UNIT4: TECHNOLOGY IN BUSINESS OPERATIONS

Key unit competence: To be able to choose an appropriate technology for a business.
Introductory activity 4.1:
1. Scan the environment in which you are in and respond to the following questions:
a) After studying the previous unit about Business Ideas and Opportunities,
Discuss the various business ideas that can be started basing on ICT opportunities.
b) What do you understand by the terms: ICT, Technology and E-Commerce?
c) Examine the impact of using technology in businesses today.
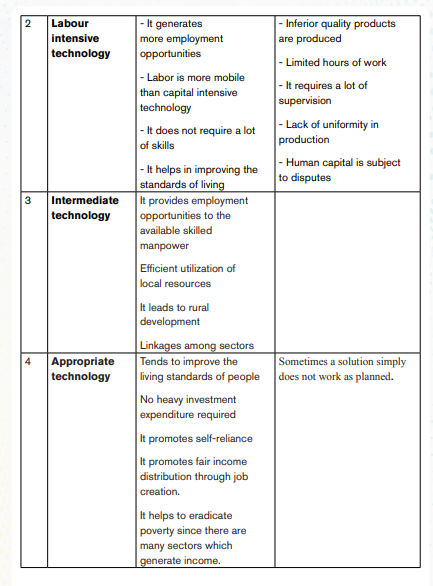
2. Differentiate the following types of technology:
– Capital intensive technology
– Labour intensive technology
– Intermediate technology
– Appropriate technology
3. From the above types, which one do you think is suitable for your school business club?
Give reasons to justify your answer

4.1.1. Meaning of technology
Technology means the use of knowledge, tools, techniques, or specific methods to solve a problem or serve a purpose.
Information Technology involves the use of electronic means to help to transmit and interpret information internally and externally.
Information and Communications Technology usually called ICT, is often used as an extended synonym for Information Technology (IT) but is usually a more general term that stresses the role of unified telecommunications and the integration of telecommunications (telephone lines and wireless signals), intelligent building management systems and audio-visual systems in modern information technology. ICT consists of all technical means used to handle information and aid communication, including computer and network hardware, communication middle waves as well as necessary software. In other words, ICT consists of IT as well as telephony, broadcast media, Electronic Billing Machines (EBM), all types of audio and video processing and transmission and network-based control and monitoring functions.
4.1.2. Types of Technology
a. Capital intensive technology:
This is a production method which uses more capital or machines than labor. It is also known as “labor saving technology” that is, we save more labor to use machines.

In Rwanda, the largest part of the population is employed in the primary sector, which uses more labor than machines. Most labor is employed in agriculture, fishing, mining, and the service sector.
Labor intensive technology has many advantages and that’s why it employs a bigger percentage in our economy. Although, it is associated with very many challenges like, being very expensive to maintain through medical insurance, wage bills, low and poor-quality output, strikes, and labor gets tired and exhausted easily, unlike the use of machines.

The following three approaches can help in making the right decision:
i) Balance cost against benefits,
ii) Look for ease of use,
iii) Take it for a test drive. However, responding to the following questions would guide someone in the selection of an appropriate technology:
• Social benefit: The technology should have social benefits to the country, in terms of job creation, as well as not having a lot of social costs like pollution (air, water and noise)
. • Health impact on users: The technology should put into consideration the health of the users as well as the population around. Some technology for example machines and mobile phones make vibrations which affect the health of the people leading them to get cancer related problems.
• Ease of use and adaptability: The technology chosen should be simple to use and easy to learn and adopt. It should be able to accommodate the skills of the available labor in a given country.
• Productivity and profitability: The technology chosen should be able to yield profits for the business as well as efficient and effective use of resources to produce much output.
• Cost effectiveness: The technology chosen should be affordable to the company and should be able to yield more returns for the capital invested.
• Institutional needs: The technology should be able to address the needs of the institution or company where it is being used. For example, banks need more capital-intensive technology in form of information communications technology as compared to labor intensive technology.
• Environmental friendly: The technology must comply with the environmental laws; thus, it should not degrade the environment. This is very common with industries which use capital intensive technology.

