Topic outline
UNIT1: INTRODUCTION TO QUICKBOOKS
Key unit competence: Create company profile in QUICKBOOKSsoftware
Introductory Activity
In today’s business environment, most financial accounting systems have
been computerized and automated in such a way that papers are not needed
or needed less and less. Mr NGOGA Frank is an accountant in ABC Ltd.
His day to day activities is to identify and record, classify, summarize, analyze
and interpret financial transactions of the company in a significant manner
and in terms of money, transactions and events which are in part of financial
character, and interpret the related results. Mr NGOGA Frank uses a manual
book keeping accounting system. This causes him a low performance in
terms of providing timely financial information to the different users for rational
decisions. To overcome this, the owner is suggesting to shift from manual book
keeping system to computerized accounting system.
a) Advise him on accounting software that can be used by the company.
b) Do you think the software will help them to handle the challenges?Explain.
1.1 General overview on QuickBooks
Activity 1.1
Holly city Technology Ltd has a paper-based database and wants to have a
computerized one to use to keep all its customers, suppliers and third parties’
data. Every day Director of Holly city technology Ltd faces different challenges
of properly keeping customer’s data because of the system they use which isa paper based database and Microsoft Excel program.
By analyzing this scenario answer the following questions:
a. Advise him on the software the company can use for solving the above
challengesb. Differentiate a paper-based database from a computerized database
QuickBooks is one of the most popular accounting software for small
businesses. Moving from manual bookkeeping or spreadsheets have grown
into many problems, difficulties, obstacles and businesses need a better option
compared to other current software.
QuickBooks can be a good choice for small and medium businesses. It is best
known for its bookkeeping software; it offers a range of accounting and financesolutions for small businesses.
1.1.1. Key concepts
a. Accounting: Accounting is a process of identifying and recording,
classifying, summarizing, analyzing and interpreting financial transactions
of an entity for a certain financial period.
b. Accounting cycle: Accounting cycle refers to a series of steps followed
by companies to systematically process financial information from source
documents to the preparation of financial statements on a monthly,
quarterly, and/or annual basis. The collective process of recording,
processing, classifying and summarizing the business transactions in
financial statements is known as accounting cycle.
c. Manual Bookkeeping: This is a way of recording business activity
transactions without using a computer system with specialized accounting
software. In this way, transactions are registered by hand in accounting
books, using a written ledger of transactions, physical records, pads of
paper and books.
d. Computerized accounting: Computerized accounting system is an
accounting information system that processes the financial transactions
and events as per Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) toproduce reports as per user requirements
1.1.2. Use of QuickBooks software in accounting records
QuickBooks provides a number of ready to use templates that business
owners can use to create invoices, spreadsheets, charts and business plan.
QuickBooks makes it easy to customize the look and feel of those documents.
QuickBooks allows the user to look at and manage purchases, sales, andexpenses in one spot.
Additionally, QuickBooks helps businesses in the following ways:
• QuickBooks like other accounting is important in digitalization of
accounting data
• Simplifies and automates data entry. For example, a point-of-sale
terminal may actually become a data entry device so that sales are
automatically “booked” into the accounting system as they occur
• Frequently divide the accounting process into modules related to
functional areas such as sales/collection, purchasing/payment, and
others.
• Is “user-friendly” by providing data entry blanks that are easily understood
in relation to the underlying transactions.
• Minimize key-stokes by using “pick lists,” automatic call-up functions,
and auto-complete type technology.
• Is built on data-base logic, allowing transaction data to be sorted and
processed based on any query structure. For example, producing an
income statement for July; providing a listing of sales to Customer
• Provide up-to-date data that may be accessed by key business decision
makers.
• Are capable of producing numerous specialized reports in addition tothe key financial statements
Application Activity 1.1
1. Define the following Terms:
a) Manual Bookkeeping
b) Computerized accounting
c) Accounting cycle2. Discuss the importance of QuickBooks
1.2. Installation of QUICKBOOKS software
Learning Activity 1.2
Holly city Technology Ltd accountant Uwimbabazi bought a laptop which
doesn’t have any accounting software
1. Demonstrate and outline the procedure will be used by Uwimbabazi forhaving QuickBooks in her computer.
Installation (or setup) of software is the act of making the program ready
for execution. Installation refers to the particular configuration of a software or
hardware with a view to making it usable with the computer. A soft or digital
copy of the piece of software (program) is needed to install it. There are different
processes of installing a piece of software (program).
Because the process varies for each program and each computer, programs
(including operating systems) often come with an installer, a specialized program
responsible for doing whatever is needed for the installation. Installation may be
part of a larger software deployment process.
