UNIT 5: TEACHING AND LEARNING RESOURCES FOR LEARNERS WITH SEN
Key Unit Competence:
Students should be able to competently design, adapt and/or produce
appropriate teaching and learning resources for learners with disability andSEN.
5.1. Educational resource for learners with SEN and its
characteristics
5.1.1. Educational resources
Educational resource is a broad term that focuses on all factors outside and
within the classroom that make teaching and learning experiences more effective.
Educational resource, simply refers to human and materials resources and any
other environmental factors that are necessary to facilitate learning.
There are a number of terms and concepts used to describe educational resources.
These terms and concepts are:
• Teaching and learning materials: These refer to equipment and
learning materials that make it easy for a child to learn.
• General educational resources: These are resources used in our
schools on daily basis. They may be visual aids, audio (aural aids) or audiovisual
aids.
• Human resources: Any human being who support learning is referred to
as human resource. In the learning process they are persons who participate
and contribute to meet the learning needs of the learners. Examples of
human resources may include: teachers, sign language interpreters, and
physiotherapists among others.
• Compensatory or assistive devices: These are resources aimed
at reducing the effect of disabilities resulting from impairments. They
enhance the functional abilities of persons with special needs. The choice
of compensatory or assistive devices for any individual is dictated by the
nature and degree of their special needs and disabilities.
• Communication resources: Communication resources are device or
facilities necessary to facilitate communication for learners with special
needs. The natural ways we communicate is by use of spoken and body
language. Learners with special needs in education particularly those with
sensory and motor difficulties experience severe limitations in the use of
verbal and body language. They require compensatory resource for easy
communication.
• Adaptation: Adaptation is the process of changing or altering activities,
materials and equipment, in order to suit a particular need. Examples
include: a toilet seat that is used to enhance a person’s sitting position
when toileting if he/ she is not able to use the ordinary toilet in the normal
way; pencil grips that help the weak or crippled hand to hold a pencil and
write and an adapted school desk that enables a person with low vision to
perform classroom activities better and keep Braille materials in-order to
locate them easily among others.
• Barrier free environment: This is an environment free of physical
barriers. The physical barriers impede access to facilitate and the surrounding
environment as well as limits. The availability of supplementary mediums
such as braille, directions, visual warning or evacuation alarms provides
public with required information
5.1.2. Objectives, quality and characteristics of good educational
resources
a) Objectives of using educational resources
The main objective of using educational resources is to provide learners with
meaningful and productive knowledge, skills, experiences and attitudes. For
this to be achieved there must be effective stimulation of the learner’s senses
through use of appropriate educational resources. The basic assumption
underling the use of educational resources is that clear understanding stems
from maximum use of senses. This is important particularly for learners with
sensory impairments because of their limitations in these senses.
b) Characteristics and qualities of good educational resources
A good educational resource should address the above mentioned aspects.
In view of this there are some basic characteristics of a good educational
resource.
Characteristics and qualities of good educational resources include:
– Motivating to the learner so as to initiate the learning process
– Relevant to the activity, subject or field being taught
– Concrete so as to present learning trough practice. Some learners with
special needs in education cannot learn to draw meaning from abstract
ideas conveyed through oral explanation.
– Able to meet the individual needs of pupils at different stage of
development. This is particularly important in inclusive classes where
children have diverse needs and abilities.
– Flexible enough to be used in generalisation and transfer of knowledge
and skills
– Simple to be manipulated and understood by the learner. Learners with
special needs may not benefit from a resource which is complicated and
difficult to manipulate.
– Safe so as not to harm, scare, frustrate or offend the learner
– Durable to withstand rough and constant handling as some learners with
special needs require a lot of extra or repeated practice with resources.
– Made from familiar materials that learners attach special interest to
because the resource is made from familiar materials.
– Age appropriate: It should be relevant to all learners at different stages
of development regardless of their needs, exceptionality and background
– Culture free: An educational resource which violates culture values of the
learner would not only offend them but is likely to cause disunity with thelocal community and hence lead to poor learning environment.
5.2. Designs, adaptation, and/or production of appropriate
teaching and learning resources for differentcategories of learners with SEN
5.2.1. Educational resources for learners with sensory impairment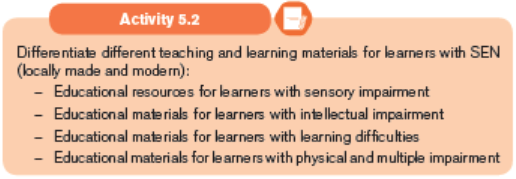
a) Educational materials for learners with visual impairment
It is common occurrence to find learners with visual impairments learning
together with their sighted peers in the same classroom. In order to achieve such
levels of inclusion, it is important that teachers make some modifications and
adaptation in the existing educational resources and the learning environment
to enable these learners maximize their participation in the learning activities.
