TOPIC 8: BUSINESS ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE
Key Unit competence: To be able to design business organization structure
Introductory Activity
Read the following paragraph and answer questions that follow: Uwineza started a maize flour processing farm in her community. She is renting the place where her business is operating from. She buys her raw materials (maize grain) from a nearby town through a fellow business person. She says she trusts her employees so they never write down anything about duties. She always meets employees at the morning assembly or uses a telephone call at a distance to assign tasks. Recently, after some advice from a friend, she discovered that she was so wrong in tasks assignments and immediately take a step forward to collect the errors previously done.
Questions:
a. What do you think Uwineza did as errors/wrong?
b. What are the likely consequences of Uwineza‘s actions mentioned above?
c. What advice would you give to Uwineza to avoid the consequences above and why?
8.1. Meaning of organization structure and department in an organization.
Activity 8.1
1. Read the following statements to identify an organization structure, give reasons to support your response
a. Claudette and Niragire playing football against Uwera and Mutesi
b. Uwimana is the deputy of one TTC, she outlined and documented the ways subjects’ teachers teach and assigned supervisory duties to different heads of departments
c. A group of fellow students with whom they are going to represent the school in a debate competition
d. A group of five girls reading science magazines in the library preparing for a science competition against another class
2. What is a department in your own point of view?
3. Give any two departments that you know
8.1.1. Organizational structure
Organizational structure is a system that outlines how certain activities are directed in order to achieve the goals of an organization. These activities can include rules, roles and responsibilities. The organization structure also determines how information flows between levels within the company.
Simply, an organizational structure is a system used to define a hierarchy within an organization. It identifies each job, its functions and where it reports to within the organization. This structure is developed to establish how an organization operates and assists an organization in obtaining its goals to allow for future growth.In order to achieve organizational goal there must be a team and teamwork
Team
A team is a group of individuals working together to reach a common goal. It can also be seen as a group of people with different skills and different tasks, who work together on a common project, service, or goal.
Teamwork
Teamwork is the collaborative effort of a team to achieve a common goal or to complete a task in the most effective and efficient way. This concept is seen within the greater framework of a team, which is a group of interdependent individuals who work together towards a common goal (From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia)
8.1.2. An organizational chart
An organizational chart is a graphical representation of a firm’s hierarchy of authority. An organizational structure is primarily represented by an organizational chart. It shows how different people and departments are linked together in the organization. People at the same rank in the business are at the same level on the organizational chart.An example of organizational chart/Organogram
8.1.3. Departments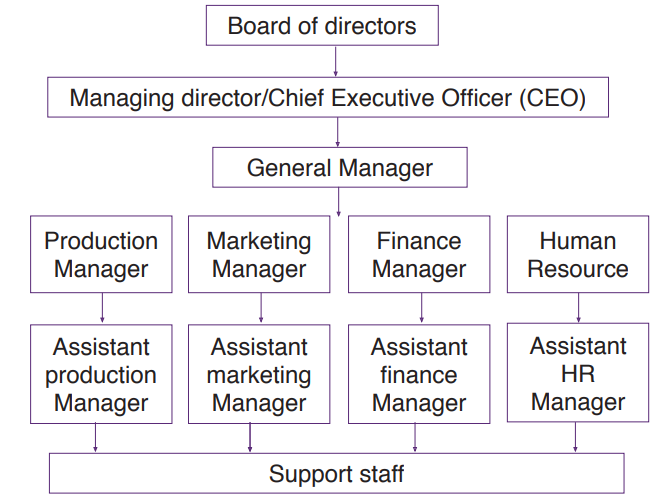
Department is also known as a section, Division or a single unit (special unit) within an organization that has specific functions which help the entire firm to achieve its goals.
Any organizational structure must be departmentalized i.e subdivided according to responsibilities.