Installation typically involves code (program) being copied/generated from
the installation files to new files on the local computer for easier access by
the operating system, creating necessary directories, registering environment
variables, providing separate program for un-installation etc. Because code is
generally copied/generated in multiple locations, uninstallation usually involvesmore than just erasing the program folder.
Common operations performed during QuickBooks software
installation include:
• Making sure that necessary system requirements are met
• Checking for existing versions of the software
• Creating or updating program files and folders
• Adding configuration data such as configuration files, Windows
registry entries or environment variables
• Making the software accessible to the user, for instance by creating
links, shortcuts or bookmarks
• Configuring components that run automatically, such as Windows
services
• Performing product activation• Updating the software versions
Steps of installing QuickBooks Software
The following are the steps to install a QuickBooks software in a computer:Step 1. Open QuickBooks set up icon, then the following window appear:

Figure 1.1. QuickBooks Install Shield wizard
Step 2: In the Welcome Window that appeared click on NEXT and get thefollowing:
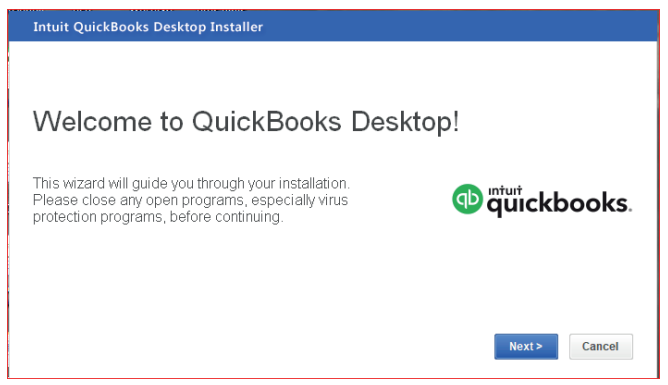
Figure 1.2. Welcome to QuickBooks Interface
Step 3: Tick on “I accept the terms of the license agreement” and click onNext
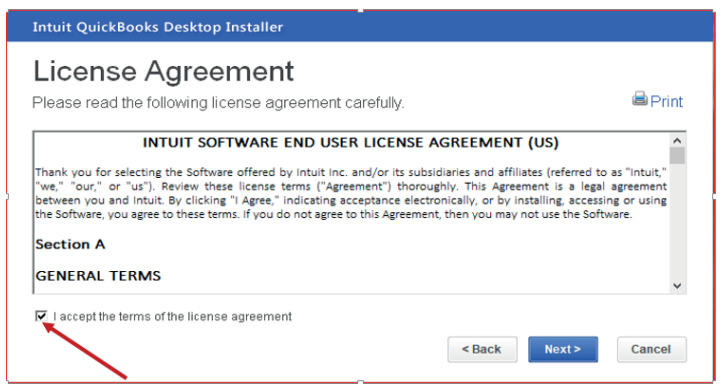
Figure 1.3 QuickBooks License Agreement Interface
Step4: After accepting the terms and conditions of QuickBooks license,
activate the QuickBooks Desktop by filling the license and product numberin their field.
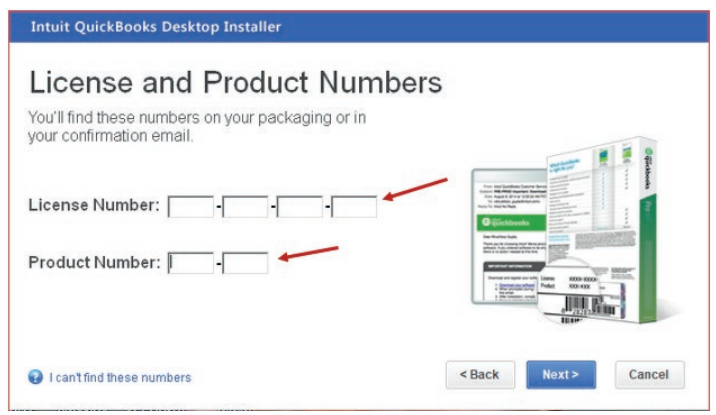
Figure 1.4 Field reserved for License Number and Product Number
After click on Next then the following window of custom and network optionswill appear.
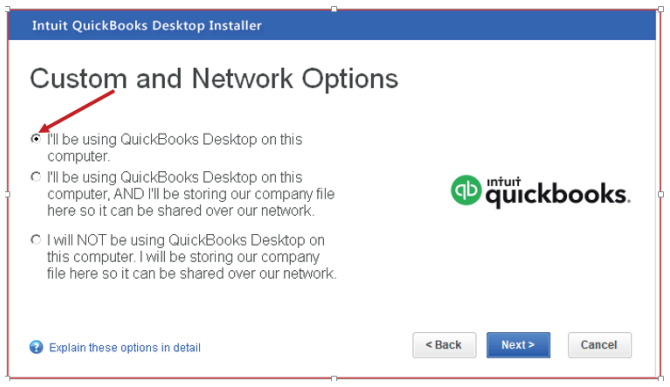
Figure 1.5 Interface used for selecting where QuickBooks Desktop will be used
Step 5: Select whether you will use QuickBooks Desktop on this computer
(which is the recommended option). Then click on Next. One of the three
options is chosen depending on how QuickBooks will be used.
Step 6: Choose installation Location
Click on browse to select the installation location. By default, QuickBooks files
are saved in local disk C\Program Files (x86) \Intuit\QuickBooks Enterprise
solutions. But the user can locate it in other locations like on desktop or localdisk D.
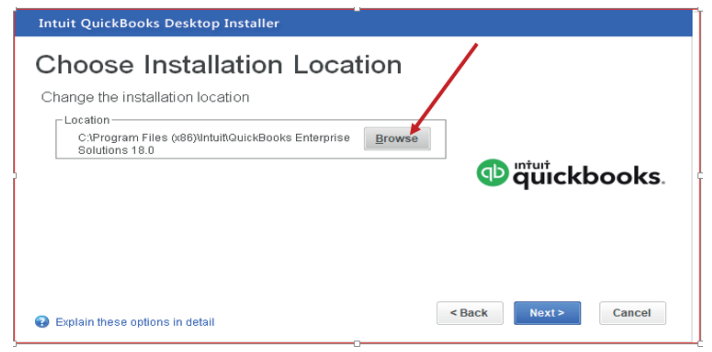
Figure 1.6 Location of QuickBooks Software
Click on install and wait for installation process
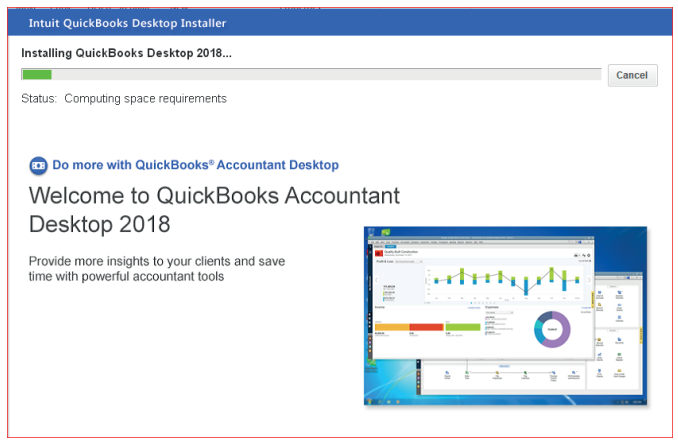
Figure 1.7 Interface with QuickBooks installation Progress
Application Activity 1.2
Assume you have got a job of being an accountant of five-star hotel
and the hotel wants to start using QuickBooks accounting software in
their accounting records. Even if the hotel manager has already bought
QuickBooks software, it is not yet installed in their computers. You are
therefore asked to help them to install it.
1. What are the steps will you follow to install QuickBooks in computer?
2. Install the QuickBooks software in one computer in the schoolcomputer lab
1.3. Creating company profile in QuickBooks
Learning Activity 1.3
ABADAHIGWA COOPERATIVE needs to use QuickBooks in its day to
day accounting records. It is necessary to ha a full complete profile of thecompany to ensure an easy and clear records of transactions.
• Suggest to the cooperative the main component of the
company profile
• Use your own example to show to the cooperative an exampleof a full complete company profile
A company profile or company file is where the user stores company financial
records in QuickBooks. Therefore, it is the first thing to do in QuickBooks. You
can create a company file from scratch or convert records previously kept in a
small-business accounting program. It is a tool to use for analyzing the financialsituation of companies.
