UNIT 2: RELIGIOUS BELIEFS AND UNITY IN DIVERSITY
Key Unit Competence:
Evaluate the unity and peaceful co-existence among religious beliefs and
propose appropriate solutions.Introductory activity
Read attentively the passage below and then answer to the questions:
In Rwanda, are several religious denominations. Rwandans, though having
the same culture, they have different religious beliefs (e.g. Chatholic, Islam,
Presbyterian, Pentecostal (ADEPR), Anglicans (EAR), Restoration Church,
Orthodox, Seventh-day Adventists, and the traditional belief).
1. Why do you think there are several denominations and religions not
just one as the creator is one?
2. Write briefly, what you know about each religious belief mentioned
above. Which distinguishes it from others (distinctive doctrine).
3. Based on biblical references: John 4:6-15; Luke 9:49-50 and
Galatians 3:26-29, what are the christian values to be lived beyond
our differences?2.1 Different religious beliefs, teachings and religious
practicesLearning activity 2.1
1. Using various resources, discuss the fundamental religious teachings
of the religious beliefs you know.
2. Establish similarities and differences of these religious beliefs.
We find many religions in the world: Judaism, Christianity, Islam, Hinduism,
Buddhism and traditional beliefs. In one religion, we find many beliefs or
confessions. In christianity, we find for example catholics, orthodox, and
protestants and different branches.2.1.1 Christian Beliefs
Christians believe in the death and resurrection of Jesus Christ who died
because of people’s sins. All Christian denominations believe that Christ is the
Word of God incarnated. They confess He came to save them through his Death
and resurrection. He rose from the dead and appeared to the apostles who
became the witnesses of what they saw (Acts of Apostles 2:32). The Christian
faith came from the apostles’ who are followed Jesus Christ. The word of God
about Christ was written in the Holy Scriptures. Thus, christians also believe in
the written Scriptures to nourish their faith.By His death, Jesus wanted to destroy the wall of hatred and conflict that was
between the kingdoms, Judea and Samaria (John 4:6-15). He worked for the
unity of the twelve families of Jacob. Love for one another was an important
concern.Like Jews Christians have no fundamental reason to live in disunity with one
another. After all the one, they believe in is One! Salvation is universal for all
who believe and confess the death and resurrection of Jesus Christ.We note that the name Christians was used at Antioch and it means the Disciples
of Christ, the ones who believe and imitate Christ (Acts of Apostles11:25-26).Today’s apostles are the gospel ministers who serve God in different churches.
Since the Pentecost event the Church is guided by the Holy Spirit as the Motor
and Soul of it who guides the operations of the church to be in consent with the
written Word of God.The following are major groups of Christianity:
• Catholicism (Roman and Orthodox Church)
The Catholicism is the large group of Christianity in the world and it is founded
in the common creed expressed in the following articles:Article 1: I believe in God, the Father Almighty, Creator of heaven
and earth. This affirms that God exists, that he is a Triune God known as the
Holy Trinity and that he created the known universe. God the father loves the
Son vice-versa and they communicate in the Holy Spirit. There are then the
relationships of Fatherhood, Filiation and of Love.Article 2: And in Jesus Christ, his only Son, our Lord. This attests
that Jesus is the Son of God and that He’s most certainly divine. So the use
of Lord with Jesus is meant to profess His divinity. The name Jesus comes from
the Hebrew Joshua, meaning “God saves.” Catholics believe that Jesus is the
Saviour.Article 3: Who was conceived by the power of the Holy Spirit and born
of the Virgin Mary. This affirms the human nature of Christ, meaning He had
a real, true human mother, and also affirms His divine nature, meaning He had
no human father but by the power of the Holy Spirit was conceived in the womb
of the Virgin Mary.
