UNIT1:GASTRODUODENAL ULCERS
Key Unit competence:Take appropriate decision on Gastro Duodenal Ulcers
Introductory activity 1.0
The image A and B illustrate the structures of stomach and duodenum. Observethem and respond to the attached questions.
1) Is there any difference between the two images (A&B)?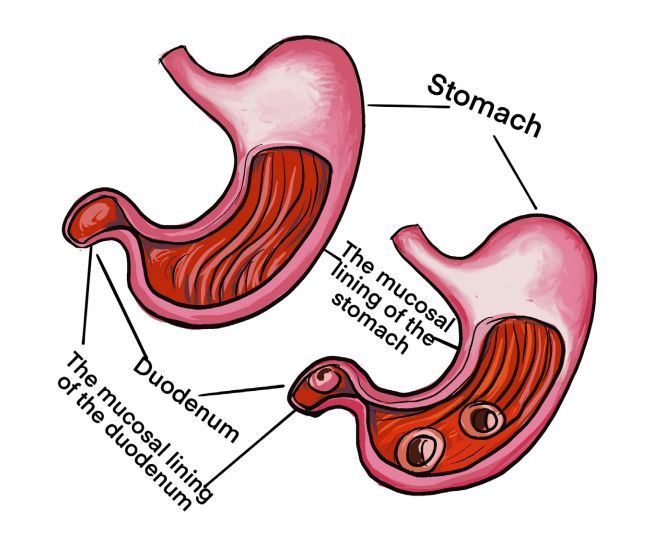
2) What explanations can you give to justify the abnormal structure of
stomach and duodenum?
3) What do you think can cause the modifications that you have observed?
4) What are the manifestations of such abnormalities in the human body?
5) How can health personnel identify or notice these abnormalities of
stomach and duodenum?6) How can these abnormalities be corrected?
1.1. Description of gastroduodenal ulcers
Learning Activity 1.1
S.D is a 47-year-old police officer who lives and works in urban area. Mr. S.D has
now been admitted to the hospital where you are allocated.
*In the past history, Mr. SD has had ‘heartburn’ and abdominal discomfort for
years, but he thought it went along with his job. Last year, after becoming weak,
light-headed and short of breath, he was found to be anemic. He said that he
took omeprazole and ferrous sulfate for 3 months before stopping both, saying
he had ‘never felt better in his life’.
*On today’s initial assessment, S.D is alert and oriented, though very worried
about his condition. Skin pale and cold; BP 136/78, P 98; his abdomen is
distended and tender with hyperactive bowel sounds; he has active upper GI
bleeding as manifested by 200 mL bright red blood obtained on nasogastric tube
that has been inserted.
* The medical doctor is now ordering different diagnostic measures and include
FBC, endoscopy and a biopsy taken from the stomach and duodenum.
*The results of FBC have indicated low Hemoglobin and low hematocrit. Tissue
biopsy obtained during endoscopy confirms the presence of H. pylori infection.
Questions related to the case study
1) Identify the biography of the patient described in the case study
2) What is the medical history of patient described in the case study?
3) Describe the signs and symptoms that the patient present and are
described in the case study
4) What are the aggravating and relieving factors?
5) What is the probable diagnostic method of this S.D?
Learning Activity 1.1
1.1.1. Definition and the Gastroduodenal ulcers
Gastroduodenal ulcers also known as Peptic ulcer (PU) disease is a condition in
which painful sores or ulcers develop in the lining of the stomach or the first part of
the small intestine (the duodenum).
1.1.2. Causes and pathophysiology of Gastroduodenal ulcers
Studies have revealed two main causes of peptic ulcers (PU): Helicobacter pylori
(H. pylori) bacteria and pain-relieving NSAID medications. There are other manyfactors of Peptic ulcers.
Risk factors for peptic ulcer disease
• H. pylori infection,
• Low socioeconomic status Crowded, unsanitary living conditions
• Unclean food or water
• Advanced age
• History of PUD
• Concurrent use of other drugs such as glucocorticoids or other NSAIDs
• Cigarette smoking
• Family history of PUD
PU disease is characterized by discontinuation in the inner lining of the gastrointestinal
(GI) tract because of an increase in the concentration or activity of gastric acid or
pepsin. It extends into the muscularis propria layer of the gastric epithelium. Some
individuals have more rapid gastric emptying, which, combined with hypersecretion
of acid, creates a large amount of acid moving into the duodenum. As a result, peptic
ulcers occur more often in the duodenum. The Pathophysiology of gastroduodenalUlcer is summarized on the figure 1.1.