Remember that learners with visual impairments have to rely on other sensory
modalities such as tactile and auditory to acquire information. Educational
resources for such learners need to be tactile, brailed or enlarged.
Some of the locally made materials, learners with visual impairmentcan use
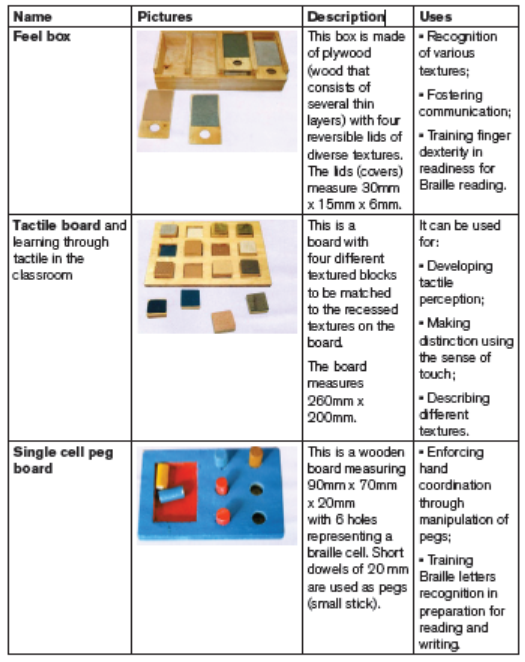
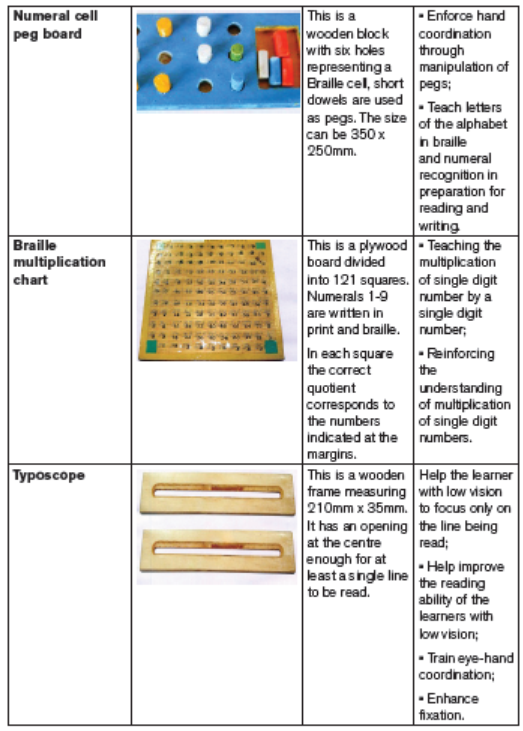
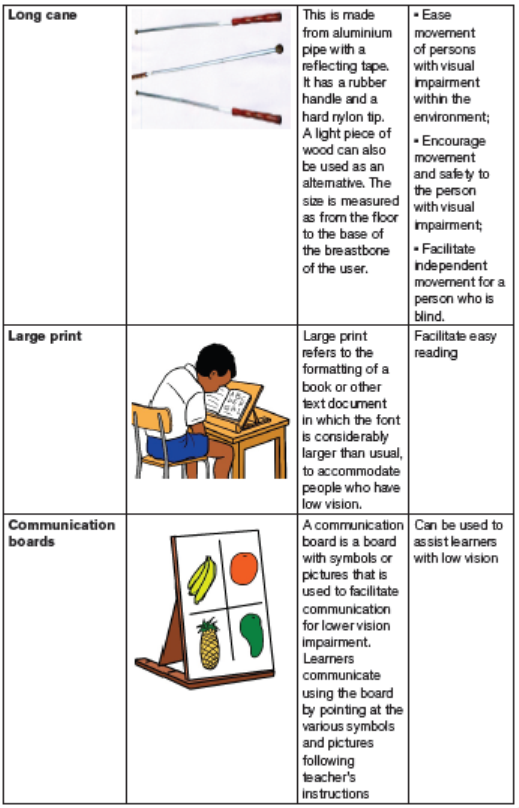
Some of the modern made materials, learners with visual impairment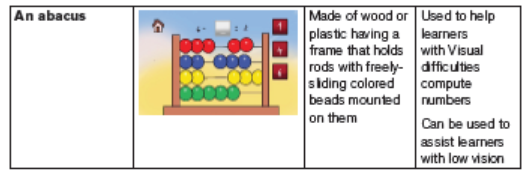
can use
Learners with low vision access print primarily through the use of optical devices
like glasses, telescopes, and magnifying lenses. In some instances, large print may
be utilized by learners to read, though some researchers suggest that this practice
does not lead to faster reading rates or more comfortable reading distances.
