UNIT 6: ENVIRONMENT CONSERVATION AND SUSTAINABILITY
Key unit competence: To use language learnt in the context of
Environment Conservation and Sustainability
Introductory activity
Picture observation and interpretationPicture interpretation

 Observe the above pictures and answer the following questions:
Observe the above pictures and answer the following questions:
1. What Fig 1,2,3,4 represent?
2. Provide the main elements of our physical environment.
3. Why is it important to protect our environment?4. Which methods can we use to conserve our environmental resources?
6.1. Talking about physical elements of environment
6.1.1. Learning activity: Reading and text analysis
Read the text below and answer questions that follow:Text: The physical environment
The physical environment can be defined as that which operates on an ongoing
basis regardless of the persons in it. This physical environment then affects
the actions of and outcomes concerning the people within it. The physical
environment includes land, air, water, plants, animals, buildings and other
infrastructures, and all of the natural resources that provide our basic needsand opportunities for social and economic development.
Say, for example, you are playing sport and it is a windy day. You have to
adjust your game to ensure that you allow for the way the wind is blowing.
All processes and behaviours take place within specific physical environments.
Within a classroom for example lighting, acoustics, size, comfort, safety, access
to technology, etc. create and add to a physical environment that is eitherconducive to learning or perhaps distracting.
Therefore, a simple definition of any physical environment would be your natural
surroundings including whether it is clean or dirty and the things within it andhow they interact to create a ‘space’
and other organisms along with various factors influencing them. The factors are
soil, air, water, light, temperature etc. These are called abiotic factors. Besides
abiotic factors, the environment is very much influenced by biotic factors which
include all forms of life like plants, animals, microorganisms etc. Man is thus
an inseparable part of the environment. Man and Environment have very close
relationship with each other. The social life of man is affected by environment.
This is the reason for various types of social and cultural activities around the
world. The hilly people have different life styles than people in the plain area.
Similarly, people around the world differ in their food, cloth, festivals etc. Allthese are influenced by the factors around him.
Natural vegetation, such as forest cover, is usually the most benign of land uses,
with higher infiltration and reduced runoff rates. The opposites of forest cover
are urbanized areas, where large surface areas are impermeable, and pipes
and sewer networks augment the natural channels. The impervious surfaces inurban areas reduce infiltration and can reduce the recharge of groundwater. In
addition, urban runoff contributes to poor water quality.Agricultural activities are major forms of land use, including row crops, rangelands,
animal farms, aquaculture, and other agribusiness activities. Cropping
activities involve soil and water manipulation through tillage and irrigation,
thereby affecting runoff water and groundwater resources. If improperly used,
fertilizer and plant protection chemicals in agricultural operations can affect
water resources and ecosystems.
Urban and agricultural land uses contribute to what is termed nonpoint source
pollution in watersheds. Nonpoint-source pollution is defined as diffuse
(spread-out) sources of contamination from a wide area of a landscape, often
difficult to be attributed to a single location. Transportation infrastructure (e.g.,
roads and airports) is another type of land use that affects water resources
through road runoff and alterations to components of the hydrologic cycle.
Therefore, a cleanliness and beauty of the environment is also important for
people’s sense of wellbeing. For many people, access to an attractive physical
environment contributes greatly to their contentedness with life. A healthy
environment also provides recreational opportunities, allowing people to take
part in activities they value. The clean, green environment is also integral part of
national identity, and guardianship of the land and other aspects of the physical
environment is seen as important part of social wellbeing.Extracted from: (Advameg, Inc., 2022)
Comprehension questions
1. What is physical environment according to the author?
2. Which activities people can do on land?
3. Why do the writers say that physical environment affects human activities?
4. Do you think physical environment can influence the food people eat?
Explain.
5. Explain the importance of healthy environment as described in the
passage.Application activity 6.1.2Vocabulary, sentence and paragraph writing
1. Explain the following words using dictionaries and interneta) Aquacultureb) Irrigationc) Recharged) Watershedse) Landscape2. Make sentences using the following words and expressions.a) land,b) air,c) water,d) plants and animals,e) buildings and other infrastructuref) natural resources3. Write a paragraph describing your physical environment6.2. Describing environmental features and their roles
6.2.1. Learning activity: Reading and text analysisRead the following text and answer questions given:Text: Environmental featuresRwanda has a temperate tropical highland climate, with lower temperaturesthan are typical for equatorial countries due to its high elevation. Kigali, in thecenter of the country, has a typical daily temperature range between 12 °C (54°F) and 27 °C (81 °F), with little variation through the year. There are sometemperature variations across the country; the mountainous west and north aregenerally cooler than the lower-lying east.There are two rainy seasons in the year. The first runs from February to Juneand the second from September to December. These are separated by two dryseasons: the major one from June to September, during which there is oftenno rain at all, and a shorter and less severe one from December to February.Rainfall varies geographically, with the west and northwest of the countryreceiving more precipitation annually than the east and southeast.
Mountains dominate central and western Rwanda. These mountains are part ofthe Albertine Rift Mountains that flank the Albertine branch of the East AfricanRift. This branch runs from north to south along Rwanda’s western border. Thehighest peaks are found in the Virunga volcano chain in the northwest; thisincludes Mount Karisimbi, Rwanda’s highest point, at 4,507 metres (14,787 ft).
Rwanda has many lakes, the largest being Lake Kivu. This lake occupies thefloor of the Albertine Rift along most of the length of Rwanda›s western border,and with a maximum depth of 480 metres (1,575 ft), it is one of the twentydeepest lakes in the world. Other sizeable lakes include Burera, Ruhondo,Muhazi, Rweru, and Ihema, the last being the largest of a string of lakes in theeastern plains of Akagera National Park. Therefore, it is very important to carefor our environment because as some the features show without it there is nolife as discussed in the following paragraphs.
No trees, no forests! No forests, no rainfall! No rainfall, no water! No water, nopower! No power, no industry! No industry, no jobs! No jobs, no money! Nojobs, no money! No money, no food! No food, no life!Perceptibly, forests are very important as this sequence show. Destroyingforests has serious environmental, economic and social consequences. Anyonein drought areas should remember that we have suffered crippling droughtsas well as water and power rationing in some parts of Africa. Recovering fromthese disasters takes a long time.In counties which heavily depend on agricultural produce both for localconsumption and for export, rain is very important. Trees attract rain and weshould do everything possible to preserve them. We should even plant more.Trees also prevent soil erosion and flooding. Soil erosion carries away theproductive soil while flooding leads to loss of life and property.In Kenya’s Western Province, Busia District, Budalangi Constituency and its
surroundings, the inhabitants cannot build permanent homes because they knowsurroundings, the inhabitants cannot build permanent homes because they knowin the month of April they have to move to high grounds because of flooding thatcauses loss of property and even life.In addition, forests provide catchment areas for some largest rivers and lakes.From these rivers and lakes, we get water for domestic use, irrigation and wecan also get sea food. On the rivers are dams from which electricity is tappedor generated.
For example, River Nile is a major hydro power generation that serves Uganda,Kenya and Rwanda. Did you know that Lake Victoria has its major tributaries inKenya and these tributaries emanate from the Mau forest?
Due to human activities in the forest, the tributaries are reducing water. As aresult, Lake Victoria on the Kenyan side is reducing in water flow and if thesituation is not checked, this will affect the people of Egypt who rely entirely onirrigation from River Nile whose source is Lake Victoria.
Moreover, forests play a significant role in our atmosphere. By absorbing carbondioxide from the air, they act as a filter thus leaving our air fresh and clean.Forests are also the most important defence against climatic changes such asglobal warming. If we destroy the forests the chain is broken as well as our lives.Adapted from (Reporter, 2009)Comprehension questions1. Why does Rwanda have a temperate tropical highland climate with lowertemperatures?2. Give and explain the rain seasons we have in a year.3. What is the importance of some environment features mentioned in thepassage?4. Which countries are served by hydro power generation from River Nile?5. What are the lakes do we have in our country and why are they important?6. Which daily temperature do we have in Kigali city as mentioned in thepassage?Application activity 6.2.2
Vocabulary and composition writing
1. Vocabulary
Explain the following words as they are used in the passage
a) Temperaturesb) cripplingc) droughtsd) precipitatione) rainfallf) constituencyg) floorh) catchmenti) filterj) carbon dioxide2. Composition writing
Write a composition talking about the environment features of your district.Read guidelines of writing an essay in unit five of this book.
6.3 Talking about problems faced by environment today6.3.1. Learning activities: Reading and text analysis
Environmental problems
Our environment is constantly changing. There is no denying that fact. However,
as our environment changes, so does the need to become increasingly aware
of the problems that surround it. With a massive influx of natural disasters,
warming and cooling periods, different types of weather patterns and much
more, people need to be aware of what types of environmental problems ourplanet is facing.
Global warming has become an undisputed fact about our current livelihoods;our planet is warming up and we are definitely part of the problem. However,
this isn’t the only environmental problem that we should be concerned about.
