UNIT 8: LESSON PLANNING
Key Unit competence: Create a quality lesson plan with clear objectives, engaging techniques and with a variety of materials.

8.1. Definition and importance of lesson planning.

During the education campaign to enhance quality education in some primary and secondary schools in Rwanda, it has found that they were two categories of teachers. The first category is made of teachers who always enter the classrooms prepared to teach and well prepared with all pedagogical documents required. They take enough time to plan all things for their learners. They focus their attention on teaching and learning activities, lesson summary, teaching and learning materials, teaching methods and techniques and provide immediate and constructive feed-back to their learners. Their leaners are very active in the classroom and that participation leads to the higher academic performance.
The second category of teachers are those who consider lesson planning, teaching and learning materials, and learners’ activities as wasting of time. For them, a note book with all the content and exercises are enough as they have been using this method successfully for long time.
1. Do you agree with the first category of teacher? Why?
2. Do you agree with the second category of teacher?
Lesson Plan:
It is a daily preparation made by the teacher. It is again a plan of action to guide the teacher. Details will vary depending on the preference of the teacher, subject being covered, and the needs of the students.
Teaching without a lesson plan is like travelling while you don’t know the destiny neither have GPS or a compass while crossing the ocean (Thungu, 2011). This means that for effective teaching and learning to take place and achieve its objectives, a lesson plan is necessary.
On one hand, a lesson plan :
– Enables the teacher to master the content as he/she prepares his/her lesson.
– Enables teacher to prepare the teaching/learning aids in advance.
– Enables the teacher to present his/her work in an organised way (systematically).
– Helps the teacher to evaluate his/her lesson work.
– Helps in the selection of a suitable teaching approaches, methods and techniques
– Helps to build the teacher’s confidence. – Helps in catering for individual differences of the learners.
– Helps in budgeting for the time to be spent on the lesson presentation.
– Helps in giving accountability of what happens in the classroom.
On the other hand, a good lesson is important for learners in the following ways:
– It involves the learner to participate in teaching and learning process actively.
– It uses multiple teaching approaches, methods, techniques and strategies thus facilitate learner’s understanding.
– It promotes higher order thinking skills; reasoning, problem solving of students.
– It presents clear expectations/objectives i.e. behaviours you wait for from students after teaching them.
– It answers the question ‘’why do I need to know this?’’
– It maintains a clear focus on the objectives.
– It stimulates students’ interests and motivates them.
– It requires and rewards participation i.e. it should encourage student’s participation by rewarding them (any learners’ effort is appreciated and encouraged).
– It allows the students the opportunity to think critically.
– It checks frequently for understanding of all students-making a follow up to see if students have understood.
– It establishes a non-threatening environment-‘’it is ok to make a mistake’ ’everyone should feel free (no fear) to try and give his/her views, because we learn from mistake, mistake is a part of learning.
– It provides for guided practice: It guides students in practice like group discussion
– It provides for independent practice: It helps students to feel free when they are practicing.
– It encourages active participation of every individual learner.
– It sets high expectations for all learners. i.e.: It sets what you want your students to reach in term of outcomes.
– It provides for all students directed closure. It should provide mutual collaboration, mutual help, and a kind of relationship among them.

