UNIT 9: SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Key unit competence: To use language learnt in the context of
Sciences and Technology
Introductory Activity Picture observation and interpretation

1. Discuss the use of the devices in fig1.
2. The people in fig2 are around the table sharing a drink but they are not talking to one another because they are busy chatting. Do you think it is a good practice? Explain.
3. Explain the use of the devices in fig3
4. Explain the use of the devices in fig4
9.1. Talking about words and expressions used in the context of science and technology
9.1.1. Learning activity Reading and text analysis
Text1: Technology is changing the World of Medicine
Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow:
A large number of digital innovations are revolutionizing healthcare and technology in medicine is here to stay. Numerous innovations and new solutions are already on the market and they have all improved healthcare drastically. Today, multiple medical issues such as congestive heart failure, diabetes, medication noncompliance, even stressful isolation, are researched
and solved with remarkable new technologies. The following are some areas researchers are targeting: The first area targeted by researchers is heart failure. One of the most common and costly diagnoses is that of heart failure, with a mortality rate closer to cancer. It includes three types of sensors –wristband, necklace and watch – which are used for testing. This type of diagnosis gives both patients and doctors continuous information on how a compromised heart is functioning.
The second area targeted by researchers is 3D printing. These days, medical researchers are considering the potential of 3D printing in medicine. For example, Kaiser Permanente’s Los Angeles Medical Centre is perfecting the use of 3D printers to replicate multidimensional models of problematic areas inside patients. Surgeons can handle the models and simulate a
variety of possible operation replicas before performing the actual surgery. Alternatively, 3D printing can be used in reproducing bones or other organs in the human body.
The second area targeted by researchers is the area of mobile applications. Today, mobile applications are available for everything. In the healthcare sector, this is especially true. Doctors and patients are discovering new ways to use technology to monitor personal health. Nowadays, tracking daily sleep patterns, counting calories, researching treatment options, and even monitoring heart rate is possible.
Thirdly, remote monitoring technology is one of the most useful and practical innovations in recent years. The systems can be used by patients in the comfort of their homes to reduce the time and financial cost of recurring visits to the doctor. By using a small device designed to measure a particular health issue, doctors can analyse a patient’s data remotely without the need
for them to come down to the hospital.
This must be the reason why the Government of Rwanda recognized that there is a need to strengthen science, technology and research and is engaged in many National and Regional initiatives to help build this capacity.
Adapted from https://www.hunimed.eu/news/technology-changing-worldmedicine/
• Comprehension questions
1. State four medical issues that are researched and solved with remarkable new technologies.
2. What are the three areas targeted by researchers mentioned in the passage?
3. State and explain the use of the three types of sensors mentioned in the passage.
4. Explain how 3D printing technology helps surgeons in their work.
5. Evaluate the use of mobile applications in healthcare sector.
6. Assess the importance of remote monitoring technology in healthcare sector
• Vocabulary activity
Use a dictionary and thesaurus to look up the missing meanings of the words/phrases in the table below. Copy the table into your book and fill in the blank spaces.