All across the world, people are facing a wealth of new and challenging
environmental problems every day. Some of them are small and only affect a
few ecosystems, but others are drastically changing the landscape of what wealready know.
“Environmental issues are defined as problems with the planet’s systems
(air, water, soil, etc.) that have developed as a result of human interference
or mistreatment of the planet.” Our planet is poised on the brink of a severe
environmental crisis. Current environmental problems make us vulnerable todisasters and tragedies, now and in the future.
Major current environmental problems include pollution, soil degradation,
overpopulation, natural resource depletion, generating unsustainable waste,waste disposal and deforestation.
The first major environmental problem is pollution. There are 7 key types of
pollution: air, water, soil, noise, radioactive, light and thermal and these are
primary factors that affect our environment in many ways. As for soil degradation,
we know that soils get damaged due to many reasons. Such reasons include:
erosion, overgrazing, overexposure to pollutants, monoculture planting, soilcompaction, land-use conversion and many more.
Overpopulation is also one of the crucial current environmental problems as
intensive agriculture practiced to produce food, it damages the environment
through the use of chemical fertilizer, pesticides and insecticides.Another crucial current environmental problem is the depletion of natural
resources. We, humans, use so many natural resources that it would need
almost 1.5 Earths to cover all our needs. This will further increase in the futuredue to massive industrialization in Asian countries like India and China.
Additionally, generating unsustainable waste is a major threat to the environment.
The hyper consumption results in non-biodegradable trash in the form of plastic
packaging, toxic e-waste, and harmful chemicals that leach into our waterways.
When this waste ends up in landfills, it generates enormous amounts of methane,
which ranks as one of the worst greenhouse gases because of its high potentialfor global warming. It creates severe explosion hazards.
Furthermore, waste disposal is the urgent current environmental problem for
plastic, fast food, packaging and cheap electronic wastes threaten the wellbeingof humans.
Deforestation is equally a major threat to environment since our forests arenatural sinks of carbon dioxide and produce fresh oxygen and helps in regulating
temperature and rainfall. The loss of trees and other vegetation can cause
climate change, desertification, soil erosion, fewer crops, flooding, increased
greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, and a host of problems for indigenouspeople.
Adapted from (Conserve Energy Future , 2022)
Comprehension questions
1. What does the term “environmental issues” refer to?
2. Mention some of the reasons that cause soil damage.
3. Why are the people making efforts to shift to renewable resources of
energy like solar, wind, biogas and geothermal energy?
4. What are the consequences of deforestation?
5. Explain the problems cause by global warming.
6. Explain the reason why people are damaging the environment throughthe use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and insecticides.
Application activity 6.3.2
Vocabulary and debate
1. Vocabulary
Make sentences using the following words and expressions.
a) Constantly
b) Influx
c) Undisputed
d) Landscape
e) Vulnerable
f) Soil degradation
g) Radioactive
h) Greenhouse gases2. Debate
Debate on the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and insecticides.
6.4. Describing different ways of protecting environment
6.4.1 Learning activity: Observing pictures and ReadingA. Picture observation and interpretation
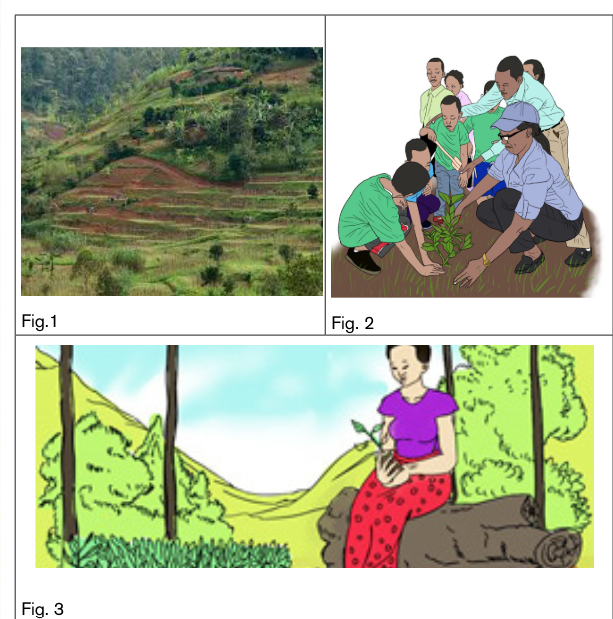 1. What do you see in Fig.1 and what do you think people in Fig.2 are
1. What do you see in Fig.1 and what do you think people in Fig.2 are
doing?