8.2. Parts of a lesson

When delivering a Mathematical lesson in P1 “addition of numbers less than 10”. Teacher Anne started by having a revision on these numbers, learners and the teacher made different operations of addition and last they end up with different exercises.
Is this order that the teacher used correct? Why and what are the main steps/parts she followed.
Lesson preparation
A well prepared lesson plan almost guarantees a successful lesson. When preparing a lesson plan a teacher should consider the following:
– The topic from which the content of the lesson is to be delivered.
– The time allocated for teaching the topic.
– The ability (individual differences) of learners.
– Previous competences (knowledge, skills and attitudes values) of learners.
– The best method approaches and techniques of teaching that can be used to achieve the lesson objectives.
– The objectives which indicate what the learners are supposed to achieve by the end of the lesson.
– The teaching and learning resources/materials available.
– The most suitable assessment procedures that would determine whether the objectives have been achieved or not.
– The teaching and learning activities that would best achieve the objectives.
Parts of a lesson
Generally the lesson is divided into three main parts whereby each one may is divided into smaller steps to make sure that learners are involved in the learning process. Below are explained the main parts and their small steps.
1. Introduction
This is the beginning or the introduction phase. Introduction is a part where the teacher makes connection between the current and previous lesson through appropriate technique. The teacher opens short discussions to encourage learners to think about the previous learning experience and connect it with the current instructional objective. The teacher reviews the prior knowledge, skills and attitudes which have a link with the new concepts to create good foundation and logical sequencings.
When it is a new lesson without much relationship with previous ones, the teacher introduces the lesson using suitable techniques such as an interesting story, dramatic demonstration, a song, a brief field trip, a game, visual stimulation (pictures, videos, charts, etc. The introduction should be brief, imaginative, motivating and link to the earlier work.
2. Lesson development
This is the essential part of the lesson. The development of a lesson will go through small steps that vary depending on subjects, lessons, and learner’s level/age. Generally, an active lesson that introduces a new concept will go through the following steps: discovery activities, presentation of learners ‘findings, exploitation, generalization/synthesis/summary and exercises, explained below:
a. Discovery activity
– The teacher discusses convincingly with students to take responsibility of their learning
– He/she distributes the task/activity and gives instructions related to the task. The teacher let the students work collaboratively on the task.
– He/she then monitors how the students are progressing towards the knowledge to be learned and boost those who are still behind (but without communicating to them the knowledge). Note: During this period the teacher refrains to intervene directly on the knowledge.
b. Presentation and exploitation of learners’ productions
– The teacher invites representatives of groups to presents the students’ productions/findings.
– After three/four or an acceptable number of presentations, the teacher decides to engage the class into exploitation of the students’ productions.
– The teacher asks the students to evaluate the productions: which ones are correct, incomplete or false. – Then the teacher judges the logic of the students’ products, makes corrections as needed, completes those which are incomplete and confirms those which are correct.
c. Summary/Conclusion and application activities
– The teacher summarizes the learned knowledge and gives examples to illustrate the learned content.
– He/she then links the activities to the learning objectives, and guides learners to make notes.
– Students carry out exercises of applying the learned content in real life contexts.
– Teacher guides learners to make the connection of what they learnt to real life situations. At this level, the role of teacher is to monitor the fixation of process and product/object being learned.
3. Assessment
In this step the teacher asks some questions to assess achievement of instructional objective. During assessment activity, learners work individually on the task/activity. The teacher avoids intervening directly. In fact, results from this assessment inform the teacher on next steps for the whole class and individuals.
An indication should be given of the linkage between this lesson and the next, if appropriate. Homework may be one of the techniques to be used. Assignment or follow-up work should be given which reinforces learning and/ or provides opportunities for further practice. Assignment may be written or require learners to investigate/observe/read. If given, assignment should be followed up in a subsequent lesson.

8.3. Key required documents for making a lesson plan

As prospective teacher, what do you think are the requirements for effective lesson planning?
For effective lesson planning, the following are key required documents:
Syllabus: This is a document which outlines everything that will be covered in a particular course and the sequence of topics. When planning, teacher should consult the syllabus to know which lesson to teach and from which unit.
Syllabus enables the teacher to choose and prepare learning and teaching materials in advance, guides the teacher on the choice of the most suitable learning activities, and suggests the best ways of evaluating learners’ achievements in specific topics among others.
Scheme of work: It is an outline of what should be taught in a given period of time such as a week, a month, a term or a year. It is done every year before the start of New Year. Scheme of work guides teacher when planning lessons, shows the flow of the lessons, helps the teacher to select suitable teaching strategies and instructional materials, guides the teacher in setting lesson objectives, enables the teacher to allocate time for teaching each lesson among others.
School time table: A school timetable coordinates learners, teachers, rooms and time slots in a school. Timetable is a way of allocating sufficient time to each subject in the curriculum. It helps in coordinating teachers’ efforts toward achieving school goals without collision, friction and duplication. It facilitates the supervision of the teachers’ work and enables the teacher to perform teaching activities on time (Thungu ,2011).
Textbooks: A textbook is a book of instruction. Its primary aim is not to impart information about a specific subject but to enable one to develop proper understanding of the subject. Textbook helps the teacher to get information/ content about the lesson to be taught.