To create a company profile, follow this procedure:
• Click on the QuickBooks Home page• Click on create new company:
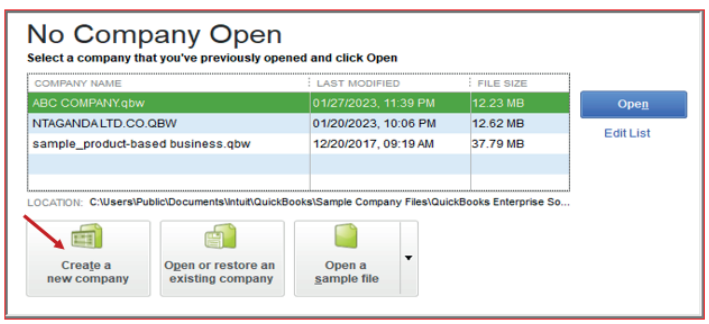
Figure 1.8 Creation of new company
• Clicking on Expressing Start
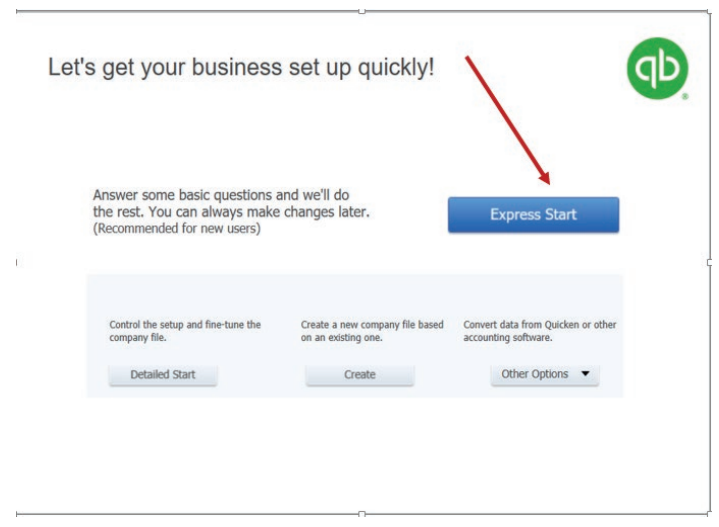
Figure 1.9 The beginning of Easy setup of company identification
After clicking on Expressing Start, an easy setup of company profile interviewstarts.
• Complete the easy setup of company profile interview:
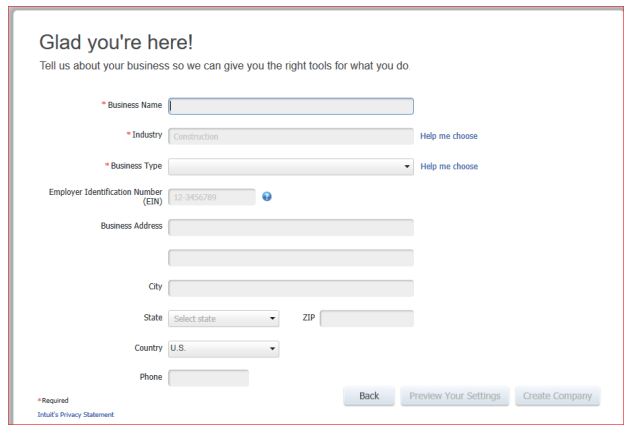
Figure 1.10 Business information interface
• Fill the business name
• For the industry, click on help me to choose so that the default chart
of accounts should not appear in the company charts of company.• Select other/none
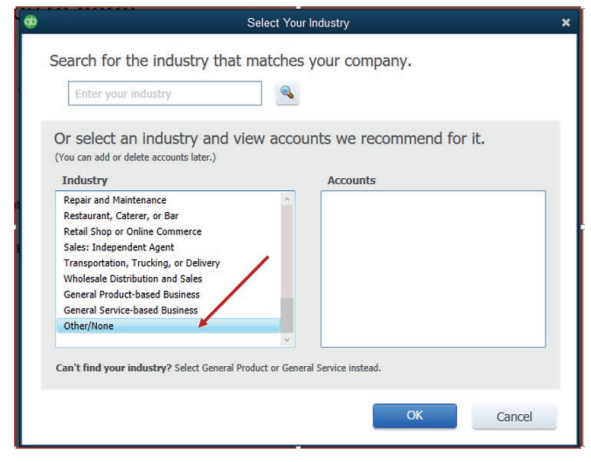
Figure 1.11 interface with a list of industry types
The selection of Other/None allows the user to have a free field of charts of
account so that he can set the appropriate charts of account according to the
transactions he will be recording.
If the user selects the Accounting or bookkeeping on the field of Industry,
the default account relating to the selected industry will appear in the chart of
accounts including the ones the user does not want.
