Topic area
Human and economic
Geography
Sub-topic area
Economic activities
Key unit competence
By the end of this unit, you should be able to
explain the impact of fishing on sustainable
development of Rwanda.
Unit objectives By the end of this unit, you should be able
to:
• Define fishing and fish farming.
• Identify the major fishing grounds of
Rwanda.
• Identify the factors favouring fishing in
Rwanda.
• State different types of fish and methods
of fishing used in Rwanda.
• State the methods used for fish
conservation and preservation in
Rwanda.
• Outline the importance and the problems
of fishing and fish farming in Rwanda.
• Identify different ways of improving
fishing and fish.
Fishing
Activity 13.1 Work in pairs.
Study the the following photograph
provided and use it to answer the questions
that follow.

1. Name the activity that is taking place in
the photograph.
2. Discuss the importance of the activity
to the people who practice it and to the
country.
3. Write down your findings and present
them in a class discussion.
Fishing refers to the activity of catching fish
for food or as a sport.
Major fishing grounds of
Rwanda
Activity 13.2
Work in pairs. 1. Using a map of Rwanda, locate the major areas where fishing is carried out.
2. Discuss the importance of the fishing grounds you have identified to the areas where
they are found and to the country.

3. Write down your findings and present
them in a class discussion.
Fishing in Rwanda mainly takes place in
lakes, rivers, swamps and ponds. The lakes
in Rwanda include Lakes Kivu, Muhazi,
Ihema, Cyohoha, Rweru, Burera, Ruhondo,
Rwanyakizinga, Hago, Kivumba, Cyambwe,
Nasho and Mugesera.

The rivers in Rwanda include Rivers Akagera,
Akanyaru, Nyabugogo, Nyabarongo, Rusizi,
Mukungwa, Base and Ruhwa.
The main swamps in Rwanda are Akanyaru
on the border of Burundi, MugeseraRweru in the south-east, Akagera swamp
along the Tanzania border in the East,
Nyabarongo and the Rugezi wetlands in
the North and Kamiranzovu in the West.
Despite the numerous fishing grounds
present in Rwanda, Lake Kivu is considered
to be the major fishing ground in the
country. It is located on the border of
Rwanda and the Democratic Republic of
Congo. The lake covers a total surface area
of some 2,700 km
2
and stands at a height of 1,460 metres above sea level. 58% of
the lake’s waters lie within the Democratic
Republic of Congo borders.
Factors favouring fishing in
Rwanda
Activity 13.3 Work in pairs.
Use Internet and your local environment.
1. Find out and explain the factors that
favour fishing in Rwanda.
2. Write down your findings and present
them in a class discussion.
Activity 13.4 Your teacher will organise a field visit for you
to one of the fishing grounds or fish farms
near your school. Work in groups of five.
1. Relate the factors that favour fishing in
Rwanda to the specific fishing ground
that you have visited.
2. Find out from the fishermen other
factors that favour fishing that are
specific to their fishing ground.
3. Write a report on the factors identified
and present it in class.
Some of the factors that favour fishing in
Rwanda include the following.
(a) Availability of planktons
Planktons are food for fish. Their availability
means the presence of different fish species.
The growth of planktons is encouraged by
the inflow from rivers that flow into the
lakes. The water carries deposits that settle
on the beds of the lakes and other water
bodies creating ideal conditions for the
growth of
planktons.
(b) Good climate
Favourable climatic conditions such as ideal
temperatures and the presence of sunlight
encourage the growth of planktons as well
as support the metabolism of fish. The
sunlight rays penetrate the waters to the
bottom of the lakes facilitating the growth
of planktons that are needed by fish for
their survival.
(c) Presence of forests
Forests provide timber for making boats,
and wood for smoking the fish. Rwanda
is blessed with both natural and planted
forests that provide products that are used
in the development of the fishing industry.
Forests such as Mukura and Nyungwe act
as water catchment areas. They ensure
continuous supply of water to the fishing
grounds.
(d) Presence of fishing grounds
The presence of numerous lakes, rivers,
swamps and ponds provide suitable fishing
grounds in the country. They provide
suitable habitats for fish and planktons.
