UNIT 2: CAREER OPPORTUNITIES
Key unit competence: To be able to make rational career choices and
related decisions
Introductory Activity
1. Identify the type of careers shown in each photograph above.
2. Identify the subjects one needs to study so as to pursue each of
the above careers.
2. 1. Meaning of career, choosing work to do and fields of
career opportunities
Activity 2.1
a. What do you understand by the term career?
b. From which fields can we obtain information concerning our
careers?
c. What could be the factors that influence choice of career?
d. Observe the images below and indicate the jobs related to eachcareer opportunities
2.1.1. Meaning of career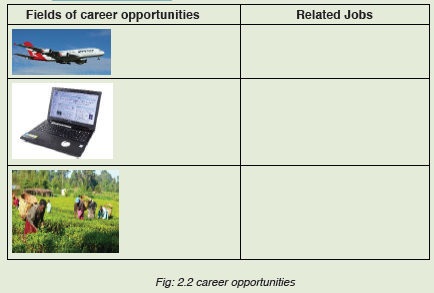
A career is a job or profession that you do for a long period of your life for
survival which enables you to achieve your goals.
It can also be defined as a profession for which one has been trained for as
an undertaking or as a permanent calling. It is what one wants to become in
the future.
2.1.2. Choosing work to do and fields of career opportunities
Work can be understood as undertaking we get involved in pursuit for our
long-life goals. Therefore, it is important to note that, work pre-trained and
done for a long time can be referred to as career.
The choice of a career is very important for every person. It requires serious
consideration, planning and analysis. Planning your career involves selfevaluation
on the following questions, who am I, what are my interests, what
work environment, what will I be doing and what are the job trends. A person
can get into many careers.
In each industry or sector of the economy, there are many careers to choose
from. Some careers require a lot of physical effort (muscle based) while
others require a lot of mental effort (knowledge based); some careers require
many years of training while others can be joined without formal training.
The following are some of the fields of career opportunities and careers
that one can pursue:
There are very many careers in the world. The main fields include:
Education field for example; head teachers, teachers, school administrators,bursars and university lecturers.
Medical field for example; doctors, nurses, surgeons, pharmacists,
gynecologists, dermatologists, physicians and so on.
Agricultural field for example; livestock farmers, dairy farmers, crop
growers, etc.
Engineering field for example, electrical engineers, civil engineers,
telecommunication engineers, mechanical engineers, land surveyors and so on
Political field for example; presidents, vice presidents, mayors, ministers,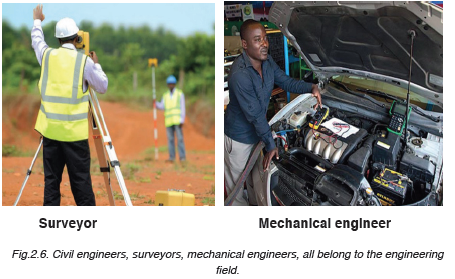
members of parliament, senators, community leaders and so on.
Construction field for example; construction engineers and so on:
Commercial and manufacturing field for example; wholesalers, retailers,vehicle manufacturing, textile production, bakeries and confectioneries.
Transport field for example; freighters, cargo couriers, pilots, air hostesses,
drivers, captains and so on.

Finance field for example; bankers, accountants, Chief Administrative
Officers (CAO), money changers, finance consultants and so on.
Security field for example; police, military and army, secret service/
intelligence,
Media field: This involves people working
as news readers, news anchors, and television and radio presenters,journalists and so on.
Hotel and tourism field for example; waitresses, waiters, chefs, tourist
guides, and so on.

2.1.3. Factors that influence career choice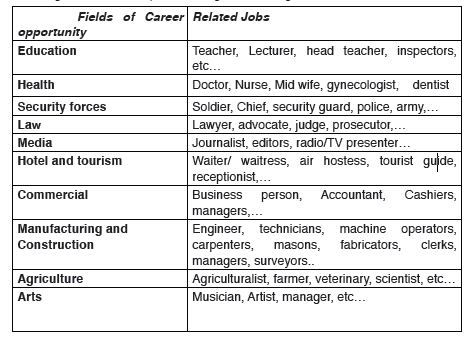
Family influence/Preference: Family background and or parents may
influence directly or indirectly one’s career. Some parents urge their children
to do subjects which lead them do certain courses.
In some cases, children are influenced indirectly by the jobs their parents do
or choose for them. For instance, if a parent is an economist, his/her children
will be influenced to do economics at advanced level to follow the footsteps
of their parents.