Article 4: He suffered under Pontius Pilate, was crucified, died, and
was buried. The human nature of Christ could feel pain and die, and he died
on Good Friday. The mention of Pontius Pilate (the Roman governor of Judea,
appointed by Caesar) by name means to place the Crucifixion within human
history.Article 5: He descended into hell. The third day he arose again from
the dead. The hell Jesus descended into wasn’t the hell of the hopeless, where
Jews and some Christians believe the devil and his demons reside. Jesus
possessed a glorified and risen body.Article 6: He ascended into heaven and is seated at the right hand of
God the Father Almighty. The Ascension reminds the faithful that after the
human and divine natures of Christ were united in the incarnation, they could
never be separated. Sitting at the right hand of the Father means to be in glory
with the FatherArticle 7: He will come again to judge the living and the dead. This
article affirms the Second Coming of Christ at the end of the world to be its
judge. After the judgment there will be eternal life or eternal sufferingArticle 8: I believe in the Holy Spirit, this part reminds the believer that God
exists in three persons the Holy Trinity God the Father, God the Son, and God
the Holy Spirit. The Council of Constantinople 381 After Christian Era (ACE)
confirmed that the Holy Spirit is consubstantial to the Father and to the Son.Article 9: The holy Catholic Church, the Communion of Saints, the
Church is holy in the intension of the Founder who is holy. It is holy without
consider one member. It is holy because Jesus always uses the Holy Spirit to
sanctify it in the SacramentsArticle 10: I believe in one Baptism that removes sins, Christ came to save
the world from sin. Belief in the forgiveness of sins is essential to Christianity.
Even many forms of Baptism, baptism is one and it removes the original sin and
other sins and Christians became new creatures.Article 11: The resurrection of the body, the Resurrection of Jesus is the
proof that after death there is other life. The resurrection of bodies will occur in
order that the judgment takes placeArticle 12: And I believe in the life everlasting. As He rose, so shall
all human beings. Death is the only way to cross from this life into the next.
Catholics believe and hope the happiness, the heavenly life after judgment. This
life is prepared here on earth and the condition is the Faith and works of love
(James 2:14-26)
The Catholicism is made of two major groups: Roman catholic Church (
recognize the authority of the Pope as the universal Church leader) as well as
the Orthodox Church ( they rejected the authority of the Pope and are it is led by
a Patriarch). There are also some slight differences in the liturgical celebration
but the doctrine remains the same.• Protestantism
Protestantism originated in the time of reformation in 1517 (ACE) with Martin
Luther tried a reform in the church. He found out that the church had started
diverting the mission left by Jesus Christ. He published and defended what he
saw was a problem in the Catholic Church. Some of them are the following:
power of indulgences, the sacraments administrated in the church. Martin Luther
declared then the schism and the foundation of Protestant Church (reformed
church) in 1717.The protestant reform or the schism in general affected the society on two
sides. One side the unity of people was broken. Sometimes the loss of human
lives and infrastructures occurred. The hatred, poverty and conflict take places.
Other side, it became a good opportunity for the Church to evaluate itself. The
Council of Trent then was held to reform the Roman Catholic Church about
theology, discipline, and Sacraments.Major Branches of Protestantism in Rwanda
1. Calvinist Church: it came from teachings and ideas of John Calvin.
They resulted in what we know as the Presbyterians today. Presbyterians
are named for their view on church leadership-the Greek word for elder
is presbyteros.2. Methodist Church: founded in the USA in 1939 by a group of Episcopal
churches from North and South America. The Methodists got their name
because their founder, John Wesley, was famous for coming up with
“methods” for spiritual growth.3. Baptist Church: It was founded by individuals that support only the
baptism of adult people and not the baptism of infants. Baptists got
their name because they have always emphasized the importance of
baptism. This baptism must be performed in form of complete immersion
like the baptism administrated by John the Baptist. The Baptist church
was founded in Amsterdam in 1609 but their first congregation in North
America dated in 1938 by William Roger.4. Pentecostal churches: it is the church animated by the Holy Spirit. It
is the church that looked back to the Pentecost event (Acts of Apostles
2:1-13) and to take source. The Holy Spirit inspires it and allows the
members to prophesy.
5. Anglican Church: the term Anglican means Church of England. It
resulted from the misunderstanding between the Pope Clement VII and
the king of England Henri VIII. The king wanted to remarry Anne Boleyn
and to divorce Catharina of Aragon. The Pope refused to annul the first
marriage; the king declared then the Church of England to bless his
second marriage.6. The Seventh-day Adventist Church: Officially, the Seventh-day
Adventist Church was founded in 1863 from mille rite movements, a
group that had studied the prophecy of Daniel 8:14 and thought Jesus
was going to come for the second time in 1844. The Seventh day
Adventist Church uphold the Ten Commandments as found in Exodus
20:1-17, which include the seventh-day Sabbath as a day of rest. For
Adventists, the Sabbath is not only for Jews only but as a commandment
of God it also concerns all people who must keep it holy if they are to be
faithful to God (Matthew. 5:17; John 14:15, Revelation 12:17)2.1.2 Non-Christian World Religions:
The theistic religions have different ways and means of believing. Some of them
believe God’s salvation through mediator Jesus Christian (Christian religions)
while others believe the direct God’s salvation without intermediary (non-
Christian religion). Among non-christians there are also people who do not
believe in God at all. These are called non-theistic religions.• Judaism
It is a theistic religion of Jews, which means they believe in the existence of
supreme God who is transcendent. Together with Christianity and Islam Judaism
considers Abraham as their ancestor. The Jewish faith is based on the Torah,
the first five books of Moses.