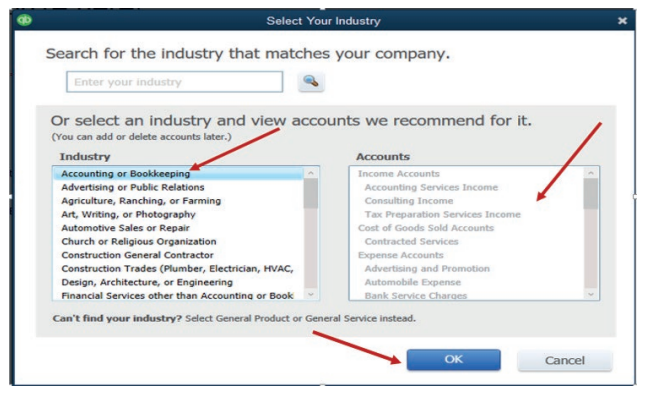
The field of Business Type should be filled according to the user’s choice. If
the user needs to continue by setting his own charts of account, he can selectOther / None. Then OK
Figure 1.12 Details of company information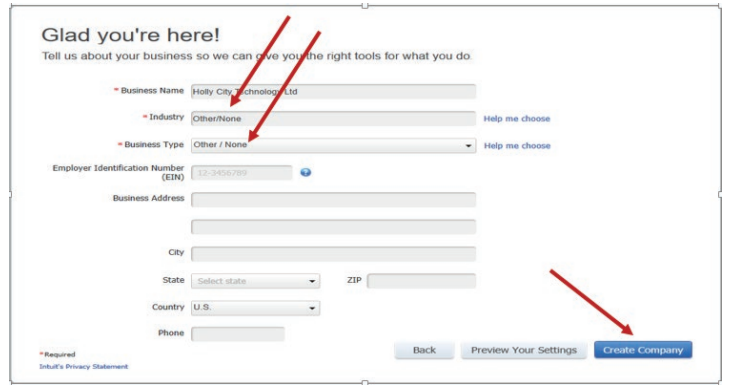
Note: For Employer Identification Number use the format xxx-xx-xxxx (Three
digits- Two digits-four digits).• After filling all fields click on Create the Company
Then wait for the company creation process until the following window appear

Figure 1.13 Interface for adding Business People, Product or Services
In the above window the user adds people to do business with, product or
services sold by the company and bank accounts. Otherwise, the user may skipto start Working tab.
Then the QuickBooks Home Page interface appears as follows:
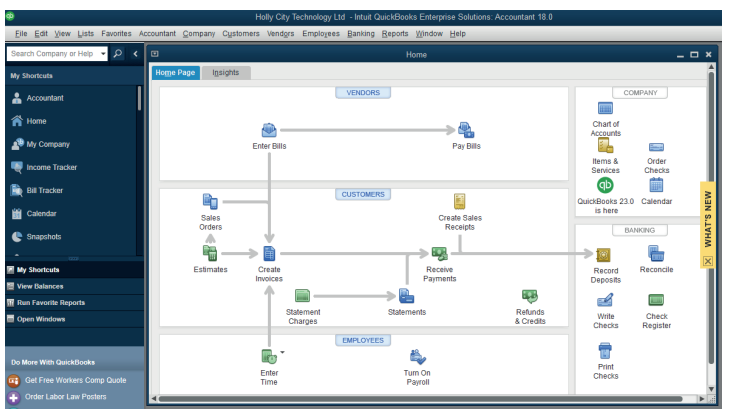
Figure 1.14 QuickBooks Home Page interface
The menu bar has fourteen menus namely: File, Edit, View, Lists, Favorites,
Accountant, Company, Customers, Vendors, Employees, Banking, Reports,Window and Help.
Application Activity 1.3
BWIZA Ltd is a small sole trade business of purchasing and selling of
Eggplants. It is located in NDUBA Sector, GASABO District KIGALI CITY
(Tel +250788567012-722567012; P.O Box 1123 Kigali).
BWIZA Ltd is facing serious problems related to the use of manual accounting,it decided to use QuickBooks. Create accompany profile for BWIZA Ltd.
1.4. Customization of company preference
Learning Activity 1.4
If the QuickBooks user wants to customize company preferences in QuickBooks
to fit his personal style and business needs he can do it with the help of
QuickBooks preferences as long as references permit the users to choose
how they want QuickBooks to manage things or to set own preferences.
• What should be the examples preferences that the user can
customize?• In which process it could be done?
Preferences allow you as the user to decide how you want QuickBooks to
handle things or set personal or company preferences.
Examples of preferences that the user can customize:
– Age from due date: The overdue days appears on the invoice,
statement or bill, that start from the due date that
– Age from transaction date: The overdue days start on the creation
date of the invoice, statement or the date of when bill receiving.
– Format: If you click this button, then this button will open the Report
Format Preferences window which authorizes you to customize Header
or Footer & Fonts and Numbers on QuickBooks reports. You can modify
the appearance of the report.
– Reports: Show items by defining how reports display the name of the
items.
– Reports: If you need to display account numbers in your reports, click
Name and Description or Name only.
– The Classify button: With the help of this button, you can reclassifyaccounts for the Statement of Cash Flows report
Preferences can be found by going to the top of the main QuickBooks Home
page and click on Edit and then preferences. Click on Edit Menu, on theQuickBooks Home page and find the following window:
A click on Preferences gives to the user the wide option to customize either his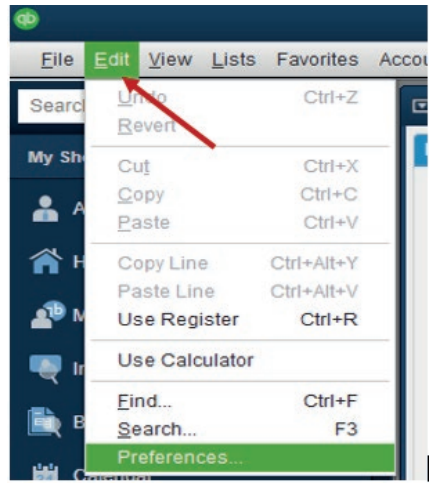
preferences or Company Preferences.