(e) Cool and well-oxygenated waterThe fishing grounds contain cool and welloxygenated water that supports fish and
growth of planktons. This is due to ideal
climatic conditions that prevail in Rwanda.
(f) Availability of adequate capitalCapital is needed in fishing to buy
equipment like fishing boats, refrigerators,
fishing nets, refrigerated trucks among
other equipment. The required capital
has been made available to the fishermen
through the provision of credit facilities such
as through the Umurenge Saccos in Rwanda.
(g) Steady supply of labour
This has contributed a lot to the development
of the fishing industry in the country. The
availability of cheap and steady supply of
labour has enabled fish dealers to gain huge
profits which they re-invest into the sector.
 Political stability
Political stability
Rwanda enjoys political stability and security.
This has allowed economic activities such as
fishing to flourish.
(i) Favorable government policy
The government of Rwanda supports
fishing activities. It provides loans, develops
infrastructure such as roads, electricity
and market centres for the industry. The
government also enforces laws that favour
fishing activities, especially those that fight
against indiscriminate fishing methods and
water pollution.
(j) Availability of ready market for fish
and fish products Fish and fish products have a high demand
among the local population. There is also
a ready and reliable market for Rwandan
fish and fish products in the neighbouring
countries, especially in the Democratic
Republic of Congo.
(k) Improved technology
The advanced technology and improved
levels of education has been beneficial to
the industry. Improved technology has led
to diversified fishing activities such as fish
farming, fish processing and preservation.
This has enabled the fishing industry to
add value to the fish and fish products to
improve their quality. This gives the fish and
fish products from Rwanda a competitive
advantage in the region.
Types of fish in Rwanda
Activity 13.5
Work in groups.
Your teacher will organise for you to visit a
fishing site.
1. Find out the types of fish caught in the
fishing ground.
2. Find out other types of fish that are found
in other fishing grounds in Rwanda. You
can refer to Geography textbooks and
the Internet.
3. Write a report on your findings for a
class presentation.
Rwanda is naturally blessed with a variety of
fish species. There are more than 20 species
of fish in Lake Kivu alone. Other lakes and
rivers also have other species. They include
the following.
• Tilapia
• Mud fish
• Stolothrisa
tanganicae
•Barbus
• Clarias
• Haplochromis
• Tanganyika
sardines
• Limnothrissa
Miodon
• Lung fish among
many others.
Methods of fishing used in
Rwanda
Activity 13.6 Work in groups of five.
Your teacher will organise for you to visit a
fishing site that is near your school.
1. Identify the fishing method(s) that are
used in the fishing ground.
2. Find out reasons why the method is used
there.
3. Find out other fishing methods that are
used in other fishing grounds in Rwanda.
4. Give reasons why the different methods
are used in the different places.
5. Write a report on your findings for a class
presentation.
These types of fish listed are caught using
different fishing methods. It should be
noted that the type of fishing method used
depends on the type of fish to be caught.
There are two categories of fishing methods
used in Rwanda. They are the traditional and
modern methods of fishing.
(a) Traditional methods of fishing
These are the less developed methods of
fishing that have been in use for many years
in Rwanda. They include the following:
(i) The hook and line method This involves using a single line or fishing
rod. The rod has a hook with bait at its end
to trap the fish as it tries to eat the bait. This
method is used to catch fish such as mud
fish, and tilapia.
 (ii) The use of fishing baskets
(ii) The use of fishing baskets
This method is used in shallow waters like in
swamps as well as in flowing rivers. Conical
shaped baskets are commonly used to catch
the fish. The baskets have small holes at the
bottom where the fish enters in an attempt
to pick the bait that is inside. Once inside the
basket, the fish cannot escape. The basket
is then removed from the water and the
fish is picked.
 (iii)Use of scoop nets
(iii)Use of scoop nets
These nets are locally known as lampara.
The nets are cast in water and lifted up at
intervals as the fish swim in water. When
used at night, lights are used to attract the
fish. This method is commonly used when
small fish are targeted such as the isambaza.
 (iv) Cast net method
(iv) Cast net method
This fishing method involves the use of a
circular net that is cast into water by use
of hands. Fish are trapped and caught as
they swim.
 (v) Spear fishing
(v) Spear fishing
This method is commonly used in light
shallow waters such as in swamps, river
banks, marshes, flood waters and shallow
rivers. In these waters, the fish can be easily
detected from the surface.

Spears are used to kill or injure the fish
before they are caught. This method is
mostly practiced when targeting the cat and
lung fish along the flooded banks of River
Akagera and in the shallow waters in the
swamps of the Akanyaru area.
(b) Modern methods of fishing
In Rwanda there are few modern methods of
fishing that are used. This is due to the small
size of the water bodies in which fishing is
carried out. It becomes uneconomical to
use modern methods of fishing when the
fish caught are in small numbers and the
sizes of the water bodies are small. The most
common modern method of fishing is the
gill net method.
(i) Gill net method
When using this method, the fishing net
is suspended in water by using floats and
weights. The net hangs in water like a tennis
net. It catches the fish by their gills as they
swim. The fish are unable to move forward
or backward. This method is commonly used
to catch fish such as tilapia in various lakes
of Rwanda.
 Task 13.1
Task 13.1
1. Define fishing.
2. Name five major fishing grounds in
Rwanda.
3. Discuss the common fishing methods
used in Rwanda.
Methods of conservation and
preservation of fish in Rwanda
Activity 13.7
Work in groups of five.
Your teacher will organise a field visit for you
to a fish farm in an area that is near your
school. In groups of five.
1. Find out the fish conservation and
preservation methods that are used in
the fish farm.
2. Relate your findings to the fish
conservation and preservation methods
used in other fishing grounds in Rwanda.
3. Discuss the effectiveness of the fish
conservation and preservation methods
in Rwanda.
4. Record your findings and prepare a
report that you will present in a class
discussion.
Fish conservation
Fish conservation refers to the protection of
fish in the fishing grounds to maintain them
and to prevent them from being depleted.
It ensures that there is a continuous supply
of fish which is an important resource. The
methods used to conserve fish in Rwanda
include the following:
(a) Using modern methods of fishing Some traditional methods of fishing such as
poisoning, use of barriers and other crude
methods are all being replaced by modern
and improved methods of fishing. Modern
methods of fishing allow for other fish to
remain in the water for reproduction and
continuous supply. The methods also ensure
that only the mature fish are caught while
the others are given time to mature and
reproduce.
(b) Use of proper fishing equipment The government encourages fishermen to
use the recommended sized nets that can
only catch the mature fish and leave the
young ones for a future generation. Fishing
indiscriminately leads to over fishing and
depletion of fish. The fishing equipment
that are used by the fishermen are strictly
monitored by the fisheries department to
ensure that the right standards are adhered
to.
(c) Artificial hatching of fish This conservation method involves hatching
the fish artificially in special ponds where
they are well taken care of. They are then
later transferred to lakes and rivers so that
they can multiply. This practice helps to
increase the number of fish reproduced. It
also protects the young fish and the eggs
against
predators enabling them to grow
to maturity.
(d) Re-stocking
This is an activity that addresses the
challenges of the over fished areas in
Rwanda. Lake Mirayi in Gashora sector in
the Eastern Province is commonly restocked
with tilapia. The fish are protected and allowed to grow for about six months before
fishing in the lake can be allowed again.
(e) Mass education
The local population and the fishermen are
sensitised on sustainable ways of utilising
water resources. The information provided
is on the use of better methods of fishing
and on how to protect water bodies against
pollution and misuse.
(f) Cross breeding The fisheries department in collaboration
with international agencies has conducted
artificial fertilisation of fish to get hybrids.
The hybrids are then replanted into selected
water bodies. This increases on fish species
and sizes.
(g) Regulated fishing periods
This has become a common practice aimed
towards the conservation of fish in Rwanda.
Specific and fixed fishing schedules are put
in place so as to allow regeneration of fish
in the water bodies. It also allows the fish
available time to grow to maturity.
 Artificial provision of planktons
Artificial provision of planktons This is practiced more in fish farms than in
natural water bodies. The practice is aimed
at enabling fish to have enough food to grow
and mature. Proper feeding allows the fish
to be more productive and to multiply at a
faster rate.
(i) Setting up strict government rules
and regulations
The government’s intervention in fish
conservation methods and programs
ensures sustainable fishing. To do this,
the government has enacted laws that regulate the exploitation of water resources
including fish. Laws have been enacted to
protect the wetlands and water bodies in
which the breeding of fish occurs.
(j) Protecting water bodies from pollution Measures are put in place to protect the
fishing grounds from pollution. Harsh
punishments have been introduced to
offenders. There is also the introduction of
cleaning exercises of the already polluted
water bodies so as to make them more ideal
for fish breeding. The water weeds such as
water hyacinth be harvested and destroyed.
(k) Protection against fish predators
In areas where fish predators are in large
numbers, efforts are put to protect the
fish from depletion. The predators can be
removed and relocated to other areas in
order to allow fish to grow and multiply.
Fish preservation
This is the keeping or storage of fish caught
for long periods awaiting consumption. Fish
is perishable and therefore needs to be
well preserved. Before the preservation of
fish, it is caught, scaled and the intestines
removed.
The methods used to preserve fish are
grouped into two. There are traditional and
modern methods of fish preservation. Below
is a description of the fish preservation
methods practiced in Rwanda.
(a) Traditional methods of fish
preservation
(i) Sun drying
This is one of the oldest methods for the
preservation of fish. Fish are caught and the intestines are removed. They are then
exposed to the sun for drying through
dehydration. Dry fish can stay longer as it
awaits consumption. This method of fish
preservation is used by most fishermen
around Lakes Kivu, Mirayi and Ihema.
 (ii) Deep frying
(ii) Deep frying
In this method, fish are first dissected and
the scales and intestines removed. They
are then dipped in boiling cooking oil until
they become hard and dry. The boiling oil
dehydrates the fish. It enables fish to be
kept for some time as they await marketing
or consumption.
 (iii) Salting
(iii) Salting
This is another method of fish preservation
used in Rwanda. Fish is salted and packed
between the layers of salt or brine. The
common type of fish preserved in this way
is tilapia.
 (iv) Smoking
(iv) Smoking Fish are dried by the smoke or directly hung
above the fire. This is done to dehydrate the
fish by removing moisture from the fish.
When it is done properly it preserves fish
for a long period. This method is used by
most fishermen in Rwanda.
 (b) Modern methods of fish
preservation
(b) Modern methods of fish
preservation These are fish preservation methods that
involve use of modern equipment.
(i) Canning This preservation method involves application
of heat to the fish that is processed and
packed in tightly sealed containers. The
containers are tightly sealed to lock out air
and heated in order to destroy any microorganisms that spoil the food. When sealing,
no air is left in the tin. This is because the dry
air contains bacteria that spoils the fish.
 (ii) Refrigeration
(ii) Refrigeration
This the major modern fish preservation
method used in Rwanda. It involves keeping
fish in very low temperatures. Sometimes,
fish is prepared and put in packages that
are put in freezers. This is purposely done
to keep fish fresh for longer periods.
 Importance of fish and fishing to
Rwanda
Importance of fish and fishing to
Rwanda
Activity 13.8 Work in pairs.
1. Explain by way of discussion the
importance of fish and fish farming to;
(a) The people of Rwanda.
(b) The economy of Rwanda.
2. Write down your answers and make a
class presentation.
Fish and fishing are of significant value
to the socio-economic development of
Rwanda. The importance of fish and fishing
are discussed below.
(a) Fishing provides jobs to people
who are employed in the fishing
industry. They include fish processers,
fishermen, fish mongers and fish
transporters.
(b) Fish is as source of food that is so rich
in proteins. Proteins are an important
component in human diet for good
health.
(c) Fishing promotes both local and
international trade hence improving
international relations and the
balance of trade between countries.
(d) Fishing promotes the growth and
development of transport networks
such as roads that connect fishing
grounds and market areas.
(e) The revenue collected by the
government through taxes in the
industry is used in the development
and provision of social services and
facilities like schools and health
centres. These facilities benefit the
society.
(f) Fishing and fish are sources of income
for people who are employed in the
industry.
(g) Fishing provides markets for other
products from various economic
sectors. Fishermen buy food stuffs
from agriculture, timber from forestry
and fishing gear and equipment from
manufacturing industries.

Fishing and fish provide raw materials
to different industries like animal feeds
industries, fish canning industries,
fertiliser-processing and cosmetic
industries.