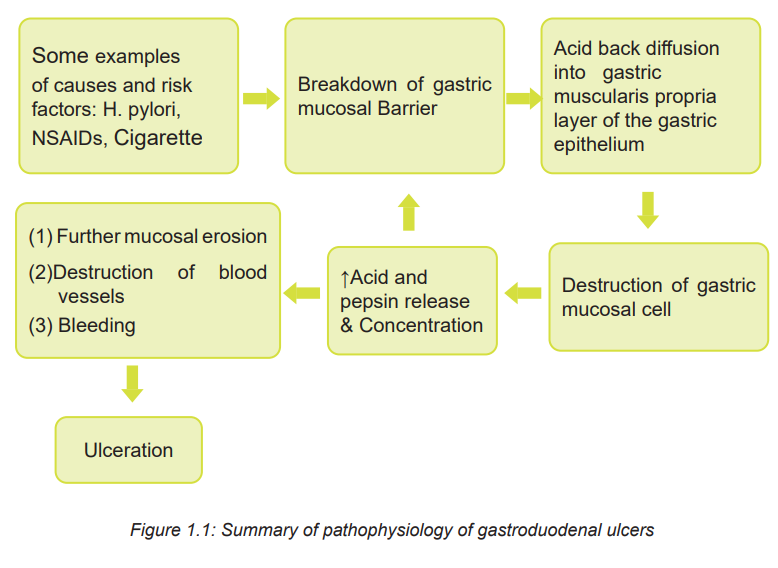
1.1.3. Signs and symptoms of Gastroduodenal ulcers
Some people with ulcers don’t experience any symptoms. But signs of a peptic
ulcer can include burning pain in the middle or upper stomach between meals or
at night. Pain that temporarily disappears if you eat something or take an antacid,
bloating, heartburn, nausea or vomiting.
In severe cases, symptoms can include dark or black stool (due to bleeding),
vomiting, weight loss, severe pain in the mid to upper abdomen. Table 1.1 comparesthe characteristics of duodenal and gastric ulcers
Table 1.1: COMPARISON OF GASTRIC AND DUODENAL ULCERS
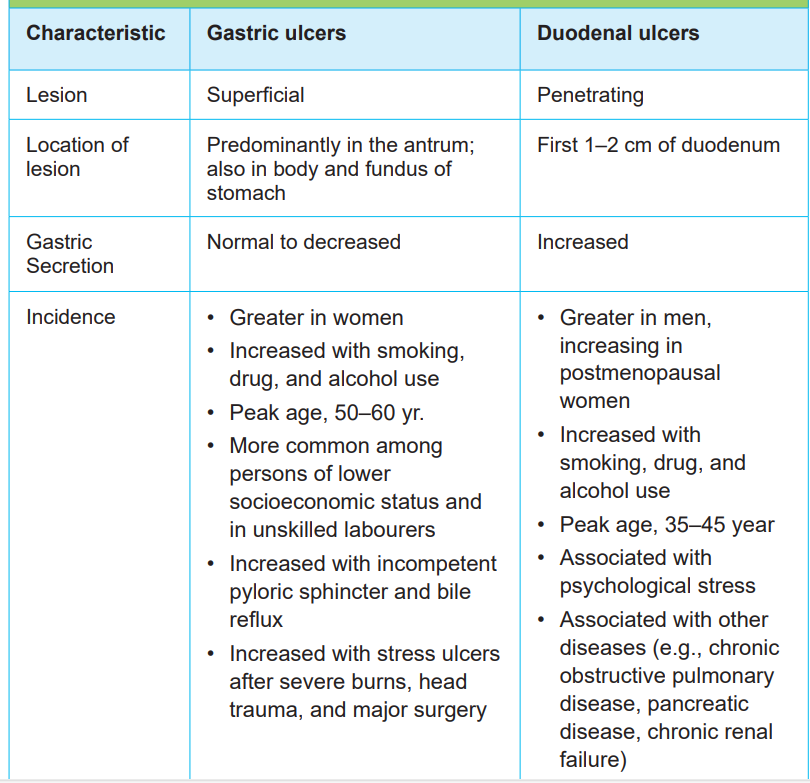
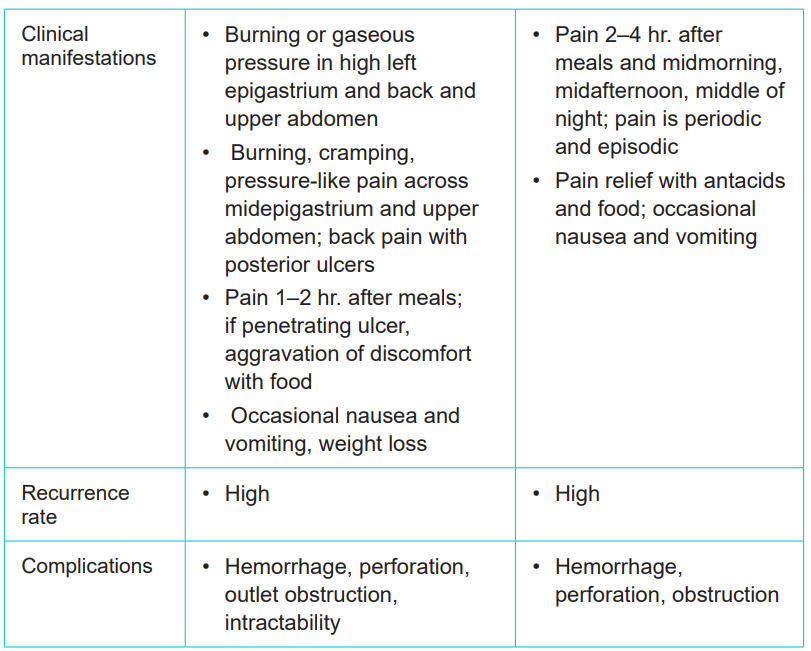
1.1.4. Diagnostic measures
The gastroduodenal ulcers can be diagnosed through a complete history, physical
examination, Complete Blood Cell Count (CBC), upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
with biopsy, Helicobacter pylori testing. Endoscopy is the most accurate diagnostic
procedure and allows for direct viewing of the gastric and duodenal mucosa
(Fig.1.2).
The Complete blood cell count may indicate low level of Hb and Ht due to chronic
