UNIT 4:MEDICAL PATHOLOGIES OF ORAL AND OESOPHAGUS
4.1. Key unit competence:
Take appropriate decision on different common medical pathologies of Oral and
oesophagus.
4.2. Prerequisite (knowledge, skills, attitudes, and values)
To achieve the above competence, the associate nurse student needs the following
prerequisites: human body anatomy and physiology, fundamentals of Nursing,
pharmacology.
4.3. Cross-cutting Issues to be addressed
4.3.1. Standardization culture
In health care system, the most case of patients is presented with medical pathology
of oral cavity and esophagus such dental caries/teeth, oral pharyngeal candida,
injuries, esophagitis. The learners have to learn oral diseases and esophagus in
order to handle and to manage the patients with oral cavity and esophagus related
diseases.
4.3.2. Inclusive education
The teacher involves the students in all learning activities concerning the kind of
learner or disabilities for example the slow learner should be reinforced in order to
catch up others, and the teacher takes into consideration respective disability of
learner.
Grouping students, Students with special educational needs are grouped
with others and assigned roles basing on individual student’s abilities.
Providing earning resources earlier before teaching session so that students get
familiar with them. After end lesson assessment, the identified slow learners are
exposed to the remedial learning activities.
Every important point is written and spoken. The written points help students with
hearing impairment and speaking aloud helps students with visual impairment.
Remember to repeat the main points of the lessons.
4.3.3. Gender education
Emphasize to learners that anybody irrespective of their gender can have medical
career mainly medical sciences. Give role models who are successful medical
pathology of oral and esophagus in the area where the learners come from. Make
sure that during classroom teaching and skills lab demonstration both boys and
girls shares and participate equally in practices, arranging and proper hygiene afterclassroom and skills lab teaching session.
4.4. Guidance on the introductory activity
This introductory activity helps you to engage learners in the introduction of medical
pathology of oral and esophagus and invite the learners to follow the next lessons.
Teacher’s activity:
• Ask students to read the text and discuss the given questions.
• Engage students in working collectively the activity
• Help students with different problems
• Ask any four students to present their findings while others are following.
• Prepare trip field to nearest health facility in order to be familiar with dental
department equipment, and health assessment for oral cavity disorders.
• Invite guest person who has specialty in oral health dental department domain
to teach the learners.
4.5. List of Lessons/sub-headings (including assessment)
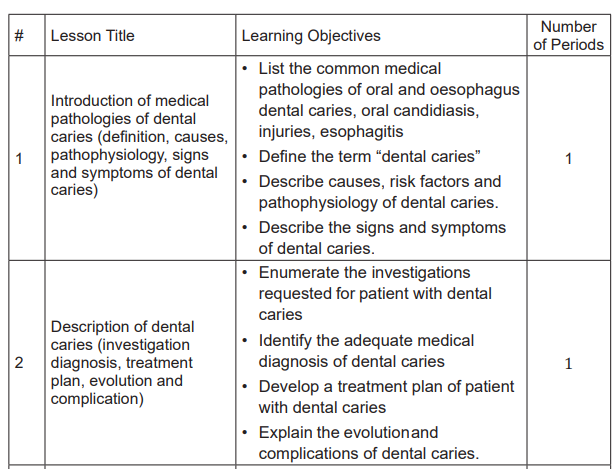
Lesson 1: Introduction of Medical Pathologies of dental caries
(Definition, causes, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms of dentalcaries
a) Prerequisites
This is the first lesson of the four unit on medical pathologies of oral and esophagus.
In this lesson, you will be dealing with the common medical pathologies of dental
caries and esophagus, which are dental caries, oropharyngeal candidiasis, injuries
and esophagitis. Definition, causes, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms of dental
caries for each disease will described. The first thing to do before starting teaching
is to remind learners that they have learnt about structure and function of teeth in
biology, health assessment of oral cavity from fundamentals of nursing. The teacher
will let students discuss the questions as indicated in introductory activity and from
the case study from learning activity 4.1 so that they can prepare themselves for
this lesson.
b) Learning objectives
• List the common medical pathologies of oral and oesophagus: dental caries,
oropharyngeal candidiasis, injuries and esophagitis.
• Define the term “dental caries”
• Describe causes, risk factors and pathophysiology of dental caries
• Describe the signs and symptoms of dental caries.
c) Teaching resources
The teacher could avail the anatomical model of the normal teeth and abnormal
teeth and ensure that the students are able to interpret. In addition, the teacher
should present to the students the library textbooks on medical-surgical nursing,
especially dental caries and indicates the pages. All students must have their
student’s books. The algorithm or protocols about oral diseases management mustbe available. There is a need of black board and chalks or flipcharts and markers.
d) Learning activities 4.1
Teacher ‘activities and methodology:
• Ask learners to do individually activity 4.1 in their student book and answer
the question number 1, 2, 3 and 4.