For example: If the user needs to customize the use of numbers on the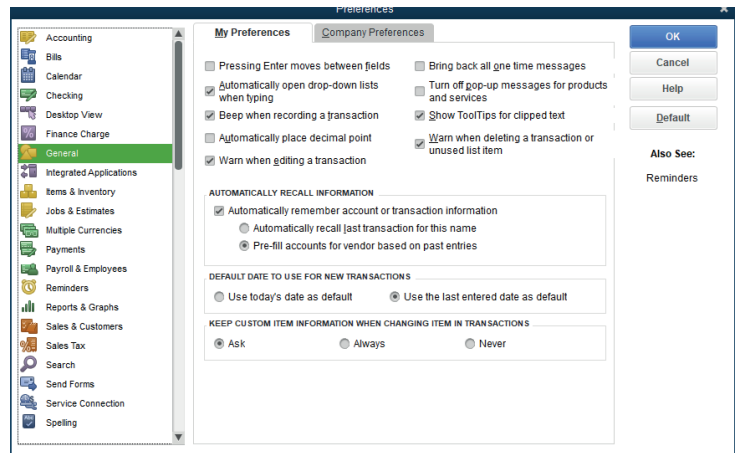
accounts, he/she must follow these steps:1. Click on Accounting
• Click on Company preference and tick on Use Account Numbers
and OK
• After clicking OK, check the accounts and see the numbers on the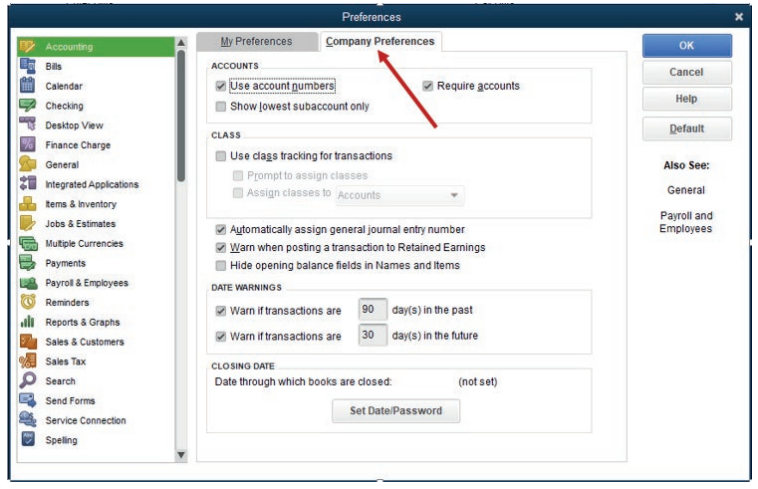
accounts
Application Activity 1.3
1. What is the meaning of customization of company preferences?
2. Give the examples of preferences that the QuickBooks user can
customize to suit its work.
3. Present a preferences window where on My Preferences, Payroll &Employees, Only Online Payroll and Last Name are selected.
End of Unit Assessment
1. Define the Installation of software
2. List the common operations performed during QuickBooks software
installation
3. MUTARA ENTERPRISE is a small sole trade business of manufacturing
of furniture items. It is located in KAGEYO Sector, Gatsibo District
in Eastern Province (Tel +250788567012-722567012; P.O Box
1123 Gatsibo). MUTARA ENTERPRISE Shop is well known for its
services performed in Society that attracts customers.
• Use the information above to create a company profile.
• Customize the charts of accounts so that they appear withrelevant codes numbers
UNIT2: CREATION OF ACCOUNTS
Key unit competence: Create charts of accounts inQUICKBOOKS
Introductory Activity
MAREBE Ltd, a sole trading company uses QUICKBOOKS accounting
software in recording its daily financial transactions. The following are items
that the company is engaged in supplying: Computers, printers, projectors,
photocopying machines and TVs. During the month of January 2023, the
transactions below took place:
1. Starting the business with capital. A part of it at bank and the remaining
amount in Cash
2. Purchase of goods by cash
3. Bought goods on credit from Yvan.
4. Sales of goods on credit to MUSOZO
5. Cash sales.
6. Sales by cheque.
7. Returning goods to Yvan
8. Payment of accountant salary by cheque
9. MUSOZO returned goods to
10. Cash payment from Yvan for the total amount due from him. A discount
of 2% is received.
Required:
a) What are the type of accounts in which the transactions above
appear?b) List the whole accounts involved in the case study.