Departmentalization can be done through 4 ways such as
a. By functions: grouping activities by functions performedt
b. By product: grouping activities by product line
c. By geography: grouping activities on the basis of territory
d. By type of customers: grouping activities on the basis of common
customers
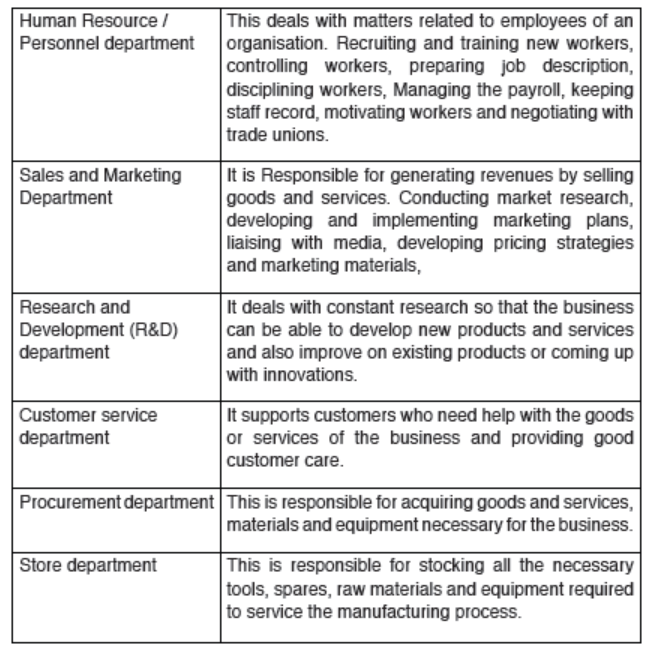
8.1.4. Some of the departments that may be found in different organizations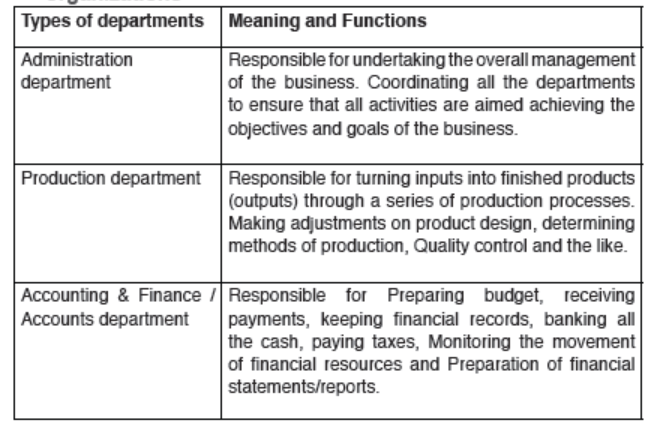
Application activity 8.1
Think as if you are working in business, with reasons to which department do you wish to work from?
1. From the list of departments, you have gone through which one
is very important to you and why?
2. From your community, identify some business organizations that
operate from there, explain how they are organized and the waythey operate in different positions.
8.2. Managerial functions
Activity 8.2
Mugisha attended a business meeting organized by Executive Secretary of the Sector together with the one in charge of business where business owners who attended were told to abide to the rules and regulations regarding the business. They were also told to properly plan and take into consideration other business managerial functions related to the effective and efficient production hence, develop particularly our sector and our country in general.
From your point of view what do you think are other managerial functions discussed in that meeting?
8.2.1. Definition of concepts
a. Management is the process of getting things done by using other
people and resources like capital, raw materials and time.
b. Business management involves planning, organizing and
coordination of the activities of an enterprise to achieve defined
objectives. Without proper coordination and planning, a business
cannot achieve its goals and objectives.
8.2.2. Managerial functions
These are special activities that are designed for a manager to perform in order to achieve the goals and objectives of an enterprise.
a. Planning: Refers to the process of setting goals and determining a
course of action, defining who, when and how to achieve them.
b. Organizing: Refers to the coordination and supervision of factors of production particularly land, capital and labor. It involves grouping activities and assigning tasks to people who would assume them. Organizing includes: Identifying tasks, assigning them to responsible workers and Developing work plans. An organization chart is one of the tools managers use to organize the people in business.
c. Leading: This involves directing/ influencing or inspiring the workers towards achieving organizational goals.
d. Staffing: Refers to identification of the right people who will do the jobs as necessary to achieve organizational objectives. This is done through recruiting them through test, training, and paying them for the work done.
e. Controlling: This refers to the evaluation of achievements compared to the plans/standards and taking measures towards success of organizational goals/objectives.
f. Budgeting: This refers to making monetary estimations of the
expected revenue and expenses of the business over a given period
of time, usually a year.