Learners who do not learn efficiently through their visual senses may access the
academic curriculum through Braille, a tactile method of reading. Like the printalphabet, it is a code-a way of presenting spoken language in written form.
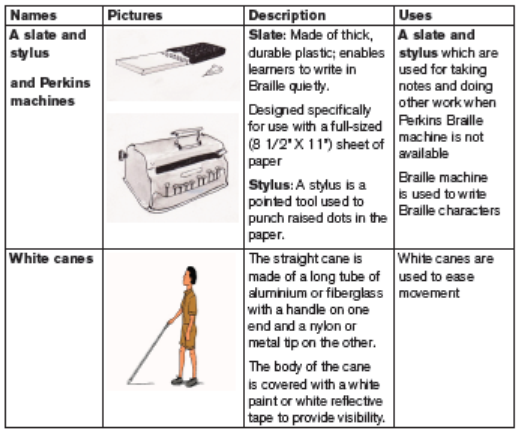
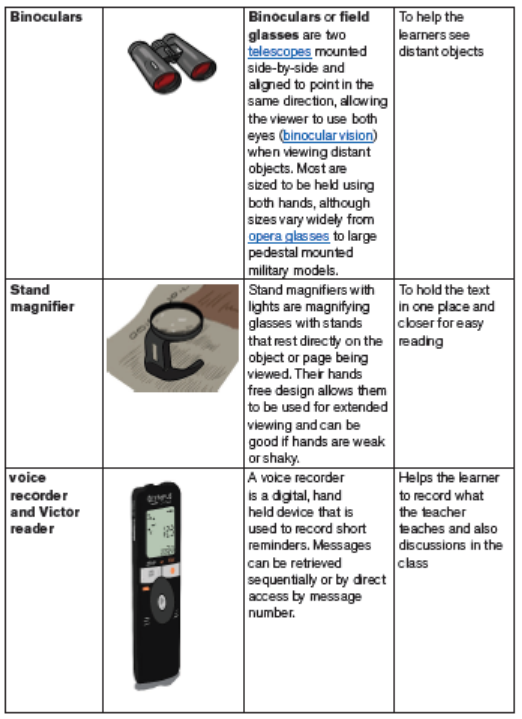
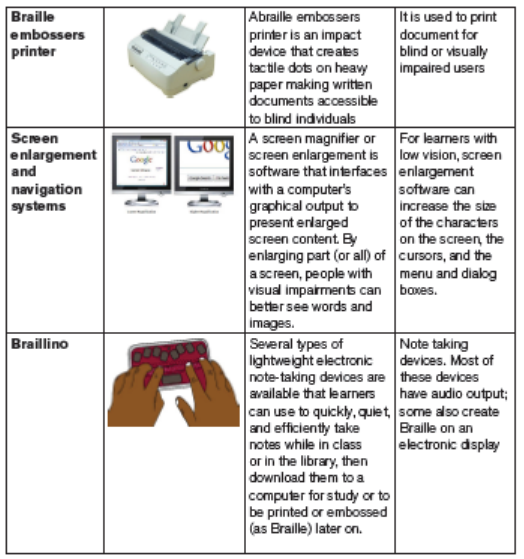
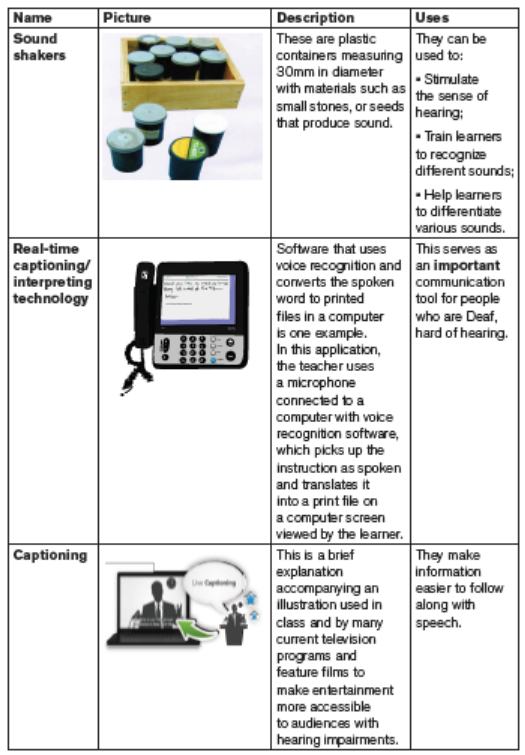
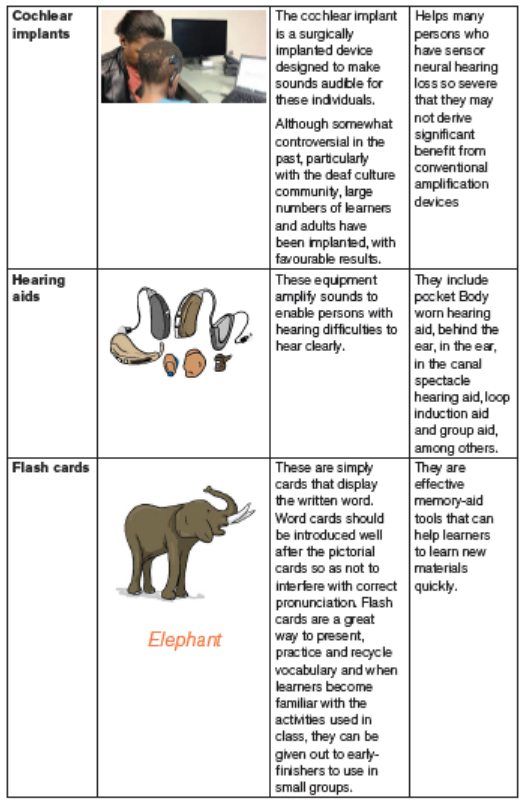
Educational materials for learners with hearing impairment
Sometimes, learners with mild hearing impairments can attend school for several
years before their impairment is identified. They are therefore at a disadvantage
when compared academically with their classmates who don’t have hearing
impairment. For this reason, it is important for you to be aware of the possible
indicators of hearing impairments and their impact on learning. Once you are
sure that a learner has a hearing impairment you need to provide appropriate
resources to support their learning.
Some of the instructional materials learners with hearing impairmentcan use
5.2.2. Educational resources for learners with intellectual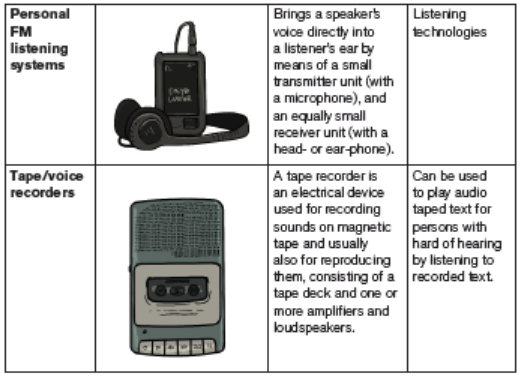
challenges
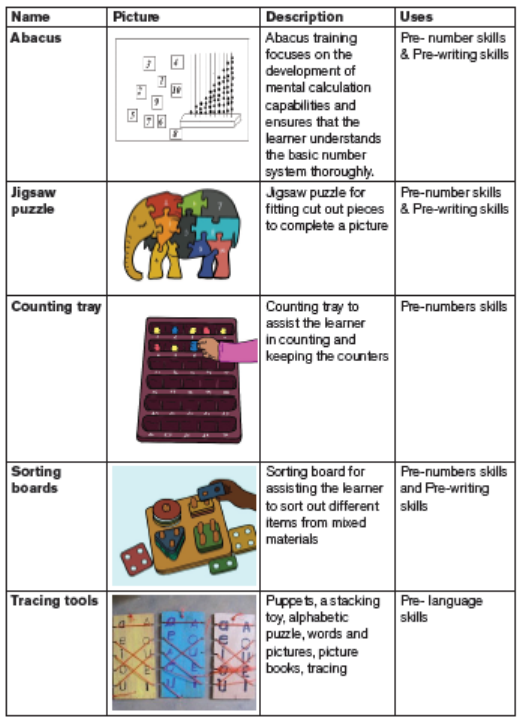
When selecting educational resources for learners with mental challenges, you
should consider the developmental levels of individual learners. Majority of the
resources required by such lectures can be selected from general classroom
resources.
The resources selected should aim at promoting the following developmental
areas: motor, social, cognitive, language and basic skills of concentration, attention,
listening, identification, turn taking, following instructions and general perceptualskills among others.
Some of the learning resources that can be used by learners with
intellectual challenges
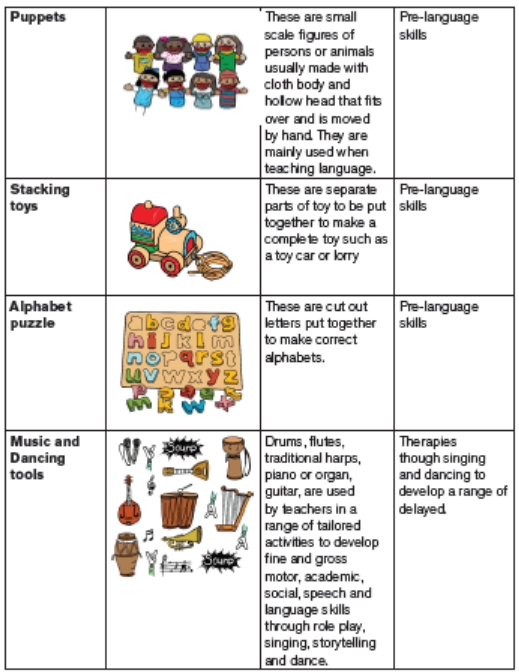
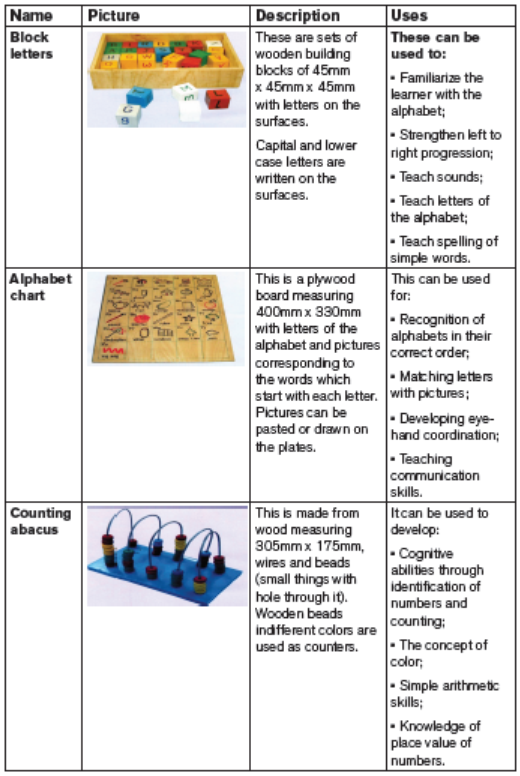
5.2.3. Educational resources for learners with learning difficulties
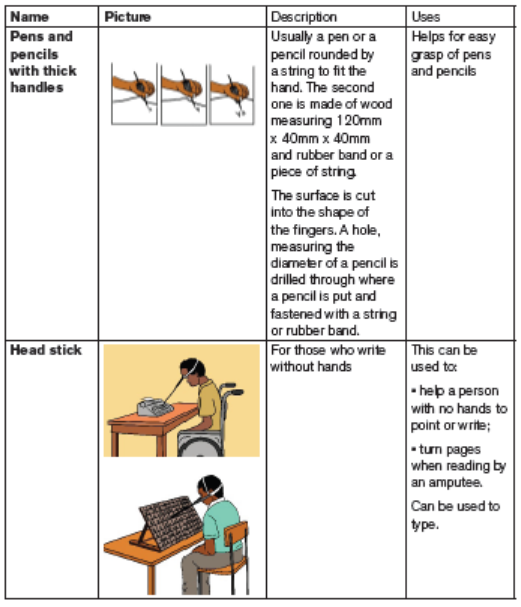
5.2.4. Educational resources for learners with physical and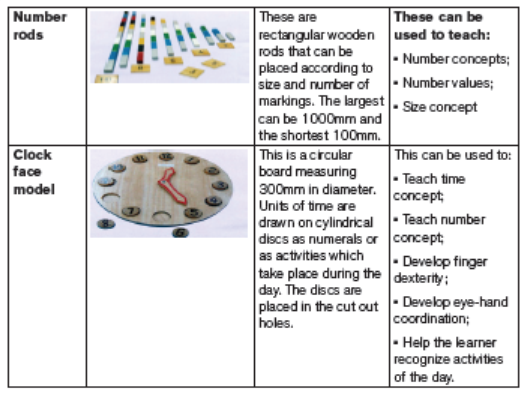
multiple impairment
Choosing educational resource for learners with motor problems demands to have
a prior knowledge and experience in identifying the learning needs of the learner.