bleeding. Helicobacter pylori results are referred to as positive or negative.
Differential diagnostic includes acute choleritiasis, cholique syndrome, myocardialinfection
Figure 1.2: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) directly visualizes the mucosal lining of the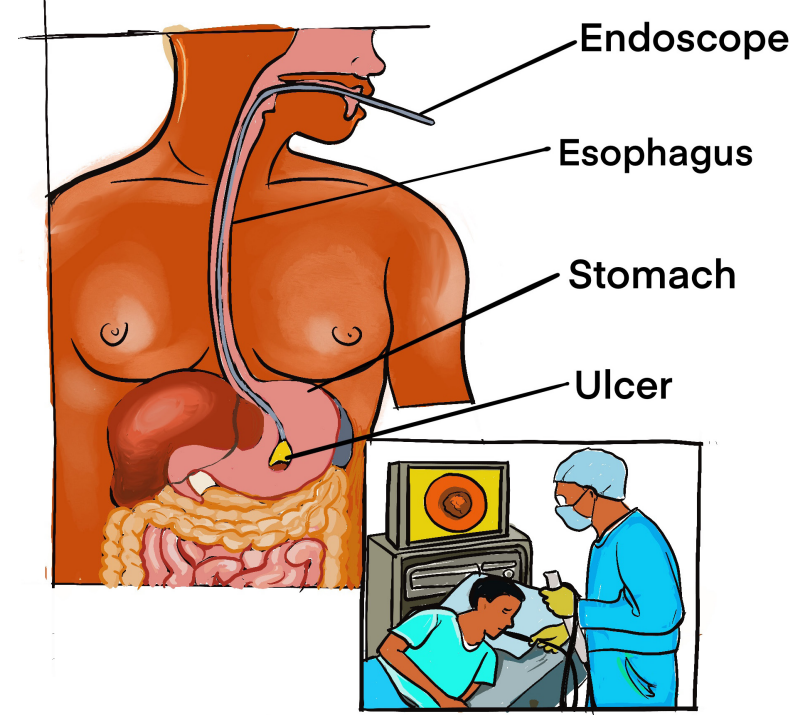
stomach with a flexible endoscope. Ulcers or tumors can be directly visualized and biopsies taken.(Lewis et.al 2012)
Self-assessment 1.1
Briefly explain the pathophysiology of gastroduodenal ulcers?
Identify other diseases that would mimic the symptoms of gastroduodenal ulcers?How would reduce the anxiety of the patient caused by the fear of endoscopy?
1.2. The management of gastroduodenal ulcers
Learning Activity 1.2
…Continuation of S.D case study
After different investigations, the medical doctor confirmed that the police officer
Mr. S.D is suffering from Gastroduodenal ulcers. Regarding the treatment,
Mr. S.D has received two units of packed RBCs and intravenous fluids. Oral
omeprazole (40 mg BID) was ordered and when he was in endoscopy they
managed to stop the bleeding.
Questions related to the case study
1) What is the surgical treatment plan adopted by the medical doctor for this
patient?