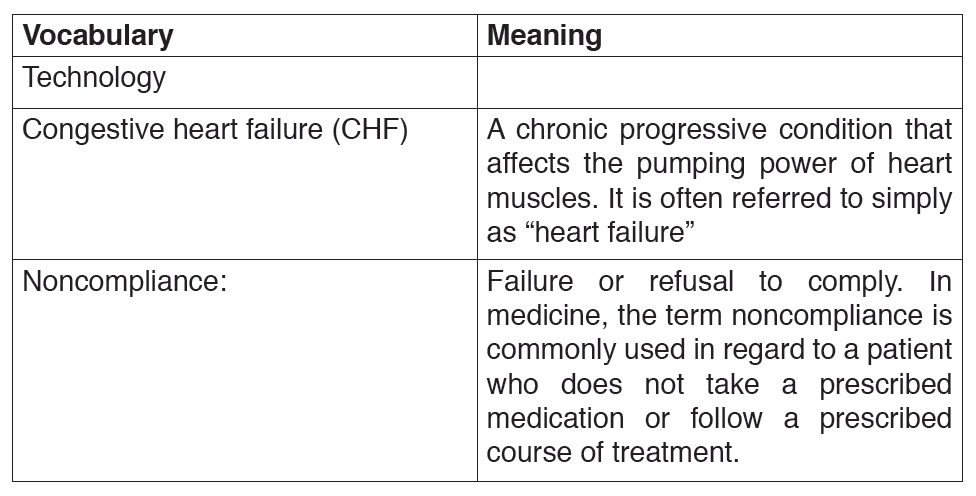
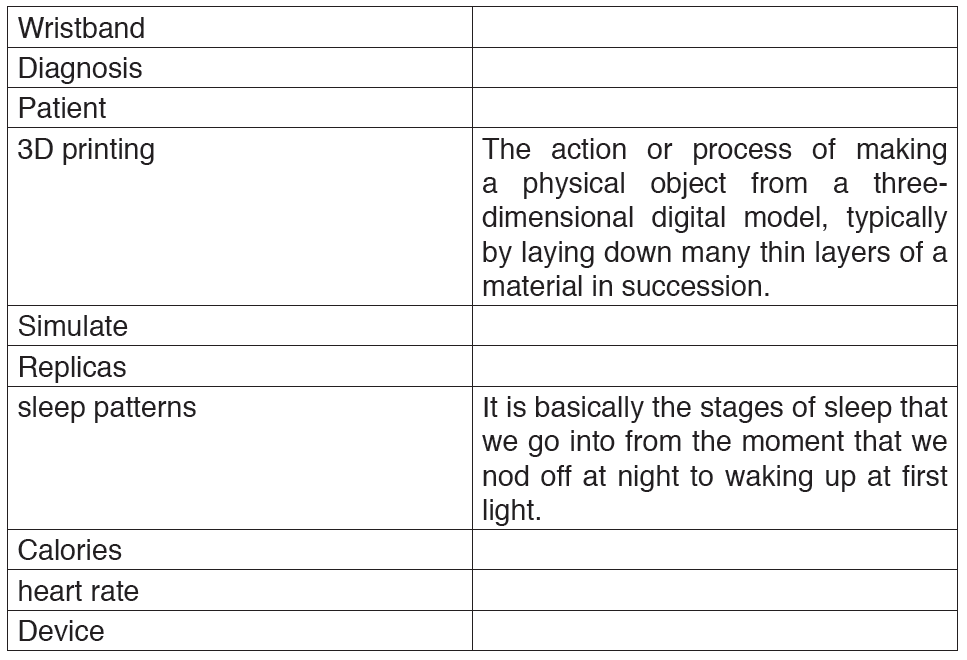
Text 2: Body systems
Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow:
Our bodies consist of a number of biological systems that carry out specific functions necessary for everyday living.
The job of the circulatory system is to move blood, nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and hormones, around the body. It consists of the heart, blood, blood vessels, arteries and veins.
The digestive system consists of a series of connected organs that together, allow the body to break down and absorb food, and remove waste. It includes the mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. The liver and pancreas also play a role in the digestive system because they produce digestive juices.
The endocrine system consists of eight major glands that secrete hormones into the blood. These hormones, in turn, travel to different tissues and regulate various bodily functions, such as metabolism, growth and sexual function.
The immune system is the body’s defence against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens that may be harmful. It includes lymph nodes, the spleen,bone marrow, lymphocytes (including B-cells and T-cells), the thymus and
leukocytes, which are white blood cells.
The lymphatic system includes lymph nodes, lymph ducts and lymph vessels, and also plays a role in the body’s defences. Its main job is to make and move lymph, a clear fluid that contains white blood cells, which help the body fight infection. The lymphatic system also removes excess lymph fluid from bodily tissues, and returns it to the blood.
The nervous system controls both voluntary action (like conscious movement) and involuntary actions (like breathing), and sends signals to different parts of the body. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord.
The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves that connect every other part of the body to the central nervous system.