4.3.1. ICT in business
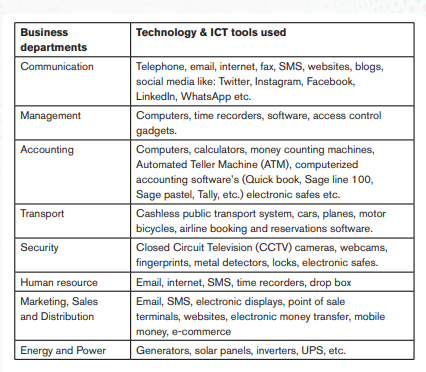
If you research and identify the various technologies that are being used in businesses, be it in your school or other business enterprises, you will figure out that ICT provides great importance in terms of communication, management, accounting and transport.
In the twenty-first century technology has become completely integrated in the business operations. Whether you are running a small start-up business or a worldwide enterprise, technology is vital in all aspects of business operations. It helps workers to communicate with one another easily which is critical to the success of a business. It is also used to protect confidential financial data which may be subject to security threat and vandalism. Fortunately, several technology tools are being used by companies in the day today running of business. Examples include use of emails, mobile phones, internet etc.
A serious analysis will show you that businesses use various kinds of technology, depending on the type of business, and department. The table below shows the types of technology and different ICT tools used in business departments.
4.3.2. Role of ICT in business
The following are some of the roles of Information Communication Technology in business.
• Makes work easier. It simplifies work in all aspects.
• Quality products. The use of ICT helps to produce better quality products that may fetch a lot of money for the enterprise thus increasing customer satisfaction.
• Complicated tasks are completed faster & with ease. For example, use of computerized accounting software like quick books, sage and pastel helps in accounting.
• Global marketing. Technology helps companies to sell around the world. People can buy and sell products online and receive payments electronically. This is possible using E-commerce sites like E-Bay, Amazon, Jumia, etc. and payments can be made using Credit cards and visa electronics cards.
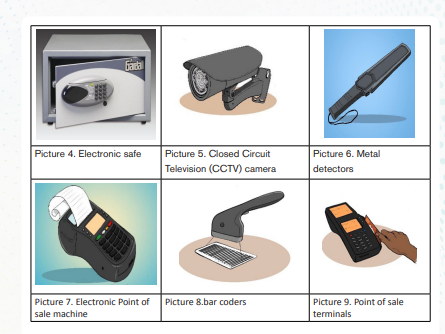
• Monitoring buying habits. ICT helps firms to monitor the buying habits of their customers and be able to stock the right products in the right quantities at the right time. E.g.: Bar code readers
• Ability to process high volumes of information and at a high speed: Computers can perform a lot of work in the shortest time possible which would require a lot of time if done manually. Examples include preparation of control accounts, financial statements and preparing payrolls etc.
• Communication. ICT enables businesses to communicate both nationally and internationally with clients and business partners. It also helps to improve communication within a company which helps managers to make informed decisions.
• Production and distribution of products. Technology plays a key role in the production and distribution of products by use of machines and transport means.
• Technology has made it easy for companies to handle large numbers of employee profiles as well as client profiles. • Technology cuts costs. For example, the costs incurred while transporting and delivery of goods can all be done using computers and the internet.
• Advertising: Information Communication technology introduced new methods of advertising particularly through the Internet which helps businesses to be known and sell worldwide hence increasing producer’s income.
• ICT improves stock control. The use of barcode scanners and point of sale terminals within shops, enables firms to know immediately what their stock levels are, reducing the need for many manual checks.
• Advertising: Information Communication technology introduced new methods of advertising particularly through the Internet which helps businesses to be known and sell worldwide hence increasing producer’s income.
• Security: Information stored on computers is safer. This is because access to information can be restricted by using passwords. Also, in some accounting software which allows multi-users, it is easy to trace which user has performed a given transaction. This reduces the risk of fraud. For example, in banks.
• Research tools: ICT helps businesses to carry out research easily about their competitors which helps them to survive. The Internet allows a business to virtually travel into new markets without the cost of an air ticket or the risks of creating a factory abroad. By doing this, businesses grow and acquire new opportunities.
• Reduces the worker’s costs, a computer can be used to perform a given task which can be done by many people. Therefore, there is reduction of costs in terms of salaries and other fringe benefits that would be incurred.
4.3.3. Problems associated with use of ICT
Much as ICT has many advantages, it also has many disadvantages in business. These challenges include the following.
• ICT needs staff training. With the various updates in technology, it will require the business to incur costs of training, either on-the job, off-the-job or induction training.
• Difficult to implement in some systems. Systems made by different companies may be incompatible and fail to work together, limiting the firm to use the latest technology.
• Sometimes the users of technology may not be able to interpret the generated information and as a result, fail to use the information for proper decision making.
• Technological unemployment. ICT automates so many processes and as a result, may result in mass unemployment of people.
• ICT heavily depends on regular and sufficient power supply which is still a challenge in developing countries • The internet provides consumers with the ability to rapidly search for alternative goods and prices which is likely to lower a firm’s profit margin.
• It does not put into consideration the use of body language which may lead people to miss-interpret messages because of the use of instant messaging, voice calls.


4.4.1. Business opportunities in ICT
Information Communication Technology itself offers numerous business opportunities.
The following are some of the businesses that can be started basing on ICT:
• Develop and design websites for individuals, organizations, and companies.
• Selling ICT equipment’s like power cables, phones, network cables, tablets, laptops etc.
• Repair ICT equipment’s like laptops, computers, and mobile phones.
• Starting and managing online shops.
• Starting training programs for people who want to use computers and such technology in their business enterprises.
• Money transfer etc.
• Offering irembo services etc.
• Manage databases for different companies
• Providing delivery services to other online retailers.
• Tax declaration services, Preparation of financial statements for clients.
• Create companies that train people about information technology
• Develop Accounting software
• Multimedia publishing
• Computer networking
• Graphics design

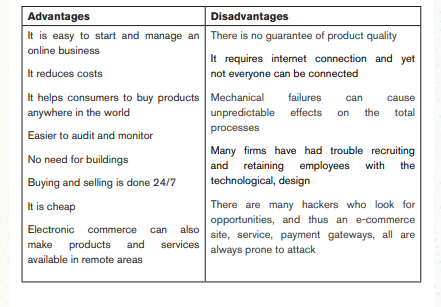
E-commerce means Electronic Commerce. In some years back, buying and selling of goods involved movement from one place to another (e.g., to the shop or market) and physically meeting between the seller and the buyer.
Today, ICT has extended the scope of buying and selling goods within and outside a country. An e-business / e-commerce is supported by internet services, and it allows businesses to transact without geographical limitations. However, e-commerce presents several advantages and challenges: