UNIT 8: EDUCATION AND PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT
Key unit competence: To use language learnt in the context of education and development
Introductory Activity
Observe the pictures bellow and answer the questions after them:
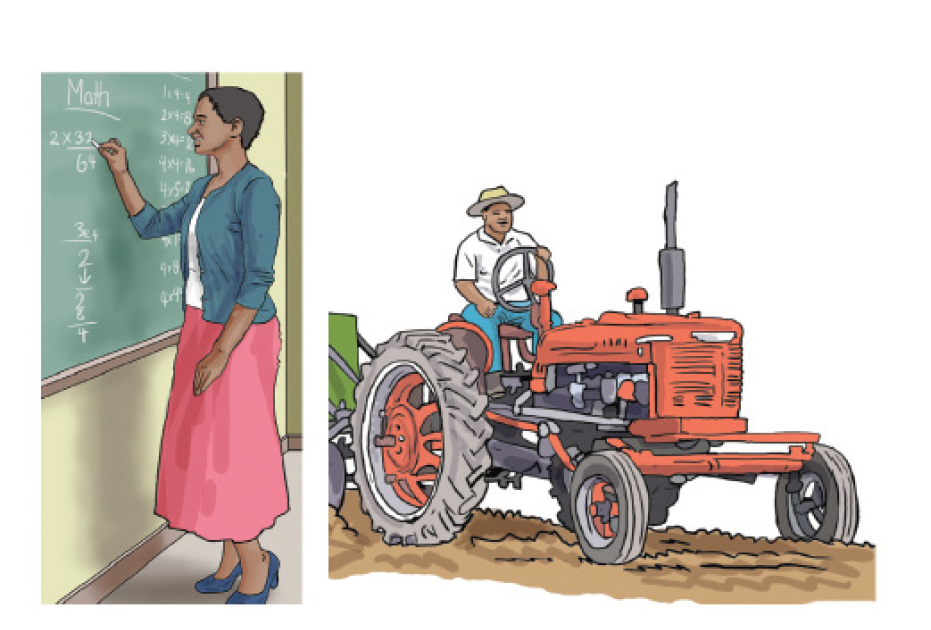

1. Discuss the two types of jobs illustrated in both the above pictures.
2. Compare the impact of each job on the lives of their respective practitioners.
3. If you were to choose between the two types of job, which would you prefer? Justify your choice.
8.1 Describing the ability at school and educational ambitions
8.1.1. Learning activity Reading and text analysis
Pre _reading: Discuss the statement below:
Both on personal and national levels, education has been shown to increase economic growth and stability. One of the most important benefits of education is how it improves personal lives and helps societies run smoothly. ... Consequently, education promotes fulfilling, fuller lifestyles.
Picture observation
Observe the picture bellow and carefully answer questions that follows:
1. What are your future plans after education?
2. Which career would you like to take?
3. Which career inspires you most?
4. Describe what is happening in the two pictures above.
5. Discuss two occupations presented in picture
• Text: Further studies in Rwanda.
There are many opportunities for further study in Rwanda.
Form any careers you have to have certain qualifications.
In order to be a doctor you have to study for a degree in medicine. It takes about six years in order to become a general practitioner.
For some of the specialized areas you might have to study abroad. In order to become a nurse you have to study for a diploma in nursing at a medical school. There are eight schools of nursing in Rwanda, one dental school, and one school of public health.
There are also five government schools of nursing and midwifery. It is also possible to get a nursing degree from university. In order to become a lawyer or accountant, you also have to go to university.
Secondary school teachers have to study for a university degree after S6.
Primary school teachers have to have a teacher’s diploma from one of the13 teacher training colleges in order to teach in the country’s primary schools.
Several countries offer scholarships for African students to further their postgraduate studies overseas. There are enough opportunities for hard-working and motivated students. Centres for Vocational Education and Training teach a number of interesting skills that enable people to be employed and to start their own businesses. They offer courses for those who wish to
become plumbers, electricians, chefs and motor mechanics. They also offer entrepreneurship courses. Learners who want to return to the family farm to continue producing food can improve their skills. Agricultural organizations offer numerous short courses, from technical and management to irrigation and fertilization.