Friends and Peer Pressure: Some people want to be close to their friends
and so, they end up choosing the same career path. Peer pressure can
also influence choice of a career because some people always want to fit
in their peer groups, so they end up opting for the same career, schools
and institutions. It is common to find students of some schools becoming
musicians while a majority of another school becoming businessmen,
doctors, teachers, etc.
Role models: These are people we admire and want to emulate. Because
we admire them, we end up taking their careers. This is, especially in
musicians and football players. People tend to pick up star performers in
the above-mentioned fields to become their role models thus taking up the
same careers.
Talent and natural ability: This is choosing a career basing on talent and
ability. It is very good if one is able to identify their talents at an early stage.
Government policy: Government policy may also influence a career
choice. For instance, when government gives scholarships to students doing
particular courses, it indirectly influences people to join careers based on
those courses. For example, if government sponsors the best performers
at form six in national exams to go and study in America. They will either be
doctors or engineers.
Demand in the job market: Demand for a particular area of specialization
may encourage people to take up that career. For instance, many people
have undertaken careers in information technology and human resource
management in Rwanda due to high demand for such professions in the job
market.
Income level and level of payment: Different careers have different
levels of payment. This may be due to the nature of employment, level of
demand and supply for its services, profitability of its products, employers’
and government policies, among other factors. People usually prefer high
paying careers to low paying careers.
Schools: Schools are important sources for acquiring information about
careers. Through career day events, learners interact with professionals,
ask questions, and get to understand about their career of interest.
It is important for learners to attend such events and ask as many questions
as they can.
Media, (Newspapers and radios, TV): The media includes: newspapers,
radios, TV set, etc. Newspapers normally have columns and articles advising
about different careers. Radio and TV broadcasters have talk shows about
careers. Learners should get time to read newspapers as well as listen to
radio and watch TV for career advice.
Potential workplace: Potential work place are useful sources of information.
If you already have a job and you are seeking for another for fear of being
“right sized” by the present employer, then it’s better to seek information
from those already employed by that organization or you may check on theirwebsite
Application activity 2.1
1. As a student of entrepreneurship, identify a field from which to
choose your career and why?
2. Distinguish between work and career
3. Case study
Hitayezu Emmanuel born 1972 in Southern province and his father
was a farmer as well a traditional medical healer. Hitayezu Emmanuel
started his primary school at Munini, he continued his secondary at GS
Kibyagira and obtained a certificate as a primary teacher, he continues
university at Kigali Institute of Education (KIE) where he graduated as
a teacher with a bachelor’s degree in education (Biology, Geography).
After his university course, he obtained further training as a traditional
medical healer and he gained more mentorship from his father on treating
different diseases using local herbs, he as well authored a book on how
to treat different diseases. He worked as a teacher shortly before being
promoted to Sector Education inspector. Apart from being a government
worker, he is a successful businessman and a prominent herbalist and
he is known to treat many diseases like severe skin irritations of any
kind.
He plans to establish a hospital to treat his patients.
Questions;
a. Which careers are identified in the above case study?
b. Identify the major characteristics that Emmanuel possesses as a
successful entrepreneur.
c. As a student of entrepreneurship identify things that motivated him
to pursue these careers.
d. What do you learn from Emanuel’s story?
2.2. Sources of career information
Activity 2.2
1. Identify places and people in your home area that can be an
inspiration to your career.
2. Use your internet, search on www.gostudy.net to choose acareer field by filling in the questionnaire provided.
2.2.1. Sources of career information
There are many sources of career information from which an individual may
choose from and these sources may include the following.
1. Parents, friends and relatives: Families and friends can be extremely
helpful in providing career information. While they may not always
have the information needed, they may know other knowledgeable
people and be able to put you in touch with them. These contacts
can lead to an “information interview” which usually means talking to
someone who can provide information about a career. This person
should have the experience to describe how he or she trained for the
job, received promotions, and the likes or dislikes of the job. Not only
can the person advise what to do but he or she can also advise what
not to do.
2. Professional societies, trade groups, and labor unions: These
groups have information on careers with which they are associated
or which they actively represent. This information may cover training
requirements, earnings, and listings of local employers. These groups
may train members or potential members themselves, or may be
able to put you in contact with organizations or individuals who have
been in that career for a long time.
3. Personal skills, talent and passion: The first place to start from
when looking for business ideas or opportunities is to look within you.