Read the provided lesson plan and identify detailed elements of a lesson plan
The introduction of CBC in schools calls for comprehensive change and new thinking with regard to instructional approaches in teaching, planning, learning and assessment processes.
To achieve this noble mission pre-service teachers are trained to plan lessons from year one. Here below is the lesson plan format followed by explanations of its key elements.
Format of a Competence – based Lesson Plan
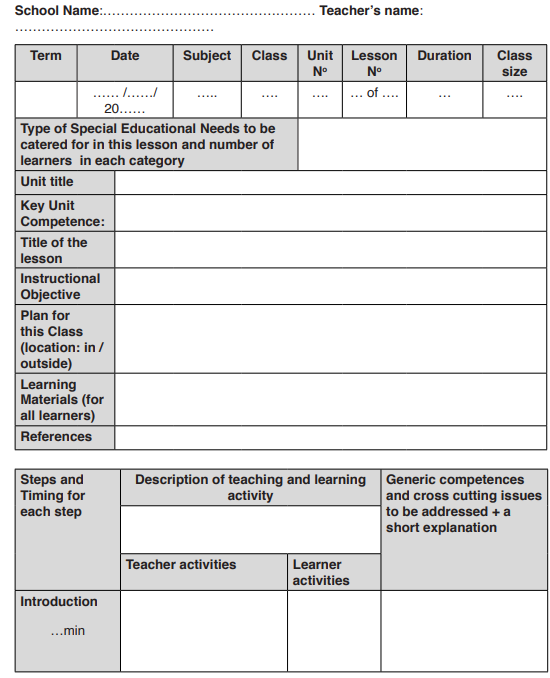
Explanation of the lesson plan format
Whereas there are many formats of a lesson plan depending on education system of every country, the Competence-Based Curriculum lesson plan in Rwanda contains the following components/parts:
a.Identification related information
This part includes school name, teacher’s name, term, date, subject, class to be taught, unit number, lesson number, duration (amount of time allocated for the lesson) and class size or number of learners.
b. Types of Special Educational Needs (SEN)
to be catered for in the lesson and number of learners in each category: the teacher mentions the type of SEN that he/she has identified in class, and the number of Learners with SEN in the class. In addition, He/she notes how those learners with SEN will be integrated or accommodated in learning activity so that they are also able to participate and learn.
c. Unit title: The name or title of the unit to be taught
d. Key unit competence: the competence to be achieved at the end of the unit
e. Title of the lesson: one unit may have several lessons; the title of the lesson to be taught during a given period is mentioned.
f. Instructional objective: to show what learners will achieve at the end of the lesson. It is set by the teacher based on learning objective from syllabus or the scheme of work and adapted to one lesson to be delivered. Instructional objective needs to be inclusive to reflect the needs of the whole class. It focuses on 5 elements such as condition, who, action/behaviour, content, standard/criteria for acceptable performance.
g. Plan for the lesson (location of the lesson): The teacher mentions whether the lesson will take place indoors (inside) or outdoors (outside).
h. Learning materials: The teacher shows the teaching and learning materials that will help him/her and learners to achieve objectives.
i. References: Teacher indicates the sources of the information/ content.
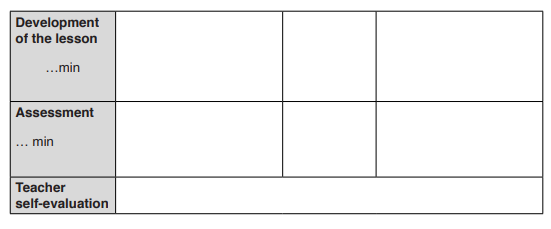
j. Column of steps and timing: there are three main steps; introduction, development of the lesson and conclusion. Timing is allocated to the three steps.
k. The column of teaching and learning activities
This column starts by a space reserved for a summary of the learning and teaching process including main techniques and resources required.
In the column of teacher’s activities, the teacher describes the activity using action verb in infinitive form. The questions and instructions provided by the teacher are also written in this column.
In column of learner’s activities, the teacher describes the learners expected activities, findings and answers. However, for some activities or answers which cannot fit in that column, the teacher will indicate them in appendix. The teachers will precise if the activities will be carried individually, in small groups, or whole class.
l. Column of the generic competences and cross cutting issues to be addressed: the teacher writes down generic competences to be developed through learners’ activities and a short explanation on how competences will be developed and cross-cutting issues adressed. The cross cutting issues to be addressed depend on the lesson content and activities.
m. Teacher self-evaluation
At the end of the lesson, the teacher evaluates its effectiveness. This is an opportunity for the teacher to reflect on the whole teaching and learning process. He/she honestly evaluates the level on which learners have achieved the learning objectives, the effectiveness of teaching methods, materials, etc.

1. Explain the reasons why a lesson plan is considered as a cornerstone or backbone of any teaching and learning process.
2. Choose one topic from the subjects in your option and make a detailed lesson plan that fulfils all the requirements.