(i) Fishing helps the country to diversify
its economy. It provides alternative
sources of income for the economy.
(j) Fishing promotes tourism especially in
areas of the country where it is carried
out as a leisure activity or for sports.
(k) F i s h i n g l e a d s to g ro w t h a n d
development of towns. In Rwanda,
Rubavu town developed out of fishing
activities. The Gashora trading centre
is also developing fast due to the
active fishing activities that take place
in Lakes Mirayi and Rumira.
(l) The fishing industry in Rwanda offers a research centre for the fisheries
departments in higher institutions of
learning.
(m) Fish and fish products are a source of
traditional medicines that are used by
the people of Rwanda.

The fishing industry has influenced
the government to set buffer zones
around the fishing grounds. This has
contributed to the conservation of the
environment.
(o) The fishing industry has contributed to
the development of other industries
that have additional advantages to
contribute to the economy. These
industries include boat construction
industries, fish processing industries
and cosmetic industries.
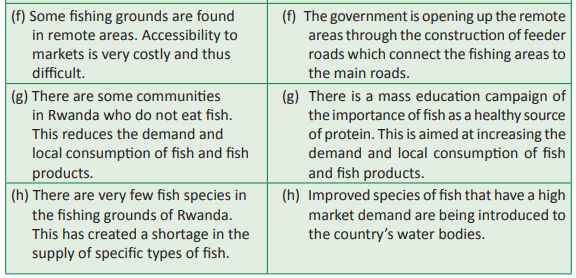
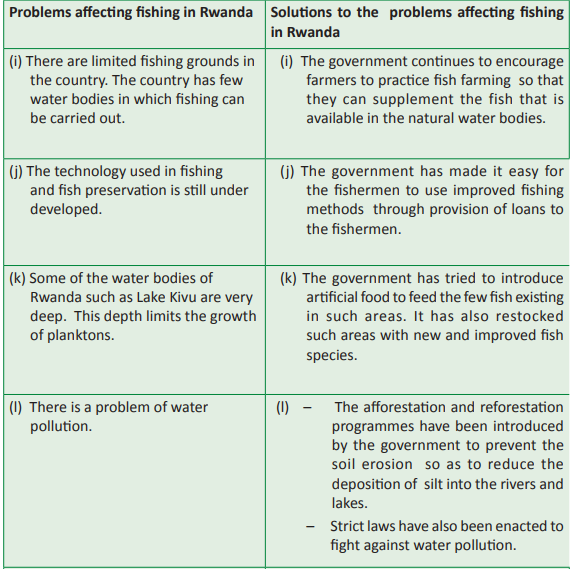
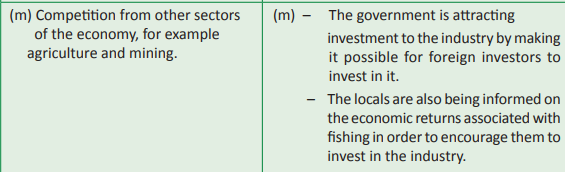
Problems affecting fishing and
possible solutions
Activity 13.9
Work in pairs.

Study the photograph provided above and
answer the questions that follow.
1. Describe the state of the water body that is shown in the photograph.
2. Discuss how its state affects fish and fishing activities.
3. Using the internet and other sources of geographical information, find out other
problems that affect the fishing industry in the country.
4. Write down your findings and present them in a class discussion.
Activity 13.10 Work in groups of five.
Your teacher will organise for you to go on a field visit to a fish farm in an area that is
near your school.
1. Find out the problems that affecting fishing in the specific fish farm and in the country.
2. Suggest some of the possible solutions to the problems that you have discussed.
3. Write down a report on your findings and discuss them in a class presentation.
In the recent past, the fishing industry in Rwanda has thrived. However, there are still a
number of challenges that face the industry. The government and players in the industry
have tried to come up with solutions to some of the problems.


 Fish farming in Rwanda
Fish farming in Rwanda
Task 13.2 1. Discuss five methods of fish preservation in Rwanda.
2. Explain the importance of fishing in Rwanda.
3. (a) Give five problems facing the fish industry in Rwanda
(b) Provide the solutions to the problems in (a) above.
Activity 13. 11 Work in pairs.