Most people miss this greatest source of career information because
of ignorance, laziness and self-doubt’s. If you are talented or having
a proven track record in a specific field, then it is time to analyze that
skill or talent. You can discover what you are good at, what career to
take by asking yourself the questions such as; what skills or talents
do you possess?, what are your hobbies?, what are you passionateabout?, do you possess a skill that people are willing to pay for?
Note: It is because of personal skills, talent and passion that some people
popular have the careers they chose.
4. Mass media: This is a wonderful source of information, ideas and
opportunities. Magazines, TV stations, Cable networks, radios,
newspapers and internet sites are all examples of mass media. A
careful look at the commercial advertisements in newspapers or
magazines, you will discover information on careers, as well as the
skills and education level required to join the desired career.
5. Guidance and career counsellors:
• Counsellors can help you make choices about which careers
might suit you best.
• Counsellors can help you determine what occupations suit your skills
by testing your aptitude for various types of work, and determining
your strengths and interests.
• Counsellors can help you evaluate your options and search for a job
in your field or help you select a new field altogether.
• They can also help you determine which educational or training
institutions best fit your goals, and find ways to finance them. Some
counsellors offer other services such as interview coaching, resume
building, and help in filling out various forms.
• Counsellors in secondary schools and post-secondary institutions
may arrange guest speakers of different career fields, field trips, or
job fairs to equip you with detailed information about careers.
6. Local libraries: These can be an invaluable source of information
since most areas have libraries, they can be a convenient place to
look for career information. Also, for those who do not otherwise
have access to the Internet or e-mail, many libraries provide this
access. Libraries may have information on careers locally and
internationally; potential contacts within occupations or industries.
Libraries frequently have subscriptions to various trade magazines
that can provide information on occupations and industries. These
sources often have references to organizations which can provide
additional information about training and employment opportunities.
7. Tertiary institutions such as colleges, universities frequently have
career centers with libraries of information on different careers, listings
of related jobs, and alumni contacts in various professions. Career
centers frequently employ career counsellors who generally provide
their services only to their learners and alumni. Career centers can
help you choose a career, build your resume, find internships and cooperations
which can lead to full-time positions, and tailor your course
selection or program to make you a more attractive job applicant.
8. Exhibitions, expos and trade shows: Another means to get career
information is to attend exhibitions and trade fairs. These are usually
advertised on the radio or in newspapers. By visiting such events
regularly, you will not only find out new products and services, but
you will as well meet sales representatives, wholesalers, distributors,
manufacturers and franchisers. These are always excellent sources
of career information.
9. Listening to customer complaints: Complaints and frustrations on
the part of customers have led to prospective career opportunities.
Whenever consumers complain badly or bitterly concerning a product or service then, you have the potential for a career opportunity. This
will prompt you to acquire more skills as a career opportunity and
also to provide better and competitive services or goods.
10. Surveys: You can carry out a survey online or offline. One can visit
different people of different career fields and find out the advantages
and disadvantages of each career field. This helps you to compare
and make an informed decision on which career to undertake.
Note. The above sources aren’t independent but rather complement each
other towards choosing an appropriate career. Therefore, in choosing career
for example teaching one can use Ministry of education and internet while
others can refer to guidance and career counselors.
2.2.2. Steps for Career development.
There is no easy path to landing your first job and it’s not just job itself you
have to consider; a job is just one step, whereas a career is a journey over
a lifetime. There are some important things to consider when planning your
career. Below are steps to guide while planning a career.
Step 1. Where am I now? (What skills do you already possess?)
Step 2. Where do I want to go? (What do you want for your career?)
Step 3. How might I get there? (What steps do you need to take to get
there?)Step 4. Who can help? (What resources might I use?
2.2.3. Career trajectory or path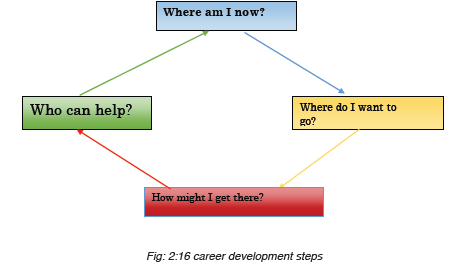
Career Pathing: Career pathing is also referred to as career trajectory.
Career pathing is the process used by an employee to chart a course within
an organization for his/her career path and career development. Career
pathing involves clearly understanding the specific knowledge, skills,
personal characteristics, and experiences that are required for an employee
to progress in the chosen career. There are different requirements for joining
and the process of going through various stages also differs. Some careers
have shorter trajectories while others have longer trajectories. Getting to the
top requires a person to pass through various stages.