The body’s muscular system consists of about 650 muscles that aid in movement, blood flow and other bodily functions. There are three types of muscle: skeletal muscle which is connected to bone and helps with voluntary movement, smooth muscle which is found inside organs and helps to move substances through organs, and cardiac muscle which is found in the heart
and helps pump blood. The reproductive system allows humans to reproduce. The male reproductive system includes the penis and the testes which produce sperm. The female reproductive system consists of the vagina, the uterus and the ovaries which
produce eggs. During conception, a sperm cell fuses with an egg cell, which creates a fertilized egg that implants and grows in the uterus. Our bodies are supported by the skeletal system, which consists of 206 bones that are connected by tendons, ligaments and cartilage. The skeleton not only helps us move, but it’s also involved in the production of blood cells and the storage of calcium. The teeth are also part of the skeletal system, but they aren’t considered bones.
The respiratory system allows us to take in vital oxygen and expel carbon dioxide in a process we call breathing. It consists mainly of the trachea, the diaphragm and the lungs.
The urinary system helps eliminate a waste product called urea from the body, which is produced when certain foods are broken down. The whole system includes two kidneys, two ureters, the bladder, two sphincter muscles and the urethra. Urine produced by the kidneys travels down the urethras to the bladder, and exits the body through the urethra.
The skin, or integumentary system, is the body’s largest organ. It protects us from the outside world, and is our first defence against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens. Our skin also helps regulate body temperature and eliminate waste through perspiration. In addition to skin, the integumentary system includes hair and nails.
Adapted from https://www.livescience.com/37009-human-body.html
• Comprehension questions
1. What are biological systems mentioned in the passage?
2. Which biological system helps oxygen to move around the body?
3. What is the role of the liver and pancreas in the digestive system?
4. Which biological system regulates metabolism, growth and sexual function?
5. Which biological system protects from falling sick?
6. Do you think our nervous system has anything to do with our sight?
Justify your answer.
7. State the three types of muscles and explain their functions?
8. What is the role of urinary system?
9. What is the body’s largest organ?
10. Hair and nails belong to which biological system?
• Vocabulary activity.
Use a dictionary, thesaurus or Internet to look up meaning of the following
words/phrases as they are used in the above passage. (The words are highlighted in the text)
a. Hormones
b. Metabolism
c. Bacteria
d. Viruses
e. Pathogens
f. Leukocytes
g. Tissues
h. Spinal cord
i. Cardiac
j. Conception
k. Perspiration
9.1.2 Application activity Compositing writing
1. Have you ever been in a hospital? Write a short composition describing a technological tool you saw there. If you never went
there, you can describe a tool you have heard of or read about.
2. Write a short composition on the importance of physical exercise for our body systems.
9.2. Describing the role of ICT devices and their side effects
9.2.1. Learning activity Reading and text analysis
Text1: The positive and negative impacts of ICT
Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow:
As it is known from time immemorial that everything in life is like the two side of a coin, there is always a positive and negative side of every phenomenon. But whether the effect is positive or negative the effects of Information Communication Technology (ICT) is far reaching and cannot be overemphasized. The Effects of ICT lens looks at how our lives have been changed, for better and for worse, by the impact of ICT. It includes both positive effects and negative effects.
One of the positive effects of ICT is access to information. Possibly the greatest effect of ICT on individuals is the huge increase in access to information and services that has accompanied the growth of the Internet.
Some of the positive aspects of this increased access are better, and often cheaper communications, such as phone calls and Instant messaging. In addition, the use of ICT to access information has brought new opportunities
for leisure and entertainment. Another positive effect of ICT is easy access to education. With ICT there are new ways of learning, such as interactive multi-media and virtual reality. ICT has also created new job opportunities, such as flexible and mobile working, virtual offices and jobs in the communications industry among others.
ICT can be used for processes that had previously been out of the reach of most individuals, such as photography, where digital cameras, photo-editing software and high quality printers have enabled people to produce results that would previously require a photographic studio.
ICT can be used to help people overcome disabilities. For example screen magnification or screen reading software enables partially sighted or blind people to work with ordinary text rather than Braille.