It is therefore your responsibility to know which activity is appropriate and hence
decide which resources are needed. Choice of educational resources should aimat meeting specific learning objectives based on different learning needs.
5.2.4. Making educational resources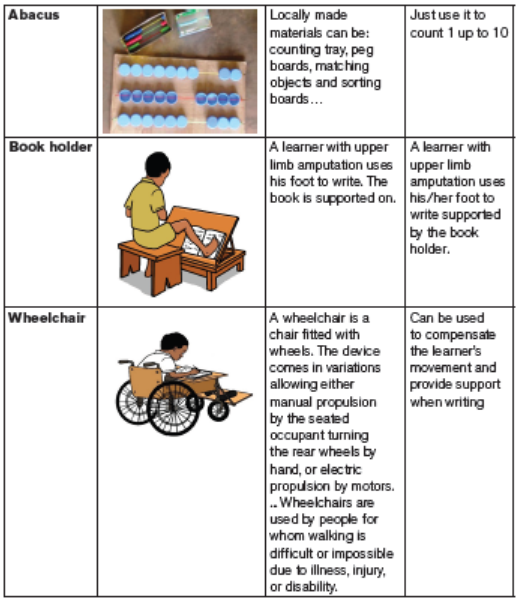
Methods and techniques of making educational materials are different. Teachers
have to think broadly according to their teaching and their learners’ needs. The
raw materials are available in the natural environment of teachers and learners;
educators are expected to be actively creative enough. Locally-made resources
respond to realities the learners live in, and enhance the teaching/ learning
process. So, thinking that educational materials are only bought is wrong, because
they can also be locally made.
a) Development outline for making low cost educational resources
The following steps should be followed:
• Try to establish the learners’ level of development or learning needs through
the process of SEN assessment.
• Decide which specific objectives are needed to help the learner overcome
his/her learning needs. The type of activity is a crucial guiding factor in
the production of resources adapted for individual learners with special
educational needs.
• Decide which immediate subject skills or activities you would like to teach
in relation to the learner’s established learning needs after assessment, e.g.
social, motor, language, cognitive, behavioural, academic and others.
• Explain in detail the process you are likely to follow when designing and
making the educational resources you have chosen in terms of:
– Clearly state the tools for making resources.
– Materials to be used in its production.
– Size of the resource you intend to make.
– Quality and quantity of the resource needed.
– Design or sketch of the resource you intend to make, clear and in details
explaining the procedures and plans to be followed in its production.
Examples of materials that a teacher can make and use:Numbers
Objective: To introduce Braille numbers
Material to use: Hard paper, marker, glue, Manila paper, paints, coloured
pencil, scissors
How to use it: Draw and fix them on the wall in the classroomFruits and vegetables
Objective: To develop cognitive skills
Material to use: Hard paper, Manila paper, coloured pencils, markers, scissors
How to make: Just cut a piece of Manila paper and draw the type of fruit you
need. Use different colours to make it attractive.Wall clocks
Objective: To develop cognitive skills, eye-hand coordination skills and fine
motor skill, numeracy.
Material to use: Manila paper, markers, glue, cords, scissors.
How to make: It is an easy exercise. Just imitate the real one that learnersknow.
Colours/ Using materials for construction
Objective: To develop classification skills
Material to use: Old paint boxes
How to use it: With these colour bottles, a teacher
explains names of colours and helps learners togroups, classify, sort and manipulate the bottles.
Geometric forms
Objective: To introduce different shapes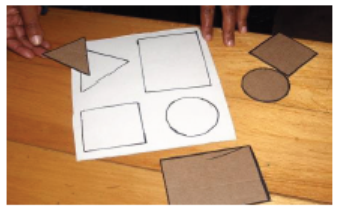
Material to use: Hard paper, markers, glue, scissors
How to make it: Draw a geometric form and cut it to produce it tangible to
learnersQuantities
Objective: To identify different weights
Material to use: Empty bottles, paint, juice, coloured water, etc.
How to use it: Use transparent empty bottles (of Nile, Inyange, Huye water)
and teach concepts like: ‘less than’, ‘equal’, ’more than’. Put the bottles in orderhelp learners to sort them according to sizes, weight, colour, etc.