The following are steps taken in choosing a career.
1. Assess yourself: This involves looking at your skills, values,
interests, personality and analyzing where your strengths and
weaknesses lie. This is important both in choosing the right career
and also for success in applications and interviews where you will
find many questions which test whether you have been through this
process. Begin by thinking about where you are now, where you want
to be and how you’re going to get there.
2. Occupational Research: Once you have understood yourself,
the next step is to investigate what options are available. It would
be more appropriate for one also to consider the current job trends.
Job trends indicate the direction in which the job market is moving
and indicate which sectors of the job market are in high demand. A
successful career plan makes this investigation as comprehensive
and exhaustive as possible.
3. Information search/ explore the options: For all the careers known
to you, identify those that you have a possibility of taking up. Get as
much information as you can about the selected career. The Internet
provides a spectacular resource to research on almost infinite number
of occupational choices. This will help you collect a rich and diverse
background on those careers that attract you most. For instance,
government statistics and related resources that track the growth or
decline for a wide range of careers are a good source of information
and are available on the Internet.
Bear in mind that technology is changing the nature of how
work is being done all over the world. Throughout history, new
inventions and innovations have created the need for new types
of jobs.
4. Make a list of potential occupations: You should have an idea
of your career preferences and research the specific skills and
qualifications required for the career. This requires a lot of research
on the various careers for better decision making on the occupation
of your interest.
5. Explore the options that interest you and ask yourself, how your
skills and interests match up with the desired career. Here you ask
yourself questions like, where are the gaps. What options do I have
to gain these skills or qualify for the desired career? What skills do I
need? Where is the work or how is the job market?
6. Narrow down your list: This is where you think about what suits
you best at this point in time. You look at different aspects such as,
your best work or training options, how they match with your skills,
interests and values, do they fit with the current labor market, do they
fit with your current situation and responsibilities, the advantages and
disadvantages of each options, what will help and what will hinder
you and finally what can you do about it?
7. Set goals: A career goal can be a specific job you want to do such
as doctor or teacher. It can also be a particular field you want to work
in, such as medicine or education. A career goal provides the means
and the direction to accomplish your career, act as action-steps
necessary to actualize your dreams and may also help you discover
career possibilities you would not have thought of otherwise. There
are several job possibilities with any chosen career. For instance, if
you choose a medical career, you may want to be a scientist, nurse,
doctor, dentist, surgeon, pharmacist, etc.
8. Create a career plan: This helps you to manage the direction you
want your career to take, the job skills and knowledge you will need,
and how you can get them.
Here, you plan the steps you need to take to put your plan into action.
It involves using all you have learnt about your skills, interests and
values together with the information you have gathered about the
career you have chosen. A career plan will increase the likelihood of
success.
9. Obtain training: This is the final stage of choosing a career.
Individuals train so as to specialize in various areas under a specific
field. Training in a specific career can be for a long term or a short
term. Short-term training includes any class or program that lasts
less than two years. All short-term training can help you get career
information, find a job, get a promotion, or earn more money. Many
programs lead to a certificate, which can give you a helpful edge in
the job market and it enables one to be a professional.
Application activity 2.2
1. Suppose you wish to choose a career after your senior six
graduation, what source of information would you put into
consideration?
2. Reflecting on your future career, give reasons why you willchoose that career
2.3. Career guidance
Activity 2.3
1. How can you define the term “career guidance”?
2. Reflecting on your choice of combinations, give reasons why
you chose that combination and who helped/influenced you to
make your choice.
3. Why is career guidance important?4. Make a list of sources where career guidance can be obtained.
2.3.1. Meaning of Career guidance
Career guidance is the act of assisting students and adults to successfully
choose the right career for themselves, manage and develop it.
Having the right and accurate information is important in the choice of a
career. The choice should be based on accurate information. Career
guidance can be obtained from various sources:
2.3.2. Sources of career guidance
i. Teachers: Teachers provide best source of career guidance to
learners because they spend most of their time with learners hence,
they understand their strengths, weaknesses, talents and skills.
ii. Parents: Some families have bias either against or in favor of
certain careers and consequently encourage or discourage their
family members to either take them up or leave them. Some people,
therefore, choose to undertake certain careers because all their
family members are taking the same career and are successful.
iii. Career guidance counsellors: These are professionals trained to
help people assess their strengths and weaknesses, evaluate their
goals and values and determine what they want in a career.
iv. Government officials. Government officials may act as models that
can guide us when approached and some have testimonies that can
help young people find strength amongst themselves
v. Heroes and mentors. For example, political and humanitarian
heroes eg Nelson Mandela his biography is a touching story and an
inspiration to many young politicians.
vi. Role models e.g. musicians, athletes
vii. Friends and relatives offer advice and support that help to shapeand develop career
Application activity 2.3
You have had a challenge of choosing a course to do after your s6.