Study the photograph below and use it to answer the questions that follow.

1. Describe the activity carried out in the photograph above.
2. State the difference between the fishing that is carried out in the picture above and
the fishing that is carried out in lakes and rivers.
3. Write down the findings and discuss the findings in a class presentation.
Fish farming is also referred to as
pisciculture. It is the raising of fish commercially in tanks
or enclosures, usually for food.
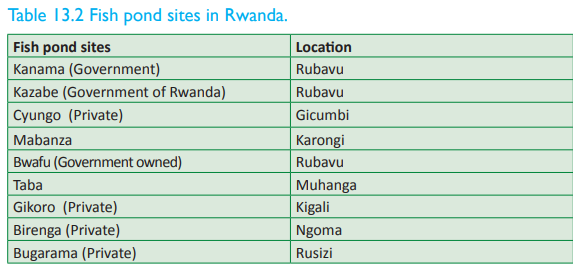
In Rwanda, fish farming is practiced in areas such as:
• Kigembe in Gisagara District
• Rwasave in Huye District
• Nyagasambu in Gasabo district
Below are some of the fish pond sites in Rwanda.
 Activity 13.12
Activity 13.12
Work in groups of five.
Your teacher will organise a field visit for you
to an area with a fish farm near your school.
1. Identify the fish types that are reared
in the farm.
2. Find out the factors that favour fish
farming in the areas under the study and
in the country.
3. Write a report of your findings that you
will share with your classmates in a class
presentation.
There are several factors that favour fish
farming in Rwanda. They include the
following.
(a) There is adequate capital that is needed
for fish farming. This has been possible
because of the credit facilities that
are extended to the fish farmers in all
sectors in Rwanda.
(b) There is a steady supply of affordable
labour force that is important in the
development of fish farming.
(c) The climate of Rwanda is favourable for
fish farming. There is adequate rainfall
and moderate temperatures that are
required for fish metabolism.
(d) The presence of a variety of water
bodies favours fish farming. The water
bodies include swamps, rivers, lakes and
other wetlands.
(e) The use of artificial feed supplements
the natural diet consumed by fish. This
has enabled the fish to grow very fast
and hence steady harvests.
(f) The presence of ready markets for fish
in Rwanda. This enables the farmers
make profits thus motivating them to
farm more.
(g) The government of Rwanda has
introduced policies that favour the
fish farming. It offers subsidies to fish
farmers and also provides them with
loans to enable them develop their fish
businesses.

The presence of improved transport
networks especially road transport has
enabled the fish farming project owners
to transport the inputs and outputs
easily to and from the market centres.
(i) The country has tried to modernise
the fish farming. This has assisted the
fish farmers to be able to use modern
technology.
Problems and prospects for fish farming in Rwanda
Activity 13. 13 Work in pairs.
Study the two photographs and use them to answer the questions that follow.

(a) Assess the safety of fish in the ponds.
(b) Other than the problem shown in the photographs above, identify and explain other
problems.
Problems affecting fish
farming in Rwanda
(a) Some farmers over fish from their
ponds due to the use of indiscriminate
fishing methods.
(b) Water in the ponds is polluted by the
artificial feeds that decompose in it.
The silt that is deposited by the run-off
also makes the ponds dirty. Fish species
such as tilapia can hardly survive in such
ponds.
(c) Some areas where fish farms are located
are remote and lack or have poor means
of transport. This creates problems
when accessing urban markets.
(d) The fish farms produce low quality fish.
This reduces the demand for fish hence
reducing the income of the fish farmers.
(e) Fish farming is a costly venture. This
makes it unattractive to many people
who might not have the required
capital.
(f) Competition from those who fish in the
natural water bodies.
(g) Lack of ready markets for the fish and
fish products.

The fish predators such as snakes and
sometimes crocodiles invade the ponds
and eat the fish.
The prospects of fish farming in the country
are bright. There is potential of expanding
the practice and hence the profits reaped
from it. This is possible with the support of
the government.
Ways of improving fishing and
fish farming in Rwanda (future
prospects)
Activity 13.14 Use the Internet, Geography textbooks,
journals and best practices from other
developed countries;
1. Find out ways in which fish farming in
Rwanda can be improved.