• Comprehension questions
1. How long does it take to become a medical doctor?
2. Can doctors specialize in heart surgery in Rwanda?
3. Can post graduate students in Rwanda afford to study overseas?
4. Where do you need to study if you want to become a nurse?
5. Where do you have to go to become a secondary school teacher?
6. Name four courses that you could study at a Centre for Technical and Vocational Education and Training.
7. How can young farmers improve their farming skills?
8. Have any of the fields of study mentioned above captured your interest as a possibility for future studies? Explain your answer.
9. Exchange notebooks for peer assessment of your answers
8.2.2 Application activity Word Meanings
Using dictionaries use the following words as used in the above text in your own sentences.
a. Degree
b. employ
c. specialization
d. Diploma
e. Course
f. Agriculture
g. Midwifery
h. Graduate
i. Undergraduates
8.2. Sexual behaviour
8.2.1. Learning activity Reading and text analysis-
Text1: Abigali’s story
Read the story bellow and discuss questions after.
“Mama, I know I have failed you, but when you get to know what happened, I know you will be more forgiving…”
“Failed me?” Her mother asked, looking inquisitively at her... “You completely let me down, Abigail. I did not expect you to have a baby before you completed school and was able to take care of yourself, and your baby! I can only hope that you have learnt your lesson. Though a baby is a blessing from God, it comes with responsibilities. Imagine what will happen when your first son
Benji grows older!” she said.
Abigail accepted her mother’s reprimand without bitterness. She was right.
Indeed, the responsibilities currently were already exhausting. ‘Anything more will destroy me though,’ she thought. ‘Every day brings new challenges!
I wonder if I will ever manage to do anything else.’ She said thoughtfully.
“Mama, I want to defer school until Benji is older.”
“No!” her mother said emphatically. “You are going back to school. If you put your education on hold, you will end up giving up on it completely. Then, what will you do with your life? Get married?”
“I will never get married!” Abigail vowed. She surprised even herself by the strength of her voice. “And, I am done with this painful breastfeeding. I’ll feed Benji on cow’s milk and porridge from now onwards,” she added petulantly, her frustration was becoming obvious.
“I know it is hard for you,” her mother told her gently. “But, of all the things you can do for Benji, please… please, breastfeed him,” she added, almost as a plea. She looked at her daughter keenly, treating her more as an equal than a child. Then she said, “As for school, Abigail, that is the place to take your fight to, in order to prove that having a baby doesn’t mean one’s life is over.”
For Abigail, motherhood had become a continuous physical and emotional pain. Her tiny breasts were now large and painful. She prayed that her mother could agree to the alternative way of feeding Benji, other than breastfeeding.
The mere imagination of his lips on her nipple made her wince. Indeed, just thinking about the forceps and scissors that had been used during Benji’s birth still made her sweat. Now, it would take a good number of years to nurture Benji to the point where he could care for himself. In the meantime, what would she be doing with her life?
“Mama, I wish I had known what I was getting myself into. I cannot take care of Benji and think about school at the same time, can I?” “You should have remembered my advice. But, as far as school is concerned, the sooner you go back, the better. It will be tough, yes; but I know you are strong enough to pull through,” she said, and she had obviously made up her mind on the matter...
Extract from the Novella, Sunrise after Midnight, by Florence.....
• Comprehension questions
1. Is Abigail happy of what she has experienced?
2. According to the passage, did Abigail listen to her mother’s advice?
3. Which advice can you give to Abigail after such experience?
4. How can we avoid such incidences?
5. Discuss with the help of dictionaries and internet, what sexual behaviour mean in a broad manner.
8.3. Life skills
8.3.1. Learning activity Reading and text analysis
Text1: True friendship
Read the text below and answer the following questions:
Horror gripped the heart of the World War I soldier as he saw his lifelong friend fall in battle. Caught in a trench with continuous gunfire whizzing over his head, the soldier asked his lieutenant if he might go out into the “no man’s land” between the trenches to bring his fallen comrade back.
“You can go,” said the lieutenant, “but i don’t think it will be worth it. Your friend is probably dead and you may throw your life away.” The lieutenant’s advice didn’t matter, and the soldier went anyway. Miraculously he managed to reach his friend, hoist him onto his shoulder and bring him back to their company’s trench. As the two of them tumbled in together to the bottom of the trench, the officer checked the wounded soldier, and then looked kindly at his friend.
“I told you it wouldn’t be worth it,” he said. “Your friend is dead and you are mortally
Wounded.
“It was worth it, though, sir,” said the soldier.
“What do you mean; worth it?” responded the Lieutenant. “Your friend is dead.”