2. Which strategies can we use to protect our environment?
3. Why is it important to protect our environment?
4. Suggest some pieces of advice to people who only care for theirbusinesses by building big industries and other related harmful activities.
B. Reading and text analysis
Text 1: Protect your environment
Many people say there is a need to protect the environment, but do not really
make any effort to do anything about it. Are you one of these people? What can
we do to encourage people to take action to protect the environment?
Most people are increasingly aware of the need to protect our environment.
Despite this, not many of us are really taking steps to reduce our impact on the
planet. In this text, I will suggest some steps each of us can take and some ways
to motivate others to do the same.Many environmental problems seem so big that only governments, local
authorities or big companies can deal with them. One example is global
warming. We need government action to reduce emissions from coal and oil
burning power stations and to develop safer sources of power. These require
tough regulations and huge investment. The loss of forests and other habitat is
another problem. How can we as individuals stop the destruction of the Amazon
or Indonesian rain forests? Yet another example is waste. When people live in
cities, other ways may be recycling, picking up trash, no polluting and decrease
pollution overall, saving animal habitats and so much more.We should care for the environment because it’s our real home, we live in it and
we don’t want a nasty living of trash everywhere with stenches, also animals
can die from our trashes such in beaches, they can get stuck in the can plastics.
We need to recycle because recycling takes trash and processes it in some way
to make a useful product. Composting falls into this category. Glass, plastics,
paper, steel, and cardboard are other materials that may be recycled. The added
benefit of compost is that it can be done in your own backyard. We still need
to recycle all the plastic that we use because it gets melted and reused again
for more supply for our needs.When we don’t recycle, we have less plastic reusing than before and causea lot more money and man labour time to recycle it for us in the landfills. Also,
most of it gets burned to dispose of it all because we have no room for all the
landfills and they cost too much to have. Really, we should all try to reuse before
recycling but either works just fine. So, when we reuse our belongings like
finding alternate uses for trash rather than disposal.Share unused portions with neighbours or charities. Donate books to the
library; give old clothing to charity, etc. Now we also need to reduce which is
includes reducing the amount of total waste by steps such as buying only the
amount you need, persuading manufacturers to reduce the amount of packaging
they use. It also includes steps such as mowing your lawn with a mulching
mower and leaving the clippings on the grass. “Waste” is never generated.
So, we don’t want to buy too much of anything for ourselves everyone needs
the same things such as water bottles, plastic bags, and much more. And for
mountainous places, it is important that people can make terraces, planting also
some trees which may protect the soil.In conclusion, our choices, however small, do have a real impact. If each of us
made took two or three simple steps to live more simply, imagine the positive
effect on the planet!Adapted from (Writefix, 2011)Comprehension questions1. Which problems did the writer say that they can be dealt with government?
2. What are the strategies identified by the writer about environmental
protection?
3. Give reasons why the environment must be protected.
4. Which materials do we need to recycle in our environment?
5. How can we protect the soil from high mounts?Text 2. A poem on environmental protection
Read the following poem and answer questions
We spoil our Earth
Is it really worth?
Polluting the air
is that really fair?
Can Smoke and Dust
Turn Earth into Hearth?
Clean the AirShow that we care
Secure our future
Say Cheese!
Plant more trees
For Earth to Breathe
Plants and Animals
Love them all
Be generous
Live life tall
Conserve water
Be a nice daughter
Harvest sunlight
For a life that is brightPlastic may be cool
But don’t be a fool
It will make you ill
Tell the whole school
Recycle everything
Don’t waste anything
If you want no tension
Go for environment protectionBy Kaarvi KhullarComprehension questions
1. Which strategies did the poet mention so as to protect our environment?
2. Why do you think that poet advised us not to be fool though plastic is
cool?
3. What can a person do if he/she wants no tension?
4. Provide the message given by the poet to schools.Application activity 6.4.2
Vocabulary, debate and composition writing.
1. Vocabulary
Explain the following words as they are used in the poem. Use a dictionary.
a) Global warming
b) Pollution
c) Stenchesd) Backyard
e) Portionsf) Charity
g) Recycling2. Debate and composition writing
a) Debate on the following topic or motion: “Human activities have
brought more harm than good on our Earth”.
b) Write two paragraphs describing different ways of protecting
environment.6.5 Language structure: Use of expressions of purpose
6.5.1 Learning activity
Read the following paragraphs and identify expressions of purpose used
The trees’ roots suck water deep from under the ground to as low as 200 feet.
They hold the soil together so that erosion is prevented. They absorb rain during
rainy days in order to help plants grow well.
