Unit 4:Ecology and Mathematics
Key Unit Competence: To use language learnt in the context ofEcology and Matematics.
Introductory activity: Brainstorm names of people and things wecannot sense.

interdependent when two or more organisms or people are dependent on each
other
organisms any life forms
transmit to send or pass something on
larvae the immature form of an insect, e.g. a caterpillaressential absolutely necessar
The composition and contents of soilRead about the composition of soil

Factors that help to form soil include:
• Living organisms: This includes organisms such as plants, animals,
fungi and bacteria.
• Topography: This is the shape or slope of the surface of land where the
soil is forming.
• Climate: The climate and weather forming affect how the soil forms.
• Core material: The core material is the minerals and rocks that areslowly disintegrating to form the soil.
Grammar focus
Abstract nouns
Nouns can be abstract or concrete. Concrete nouns are tangible. This means
that you can experience them with your five senses: you can touch them, hear
them, feel them, taste them or smell them. Abstract nouns refer to intangiblethings, such as feelings, ideals, concepts and qualities.
Example: I have a dream. ‘Dream’ is an abstract noun because you cannot tasteit, see it, feel it, hear it or smell it.
Here are other examples of abstract nouns:
• beauty • bravery
• courage • enthusiasm• hatred • intelligence
Activity 1: Change adjectives to abstract nouns
Complete the following sentences by changing the adjective in brackets into an
abstract noun.
1. He is a man of ______ . (courageous)
2. The people in this part of the country live in ______ . (poor)
3. ______ to animals is a punishable offence. (cruel)
4. The man showed great _____ of character. (strong)5. I have great ______ in welcoming you. (pleasing)
Activity 2: Label a diagram
When we draw a diagram to explain something, we must make sure that the
diagram is easy to understand. Using labels helps the reader to identify the
different parts of the diagram.
1. In your group, use the diagram on page 44 to discuss the composition of
the Earth’s surface.
2. Working alone, do research and draw a diagram to show the different parts
of the Earth’s crust.3. Label your diagram.
Read about the composition of soil
When plants decay, they break down in the soil to form rotting organic
matter called humus. This increases the nutrients available for moreplants to grow.

Grammar focus
Passive voice
We use the passive voice to show interest in the person or object that is
experiencing an action, rather than the person or object that is performing
the action. In the reading on the composition of soil, there are several sentences
where the passive voice is used, for example: Soil is made up of several things. In
the active voice, this sentence would be: Several things make up soil. Can youfind more sentences in the passive voice?
Activity 4: Write a description of the composition of soil
Copy the following paragraph into your exercise book and fill in the blanks.
Plants obtain _______ from the soil. Soil is the outer, loose layer that covers the
surface of the _______. Soil quality depends, not only on the chemical
composition of the soil, but also on the _______ (regional surface features) and
the presence of _______ organisms. The four major components of soil are
_______ mineral matter, _______ matter, water and air. Soil is the base of life on
Earth because it has most of the important _______ in which plants need to
grow. Those plants in turn feed animals and _______. Soil is also where much of
our fresh _______ is stored. Fresh water travels through the soil being _______ as
it goes. It often ends up in underground _______ called aquifers, where we canget it when we need it.
Soil erosion
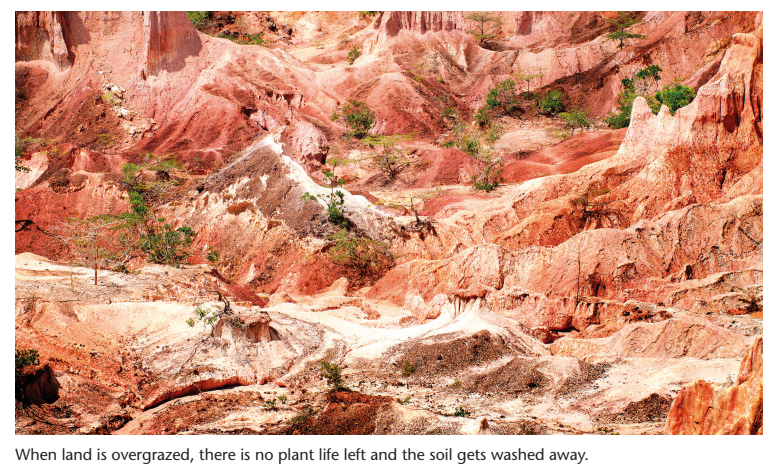

Read about soil erosion
Soil erosion occurs when the topsoil disappears for some reason. Erosion
can occur naturally as a result of wind or water, or as a result of human
activities. It becomes a problem when human activity causes erosion tooccur much faster than under natural conditions.