• Provide the necessary materials.
• Move around in silence to monitor if they are having some problems
• Remember to assist those who are weak but without giving them the
knowledge.
• Invite any five students to provide their answers
• Ask other students to follow carefully the answers provided by students
• Note on the blackboard, flipchart and whiteboard to take note of the main
students’ ideas.
• Tick the correct responses and correct those ones, which are incorrect and try
again to complete those, which are incomplete.
• Harmonize and conclude on the learned knowledge and still engage student
in making that conclusion.
Student‘s activity
• The students answer the questions individually in learning activity 4.1 in their
student book
• The students ask the problems that may be raised from the provided activity
if any in order to get clarification
• Some students present the findings from the learning activity while others are
following carefully.
• Summarize the content with the teacher and coming up with the conclusion.
Expected answers to introductory activity 4.0
1. The possible types of oral health problems illustrated by the picture B, C, D
and E might be dental diseases, dental caries, dental accident, teeth eruption,
teeth fracture, candidiasis, oral epithelial carcinoma, stenosis of the esophagus,
narrowing of the esophagus, esophagitis
2. The picture A looks normal, the picture B may be presenting necrotic dental
tissue, dental tissue damage, darkness of oral cavity etc. The picture C indicates
oral whitish, swollen tonsils. The picture D may indicate bleeding in the teeth,
cut off the teeth. The Picture E indicates the redness of esophagus, narrowedesophageal lumen.
3. Poor hygiene especially retained food is suggestive risk factor in the development
of dental caries as microorganisms invade the teeth surfaces and attract the
microorganisms that later damage the dental tissue resulting from dental caries
4. The possible risk factors in diseases process on picture B is poor hygiene, lack
of brushing with adequate tooth paste, elderly, childhood, poor diet
The picture C is having risk factors such as chronic immune depressive disease,
chronic severe infection, and malnutrition.
Lesson 2: Description of dental caries (investigation diagnosis,treatment plan, evolution and complication)
a) Prerequisite
This is the second lesson of the fourth unit on medical pathologies of oral and
esophagus in sensory organs. In this lesson you will be dealing with the description
of dental caries such its investigation, diagnosis treatment plan evolution and
complication. The first thing to do before starting teaching is to remind learners thatthey have learnt about lesson one of dental caries.
b) Learning objectives
After completion of this lesson, the student will be able to:
• Enumerate the investigations requested for patient with dental caries
• Identify the adequate medical diagnosis of dental caries
• Develop a treatment plan of patient with dental caries• Explain the evolution and complications of dental caries.
c) Teaching resources
The teacher could avail the Snellen chart, slip lamp, and ensure the students
are able to interpret them. In addition, the teacher should present to the students
the library textbooks on medical-surgical nursing, especially oral Diseases and
indicates the pages. All students must have their student’s books. There is a need
of black board and chalks or flipcharts and markers. Algorithms about assessmentand management of dental caries must also be displayed.
d) Learning activities
Teacher’s activities and methodology
• Ask learners to do individually activity 4.1 in their student book and answer
the questions related.
• Provide the necessary materials.
Move around in silence to monitor if they are having some problems
• Remember to assist those who are weak but without giving them the
knowledge.
• Invite any five students to provide their answers
• Ask other students to follow carefully the answers provided by students
• Note on the blackboard the main student’s ideas.
• Tick the correct responses and correct those ones, which are incorrect and try
again to complete those, which are incomplete.
• Harmonize and conclude on the learned knowledge and still engage student
in making that conclusion.
• Use brainstorming while collecting the answers from different learners.
• Judge the answers from learners by conforming the right responses.
Student’s activities
• The students answer the questions individually in learning activity 4.1 in their
student book
• The students ask the problems that may be raised from the provided activity
if any in order to get clarification
• Some students present the findings from the learning activity while others are
following carefully
• Summarize the content with the teacher and coming up with conclusion.
• Attempt to answer the self-assessment questions 4 .1
The expected answers from Questions of learning activity 4.1
1. The signs and symptoms that the patient was presenting were tooth sensitivity
to hot meal, constant tooth pain, dark spots on the teeth, and bad breath. In
addition, the physical exam reveals cavities in teeth and tenderness on palpation
(pain), facial swelling. The x-ray reveals the presence of holes in the 34, swelling
of gingiva, and fever with body temperature of 38.8°C. An acutely swollen and
reddened area of the soft gingiva is noted in her mouth, and an elevated WBC
of 16,000/mm3,
2. The x-ray and Full Blood Count (FBC) were performed
3. The medical problem is Dental caries
4. Treatment plan involved the use of Antibiotic like Amoxicillin 500mg TDS 7/7,and Ibuprofen 400mg TDS 4/7 for pain relief.
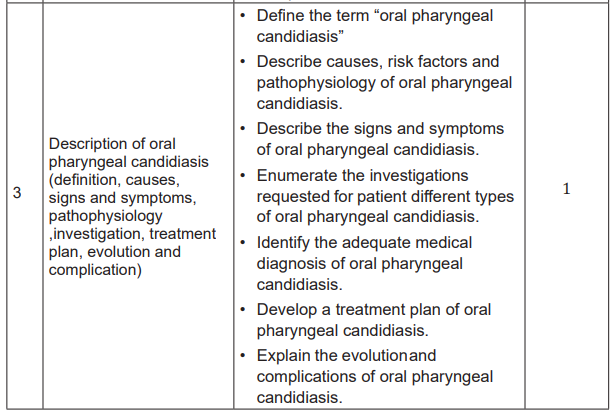
Lesson 3: Description of oral pharyngeal candidiasis
(definition, causes, pathophysiology, signs and
symptoms, investigation, treatment plan, evolutionand complication)
a) Prerequisites
This is the third lesson of the fourth unit about medical pathologies of the oral
and esophagus. In this lesson, you will be dealing with the description of different
causes and risk factors of oral pharyngeal candidiasis, pathophysiology, signs and
symptoms, investigation, management, evolution and complications. The first thing
to do before starting teaching is to remind learners what they have learnt about the
anatomy and physiology of the sensory organs (oral cavity), health assessment of
oral cavity from fundamentals of nursing. The students will discuss the questions
from the case study from learning activity 4.2 so that they can prepare themselves
for this lesson.
b) Learning objectives:
After completion of this lesson, the student will be able to:
• Define the term “oral pharyngeal candidiasis”
• Describe causes, risk factors and pathophysiology of oral pharyngeal
candidiasis.
• Describe the signs and symptoms of oral pharyngeal candidiasis.
• Enumerate the investigations requested for patient different types of oral
pharyngeal candidiasis.
• Identify the adequate medical diagnosis of oral pharyngeal candidiasis.
• Develop a treatment plan of oral pharyngeal candidiasis.
• Explain the evolution and complications of oral pharyngeal candidiasis.
c) Teaching resources
The teacher could avail the oral cavity anatomical model, Penlight and tongue
depressor and ensure the students are able to use them. In addition, the teacher
should present to the students the library textbooks on medical-surgical nursing,
especially oral pharyngeal candidiasis Diseases and indicates the pages. All
students must have their student’s books. There is need of black board and chalks
or flipcharts and markers. Algorithms about assessment and management ofconjunctivitis must also be displayed.
d) Learning activities
Teacher’s activities and methodology
• Ask learners to do individually activity 4.2 in their student book and answer
the questions related.
• Provide the necessary materials.
• Move around in silence to monitor if they are having some problems
• Remember to assist those who are weak but without giving them the
knowledge.
• Invite any five students to provide they answers
• Ask other students to follow carefully the answers provided by students
• Note on the blackboard the main student’s ideas.
• Tick the correct responses and correct those ones, which are incorrect and try
again to complete those, which are incomplete.
• Harmonize and conclude on the learned knowledge and still engage student
in making that conclusion.
• Use brainstorming while collecting the answers from different learners.
• Judge the answers from learners by confirming the right responses.
Student’s activities
• The students answer the questions individually in learning activity 4.2 in their
student book
• The students ask the problems that may be raised from the provided activity
if any in order to get clarification
• Some students present the findings from the learning activity while others are
following carefully
• Summarize the content with the teacher and coming up with conclusion.
• Attend the library for reading related book of oral candidiasis conditions
• Attempt to answer the self-assessment questions 4.2
The expected answers from Questions of learning activity 4.2
1. Signs and symptoms that the patient was presenting are soreness, cotton
like feeling in the mouth, loss of taste, dysphagia, cracking and redness at the
corners of the mouth.
2. The problem that the patient may be presenting would be oral lesions, oral
thrush, oral cavity tissues trauma etc.
3. Full Blood Count of 112,000/mm3
4. The treatment plan includes Antifungal drugs were prescribed such as
Fluconazole 800mg OD 14/7, or oral Nystatin 500000UI QID7/7 and Oral
paracetamol 500mg TDS 3/7 for pain relief
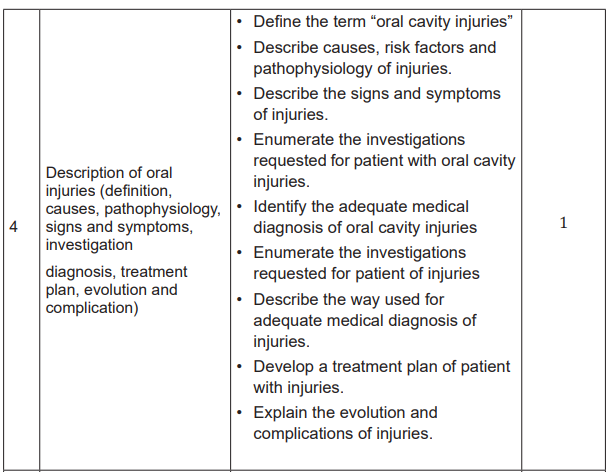
Lesson 4: Description of injuries (Definition, causes
and risk factors, Pathophysiology, signs and
symptoms, investigation, diagnosis, treatment plan,evolution and complication)
a) Prerequisites
This is the third lesson of the fourth unit about medical pathologies of the oral and
esophagus. In this lesson, you will be dealing with the definition, causes and risk
factors, Pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, investigation, diagnosis, treatment
plan, evolution and complication of oral injuries. The first thing to do before starting
teaching is to remind learners what they have learnt about the anatomy and
physiology of the sensory organs (oral cavity), health assessment of oral cavity
from fundamentals of nursing. The students will discuss the questions from the
case study from learning activity 4.3 so that they can prepare themselves for this
lesson.
b) Learning objectives:
After completion of this lesson, the student will be able to:
a. Define the term “oral cavity injuries”
b. Describe causes, risk factors and pathophysiology of injuries.
c. Describe the signs and symptoms of injuries.
d. Enumerate the investigations requested for patient with oral cavity injuries.
e. Identify the adequate medical diagnosis of oral cavity injuries
f. Enumerate the investigations requested for patient of injuries
g. Describe the way used for adequate medical diagnosis of injuries.
h. Develop a treatment plan of patient with injuries.
i. Explain the evolution and complications of injuries.
j) Teaching resources
The teacher could avail the oral cavity anatomical model and Penlight and tongue
depressor and ensure the students are able to use them. In addition, the teacher
should present to the students the library textbooks on medical-surgical nursing,
especially oral pharyngeal candidiasis Diseases and indicates the pages. All
students must have their student’s books. There is need of black board and chalks
or flipcharts and markers. Algorithms about assessment and management ofconjunctivitis must also be displayed.
k) Learning activities
Teacher’s activities and methodology
• Ask learners to do individually activity 4.3 in their student book and answer
the questions related.
• Provide the necessary materials.
• Move around in silence to monitor if they are having some problems
• Remember to assist those who are weak but without giving them the
knowledge.
• Invite any five students to provide they answers
• Ask other students to follow carefully the answers provided by students
• Note on the blackboard the main student’s ideas.
• Tick the correct responses and correct those ones, which are incorrect and try
again to complete those, which are incomplete.
• Harmonize and conclude on the learned knowledge and still engage student
in making that conclusion.
• Use brainstorming while collecting the answers from different learners.
• Judge the answers from learners by conforming the right responses.
Student’s activities
• The students answer the questions individually in learning activity 4.3 in their
student book
• The students ask the problems that may be raised from the provided activity
if any in order to get clarification
• Some students present the findings from the learning activity while others are
following carefully
• Summarize the content with the teacher and coming up with conclusion.
• Attend the library for reading related book of oral cavity condition• Attempt to answer the self-assessment questions 4.3
The expected answers from Questions of learning activity 4.3
1. oral mucous lesions involving multiple oral cavity structure with high sensitivity
on palpation following accidental tooth bite after patient fall during sport with
the presence of whitish, linear, filament like plicae formation observed via
inspection body temperature was 36.8°C, Blood pressure 100/60 mmHg, pulse
rate: 64beats per minute, respiratory rate was 16 breaths per minutes the x-ray
was performed and revealed the presence of slight tooth fracture
2. Medical problem could be like tooth fracture, oral mucous lesions
3. The only x-ray was performed to rule out any tooth fracture
4. The medical treatment included Antibiotic drugs were prescribed such as
amoxicillin 500mg TDS 7/7 for bacterial infection prevention and saline water tobe used to wash out, Diclofenac tablet 100mg TDS 3/7 for pain relief
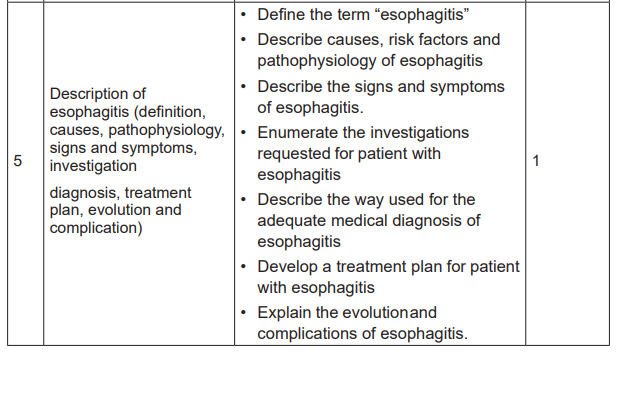
Lesson 5: Description of esophagitis (definition
causes, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms,
investigation, treatment plan, evolution andcomplication)
a) Prerequisite
This is the fifth lesson of the fourth unit about medical pathologies of the oral
and esophagus. In this lesson, you will be dealing with the definition, causes and
risk factors, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, investigation, management,
evolution and complications of esophagus. The first thing to do before starting
teaching is to remind learners what they have learnt about the anatomy and
physiology of the sensory organs (oral cavity), esophagus, health assessment of
oral cavity from fundamentals of nursing. The students will discuss the questions
from the case study from learning activity 4.4 so that they can prepare themselvesfor this lesson.
b) Learning objectives
After completion of this lesson, the student will be able to:
• Define the term “esophagitis”
• Describe causes, risk factors and pathophysiology of esophagitis
• Describe the signs and symptoms of esophagitis.
• Enumerate the investigations requested for patient with esophagitis
• Describe the way used for the adequate medical diagnosis of esophagitis
• Develop a treatment plan for patient with esophagitis
• Explain the evolution and complications of esophagitis.
c) Teaching resources
The teacher could avail the oral cavity anatomical model, Penlight, and tongue
depressor and ensure the students are able to use them. In addition, the teacher
should present to the students the library textbooks on medical-surgical nursing
especially esophagitis disease and indicates the pages. All students must have
their student’s books. This lesson will be taught with different aids like (white board
or black board, computer, chalks or flipcharts and markers. Algorithms about
assessment and management of esophagitis must also be displayed.
d) Learning activities
Learning activities should be directly related to the learning objectives of the course
and provide experiences that will enable students to engage in practice and gain
feedback on specific progress towards those objectives. The various learning
activities will be carried out such as: taking notes, course work and reading textbook
related to the lesson, group assignment and summarize the content, engagement
in debate and other clinical learning activities such as case study.
Teacher’s activity:
• Ask learners to do individually activity 4.4 in their student book and answer
the questions related.
• Provide the necessary materials to the students.
• Move around in silence to monitor if they are having some problems
• Remember to assist those who are weak but without giving them the knowledge.
• Invite any five students to provide their answers
• Ask other students to follow carefully the answers provided by students
• Note on the blackboard the main student’s ideas
• Tick the correct responses and correct those ones, which are incorrect and try
again to complete those, which are incomplete.
• Use brainstorming while collecting the answers from different learners.
• Judge the answers from learners by confirming the right responses.
• Harmonize and conclude on the learned knowledge and still engage student
in making that conclusion.
Student’s activities
• The students answer the questions individually in learning activity 1.5 in their
student book
• The students ask the problems that may be raised from the provided activity
if any in order to get clarification
• Some students present the findings from the learning activity while others are
following carefully
• Summarize the content with the teacher and coming up with conclusion.
• Attend the library for reading related book of esophagus condition• Attempt to answer the self-assessment questions 4.4
3. The three types of medical investigations to rule out the esophagitis diagnosis
include Barium X-ray, Endoscopy and biopsy.
4. Reflux esophagitis may include over-the-counter treatments. These include
antacids (Maalox, Mylanta, others); medications that reduce acid production,
called H-2-receptor blockers, such as cimetidine (Tagamet HB); and medications
that block acid production and heal the oesophagus, called proton pump
inhibitors, these include H-2-receptor blockers as well as proton pump inhibitors,
such as esomeprazole (Nexium), omeprazole (Prilosec). The metoclopramide
may be prescribed.
5. The three major complications of esophagitis include scarring or narrowing
(stricture) of the esophagus, tearing of the esophagus lining tissue from retching
(if food is stuck) or during endoscopy (due to inflammation), Barrett’s oesophagus.
1.6 Summary of the unit
Medical pathology is a branch of medical science primarily concerning the diseases
affects different human organs such as respiratory tract organs, cardio-vascular
organs, digestive organs, uro-genital organs, sensory organs etc. This unit of
medical pathology of the oral and esophagus described the most common oral
cavity and esophagus conditions that are frequently observable in Rwanda such
dental caries/teeth, oral-pharyngeal candidiasis, injuries and esophagitis. The
medical conditions of oral and oesophagus are described by the definition, clinical
features, causes and risk factors, pathophysiology, investigation, treatment plan,
evolution and complications. The student who will be complete this content will
be able to take appropriate decision on different common medical pathologies in
terms of diagnosing, treatment and prevent the complication of dental caries, oral
pharyngeal, injuries and esophagitis.
1.7 Additional Information
Common additional oral cavity disorders.
• Gingivitis
• Cancer of the esophagus
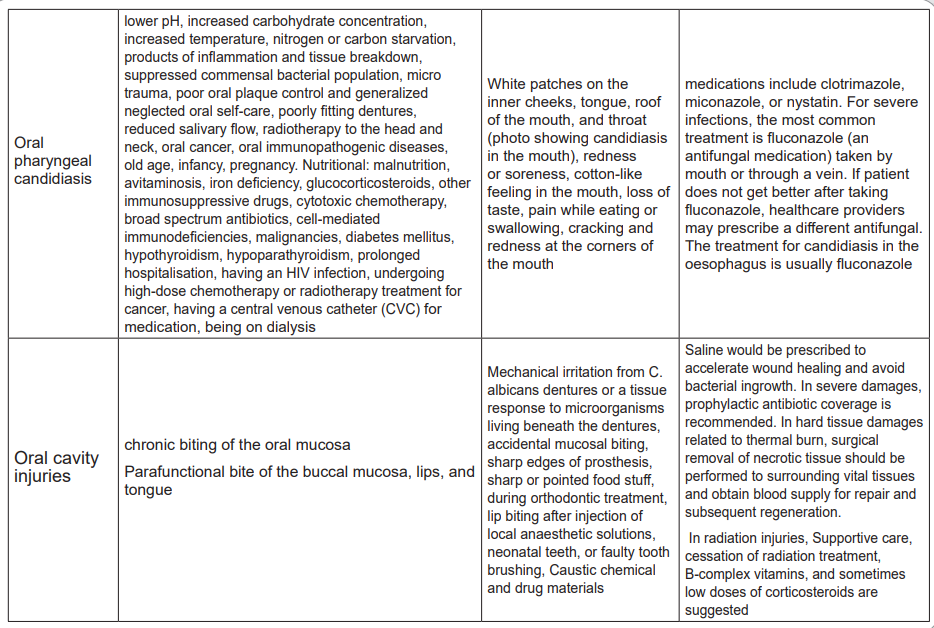
1. GINGIVITIS
Gingivitis is an often-painful inflammation of the gums, or gingiva. It typically occurs
due to plaque buildup on the teeth. People may generally refer to this as gum
disease. Gingivitis is an early form of gum disease and typically produces mildsymptom
Causes
The most common cause of gingivitis is the accumulation of bacterial plaque
between and around the teeth. Dental plaque is a biofilm that accumulates naturally
on the teeth. It occurs when bacteria attach to the smooth surface of a tooth.
Several underlying conditions and outside factors trusted source can increase plaque
formation or a person’s risk of gum inflammation. Changes in hormones: this may
occur during puberty, menopause, the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. The gums
might become more sensitive, raising the risk of inflammation. Some diseases:
cancer, diabetes and HIV are linked to a higher risk of gingivitis; medications that
reduce saliva production can affect a person’s oral health. Dilantin, an epilepsy
medication, and angina drugs can also cause abnormal growth of gum tissue,
increasing the risk of inflammation, smoking, age, family history of gingivitis are
also a risk factor of gingivitis.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of gingivitis might include gum inflammation and
discoloration, tender gums that may be painful to the touch, bleeding from the gums
when brushing or flossing, halitosis or bad breath, receding gums, soft gums
However, in mild cases of gingivitis, there may be no discomfort or noticeable
symptoms
Adequate diagnosis
A dentist or oral hygienist will check for symptoms, such as plaque and tartar in the
oral cavity. They may also order tests to check for signs of periodontitis. This can
be done by x-ray or periodontal probing, using an instrument that measures pocket
depths around a tooth
Treatment Plan
If diagnosis happens early and treatment is prompt and proper, a person may be
able to treat gingivitis at home with good oral hygiene. However, if symptoms do
not resolve, or the condition affects a person’s quality of life, they may wish to seek
professional help.
Treatment often involves care by a dental professional and follow-up procedures
carried out by the patient at home. A person may be able to prevent gingivitis at
home by practicing regular good oral hygiene. This includes brushing teeth at least
twice a day, using an electric toothbrush, flossing teeth at least once a day, regularlyrinsing the mouth with an antiseptic mouthwash Top of Form
Complications
Some complications include abscess or infection in the gingiva or jawbone,
periodontitis a more serious condition that can lead to loss of bone and teeth,
recurrent gingivitis, trench mouth, where bacterial infection leads to ulceration of
the gums
2. Cancer of Esophagus
Oesophageal cancer is a serious condition. Clients usually do not experience
symptoms until the disease has progressed to interfere with swallowing and
passage of food, leading to weight loss.