Mary lives in Gakenke District which is a mountainous area. Last year, she
planted different trees so as to protect the soil. However, her neighbours did
not do the same and affected her soil later. The local leaders sensitize every
person to make terraces and some irrigation so that they could not get affected
by soil erosion again.NotesExpressions of purpose: to, in order to and so as to.
a) In order to
We can use ‘in order to’ or ‘so as to’ instead of ‘to + infinitive’. This just makes it
a bit clearer that we are talking about goals or intentions and it’s also a bit moreformal. It doesn’t change the meaning.– I went to London in order to study Environmental education.– I went to London so as to study Environmental education.Use to, so as to, and in order to express purpose in the affirmative form.
Examples:– He is looking for a part time job to save some pocket money.– She wakes up early in order to be on time to work.– They visited him so as to offer their condolences for the death of hiswife.Use so as not to and in order not to express purpose in the negative form.Examples:– They woke up early in order not to be late.– She exercises regularly so as not to get fat.– He helped the new policewoman so as not to fail in her first mission.b) Purpose with so that Application activity 6.5.2
You can also express purpose with so that. In this case you generally need to
use a modal.
Examples:
– He turned down the music so that he wouldn’t disturb the neighbours.
– He got a visa so that he can travel to the USA.
– He decided to stay in England for a while so that he could practice hisEnglish language.
A. Choose the correct expression of purpose1) Concentrate on your exercise … make any mistakes.a) So as not tob) toc) So that2) You have to wake up … be on time.a) Tob) In order not toc) So that3) You have to register … participate in the forum.a) In order tob) So as not toc) So that4) She left work early … be at home when he arrives.a) So as not tob) Toc) So that5) Ships carry life boats … the crew can escape when the ship sinks.a) So as not tob) Toc) So that6) These men risk their lives-… we may live more safely.a) tob) in order not toc) so thatB: Using expression of purpose, write a paragraph talking about the role of physical environment in socio-economic sector.
End of unit assessment 6.6
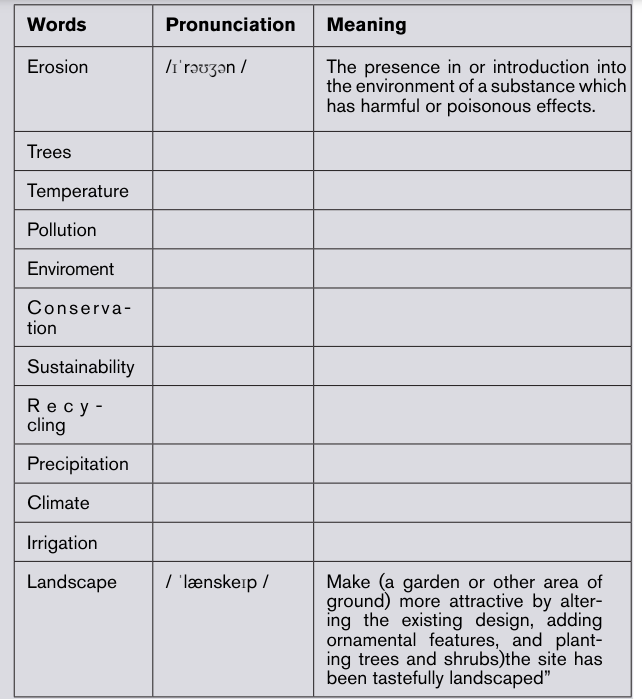
A. Use a dictionary and thesaurus to look up the missing pronunciation of
the words/phrases in the table below. Copy the table into your book andfill in the blank spaces and practice reading them.
 B. Suppose that you are appointed to be trainer in a given district and the
B. Suppose that you are appointed to be trainer in a given district and the
training agenda is all about environment conservation and sustainability.
The following are issues to be addressed in the training.a) Strategies to keep different materials lying around in the community.b) Ways to protect our soil from erosion.c) Challenge of deforestation in the community.d) A problem of water from houses.C. Write an essay describing how you will address the above issues to be
presented to the Land manager. Make sure you pay attention to the use of
expression of purpose in your writing. Words limit (300 words).
D. Rewrite the sentences below using to, in order not to, so that…a) I sent her a bunch of flowers because I wanted to make it up withher.b) I entered Mr. Green’s office because I wished to talk to him aboutenvironment.c) I came back because I had to take care of my parents.d) She winked at me because she wanted to let me know that she wasjoking.e) I have come because I’d like to give you a piece of advice onenvironmental protection.E. Match the beginnings of the sentences to the correct endings.