UNIT 3: IDENTIFICATION, ASSESSMENT AND REFERRAL FOR LEARNERS WITH SPECIAL EDUCATIONAL NEEDS AND DISABILITIES
Key Unit Competence:
Students should be able to competently identify, assess and recommendreferral for learners with SEN and Disabilities.
Introductory activity
Kaneza is a beautiful girl and turned seven years this year. She lives with
both her parents at Cyimihurura sector. She does not attend school simply
because her parents think that she is intellectually challenged. Kaneza seems
to misunderstand what is being said. Whenever her parents ask her to find
something, she would bring different thing. For example, they would ask her
to bring a basin and Kaneza would bring a pan. Thought of parents had no
confirmation from a specialized personnel, they believed that Kaneza has
mental challenges and therefore find it useless to take her to school. One
day, Kaneza was playing with other children and the teacher passed by. As
an experienced teacher, she noticed something in Kaneza’s behaviour which
attracted her attention. Kaneza wanted to watch a movie from a smart phone and
she holds the smart phone so close that anyone would suspect an abnormality
in her vision. The teacher was so much concerned and wanted to know more
about Kaneza. The teacher discovered that Kaneza was kept at home by her
parents who taught she has intellectual challenges. The teacher advised the
parents to bring Kaneza to school and eventually the school Multidisciplinary
Team assessed Kaneza. The assessment report indicated that Kaneza has a
low vision with no indication of intellectual challenges. The assessment team
decided to refer Kaneza to the hospital for further assessment and treatment.
Kaneza was placed in an inclusive school and the teachers developed a plan to
support her in her studies. She is now succeeding very well in her academics.
Questions
1) What was the situation of Kaneza before she was found by the teacher?
2) What happened when KANEZA was brought to school by her parents andteacher?
3.1. Definition, Purposes, Principles and Types of SpecialEducational Needs Assessment
Activity 3.1
1) What do you understand by the term” Special Educational Needs
Assessment?
2) Why should we do assessment in Special Education?
3) Dou you think Special Education Needs Assessment should be done by
only teachers? Who else do you think should be part of the team? Mentionat least three people who should be part of the team.
3.1.1. Meaning and purpose of SEN assessment
An assessment in special education is the process used to determine a child’s
specific learning strengths and needs, and to determine whether or not a child
is eligible for special education services. Assessment in special education is a
process that involves collecting information about a student for the purpose of
making decisions.
Disability and other special educational needs Assessment in educational settings
serves five primary purposes:
• Screening and identification: To screen children and identify those
who may be experiencing delays or learning problems. Identification is the
process of singling out suspected cases of children with special needs in
education and/or disability for the purposes of assessment and intervention.
Identification of children suspected to have disabilities may be done by the
following people: Parents, Doctors and nurses, social workers, teachers,
siblings and peers. Early detection of disability, learning disabilities and other
form of special educational needs simply means to screen a child at early
stage of hi/her life with the purpose of designing adequate intervention as
earlier as possible. It is a process of providing with adequate special needs
and disabilities with the necessary and adequate support to fight against
special educational needs and disability . This should be done as early as
possible. It may take the form of guidance and counselling to both learner and
parents, placement to education programme, referral for medical intervention,
provision of home training programs. Every child is unique and may have his/
her own strengths and weaknesses. It is natural that some children may excel
in certain areas but have deficiencies in other areas. Here are some steps
that leads to normal identification:
– Causes of Children’s Problems: suspect the child’s exception goes with
looking for the root of the problem. Developmental and learning problems
of children may be associated with a combination of factors. Teacher
needs to view the children’s developmental condition, family, the school
and surrounding society.
– Monitoring children’s learning: teacher has to check the progress of the
learner, age related, child’s performance, attendance of a child in the
class, duration, pervasive and severity. However, if there are noticeable
and persistent discrepancies in development compared with that of their
peers, teachers and parents should be alert and discuss whether followup
actions need to be taken.
• Eligibility and diagnosis: To determine whether a child has a disability
and is eligible for special education services, and to diagnose the specific
nature of the student’s problems or disability
• IEP development and placement: IEP is developed to provide detailed
information so that appropriate decisions may be made about the child’s
educational placement.