As far as negative effects are concerned, ICT has caused Job loss, reduced personal interaction and reduced physical activity.
As for Job loss, one of the largest negative effects of ICT can be the loss of a person’s job. This has both economic consequences, loss of income, and social consequences, loss of status and self-esteem. Job losses may occur for several reasons, including the replacement of manual operations by automation. This can happen when, for example, robots replace people on an assembly line. People can also lose jobs due to Job export. This is when Data processing work is sent to other countries where operating costs are lower. Multiple workers can also be replaced by a smaller number of people who are able to do the same amount of work using machines.
Personal interaction and physical activity have also been negatively affected by ICT. Being able to work from home is usually regarded as being a positive effect of using ICT, but there can be negative aspects as well. Most people need some form of social interaction and physical exercise.
Adapted from https://ajahana.wordpress.com/2012/06/27/the-positive-andnegative-impacts-of-ict-5/
• Comprehension questions
1. What do you understand by “everything in life is like the two side of a coin”?
2. What strengthened the huge increase in access to information?
3. Explain how ICT has created new job opportunities.
4. Using an example, explain how ICT has enabled people to do processes that had previously been out of the reach of most
individuals.
5. In which ways can ICT make people lose their jobs?
• Vocabulary activity
Use a dictionary, thesaurus or Internet to look up meaning of the following
words/phrases as they are used in the above passage. (The words are highlighted in the text)
a. phenomenon
b. Overemphasized
c. Lens
d. Information
e. Internet
f. Leisure
g. Entertainment
h. Virtual reality.
i. Manual operations
j. Automation
k. Job export
9.2.2 Application activity Sentece writing, CompositIon and Debate
1. Use each of the above words in a sentence of your own to illustrate how they are used.
2. Writer a 100word composition on smartphone addiction.
3. Debate
Referring to notes on debating techniques in unit 5, debate the following motion.
“This house believes that ICT has done more harm than good”
9.3. Language structure: Word formation
Introduction:
In linguistics (particularly morphology and lexicology), word formation refers to the ways in which new words are made on the basis of other words or morphemes. This is also called derivational morphology.
Most English vocabulary arises by making new lexemes out of old ones. This can be done either by adding an affix to previously existing forms, altering their word class, or combining them to produce compounds. Below are some types of word formation processes.
1. Derivation
Derivation is the creation of words by modification of a root without the addition of other roots. Often the effect is a change in part of speech.
Examples
• Empty-emptiness (adjective was changed into a noun)
2. Affixation
(This is like a subtype of derivation)
Affixation is the process of adding a morpheme or an affix to a word to create either a different form of that word or a new word with a different meaning.
Affixation is the most common way of making new words in English. An affix is a word element of English grammar used to alter the meaning or form of a word and comes in the form of either a prefix or a suffix. The two primary types of affixation are prefixation, the addition of a prefix, and suffixation, the addition of a suffix.
3 Prefixation
Prefixation is a morphological process whereby a bound morpheme is attached to the front of a root or stem. The kind of affix involved in this process is called a prefix. Prefixes include examples like; “un-,” “self-,” and “re-,”
Example:
The prefix un- attaches to the front of the stem selfish to form the word unselfish.