Causes and risk factors
The major cause of oesophageal cancer is chronic irritation of the oesophagus from
any source. Alcohol abuse and cigarette smoking, clients with GERD are at higher
risk for adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus, other risk factors include habitual
ingestion of hot liquids or foods, poor or inadequate, oral hygiene, and nutritional
deficiencies
Signs and symptoms
Mild, with vague discomfort and difficulty swallowing some foods, Weight loss,
progressive dysphagia. As the disease continues the client resorts to consuming
liquids only.
He or she may experience regurgitation of food, haemorrhage, haemoptysis
(Vomiting of blood), back pain and respiratory distress due to expansion of the
tumour, loss and weakness.
Investigation
A barium swallow demonstrates a filling defect caused by a space-occupying mass. A
biopsy of tissue removed during esophagoscopy or an esophagogastroduodenoscopy
reveals malignant cells.
A bronchoscopy may determine whether the cancer cells have affected the trachea.
Computed tomography (CT) of the chest and abdomen to determine whether
metastasis has occurred. If oesophageal cancer is diagnosed in early stages,treatment.
Treatment Plan
If oesophageal cancer is diagnosed in early stages, treatment is directed at a cure
and includes surgery, chemotherapy, and/or radiation. The surgery is a complete
resection of the oesophagus (esophagectomy), which involves removing the tumor
and a wide margin of tumor-free tissue as well as surrounding lymph node
Additional activities
Remedial activities
1. Using different literature, define the following medical pathology of oral and
oesophagus medical condition
a. Dental caries
b. Oral candidiasis
c. esophagitis
ANSWERS:
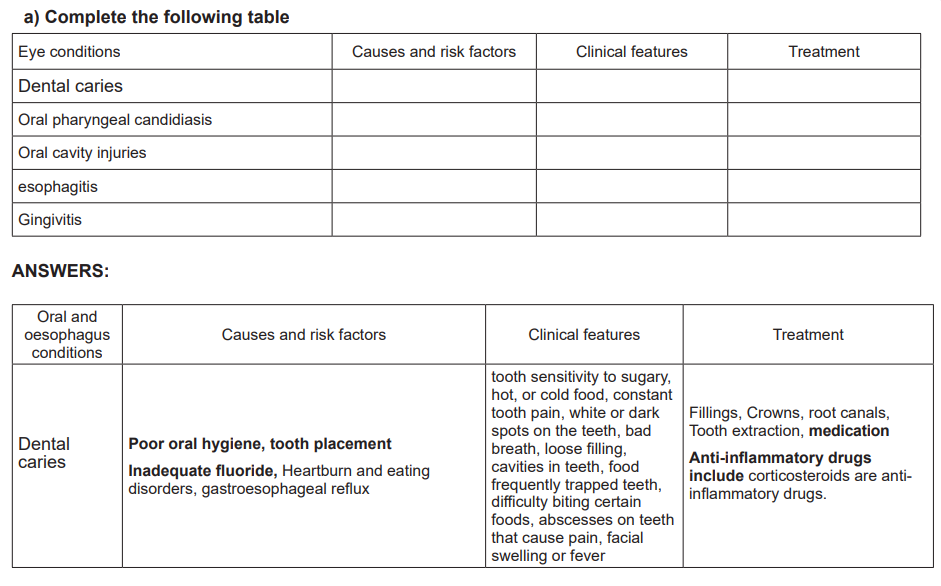
a. Dental caries also known as a dental decay is defined as a disease that is
caused by the breakdown of tooth enamel or it is a chemical dissolution
of a tooth surface that brought about by metabolic activity in a microbial
deposit covering a tooth surface at any given time.
b. Oral candidiasis is an infection caused by a yeast (a type of fungus) called
candida which normally lives on the skin and inside the body in area
such as the mouth, throat, gut and vagina, without causing any problem
problems.
c. Esophagitis is defined as an inflammation that may damage tissues of the
esophagus, the muscular tube that delivers food from the patient’s mouth
to the stomach.