2) In group discuss the different medication prescribed to this patient3) List potential complications which may happen to this police officer
1.2.1. The treatment plan of Gastroduodenal ulcers
Medications to treat peptic ulcer include:
• Proton pump inhibitors (PPI): These drugs reduce acid, which allows the ulcer
to heal (e g: nexium).
• Histamine receptor blockers (H2 blockers): These drugs also reduce acid
production (e g: Tagamet).
• Antibiotics: These medications kill bacteria (e g:Amoxicillin).
• Protective medications: Like a liquid bandage, these medications cover the
ulcer in a protective layer to prevent further damage from digestive acids and
enzymes (e g: Carafate).
• Several treatment options are combined to cure H. pylori without recurrence.
Triple therapy has the best eradication rate
• Endoscopy procedure treatment:
• Doctor may treat peptic ulcers during an endoscopy procedure by injecting
medications
• Doctor can also use a clamp or cauterization (burning tissue) to seal it off and
stop the bleeding.
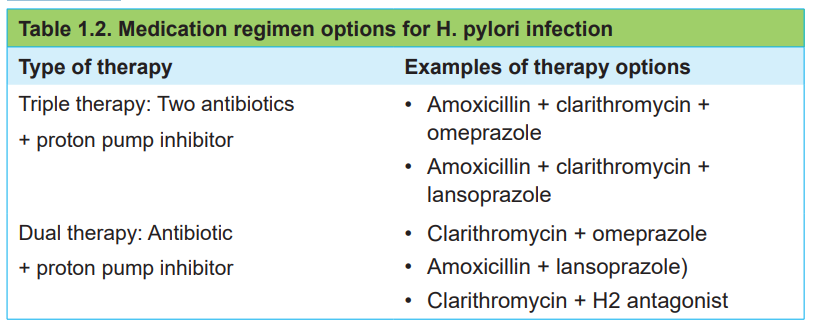
To eradicate the H pylori infection dual or triple therapy is recommended as indicatedin table 1.2.
1.2.2. Associate nurse decision making
In the hospital, the associate nurse will perform tasks that are delegated by
registered nurses. The primary focus of care for peptic ulcer disease is educating
patients. The teaching guide will include detail the following:
– Describe dietary modifications
– Explain the rationale for avoiding cigarettes
– Emphasize the need to reduce or eliminate alcohol ingestion
– Explain the rationale for avoiding OTC drugs unless approved by the
patient’s health care provider.
– Explain the rationale for not interchanging brands of antacids and
– H2-receptor blockers that can be purchased OTC without checking with
the health care provider Emphasize the need to take all medications as
prescribed
– Explain the importance of reporting any of the following:
– Describe the relationship between symptoms and stress. Stress reducing
activities and relaxation strategies are encouraged.
– Encourage patient and caregiver to share concerns about lifestyle changesand living with a chronic illness.
1.2.3. Complications of gastroduodenal ulcers
Perforation, abscess of the appendix, and peritonitis are major complications of
gastroduodenal ulcer. With perforation, the pain is severe, and temperature iselevated to at least 37.7°C.
Self-assessment 1.2
Mr. S.M a patient on your department unit, has a duodenal ulcer. His wife runs to
the nursing station and says that you need to help her husband, he is in terrible
pain. As you enter the room, you see Mr. SM bent knee-to-chest position on the
bed. He is crying and says he has excruciating abdominal pain.
1) What additional data would you gather?
2) What emotional support would you offer to Mrs. SM?
3) After orders are obtained, what actions will you anticipate implementingunder supervision
1.3 End unit assessment
End of unit assessment
1) What are the most frequent symptoms of Gastroduodenal ulcers?
2) What are the diagnostic measures of Gastroduodenal ulcers?
3) The nurse is teaching the client and her family about possible causes of
peptic ulcers. How does the nurse explain ulcer formation? Choose the
best answer.
a) Caused by a stressful lifestyle and other acid-producing factors such as
Helicobacter pylori
b) Inherited within families and reinforced by bacterial spread of
Staphylococcus aureus in childhood
c) Promoted by factors that tend to cause over secretion of acid, such as
excess dietary fats, smoking, and H. pylori
d) Promoted by a combination of possible factors that may result in erosion
of the gastric mucosa, including certain drugs and alcohol
4) Duodenal and gastric ulcers have similar as well as differentiating features.
What are characteristics unique to duodenal ulcers (select all that apply)?
a) Pain is relieved with eating food.
b) They have a high recurrence rate.
c) Increased gastric secretion occurs.
d) Associated with Helicobacter pylori infection.
e) Hemorrhage, perforation, and obstruction may result.
f) There is burning and cramping in the midepigastric area.
5) What are the dietary modifications would you recommend a patient withgastroduodenal ulcers?