Other examples include:
9.4. Suffixation
Suffixation is a morphological process whereby a bound morpheme is attached to the end of a stem. The kind of affix involved in this process is called a suffix. Suffixes come in the form of ending elements like; “-hood,”“-ing,” “-ness,”, “-ed…”
• Communicate-communicator
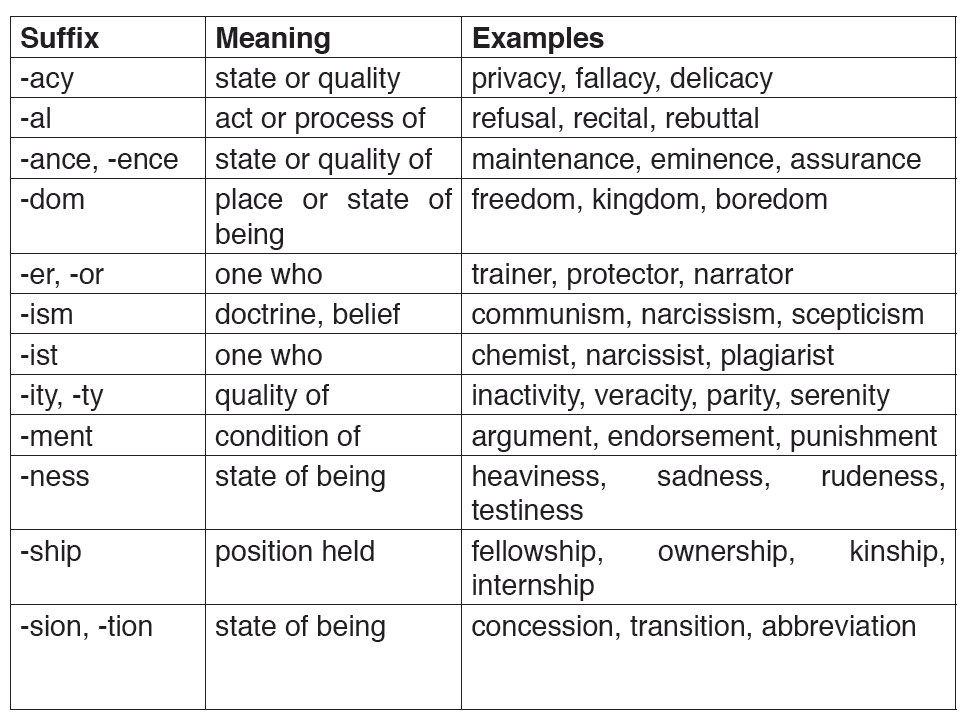
Think of the 26 common suffixes in the table as clues to the meanings of words. Keep in mind, though, that the meanings of words are best determined by studying the contexts in which they are used as well as the parts of the words themselves.
Noun Suffixes
Verbs suffixes
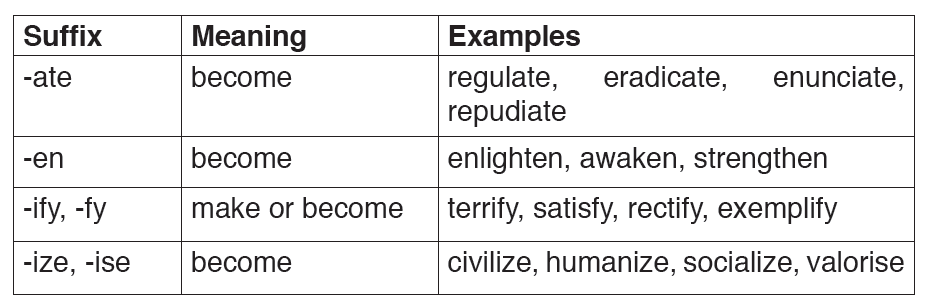
Verbs can end with either -ize (the American spelling) or -ise (the British spelling). Examples include finalize/finalise and realize/realise.