2. Oesophageal candidiasis is one of the MOST common infections in the following
group of people:
a. People with Non communicable diseases
b. People living with HIV/AIDS
c. People with low salt intake diet
d. People with hearing bulimiaANSWER: b
1.9.2 Consolidation activities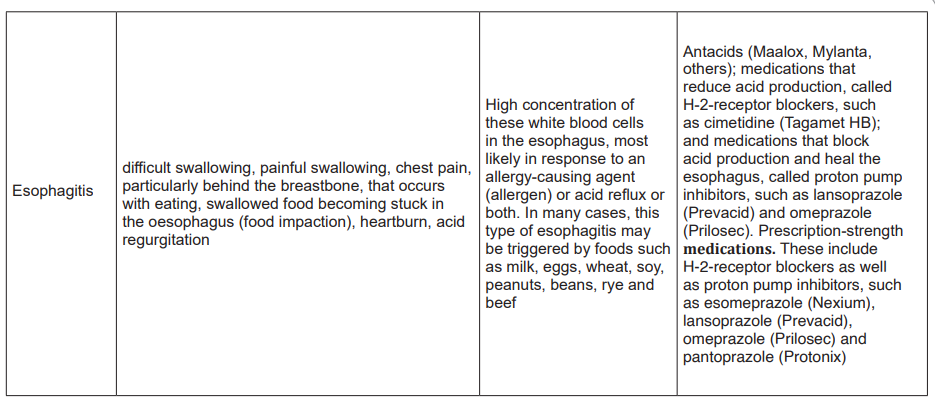
A common disease of oral tissue characterized by painful, inflamed, and swollen
gums is:
a. Candidiasis.
b. Gingivitis.
c. Herpes simplex.
d. Periodontitis.
ANSWER: b
The incidence of most dental caries is directly related to an increase in the dietary
intake of:
a. Fat.
b. Protein.
c. Salt.
d. Sugar.
ANSWER: d
Usually, the first symptom associated with oesophageal disease is:
a. Dysphagia.
b. Malnutrition.
c. Pain.
d. Regurgitation of food.
ANSWER: a
Extended activities
1. The nurse suspects that a patient who presents with the symptom of food
“sticking” in the lower portion of the oesophagus may have the motility disorder
known as:
a. Achalasia
b. Diffuse spasm
c. Gastroesophageal reflexd. Hiatal hernia
ANSWER: c
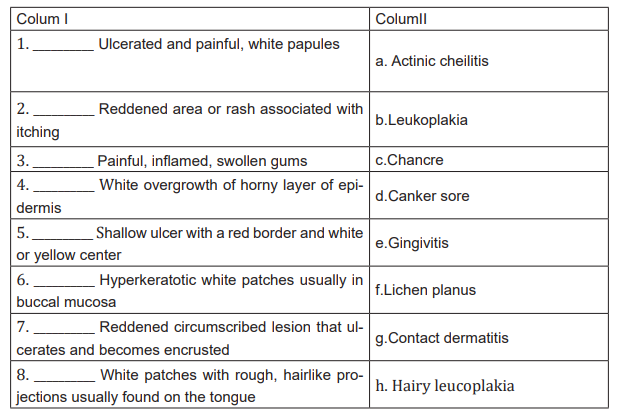
1. Match the abnormality of the lips, mouth, or gums listed in column II with itsassociated symptomatology of the lip, mouth, or gums listed in column I.
1. Discuss the following topics with your classmates.
1. Discuss at least eight healthy oral hygiene habits that have been found to
promote good dental health.
Answer:
1. Discuss the nursing interventions for a patient with cancer of the oesophagus.
Answer:
2. CASE STUDY: Cancer of the Mouth
Edith, a 64-year-old mother of two, has been a chain smoker for 20 years. During
the past month she noticed a dryness in her mouth and a roughened area that is
irritating. She mentioned her symptoms to her dentist, who referred her to a medical
internist.
Q1. On the basis of the patient’s health history, the nurse suspects oral cancer.
Describe what the nurse would expect the lesion to look like.
…………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………….
Answer:
Q2. During the health history, the nurse noted that Edith did not mention a late
occurring symptom of mouth cancer, which is:
b. Drainage.
c. Fever.
d. Odor.
e. Pain.
Answer: d
Q3. On physical examination, Edith evidenced changes associated with cancer of
the mouth, such as:
a. A sore, roughened area that has not healed in 3 weeks.
b. Minor swelling in an area adjacent to the lesion.
c. Numbness in the affected area of the mouth.d. All of the above.
Answer: d
Q4. To confirm a diagnosis of carcinoma of the mouth, a physician would order:
e. A biopsy.
f. A staining procedure.
g. Exfoliative cytology.h. Roentgenography.
Answer: aQ5. What is the differential medical diagnosis of esophagitis?
Answer:
The differential medical diagnosis of esophagitis includes acute coronary syndrome
with atypical chest pain, malignancy, peptic ulcer disease, rings and webs,
pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, achalasia, and esophageal motility disorderQ6. Differentiate periodontal disease from pulpitis?
Answer:
Periodontal (gum) disease is the infection of the gum tissue, and is a more severe
version of gingivitis while Pulpitis is the infection of the tooth’s pulp, which is madeup of blood vessels, nerves and connective tissue