The Jewish bible does not contain the New Testament because they do not
accept Jesus Christ as the promised Messiah. It contains three parts Torah/
Law (five books of Moses), Nebiim (Prophets) ant Ketubim (other writings). In
Judaism belief, the promised Messiah is still to come.• Islam
It is also a theistic religion. Islam means submission under Allah’s laws.
Muhammad, the prophet of Allah started receiving the content of the Qur’an
from 610 up to 632. Officially, Islam was founded in 622. Muhammad was born
at Mecca probably in 570. He went in Medina by exile. Fundamental beliefs for
Islam are the following:
– The oneness and unity of God (tahwid): the creator, sustainer,
ruler, and judge of the universe.– Prophets: Muhammad and the prophets of the Hebrew Bible, including
Abraham and Moses, and of the New Testament, Jesus and John the
Baptist.– Scriptures: God’s revelation was received in the Torah, the Psalms,
the Gospels and the Qur’an. The latter (in 114 chapters called surahs)
is approximately four-fifths the size of New Testament.– Angels: as part of God’s creation. They act as God’s agents and
serve Him by protecting humans, relaying His messages, or performing
different functions.– Day of Judgment: it includes the destruction of the world and all
creatures, resurrection of the body, and judgment, reward (heaven),
and punishment (hell) for all creatures.– Divine predestination: Muslims believe that Allah knows everything
event what will happen, and is responsible for everything.These core beliefs are completed by five required observances, which the Qur’an
prescribes all practicing Muslims accept and follow. These observances, called
“The Five Pillars of Islam”, include to believe, to pray, to give to charity, to fast
and to go on pilgrimage.
1. Shahadah (creed): there is no God but Allah, Muhammad is his Prophet
2. Salah (prayer): prayer five times a day
3. Zakah (almsgiving): an annual sum for the care of the poor
4. Sawm (fasting): observation of Ramadan the month of fasting
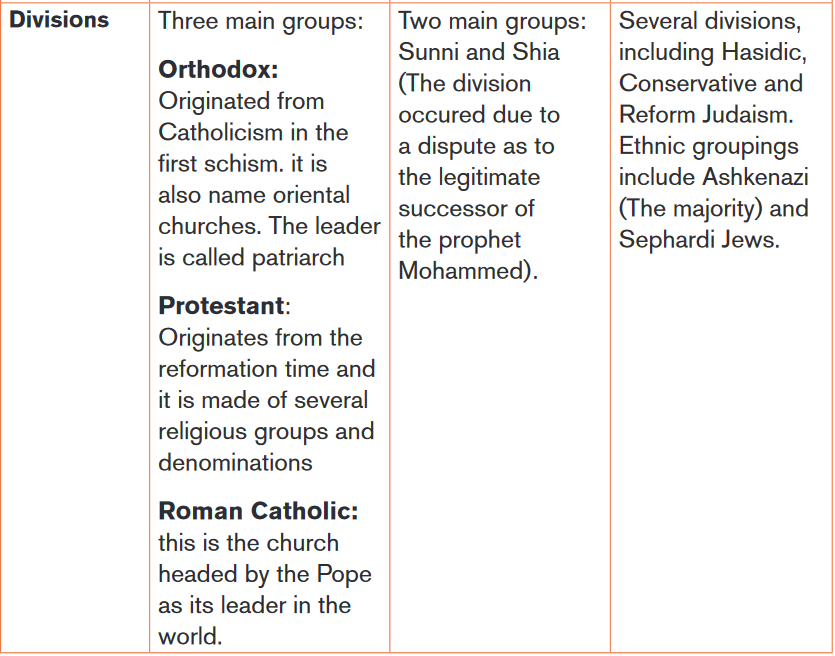
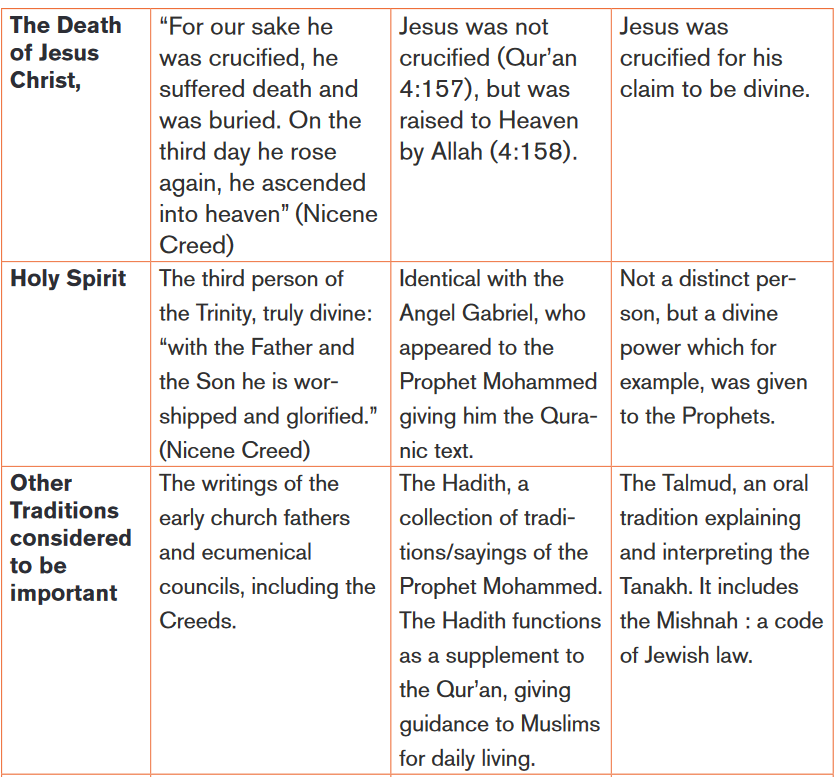
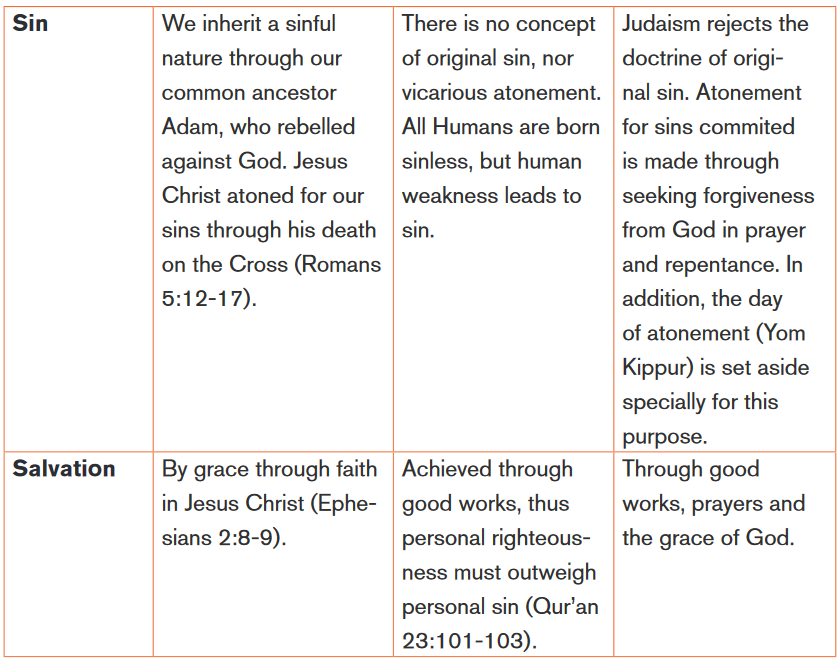
5. Hajj (pilgrimage): pilgrimage to Mecca once in a lifetimeThe following table shows some aspects of among Judaism, Christianity and
Islam.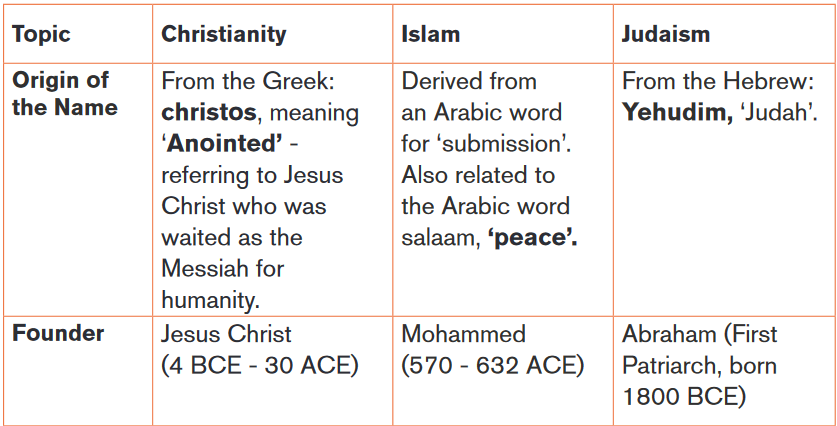




• Buddhism
Buddhism is non-Chrisitian religion. It is based on teachings, traditions and
beliefs of Gautama Buddha. The name Buddha means knowledgeable one. He
said education is a guide, knowledge is a key. For Buddhists the purpose of
life is to end the suffering. Life is determined by Kharma: law of action or law of
cause and effects: suffering or good life are the effects of bad or good action.