• Instructional planning: To develop and plan instruction appropriate to
the child’s special needs
• Evaluation: To evaluate student progress
3.1.2. General principles of SEN assessment
The guiding general principles help the assessors to keep in mind that:
a) A child with special educational needs should have their needs met
b) The special educational needs of children will normally be met in mainstream
schools or settings.
c) The views of the child should be sought and taken into account
d) Parents have a vital role to play in supporting their child’s education
e) Children with special educational needs should be offered full access to a
broad, balanced and relevant education.
3.1.3. Types of SEN assessment
There are many types of assessment that can be carried out in school to specify
and verify learners’ educational progress, abilities and difficulties and difficulties. It
is important to note that the selection of a particular type of assessment depends
on the nature of information that you as the teacher would like to obtain.
There are three basic types of assessment
• Baseline assessment
• Continuous assessment
• Terminal assessment.
a) Baseline assessment
It is the types of assessment that is used to establish what a leaner is able to do
in a specific education area? For example, in a classroom, you may sometimes
wish to establish what learners know before you introduce a new concept to
them. Baseline is used to establish the skills and abilities that a learner already
has in order to determine the starting point for instruction that would address
her/his educational needs.
The process of baseline assessment and its role
The baseline assessment may be carried out through observation of learners
either individually or when they are interaction with their peers, family and other
community members, at the beginning of a programme. It can be done through
formal and informal test. In inclusive classroom, the findings of baseline
assessment may help you determine the level at which you start a particular
skill or content.
b) Continuous assessment
It is the types of assessment that is carried out during the course of a program
to monitor the progress of the learners. The continuous assessment that are
administered in school and colleges.
This is the assessment which is suitable for learners with special needs in
education because the findings are used to modify the content that has not
been mastered by and also to modify the teaching techniques.
c) Terminal assessment
It is a form of assessment that is carried out at the end of an educational
programme. The information obtained through terminal assessment should
enable you to determine the learner’s achievement at the end of a given
instructional period and the areas in which the leaner still needs more support.
3.1.4. Role of Special Educational Needs assessment team
members/ Multidisciplinary Team (MDT)
After the child is identified to possibly have a certain disability or other Special
Educational Needs (the identification is in most cases done by parents or
teachers). The child should be referred to the Multidisciplinary Team (MDT) for
proper assessment.
It is a group of experts from multiple professional backgrounds, who meet to
pursue a common goal, such as SEN assessing, evaluating a learner for placement
in education or creating an individual plan for the learner. In teaching learners with
special needs in education, consideration should be made of human resources
who offer support to such learners. It is a multidisciplinary team which brings
together professionals from within and beyond the school. Multidisciplinary
teams have the potential to offer a range of services to support learners with
special needs.
a) Here are some professionals who may be a part of assessment:
– Teacher
– Speech therapist
– Audiologist
– Physiotherapist
– Ophthalmologist
– Occupational therapist
– A medical doctor/ a nurse
– Educational psychologist
– Social worker
– Parents
– A learner/ A child
4. Teacher
S/he is the person who plan and conducts lessons. Some teachers may be
trained to teach children with special needs. The role a teacher plays in a
learning process include:
– Teaching of academic subjects
– Preparing teaching and learning materials
– Adapting educational resources for learners with special needs
– Collaborating with parents, community and other professional in related
fields
– Guiding and counselling learners and parents
– Organizing and training learners in co-curricular activities among others.
5. Speech therapist
This is highly trained professional who assists persons with speech and
language problems. The main roles are:
– Screening children for early identification of a communication difficulties.
– Assessing receptive and expressive language
– Subsequent remediation of difficulties related to articulation and voice
6. Audiologist
These are persons trained to perform the following roles:
– Assess learners who exhibit hearing loss and indicate the range and degree
of hearing loss
– Assess the need for amplification devices.
– Provide advice on special placement
7. Educational psychologist
S/he has the role to conduct an in-depth assessment for identification of
problems in areas of intellectual and behavioural functioning.