Identify at least four people in your school that can offer career guidance
to you?
2.4. Career options /types of employment/ employment
options
Activity 2.4
Many people are confused today whether to engage in paid or selfemployment.
Advise them by showing them a list of advantages and
disadvantages of each of the following
a. Self-employment
b. Paid employment
Employment opportunities
Employment opportunities refer to anything that an individual can pursue to
earn a living.
There are two forms of employment:
1. Paid employment
Paid employment is when you work for someone else who pays you a salary
or wage at the end of the month/ day/week... The salary is paid by theperson, company or government department that employs you.
Benefits of paid employment
• Income is specific and regular (steady/consistent income)
• Favorable hours of work: Fixed time of work- spare time for leisure
• Limited liability: Not directly affected by business losses and debts.
• No exposure of personal assets to business losses
• Fringe/ financial benefits such as housing allowances, medical care,
free transport
• Pension on retirement
• Defined specific tasks
• Allows specialization: Tasks are allocated to those who can do them
better.
• It is easy for the government to collect taxes. E.g. PAYE (Pay As You
Earn) tax.
Challenges of paid employment
• Fixed income even when output increases
• You cannot be innovative because you work on orders
• Poor working conditions since conditions are determined by employer.
• Lack of independence
• Relatives cannot be made part of business
• Limited freedom of expression
• Limited decision making
• You are exploited by the employer
• High level of job insecurity
Self-employment
This is where an individual privately utilizes his/ her own resources to start
and operate his/ her own business. When you are self-employed, you work
for yourself. You are the owner of the business. You are the entrepreneur.
You do not get a salary or wage but rather you get profits from the business.
Benefits of self-employment
• Raise more employment opportunities
• You become your own boss and therefore you are independent
• You determine your own time of work
• More income from profits
• Higher status in society
• Positive contribution to the society’s wellbeing by providing goods and
services
• Better standard of living because of better income
• Allow your children to participate and learn business.
• More productivity
• High degree of job security
• Improved creativity and innovation
• It promotes confidence and self-esteem
Challenges of self-employment
• Risk of losses
• Uncertain Income. It varies depending on variation of profits
• Long and irregular hours of work: Most entrepreneurs work -on
weekends, nights and public holidays.
• No defined tasks: No well-defined job description. Entrepreneurs do all
kinds of jobs in their enterprises.
• Unlimited liability: self-employed persons are responsible for all risks
and debts of the business
• No fringe benefits: Entrepreneurs do not enjoy extra benefits from the
company
• Increased expenditures: Self-employed people spend a lot of money tomeet the legal requirements of a business. e.g: taxes, licenses.
Application activity 2.4
Reflecting on your community;
1. Identify the various activities/work done by various people.
2. Classify the people with their activities as those working for
themselves and those working for others.
3. How do you call those working for themselves and those working
for others
4. What are the challenges of taking business as a career?
Skills lab 2
1. Conduct a personal assessment test and find out what things you are
passionate about, Your strength and weaknesses. Discuss possible
Career choices that align with your strength and passion. Create
departments in the Business club that will enable various members
to get initial experience in the careers of their choice.
2. Design a flyer that promotes the Student Business Club to new
senior 4 students. The flyer should be attractive and present at least
3 arguments why students should start business projects while theyare in school.
End unit 2 assessment
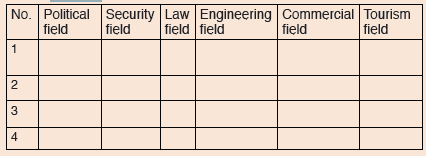
1. Read the sentences in the table below and indicate true or false.
a. A journalist belongs to the education field.
b. A DJ belongs to the media field.
c. Teachers belong to the medical field.
d. Police officers belong to the political field.
e. Pilots belong to the air field.
f. A barrister and chef belong to the same field.
g. Accountants and bankers belong to the finance field.
h. Lawyers and teachers belong to the same field
Formulate 5 interview questions you can ask an entrepreneur in
your community to find out the advantages and disadvantages
of running a business.
2. Give examples of careers one can take in each field by filling inthe table