Soil plays a very important role in supporting life on Earth. When soil is
eroded, it affects the ecology of the area where erosion has occurred.
Plants use soil, not only for nutrients, but also to anchor themselves in the
ground using their roots. Many animals, fungi and bacteria rely on soil asa place to live.
The atmosphere is affected because changes in the soil affect the rate at
which gases, such as carbon dioxide, are released into the air. The qualityof water is affected because the soil helps to filter and clean our water
Activity 5: Describe the process of soil erosion
Write sentences about what will happen if too many goats are allowed to grazeon a hillside. Make sure you organise your sentences in the right order.
erosion gradual wearing away; ecology the branch of biology that deals with therelations of organisms to one another and to their physical surroundings
Read about the effects of soil erosion
When the topsoil is eroded from an area, the area loses its most nutrientrich layer, and therefore the ability of the soil to produce crops is reduced.
When the organic matter that is found within the top layer of soil is
removed, the soil can no longer ‘hold’ water. This means that the area is
more susceptible to extreme weather conditions such as droughts. As the
soil is eroded and runs down to waterways, river banks can be eroded,
causing rivers to break their banks during heavy rains. This causesflooding and more damage to the surrounding area.
Wind can also cause soil erosion by moving topsoil. Wind can also
damage young seedlings by blasting them with sand and other small
particles. Wind can uncover and expose some seedlings, while at the sametime covering other seedlings with too much soil.
Soil erosion can be caused by human activities such as over-farming and
overgrazing, or by natural phenomena such as wind. Over-farming occurs
when farmers use their land too extensively without giving it time to rest
and replenish. Instead of rotating crops so that the nitrogen isreplenished in the soil, some farmers exhaust the land.
Overgrazing occurs when farmers keep too many animals for the
available vegetation. All the vegetation is eaten by the animals. There are
no roots left to hold the soil together, and no leaves to make humus. This
leaves the land bare and exposed to wind and rain. In East Africa this is aserious concern, especially in the highland areas of Rwanda and Burundi.

Activity 6: Identify the stages of soil erosion
Look at the pictures below and then match each one to the correct sentence.
1. All the vegetation has been eaten, the land is overgrazed and there is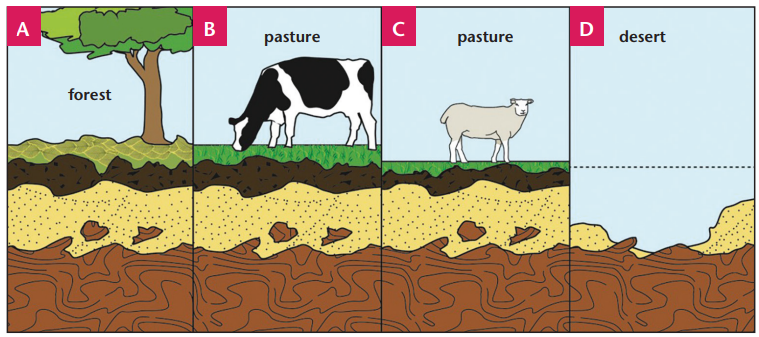
nothing to stop soil erosion. The land becomes a desert.
2. When the land cannot sustain the cattle, sheep and goats are grazed there
instead.