He/she does this through:
– Selecting and administering appropriate tests.
– Scoring and interpreting the findings
– Offering guidance and counselling services to the child and family.
8. Ophthalmologist
These are doctors who are specialized in the treatment of eye disease and
conditions.
9. Social worker
Those are especially trained people who act as a link between the schools,
family and community in:
– Assisting teachers and parents to solve problems related to disabilities
through their influence and knowledge.
– Advising families on how to care for their children with special role in
education and places where they can find help and support.
10. Physiotherapist
These are trained professionals who play an essential role in the management
of motor difficulties through the use of exercises. They train with moto abilities
in the following abilities:
– Correct body posture
– Movement of limbs
–Strengthening of weak muscle or paralysed parts
– Balance and control of body
– Body coordination
11. Occupational therapist
An occupational therapist is a paramedical staff who is trained in art and
science of directing a person’s participation in selected tasks in order to
restore, reinforce and enhance performance in activities of daily living.
They play an essential role in programming and delivering instruction adaptation
and exercises which help:
– Children with special needs learn to participate in useful activities of daily
life.
– Adults with special needs to maintain their capacity and abilities to function
in daily living activities at a level, which allows as independence as possible.
– Children and adults in diminishing or correcting dysfunctional so as to
promote and maintain health.
12. Medical Doctor / nurse
This person employed by the school or attached to the school to attend to sick
or injured learners within the school.
They have the role of:
– Provide teacher with the information about leaner whose sensory moto or
other health problems could classroom performance.
–Give instructions on handling seizure activity and managing leaners with
orthopaedic involvement.
b) Parents
Parents are crucial members of the team because they have unique knowledge
of their children’s strengths and needs. Therefore, their specific roles include:
– Identifying and articulating their child’s special educational needs,
– Request for SEN assessment for their child if they suspect any special
education needs;
– Provide background information of their child during the SEN assessment
processes.
c) School administration
The concerned school managers comprise mainly of the head teacher and the
director of studies, and their responsibilities in SEN assessment include:
– Establishing and monitor the school mechanisms of identifying learners
with special educational needs;
– Establishing the school mechanisms of conducting special educational
assessment processes
– Keep records of the learners with special educational needs;
– Ensure that the school improvement plans and subject plan include special
needs and inclusive education as priority;
– Schedule, lead and coordinate the special educational assessment
processes;
– Invite and ensure the support to the SEN assessment team
– Ensure the inclusiveness during the SEN assessment processes by providing
interpreters or any assistive provisions where necessary;
– Ensure a productive involvement of the learner’s parents;
– Ensure a productive involvement of relevant specialists and experts during
the SEN assessment processes.
c) Local leaders
The local leaders, especially those in charge of education can be involved in
special education needs assessment, and their responsibilities may include,
but not limited to:
– Ensuring that the necessary provision is made for learners with special
educational needs’.
– Ensuring that schools have programs for SEN assessment in their scheduled
activities and records for learners with special educational needs.
– Ensuring that teachers are skilled in identifying and providing for learners
with special educational needs.
– Ensuring that learners with special educational needs are identified and
participate in SEN assessment processes in all schools.
– Ensuring support for school in relation to SEN assessment programs and
procedures
d) Learner
“Nothing about me without me”. This is a slogan that is common to persons with
Disabilities. It simply means that learners with Disabilities and other Special
Educational Needs should be involved in every decision that is taken about
them. In Special Educational Needs Assessment, learner should be present
and be informed on the decision taken about him/ her. He/ she may also havesome useful information that can help the team as they take decisions.
3.2. Areas of SEN assessment and Components of Special
Educational Needs Assessment tools
3.2.1. Areas of Special Educational Needs Assessment
When carrying out assessment, it should enable the assessor to determine
the learner’s development and educational needs. Any assessment in Special
Education should covers the following aspects:
• Intelligence: Assess the child’s ability to reason, to think abstractly, and
to solve problems. An example of assessment tools includes: Wechsler test
and Stanford- Binet intelligence test.