“Yes, Sir”the private answered. “But it was worth it because when I got to him, he was still alive and I had the satisfaction of hearing him saying, “Jim…, I knew you’d come.”
Many times in life, whether a thing is worth doing or not, really depends on how you look at it. Take up all your courage and do something your heart tells you to do so that you may not regret not doing it later in your life. May each and every one of you be blessed with the company of TRUE FRIENDS.
A true friend is one who walks in, when the rest of the world walks out. War doesn’t determine who’s right. War only determines who’s left.
Extract from Military Story: True Friend by STEPHEN on JUNE 19, 2011
Comprehension questions
a. Who is a true friend according to the passage?
b. What does mortally wounded mean?
c. Did this private soldier have any life skill? Discuss.
d. Explain the statement” it’s worth it”_ _ _ according to the text.
• Note:
Life skills are skills for adaptive and positive behaviour that enable humans to deal effectively with life. Gaining life skills is vital for one to meet life challenges. Examples of life skills: Critical thinking, cooperation, conflict resolution, decision making, problem solving, love for work well done, etc.
8.3.2. Language structure: Conditional clauses
Notes:
There are several kinds of conditional clauses,
They express different conditions and are followed by main clauses that show the results of such conditions.
Below are some of the types of conditional clauses:
1. Zero conditional.
This is used to refer to general truths.
Examples:
a. If it rains, the grass gets wet.
b. If the sun shines, it gets hot.
Both main clauses show obvious results.
2 1st conditional
Refers to a possible condition and its subsequent or probable result.
Examples:
a. If you work hard every day, you will pass examinations.
b. If you read for half an hour every day, your English will improve.
The main clause is in the present or future when it expresses a real situation.
The first conditional is also called a ‘will’ conditional. It is a sentence that talks about the future with a given condition in mind. The sentence also talks about the result of this condition. The events in the main part of the sentence depend on the condition given in the conditional clause. The main part of the sentence is called the independent - clause and has the modal ‘will’. There
is a real possibility that this condition will happen.
3. 2nd conditional t
The second conditional clause expresses a situation that may take place now or any time but not yet real because it has not happened. It therefore refers to a possible condition that might have a certain result.
Examples:
a. If you went to bed earlier, you would not be so tired.
b. If my English was good, I could get a job in the UK.
4. 3rd conditional clause
This conditional is expressed in the past and shows a situation that is different from reality.
Examples:
a. If he had studied harder (which he didn’t), he would have passed the examinations (which he didn’t either).
b. If my English was good (which it is not the case), I could have got a job in the UK (which I have not).
c. If we had looked at the map(which they didn’t), we would not have got lost(they got lost).
N.B.
• When an if- clause comes first, a comma is used. But when the mainclause comes first, no comma is used.
• A conditional clause can begins with if or unless. Both if and unless, express conditions.
Examples:
a. Unless I read my books, I will not be promoted.
b. If I don’t read my books, I will not be promoted.
• When __ clauses can also be used to replace if clauses, they mean the same.
Examples:
a. When/if I finish my studies, I will become a business man.
b. When/if I finish my Education, I will be a lecturer.
Exercises
1. Complete the sentences bellow correctly:
a. If you had done your homework ________.
b. If I was a farmer,__________________,
c. If he had read English for half an hour every day ________.
d. If you had looked after your textbooks ________.
e. If I was a doctor,______________________
f. If I was a lecturer,__________________
g. If your English was better, ________.
h. If you went to bed earlier, ________.
2. Use two of the words below in sentences of your own to show that you understand their meaning:

3. Give the correct form of the verbs in brackets.
i. Last year they (start) secondary school.
ii. They (be) nervous about starting a new school.
iii. Some of them (go) to boarding school
iv. They (learn) to take responsibility for their own work
v. The teachers (keep) them very busy during their first term.
vi. Make 9 sentences using if clauses (three sentences in each type)
8.5 End unit assessment
1. This section can be used for formal assessment or for revision.
Write three sentences expressing your aspirations for future education. Use appropriate conditional clauses.
2. Provide the correct conditional in the sentences below.
a) If you were not late for school every day ________.
b) If he had spent more time on his studies ________.
c) ________ she would have won a bursary.
d) If you had done more research on careers ________.
e) If you had completed your further studies ________.
3. Debate on advantages and disadvantages of early pregnancies.
4. Referring to the story above and unit 5 in this book. Use the 2nd.
conditional clause in your own sentences. make 5 of them.
5. Discuss the importance of education.