2. Write down a report on your suggestions
and discuss them in a class presentation.
Some of the ways in which the fishing and
fish farming can be improved include the
following:
(a) Development of new agencies that
deal with fishing
The government should consider establishing
more agencies to address the issues that
affect inland fishing in the country.
(b) Development of a fish farming plan
for the country
The government should draw a master plan
that clearly shows the future of fishing in
the country.
(c) Protection of the country’s fishing
grounds The government should recruit more people
to guard the fishing grounds of the country.
The guards should be properly trained and
given equipment to enable them carry out
their duties well.
(d) Restoration and protection of
watersheds
The government should put in more
emphasis on the afforestation and
reforestation programmes especially in
the watersheds as a way of controlling the
problem of silting in the water bodies.
(e) Control of water weeds
There should be a serious campaign against
water weeds especially the water hyacinth.
The government in collaboration with the
local communities should look for ways of
removing the already present weeds and to
prevent others from growing.
(f) Restocking of over fished lakes The government should restock the lakes
and rivers with low populations of fish.
(g) Purchasing feed-making machines
The government through fishing agencies
should increase the production of fish feeds.
There is an urgent need since fish in both
natural water bodies and fish farms need feeds that are more nutritious in order to
improve their quality and size.
 Commercialising fish farming
Commercialising fish farming
The government should continue to
encourage the population to embrace
commercial fish farming as an alternative
source of income.
(i) Development of infrastructure
around the fishing grounds
The government of Rwanda should develop
infrastructure especially roads leading to
fish farms, fishing grounds and markets.
(j) Increasing sheltered places
The government should plan to build
various sheltered and well facilitated places
where the fishermen can store and preserve
their catch as they await marketing.
(k) Establishment of regional fishery
promotion centres
The government should plan to increase
fishery promotion centres throughout the
country.
(l) Increasing the fish hatchery centresThe government should plan to establish
more places where improved breeds of fish
can be hatched and the fingerlings sold or
given to the locals for free.
(m) Introduction of new and
improved breeds of fish
Intensive research should be conducted
especially on crossing-breeding fish species.
This is aimed at introducing new and
improved species of fish which will mature
fast within a short time.
 Emphasising cage fishing
Emphasising cage fishing
The government should emphasise fish
farming using cages in various lakes. These
will add on to already established cages.
 Future prospects
Future prospects
Currently, both the production levels of fish
and the produce’s market are promising.
Fishing is a technologically-oriented business.
Much of the private sector should be
involved in it but with advisory services from
the government. The government should
come up with a special centre to manage
and take care of the fishing sector.
Activity 13.15
Work in groups.
With the guidance of your teacher and
a professional resource person from the
government fisheries department in the
sector where your school is located;
1. Come up with a proposal for a fish
farming project in your school. Share your
project proposal with the management
of your school.
2. Dig up a fish pond and ask for a
supply of fingerlings from the fisheries
department.
3. Seek for assistance from your school
administration to provide you with the
fish feeds before the first harvest.
4. Seek for professional advice on how to
take care of the fish up to when they are
ready for harvesting.
5. Sell the fish to the nearby market or to
your school to supplement the school’s
diet.
6. Write up a report on the project and
share it in a class presentation.
Task 13.3
1. Describe the state of fish farming in
Rwanda.
2. Explain five factors that favour fishing in
Rwanda.
3. (a) Discuss five problems that affect
fish farming in Rwanda.
(b) Give solutions to the problems
highlighted in (a) above.
Case studies
Fishing in Lake Kivu
This is one of the great lakes of Africa. It is
situated in the Albertine Rift which is part
of the Western arm of the East African
Rift valley. It is the largest lake in Rwanda,
covering a total surface area of about
2700 km
2 . It is located on an elevation of
1460 metres above the sea level. It is 89
kilometres in length and 48 kilometres in
width. Its water volume is about 500 km
3
.
The lake is 480 metres deep. It hosts an
island known as Idjwi. The shore of the Lake
on the Rwandan side is made up of Rubavu,
Karongi and Rusizi.

Lake Kivu has well-organised and closely
monitored fishing activities. Fishing
is regulated especially when the fish
population shows signs of dropping or when
the new fingerlings have been introduced.