2.1. Creating charts of account names
Learning Activity 2.1
1. What is the meaning of charts of account?2. List the 2 uses of chart of account in accounting process
A Chart of Accounts is a list of financial accounts set up, usually use by
an accountant, an organization, and available for use by the bookkeeper for
recording transactions in the organization’s general ledger.
In QuickBooks, Chart of Accounts is a list of all the accounts that QuickBooks
uses to track financial information. These accounts are used to categorize your
transactions on everything from sales forms to reports to tax forms.
The Chart of Account allows to break down all the transactions that a business
made during a specific period into different subcategories.
By separating out the revenue, liabilities, assets, and business expenditures, a
chart of accounts enables to gain insight into the effectiveness of different areasof a business.
The following are the steps for creating Charts of Account in QuickBooks:• In the QuickBooks Home page, click on Charts of accounts
Figure 2.1 First step of Chart of Accounts Creation
If the option Other /None was chosen in setting company profile, on business
type select industry, the charts of account windows appear empty and this gives
a free space to the company account as you want.
It also gives the option to create a New Account by Clicking on Account asillustrated in the windows below:
Figure 2.2 Option of Creating New Chart of Account
• Click on Account and New
• Choose the type of account from the window below and click onContinue.
The types of account can be Income, Expenses, Equity, Liabilities, Assets,Bank, Loan, Credit cards, Other types of account.
Figure 2.3 Selection of Account Type
Depending on the nature of transaction, the user can select the type of accountthat can be affected by the double entry recording.
Example 1:
1. Starting the business with capital. A part of it at bank and the
remaining amount in cash.
This transaction affects Capital, bank and cash accounts. To create capital
account, classify it in equity type by ticking the Equity radio button, write the
name of account which is CAPITAL and click Continue. Follow the same
process for bank and cash account.
Some accounts have Sub Accounts. The user has to make sure that each
account created falls under the account type and Sub Account in which it
belongs to.
Create Sub-accounts QuickBooks lets the user create sub-accounts of other
accounts. This lets you track the details on about the account in more details
than a regular account offers. To add sub-accounts, do the following:
1. Go to the Chart of Accounts
2. Choose the account you want to make a sub-account and click the down
arrow next to Choose Edit account.
3. Edit the account and select the checkbox labeled Is sub-account.4. Choose the main account that it will be a sub-account of.
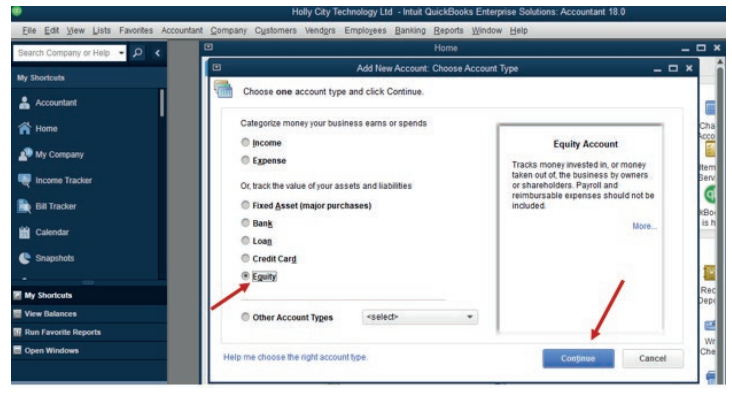
Figure 2.4 Equity Account is selected.
If there are other account found that do not fall into these types, there is an
option to search from Other Account Types which gives the types of accountbelow:
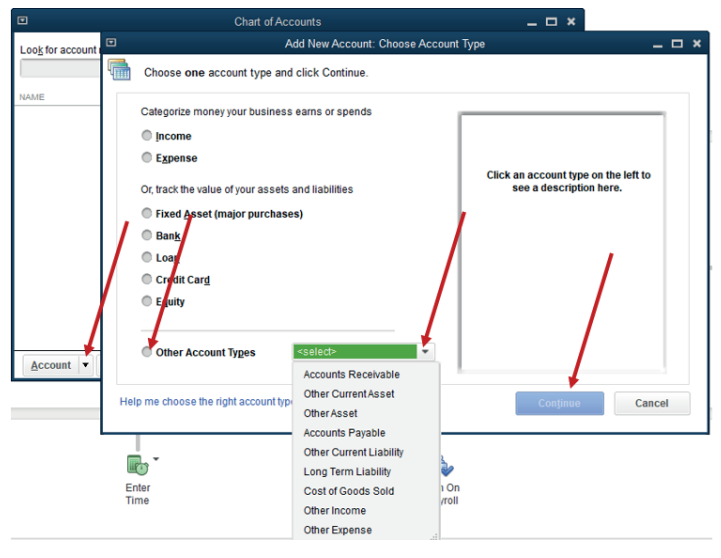
Figure 2.5 Selection of Account Type.