Buddha fixed teachings called Dharma. They are cosmic laws and order: right
way of living including duties, rights, laws, conducts, virtues. The duties we
find in Dharma are self-control, humility, serving others, outcast. The Buddhists
believe also the reincarnation of the soul.• Hinduism
Hinduism is no-theistic religion. It originally come from India. They believe
in a supreme and absolute spirit called Brahman that is the world Soul. It is
considered as god creator. Other gods are Vishnu, god preserver, protector
and Shiva, god destroyer. They also have thousands of other gods in Hinduism
beliefs.The purpose of life in Hinduism is to join soul Brahman. The bad behaviour
for Hinduism means lower state of life, to be considered as an animal and orplant. The Tenets are beliefs and traditions of Hinduism. Among them there
are Dharma: ethics and duties, Samsara: Rebirth by cycle of death and rebirth,
Karma: right action, Moksha: liberation from cycle of Samaras that means to be
free from suffering in cycle of death and rebirth.
The old main document of Hinduism is Vedas. Apart from three main gods of
Hinduism there are thousands of other gods and Hindus worship spirits, trees,
animals, planets. Nirvana is the Highest state one attains. Stage of complete
freedom: good behaviours, intellectual ability, devotion thought, contemplation,
meditation, devotion to a favourite god. Suffering for Hinduisms is not punishment
but the result of action. The actual texts they use are called Shastra.2.1.3 Traditional Beliefs
The members of traditional beliefs know the real God. They believe also the
spirits and they use their power. Their faith is based on ancestor’s intercession.The ancestors are intermediary between God and living people. Example in
Rwanda: The cult of appeasing/pacifying the living dead is called Guterekera.
To consult the specialist of divination or prediction in order to know the cause
of misfortune is called Kuraguza. The cult of Lyangombe expressed by the rite of
kubandwa as a practice in which its adherents hope to live earthly happiness.The cult of ancestors is different from the cult of the Saints. The people practice
the cult of ancestors because they are afraid of then while the cult of the saints
is characterised by communion. The traditional beliefs have negative effects like
human sacrifice, wasting of resources, the immoral acts, etc. As positive effects
we can say that formerly for example the members of the cult of Lyangombe
lived with shared peace, unity, and honesty in the pact of love.To become a full member of Lyangombe required to attend the rite three times.
The first rite was to enter in the family of imandwa (Kwatura). The second rite
to emphasize the first (Gusubiza ku ntebe). The third was that the new member
become mature (Gutonora).Application activity 2.1
1. Discuss the fundamental religious teachings of the following
religious beliefs
– Christianity
– Traditional beliefs
– Buddhism
2. What do you think are the similarities between Chrisitianity, Islam
and Judaism?2.2 Significance of Religious Unity in Diversity
Learning activity 2.2
1. Christianity is based on the person and mission of Jesus. Discuss.
2. What can be the negative and positive impact of pluralism in
christianity?Unity in diversity is a concept which signifies unity among individuals who have
certain differences among them. These differences can be on the basis of culture,
language, ideology, religion, sect, class, ethnicity. Concerning religious beliefs,
though created by one God, people have various approaches and beliefs about
him. The most important element is to see the diversity as strength not as a
weakness and then strive for unity of humanity.