• Language Development: Ability to understand incoming spoken
language and ability to convey ideas and relate information through oral
language. Example of tools include: Wechsler verbal scale and Test of
language development
• Auditory skills: Ability to break words into syllables and/or discrete sound
components. Example of tools include: Wepman Auditory Discrimination
Test –2nd Edition
• Visual Skills: Ability to detect subtle likenesses and differences in visual
stimuli such as symbols, pictures, and designs. Example of tools includes:
Wechsler Performance Scale.
• Motor skills: Ability to control fine muscle movements, as in writing,
drawing, and cutting and ability to coordinate large muscle movements
as in running, walking, skipping, and throwing. Examples of tools include:
Observation of gross and fine motor activities.
• Social and emotional adjustment: You assess the ability of the child to
maintain good relationship with others and the level of social maturity and
appropriateness of Behaviour. Examples of tool include: Child Behaviour
Checklist
• Academic skills and Achievements: In these areas, you assess the
following skills: Reading and phonics skills, spelling skills, Handwriting
skills and mathematical skills. Example of tools include: Wechsler Individual
Achievement Test (WIAT) or Woodcock-Johnson, Revised-Tests of
Achievement (WJ-R ACH).
• Physical health and Development History: You gather information
about the development history of the child. You can use interview guide
with parents to gather this information.
3.2.2. Components of Special Educational Needs Assessment
tools
Special Educational Needs Assessment tool is a set of questions that are used
to gather relevant information about the child, determine his/ her strengths
and weakness for the purpose of helping her/ him. Special Educational Needs
assessment tools may have already been developed and the assessors have to
only adapt it to the present situation or the assessors will have to develop their
own assessment tools. SNE assessment tool should have the following parts:
Part one: Background Information
This part covers personal information about the child. This information should
include the name of the child, date of birth, gender, place of residence, father
and mother names, their age, marital status, educational level, occupation.
Part two: Developmental Information
This part should talk about the birth history of the child, humanization and
medical history of the child and the mother and the family medical history. In
this stage, you have to get information about the condition of the child at birth,
any chronic illness since birth or any involvement in accident since birth.
Part three: Social relationship
Here, you gather information about the social relationship of the child with
other members of the family, school and community.
Part four: Academic information
Here, you gather information about the academic ability of the child. You have
to find out whether the child is in the school or not, the academic difficulties
and the interventions that were provided to the child.
Part five: Functional Information
Here, you gather information about the fine and gross motor ability of the child.
Questions should indicate whether or not a child has difficulties in fine or gross
motor activities. The information about the child’s visual and hearing conditions
should also be gathered. Any intervention that was provided to the child should
also be indicated. (Examples: medical, rehabilitation intervention, counselling).
Part Six: Summary and Recommendations
This is a very important part of the assessment tool. You provide short statements
of the child’s strengths and weakness. You also have to draw recommendations
which will be used to help the child. Recommendations should be related to
education, medical or rehabilitation.
Part Seven: Placement option
Here, the team take a decision on placement option. The child may be placed
in regular school, special school or special unit.Part Eight: Assessment team members and their signature

3.3. Procedures and Processes of SEN assessment and referral
a) SEN Assessment procedures
When conducting an assessment, you should follow the following procedures:
– Planning for assessment
– Selecting assessment tools
– Administering the test tools
– Analysis and interpretation of findings
– Communicating the findings
– Referral for diagnosis assessment
– Planning for intervention.
b) Planning for assessment
Before the assessment process, you and the other team members should have
a planning schedule in order to:
– Determine what is to be assessed and how the information will be gathered
– Clarify referral questions such as: does a learner require assessment related
to a learning difficulty or what are, his/her possible additional difficulties.
– Determine assessment objectives where you prioritize the area on which
you should focus
– Review the existing information about the learner especially from parents
and other teachers.
– Assign role and responsibilities of members to ensure that information is
collected in a variety of ways across multiple settings.