3. The soil is fertile and lots of plants grow in it.4. Cattle are grazed and the smaller plants are eaten.
Plants
In the next section, you will learn more about plants.Activity 7: Identify the ratio of plants to other species on Earth
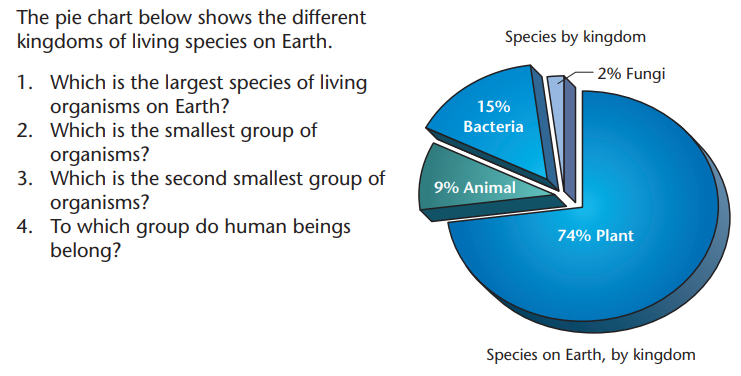
Read about the parts of a plant
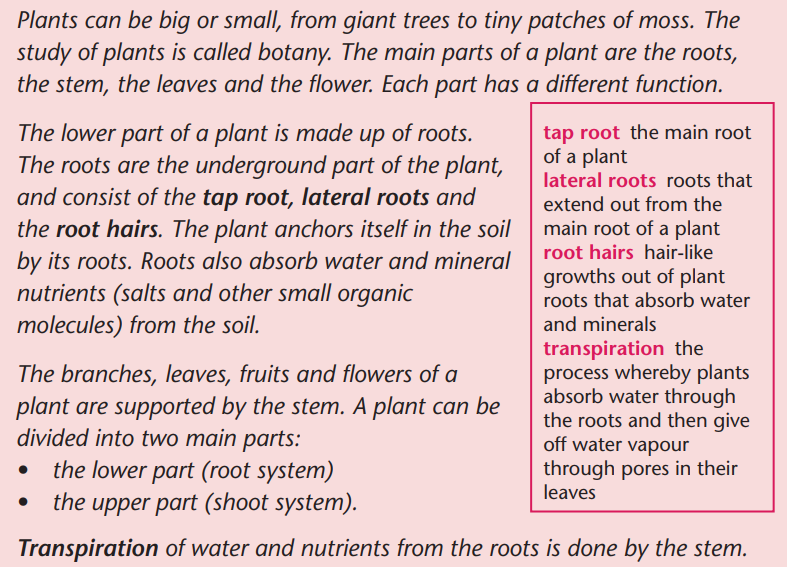
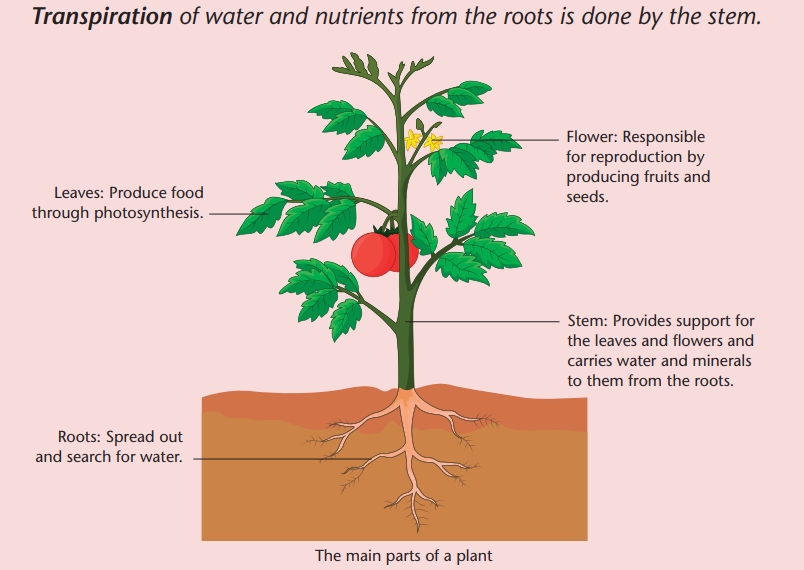
Grammar focus
Word formation
When we make sentences, we use words. In English there are two main ways of
creating new words, borrowing and derivation.