g. Coordination: This refers to bringing together different workers and departments of the business so that they work in harmony and strive to achieve the set goals.
h. Motivating: This involves inspiring and encouraging workers by
appreciating the work well done, allowing them to participate in
decision making, paying their salaries on time and giving them
incentives, bonuses and benefits. This encourages the workers to
work harder, increase the output/productivity and improve on its
quality.
i. Commanding: This involves giving orders and instructions to staff members so that the targets and deadlines are met.
j. Communicating: This involves passing on information between
people and departments. The manager passes on information
regarding responsibilities, targets to achieve, suppliers, laws andregulations, …
Application activity 8.2
Mugabo is a business owner who always commands his employees in harsh voice and assigns them tasks basing on nepotism. While recruiting employees Mugabo never set exams for selection but rather considered groupmates, neighbors and his relatives.
From the passage above, justify your example what managerial functions does Mugabo fail to obey/follow?8.3. Personnel (Human Resource) Management
Activity 8.3
Analyse the following case study; Mr. Busan’s factory is among the oldest brick making factories that has been operating in their area. It started operating in the first half of the 20th Century. It employs over 200 employees and owns production machines. Last year, the external auditor of the factory found out that the business was about to collapse. When the manager read the report, he was shocked about the eminent collapse of the business and could not figure out what to do to prevent the business collapse. He consulted many people for help, but he was not able to get a clear solution.
a. As an entrepreneurship student, what do you think could be the main cause of poor performance of that oldest brick making factory?b. Suppose you are appointed as the manager of this factory, what can you do so that this business does not collapse?8.3.1. Meaning of Human Resource ManagementHuman Resource Management is a process or a managerial activity that consists of four main activities, namely, acquisition, development, motivation, as well as maintenance of human resources.It involves several functions concerned with the management of people at work. It includes manpower planning, employment, placement, induction, training, motivation and appraisal and compensation of employees. For the performance of these activities efficiently, a separate department known as Personnel Department is created in most of the organizations. This department deals with matters related to employees of the organization.8.3.2. Human resource management process• Human Resource Planning, i.e., determining the number and kinds of personnel required to fill various positions in the organization.• Recruitment: Recruitment refers to the overall process of attracting, shortlisting, selecting and appointing suitable candidates for jobs within an organization. Recruitment can also refer to processes involved in choosing individuals for unpaid roles.• Selection and placement of personnel, i.e., employment function. This requires to ensure that the right people are recruited and placed to the right jobs through selection exam/test.• Induction: is the process where new employees are welcomed in thebusiness /company and are prepared for their new duties.• Training and development of employees for their efficient performance and growth. Enabling employees to carry out their responsibilities effectively and make use of their potential.• Appraisal of performance of employees and taking corrective steps such as transfer from one job to another is evaluating the performance of employees and to identify the abilities of a person for further growth and development.• Motivating the workforce by providing financial incentives and avenues of promotion.• Remuneration of employees. The employees must be given sufficient (equivalent to work done) wages and fringe benefits to achieve higher standard of living and hence higher productivity.Note: According to Edwin Filippo; Performance appraisal is the systematic, periodic and an impartial rating of an employee’s excellence in matters pertaining to his present job and his potential for a better job.According to Cummings, the overall objective of performance appraisal is to improve the efficiency of an enterprise by attempting to mobilize the bestpossible efforts from individuals employed in it. Such appraisals achieve four objectives including the salary reviews, development and training of individuals, planning job rotation and assistance promotions.8.3.3. Functions of human resource management
The main functions of human resource management are classified into two categories
Managerial Functions: Planning, Organization, Directing and Controlling
Operative Functions which include the following;
• Identifying the need for workers in the organization
• Recruiting and training of Personnel
• Managing the payroll
• Compensating or remunerating Personnel• Maintaining Good Industrial Relations
• Keeping staff records
• Appraising the performance of employees
• Disciplining workers
• Preparing job descriptions and specifications
• Motivating workers
• Negotiating with trade unions• Counseling and guiding workers
Application activity 8.3
Claudette is a human resource manager of Berwa enterprise, who is
humble, always manages her employees in harmony and handle every personal issue accordingly. She normally performs her duties the way they are, whenever employees’ challenges happen Claudette addresses those issues with integrity and professional manner, she always faces the person to whom they are talking to, listen carefully and takes step forward to solve any complaint of that person. Claudette is the best employee of Berwa enterprise in 2018 .
