using the characteristics of an entrepreneur
could help you in your daily life. (5 marks)Total (20)