Borowing: through this process, English entered complete words from other
languages without making any change on them.Example: voyage, souvenir, kimono, pinjama, fiancée, …
Derivation: through derivation, English create new words after making some
changes on them. The process of derivation uses two techniques,
composition and Affixation.
• Composition: word creation by composition is made by adding a word to
another. We find this in many compound words. Example: facebook,
chalkboard, roothairs, taproot, sunlight, …
• Affixation: word creation though affixation is done by adding a preffixe
and/ or a suffixe to a word or fraction of word called Root. Like plants,
words have roots, the basis which they are built. Prefixes are justintroductory words or particle; and suffixes are ending words or particles.
Example:
• product (root): re-product, product-ion, re-product-ion.
• trans- pirat-ion
• photo-synthes- is• pollin-ation, pol-ar
Some common affixes:
Prefixes: pre-,mono-, di-, re-, photo-, multi-, trans-, dis-, im-, ex-, …Suffixes: (-ation)-ion, -al, -er, -ar, -iar, -om, -en, -sis, -gy, -ment, …
Identifying affixes and roots help us understand the meaning words.
Activity: Pick five words to illustrate Word Borrowing and five other words
from derivatives in the text below about “Label a plant “; then explain parts ofthe formation.
Activity 8: Label a plant
Go into the school grounds or surrounding area, and pick a small plant. Bring it
back into the classroom, draw it and label it. Make sure you include thefunctions of each part.
Read about the importance of plants
The production of food for the plant is done by the leaves through the
process of photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide from the air is taken into the
plant by the leaves. The carbon dioxide mixes with water that has come
from the air and the roots. Energy from the sun helps this process and
turns the water and carbon dioxide into glucose. Glucose is the plant’s
food and gives it energy to grow. During the process of photosynthesis,
the plant breathes out oxygen into the atmosphere. This is veryimportant, because oxygen is needed by human beings in order to


Activity 9: Ask and answer questions
Take turns to ask each other the following questions and supply the correct
responses.
Q. What are the functions of the roots of a plant?
A. The functions of the roots are _______ .
Q. What is the function of the stem of a plant?
A. The function of the stem is _______ .
Q. What is the function of the leaves of a plant?
A. The function of the leaves is _______ .
Q. What is the function of the flower of a plant?A. The function of the flower is _______ .
Activity 10: Explore your environment
Reread the texts about plants and their importance to humans.
1. Make a list of plants in your environment at school.
2. Why do you think we need plants in our lives?
3. Do you think plants can be harmful to humans? Explain your answer.
4. Describe the relationship between plants and the environment.
5. Compare your answers with those of your friends. Discuss your answers withthe rest of your class.
Activity 11: Identify sentences in the passive voice
There are a number of passive sentences in the readings about plants. For
example: Transpiration of water and nutrients from the roots is done by the stem.
The underlined words show the object being used to start the sentence. Findthree more sentences from the passage that are written in the passive voice.
Grammar focus
Countable and uncountable nouns
Countable nouns are things we can count using numbers. They have a singular
and a plural form.
For example: one dog, two dogs.
Uncountable nouns are the things that we cannot count with numbers.
For example: rice, tea, water.We always refer to these nouns in the singular. We do not talk about many rices!
Read about types of plants
There are over 280 000 different plants on Earth, but we can divide these
into 4 main groups: mosses, ferns, conifers and flowering plants.
Mosses are land plants, but they do not have seeds or flowers. Mosses
reproduce with spores. Mosses do not have stems or large roots to
transport water and nutrients, so they live in moist environments and aresmaller than other land plants.

Flowering plants represent the most widespread group of plants on Earth.
Flowering plants are found in most habitats, from deserts to the polar
regions. Flowering plants include species of trees, grasses, shrubs and
herbs. The flower attracts many animals which assist in pollination,
making the process of pollination more efficient. The seed develops in an
ovary, which becomes a fruit. The fruit serves to help seed dispersal, as
animals eat the seeds. Birds and mammals may deposit the seeds a longway from the original plant.
There are 8 000 species of grasses, which are plants with small flowers.
Grasses provide food for many grazing animals, including buffalo andzebra. Grasses can provide food such as grains like rice, wheat and corn.