Pre-planning enables the assessment team to carry out the listed activities and
sharpen the focus of the assessment. It also enables the team to include the
family not only in the data gathering process but also in the child’s program
from the beginning.
c) Selecting assessment tools
The assessment process begins with careful planning followed by the selection
or development of appropriate assessment tools. Those tools will determine
the success of the data gathering process. The appropriateness of the tools
depends on the context in which it will be used.
Before deciding to use tool you need to think about:
– Its purpose: assessment tool should provide the particular information
needed to answer the assessment questions
– Appropriateness for the learner: a tool should fit the learner’s needs and
abilities.
– Appropriateness of assessor: the tool should match your professional skills
– Technical adequate: the tool should enable collection of reliable and valid
data.
– Efficient: the tool should enable collection of the needed information with
minimum expenditure of time and effort.
d) Administering the tool
The assessment does not begin immediately you select or develop the
appropriate tool. You must first ensure that you or the professional responsible
for testing are adequately prepared to administer and score the test. A
conducive environment is also needed. They should be introduced to the
testing experience.
e) Analysis and interpretation of findings
The assessment of findings should be individually and collectively reviewed by
the assessment team. However, the analysis and interpretation of findings is
done in the following steps:
– Checking data accuracy: involves accuracy of scoring, clarity of notes,
completeness of the information gathered, the presence of gaps, in which
case call other members of the team or parents for additional information.
– Writing the assessment report: are report incorporated into records that
follow the learner and the family for many years. The report should be written
using statements which are easy to communicate to parents and which
would also be useful to those who will be planning the learner’s educational
programs in terms of teaching.
– Translating test results: findings should be translated into teaching goals to
form the basis for your instructional objectives and classroom teaching. The
findings should be shared of communicated. This should involve discussion
with team members and parents.
The placement is the act of putting a learner in the most appropriate educational
setting or position. It is a very important step taken after assessment and
identification of the learner’s needs and abilities. It is during placement that
you refer the learner to the most appropriate educational programs for early
intervention. The choices of educational placement option depend on the age
of the child, type and degree of the difficulty.
In this case you may place a learner in:
– An inclusive educational setting
– Special school
– Integrated unit
– Vocational training centre
– Rehabilitation centre
– Home training programmeSpecial Educational needs assessment steps
f) Referral for diagnostic assessment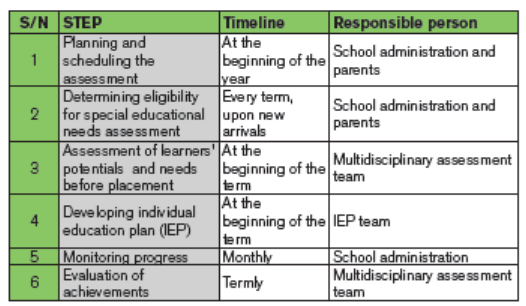
A referral is a process or steps a teacher takes to get extra assistance for
a student with whom they work directly on a regular basis. It is completed
when a teacher believes that a student needs some intervention to help them
overcome obstacles that may be preventing them from being successful.
In this instance, there are three types of referrals:
• Referrals for disciplinary issues: done when they want the principal or
school disciplinarian to deal with a student issue.
• Referrals for special education evaluations: is a request for a student
to be evaluated to determine whether the student may receive different
special education services.
• Referrals to receive counselling services: should be made for a student
for any number of legitimate concerns and does not always necessitate the
teacher to take intervening steps prior to filling out the referral.
Assessment is used to facilitate referral of the child for further assessment.
If the assessment team finds that the child needs further assessment, they
should refer him/her to a specialist for assessment. The specialist may be
clinical psychologist, paediatrician psychiatrist, a reading specialist or speech
pathologist. The specialist will do further assessment to diagnose the problem.
Referral is also one of the decisions from the special educational needs
assessment team. Health workers and/or physicians might inform the parents
about their learner’s problem, or parents might ask for advice from any specialists
if they have any worries. Either way, parents ought to consult with the learner’s
class teacher, the SENCO (Special Educational Needs Coordinator) or the
head teacher and find out if:
– The learner is having educational difficulties and/or has SEN,
– The learner is able to work at the same level as peers the same age,
– The learner needs any specific type of help,