1. Basing on this ‘scenario what do you think is /are her duty/duties
in Berwa enterprise?
2. Is/are her duty/duties important in Berwa enterprise? Give your
point of view.
8.4. Importance of human resource management
Activity 8.4
Bikorimana’s enterprise is employing nine employees where they timely attend the work in the enterprise, try whatever they can to improve and innovate the business products/services. By the end of almost every month they wait to be paid as contracted but in vain, this activity of payment takes a long process till it reaches the district labor supervisory office.From this scenario:
1. What do you think will be productivity efficiency of Bikorimana’s
enterprise?
2. Advise Bikorimana’s human resource department on what to
do?
3. If you were one of employees in Bikorimana’s enterprise, wouldyou remain working there? Explain your position
Human Resource Management is a management function concerned with hiring, motivating, and maintaining workforce in an organization. Human resource management deals with issues related to employees such as hiring, training, development, compensation, motivation, communication, and administration.
Importance of Human Resource management are discussed here below:
• Strategic Management
Human Resource Management improves the company’s bottom line with its knowledge of how human capital affects organizational success. Leaders with expertise in HR strategic management participate in corporate decision-making that underlies current staffing assessments and projections for future workforce needs based on business demand.
• Wages and Salaries: Increased production
HR compensation specialists develop realistic compensation structures that set company wages competitive with other businesses in the area, in the same industry or companies competing for employees with similar skills. They conduct extensive wage and salary surveys/research to maintain compensation costs in line with the organization’s current financial status and projected revenue.
• Analyzing Benefits: qualified, experienced and skilled workers
Benefits specialists can reduce the company’s costs associated with
turnover, attrition and hiring replacement workers. They are important to the organization because they have the skills and expertise necessary to negotiate group benefit packages for employees, within the organization’s budget and consistent with economic conditions. They also are familiar with employee benefits most likely to attract and retain workers. This can reduce the company’s costs associated with turnover, attrition and hiring replacement workers.
• Safety and Risk Management
Employers have an obligation to provide safe working conditions. Workplace safety and risk management specialists from the HR area manage compliance with occupational Safety and Health Administration regulations through maintaining accurate work logs and records, and developing programs that reduce the number of workplace injuries and fatalities. Workplace safety specialists also engage employees in promoting awareness and safe handling of dangerous equipment and hazardous chemicals.
• Minimizing Liability Issues
HR employee relations specialists minimize the organization’s exposure and liability related to allegations of unfair employment practices. They identify, investigate and resolve workplace issues that, left unattended, could spiral out of control and embroil the organization in legal matters pertaining to federal and state anti-discrimination and harassment laws.
• Training and Development
HR training and development specialists coordinate new employee orientation, an essential step in forging a strong employer-employee relationship. The training and development area of HR also provides training that supports the company’s fair employment practices and employee development to prepare aspiring leaders for supervisory and management roles.
• Employee Satisfaction that leads to increased production
Employee relations specialists in HR help the organization achieve high performance, morale and satisfaction levels throughout the workforce, by creating ways to strengthen the employer-employee relationship. They administer employee opinion surveys, conduct focus groups and seek employee input regarding job satisfaction and ways the employer can sustain good working relationships.
• Recruitment and Onboarding
HR recruiters manage the employment process from screening resumes to scheduling interviews to processing new employees. Typically, they determine the most effective methods for recruiting applicants, including assessing which applicant tracking systems are best suited for the organization’s needs.
• Hiring Processes
HR professionals work closely with hiring managers to effect good hiring decisions, according to the organization’s workforce needs. They provide guidance to managers who aren’t familiar with HR or standard hiring processes to ensure that the company extends offers to suitable candidates.
• Quality products/services
Human resource management help employees in timely payment and motivates them either through fringe benefits or non-fringe benefits. These motivate employees to hardworking that leads to improved/quality products/ services.
Application activity 8.4
1. From the above importance of human resource management,
discuss their impact on business performance
2. Discuss how your employee’s management will help you achieve
your goals?