• Teamwork and cooperation
First of all, following Religious unity in diversity implies an interaction between
many types of individuals of various religious beliefs on various scales. Though
these individuals may have slight doctrinal differences among them, they have
common purpose which is helping people to live a meaningful live as willed by
the creator. In addition to this, all of them belong to the same family of humanity
and were created by the One God.Working together and cooperate is the most needed value in various religious
beliefs. This implies avoid and fighting against doctrinal extremism, terrorism
in the name of religions, solving conflict, and promoting sustainable peace,
tolerance for all as well as striving for common good for all humanity regardless,
religion, ethnic groups, races, gender sex, nationality. The team work can be
easily manifested even in the small instances for example in workplaces, schools,
public places, churches.Furthermore, this interaction would build up a tolerance in people. Hence,
people would respect the opinion of others. The true and genuine religious unity
certainly enhances the quality of teamwork and wellbeing for all. This is because
of the development of trust and bonding among people increases and people
interact, make dialogue and work together in efficient way.• Promotion peace
In the course of time, Religious beliefs have caused tension among the adherent
leading to conflict, terrorism and war. The examples are wars that were led in
the mane of defending a given set of beliefs to non adherent to this religion.
Religious unity is a tremendous tool for sustainable peace in the world since
the unity allows people of various religious beliefs, cultures and societies to
live together peacefully and harmoniously with conscience of respect of other
people’s beliefs, understanding one another and respect of human dignity above
all things irrespective of differences.• Respect of human dignity
Respect for human dignity is the driving force for morality and wellbeing in the
society. Before people see themselves in the mirrors of religion, race, ethnic
groups they have an obligation to understand that they belong to the bigger family
of humanity. This is the basis for fighting against any feeling or actions of racism,
discrimination, conflict and oppression. Jesus himself prayed for this unity of
believers in the following world:“I do not ask for these only, but also for those who will believe in me through
their word, that they may all be one, just as you, Father, are in me, and I in you,
that they also may be in us, so that the world may believe that you have sent
me. The glory that you have given me I have given to them, that they may be one
even as we are one, I in them and you in me, that they may become perfectly
one, so that the world may know that you sent me and loved them even as you
loved me” (John 17:20-23).For the world to change and believe in good news, the adherent must be eager
to maintain unity of the spirit in the bonds of peace.• Interdependence and complementarily

All Religious leaders, Politicians, thinkers, scientist strive to create a more stable,
just and peaceful society. Humans vested by various capacities and talents
are interdependent one another. Religious believers also are interdependence
not only in matters of their theological teachings but also finding solutions
to challenges of live of everyday. For example fighting against global warmth
is not a responsibility of one nation or one Religious belief. This affects the
whole humanity. Religious believers need collaborative effort to fight against
this collective challenge. Unity of all Religions must be a commitment for all
to journey together is accomplishing the mission assigned by the creator:
Subduing the Earth.
Christians created a social movement whose aim is to strengthen unity of all
believers. This movement is called Ecumenism. The movement is based on
four aspects: collective challenges, common purpose, social solidarity and
sustainable interaction. The following part shows the commitment towards
human solidarity and unity by this movement:“We long for the visible openness of Christ affirming the gift for all, young and
old, Women and Men, lay and ordained. We expect healing of human community,
the wholeness of God’s entire creation. We trust in liberating the powers of
forgiveness, transforming enmity into friendship and breaking the spiral of
violence. We open ourselves for a culture of dialogue and solidarity sharing life
with strangers and seeking to encounter with those of other faiths” (Ecumenical
Review 1998: 267).The unity of all humanity is a solution to many global challenges that are affecting
the world in general. The differences and diversity should be seen as strength
not as a weakeness. Religous diversity is richness for humanity. Respect for
human dignity, solidarity, interdependance, teamwork and complementarity
should be enhance and strenghened so that all religious believers strive for
common good for all humanity.Application activity 2.2
1. In your own words, explain the meaning of unity in diversity and its
necessity in the world, particularly in Rwanda?
2. Discuss the significance of religious unity in diversity in the world.2.3 End Unit Assessment
End of unit assessment
1. Discuss fundamental teaching of the following Religious Beliefs:
– Protestantism
– Judaism
– Islam
– Traditional beliefs
2. Compare and contrast the teaching of Judaism, Christianism and
Islam in matters of beliefs and practices.
3. Assess the importance of religious unity in the world, particularly in
Rwanda.