Adjective Suffixes
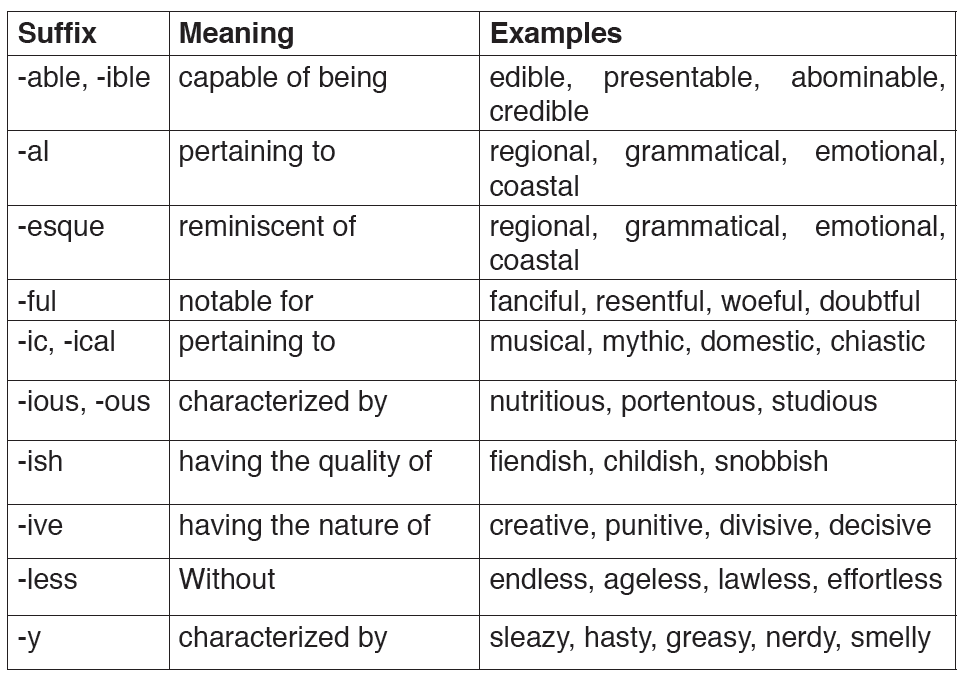
The examples above are adopted from https://www.thoughtco.com/commonsuffixes-in-english-1692725
Exercises
1. Use prefixes to find the opposite of these verbs:
a. Use
b. Agree
c. Engage
d. Behave
e. Understand
f. Fold
g. Spell
h. Connect
i. Close
2. Complete the sentences by writing the correct prefix from the table below in the blank space. You can use a dictionary to help
you

a.I just can’t believe it! The story is _____believable!
b. No, that answer is _____correct. It is wrong.
c. Let’s look at this information again. We should _____view it before the test.
d. I saw Kalisa just a moment ago, but now I can’t find him! It seems that he _____appeared!
e. Oh, I’m sorry, I didn’t hear you correctly. I _____understood you.
f. The subway does not go over the land like a normal train. It moves_____ground.
3. Put the words in brackets in the appropriate form (use prefixes or suffixes):
a. He was acting in a very………………. way. (child)
b. She looked……………. She started to cry. (happy)
(succeed)
d.The team that he supported was able to win the……………….(champion)
e. I couldn’t find any……………………in his theory. (weak)
f. He wants to be a……………………………when he grows up.
(mathematics)
g. There were only a……………………… of people at the match.
(hand)
h. The road was too narrow, so they had to……………………it.
(wide)
i. I think that you should……………………… your decision. It may not be the best thing to do. (consider)
j. You need a…………………….of motivation, organization and hard work to realize your dreams.(combine)
9.5 End unit assessment
1. Use a prefix or a suffix to make a new word out of the word in brackets. Complete the sentence with it.

a. I can’t answer this question. It’s………… (possible).
b. Don’t stand near the water. It’s too………… (danger).
c. I don’t like this fish. It’s not very well………… (cook).
d. Kate started crying because she was so………. (happy)
e. If you have a haircut it will change your………………………(appear)
f. Paul never waits in queues. He is too……………(patient)
g. Thank you for your advice. You have been very…………(help).
h. Stealing other people’s money is………………(honest)
i. Our science………………is very young. (teach)
j. Harry didn’t think the book was very………… (interest).
k. A million pounds was given to the hospital by an…………person(known)
l. When you…………. this paragraph, make it a bit shorter (write)
m. That was a great film. It was really……………. (enjoy)
n. Mary was wearing a/an……………….hat (usual)
o. I like this town. The people are very………………(friend)
p. I don’t think you’re right. I…………with you completely (agree)
2. Identify at least five words formed through the process of affixation in the following paragraph.
One of the positive effects of ICT is access to information. Possibly the greatest effect of ICT on individuals is the huge increase in access to information and services that has accompanied the growth of the Internet. Some of the positive aspects of this increased access are better and often cheaper communications, such as phone calls and instant messaging. In addition, the use of ICT to access information has brought new opportunities for leisure and entertainment.
3. Write a short composition on advantages and disadvantages of social media in society.