Skills lab 8
Discuss the staffing needs you have in the school business club basing on your unique needs to run the club effectively and;
a. Identify the Functions you need to put on the business organisation chart and why
b. Describe the tasks to be done under each function on the chart
c. Show how each function support each other to lead to clubachievement of it’s goals.
End unit 8 assessment
Fill in the gap the following:
i. …………………………...is a process, which consists of four
main activities, namely, acquisition, development, motivation,
as well as maintenance of human resources.
ii. …………………………. Is one of the managerial functions
consisting of:
a. preparation of task force;
b. allocation of work to individuals;preparation of task force;
c. allocation of work to individuals;
d. integration of the efforts of the task force; and coordination of
individual work with that of the department2. Design an organizational chart of your school.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Akazi Kanoze Youth Livelihood project, (2009), Work Readiness
Trainers’ Manual
2. Educate! Exchange,( 2017), Resources & Competency-based
Entrepreneurship Subject S4 Skills Lab Lesson Plans
3. Kalungi Rogers, Ngobi Dennis, Mutegaya Herbert, Okoroi David,
Entrepreneurship for Rwanda Secondary Schools, Learner’s Book
4. Mark Ssempija (2011), Entrepreneurship Education for Advance
level and business institutions, Kampala. Uganda: Book shop Africa
5. Mark Amon Mugaru, Edward Erasmus Kayanja (2017), Ordinary
Level Entrepreneurship. Kigali, Rwanda: MASTEP General Suppliers Ltd
6. Richard Barekye, Alele Kevin. (2016). Entrepreneurship for Rwandan school (senior 1 students’ book). Kigali, Rwanda: East African Educational Publishers Ltd
7. Rwanda Education Board, (2015), Advanced Level Entrepreneurship syllabus for Rwanda General Education
8. Rwanda Education Board (2018) Entrepreneurship Senior 5 -
Content and activities: Experimental version, Kigali, Rwanda
9. T Manimbi and S Paarman , Entrepreneurship FOR RWANDA S1
Student’s Book
10. Microsoft. (2019). job-specification-sample-marketing-manager.
Retrieved September 16, 2019, from www.thebalance.com:
https://www.thebalance.com/job-specificationsample- ; marketingmanager-1918560
11. Schneider Electric. (2005). tac-best_practices_for_telecom_
network_reliability.pdf. Retrieved March 26, 2018, from www.tac.
com: https://www.schneiderelectric.co.uk/.../best_practices_for_telecom_network_reliabilit...
12. Mutamba, A. H. (2008). In entrepreneurship. kampala: mk publishers.
13. Schneider Electric. (2005). tac-best_practices_for_telecom_
network_reliability.pdf. Retrieved September 10, 2019, from www.
tac.com: https://www.schneiderelectric.co.uk/.../best_practices_for_
telecom_network_reliabilit...
14. Http://www.teammate360.eu/index.php/en/teammatehttps://www.
thebalance.com/leadership-definition-2948275http://courses.
washington.edu/ie337/team.pdfhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/
Teamwork
15. H t t p : / / s m a l l b u s i n e s s . c h r o n . c o m / 5 - s o u r c e s - p o w e r -
organizations-14467.htmlhttp://smallbusiness.chron.com/5-sourcespower-
organizations-14467.htmlhttps://www.mindtools.com/pages/
article/newTMC_00.htm http://s3.amazonaws.com/inee-
16. Assets/resources/14_PEP_Facilitators_Manual_for_Community_
Workshops_EN.p df
17. Http://www.cheryltay.sg/5-steps-for-effective-problem-solving/
18. Https://sites.google.com/a/studentmba.org/ms-desalvo-sclassroom-
page/civicsand-government/unit-1a-nature-of-powerpolitics-
and-governmenthttps://www.slideshare.net/danishmahusay/
essentials-of-leadership-1
19. Http://www.teammate360.eu/index.php/en/teammatehttps://www.
thebalance.com/leadership-definition-2948275http://courses.
washington.edu/ie337/team.pdfhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/
Teamwork
20. H t t p : / / s m a l l b u s i n e s s . c h r o n . c o m / 5 - s o u r c e s - p o w e r -
organizations-14467.htmlhttp://smallbusiness.chron.com/5-sourcespower-
organizations-14467.htmlSource:https://pt.slideshare.net/KritikaKeswani2/10-characteristics-of-successfulteam