Fishing in the lake is for commercial
purposes. Cage fish farming has also taken
a lead in the lake.
Lake Kivu has about 28 species of fish. To
boost the fish species, the government has
introduced the following new species:
• The longfin tilapia
• Oreochromis leucostictus tilapia
• Redbreast tilapia
Fishing on Lake Rweru
This lake is located along the border of
Rwanda and Burundi. The lake covers a
surface area of about 100 km
2
. The Rwandan
part has a total surface of 20 km
2
. Lake Rweru is shallow and its depth is estimated
to be between 2.1 – 3.9 metres. The lake
has numerous swampy areas with dense
papyrus vegetation that occupy most of the
areas near the lake. There are also several
floating islands.
The lake is threatened by water weeds
especially the water hyacinth. The weed
is steadily spreading on to River Akagera.
Fishing is less developed on this lake. The
total annual fish output is at between 200-
250 tonnes. The fishery policies are not
fully implemented on the lake due to the
challenges associated with it. The effects
of the political turmoil in Burundi and the
constant in-coming of alien fishermen from
Burundi who use non-recommendable
fishing methods that tend to overfish
the Rwandan territorial waters are great
challenges in the lake.
 Fishing in Lake Ihema
Fishing in Lake Ihema
Lake Ihema is located to the south of the
Akagera National Park in the savanna
grasslands of the Eastern Province. It covers
a total area of about 90 kilometres, with an
elevation that stands at 1292 metres above
sea level. Lake Ihema is a shallow lake with
the depth of between 5-7 metres.
It has a wide range of biodiversity, but fish is
limited. The lake is bordered by swamps and
papyrus vegetation which have provided
excellent sites for a number of flora and
fauna. The lake is bordered on its eastern
side by Tanzania. Lake Ihema is known for
its habitable conditions that favour the presence of hippopotamus and crocodiles.
There was restricted fishing on the lake
in the past years. However, recently the
government allowed fishing and started
restocking the lake with new fingerlings
in order to enrich it. Fishing on the lake
is affected by water weeds especially the
water hyacinth. The weeds have affected
the quality of water in the lake. The
weeds host a lot of snakes and crocodiles
that contribute to the reduction of the
population of fish. The few fish that are
present are overfished. All these challenges
have had negative effects on the fishing
operations and the general biodiversity in
the lake.
Did you know? • Fishing in Rwanda is mostly practiced in Lake Kivu.
• Fishing in Rwanda is mostly for the purposes of self consumption.
• The presence of methane-producing organisms in Lake Kivu limits the development
of aquatic life.
• Fishing in Rwanda is underexploited. Lake Kivu is well-stocked and could support an
annual catch of 5,000 tonnes.
• The potential of Lake Ihema is also underutilised.
End of unit revision task
1. (a) Define fishing.
(b) Name the major fishing grounds of Rwanda.
2. Discuss five factors that favour fishing in Rwanda.
3. (a) Name five types of fish found in the fishing grounds of Rwanda.
(b) Describe the common methods of fishing in Rwanda.
4. (a) What is fish conservation?
(b) State five measures used by the government to conserve fish.
(c) State and describe five methods of fish preservation used in Rwanda.
5. Evaluate the contribution of fishing to the economy of Rwanda.
6. Highlight four problems that affect the fishing industry in Rwanda and suggest solutions to
the problems listed.
7. The fishing industry in Rwanda has flourished in the recent years. Discuss some of the factors
that have favoured its growth and development.
8. (a) What is fish farming?
(b) Explain five problems that affect fish farming in the country and suggest
their solutions.
(c) Discuss the future prospects of fishing in Rwanda.
9. In what way can fishing and fish farming be improved in Rwanda?
Political stability
Artificial provision of planktons
Fishing and fish provide raw materials to different industries like animal feeds industries, fish canning industries, fertiliser-processing and cosmetic industries.
The fishing industry has influenced the government to set buffer zones around the fishing grounds. This has contributed to the conservation of the environment.
The presence of improved transport networks especially road transport has enabled the fish farming project owners to transport the inputs and outputs easily to and from the market centres.
The fish predators such as snakes and sometimes crocodiles invade the ponds and eat the fish.
Commercialising fish farming
Emphasising cage fishing