Activity 12: Make notes
When we are studying information, it is useful to make notes. Using words,
when we make notes, we write a brief phrase about the most important points
of what we are reading. This helps us to know what is important and must belearned.
Reread the passage ‘Read about types of plants’ and make notes on the mostimportant information. Include any mathematical information that is relevant.
Activity 13: Discuss plants that are useful to humans
In your group, discuss the different plants that are useful to humans. See if youcan group them into trees, shrubs, flowers, grasses and herbs.
Activity 14: Classify plant typesLook at the following pictures and answer the questions that follow.
1. Classify each of the plants as a tree, a flowering plant, a shrub, a herb or a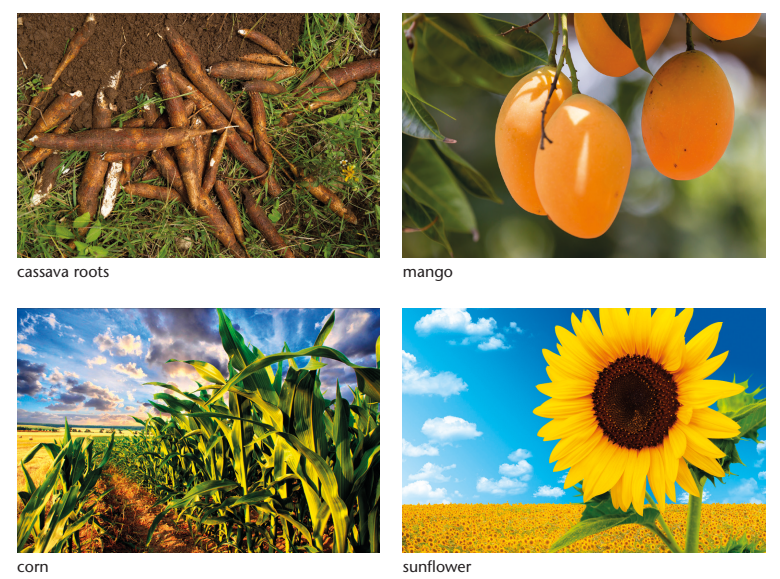
grass.2. Match the following names of the plants with the correct description.
Activity 15: Conduct a survey
Do you know the answers to the following questions?
• How many kinds of plants live around you?
• Which plants are common and which are rare?
• What is the average tree size?• When do the plants flower?
You can answer these questions by conducting a plant diversity survey. In order
to do this, you will need to complete the following steps:
1. Choose an area of your neighbourhood in which to conduct the survey.
2. Mark out the area to be surveyed. An area of 2 m by 2 m is sufficient.
3. In your notebook, write down the names of all the different types of plants
in your survey area. Count how many of each species there are, and make a
note of your findings.
4. Create your statistics. Add up the total number of plants and then calculate
each type of plant as a percentage of the total.
5. Calculate the average number of each plant type.
6. Draw a table showing the different classes and species of plants found.
7. In class, discuss your findings and describe any interesting facts that
emerged from your survey. Talk about what types of plants you saw and alsowhat you did not see. Use ‘why’ questions to get answers from each other.
Vocabulary, pronunciation and spelling
Activity 16: Use your dictionary
Look up the following words in your dictionary. Write the word and its meaning
in your exercise book. Practise saying the words with a partner or in a group.
organism decayed topography
inorganic nutrients erosion
habitat susceptible humus
transpiration photosynthesis reproductionto harbour multicellular pollination
Assessment
1. Find at least five abstract nouns in this unit, for example ‘cultivation’
(from the verb ‘cultivate’) and ‘importance’ (from the adjective
‘important’). (5 marks)
2. Choose the most appropriate meaning for each of the following words.
a) cultivate
to grow plants
to plant
to have crops for food
to grow plants and animals for food
b) root crops
stems rich in carbohydrates
substitute for cereals
underground crops
crops with roots
c) harbour
bring
shelter
cause
train (3 marks)
3. Explain the importance of humans to both plants and soil. (2 marks)
4. In your own words, describe how human activities cause soil
erosion. Use examples and illustrations. (10 marks)Total (20)