Example 2:
1. Discount received.
This transaction affects Discount received and creditor (account payable)
account.
These two accounts do not fall in the first account types. To create Chart of
Account, follow this procedure:
• From Other Account Type, select Other Income as account type
of discount received and Other Current Liability Account type forcreditor (account payable) then click Continue.
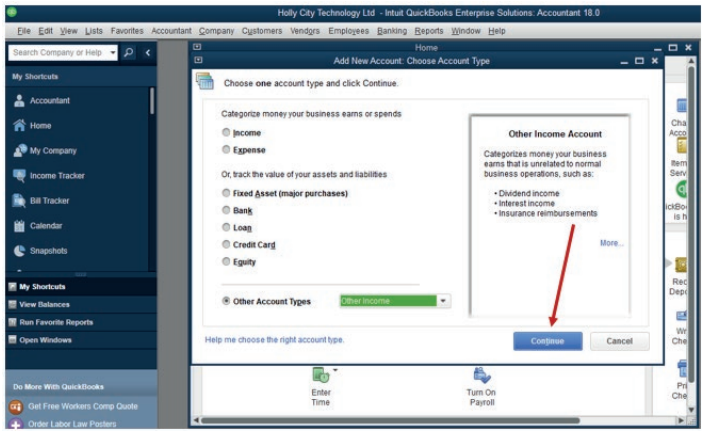
Figure 2.6 Interface of additional Income Account
Discount received is an Income type of account, Sub Account of Other income.
Creditor is an account payable type of account (Creditors), Sub Account of
Other current liabilities
• The other income account type appears then Account name field is
filled.
If it is the last account created, click Save & Close. But if there are moreaccount to add, click Save & New.
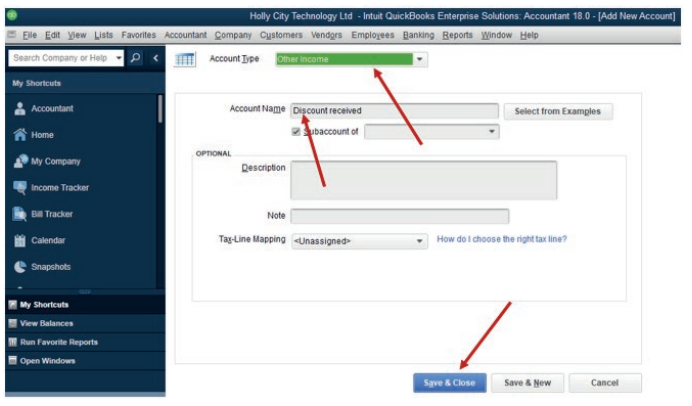
Figure 2.7 Saving New account type and New Account Name.
• Click Save & New.
Application Activity 1.3
1. Match the accounts with their corresponding account types
2. The transactions below have been extracted from the books of
BWAIZA CO.
a) Starting the business with cash in hand
b) Bought office equipment by cash
c) Purchase of goods by cash
d) Sales of goods by cheque
e) Credit sales to AKALIZA Queen
Prepare the charts of account
2.2. Changing the account namesLearning Activity 2.2
The QuickBooks user creates the Charts of Accounts for the business. It
may happen that some of the accounts created seem to be not necessary
or are duplicated.
• What can you do if you are a QuickBooks user and you find a
situation like that?
• What do you think will be the dangers of keeping the unnecessaryaccounts in the business file?
If the user finds that some chats of account name have to be changed, he can
do the following:• Click on Charts of Account on QuickBooks Home page
The list of account appears, and the user make a right click on the account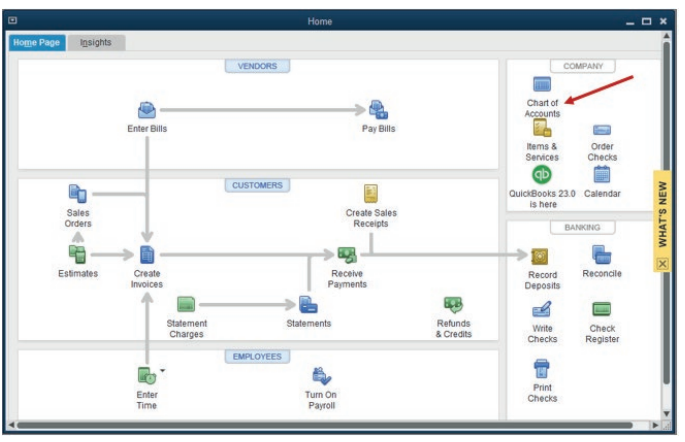
whose name is to be changed
The user will find the following windows and the account name to be changed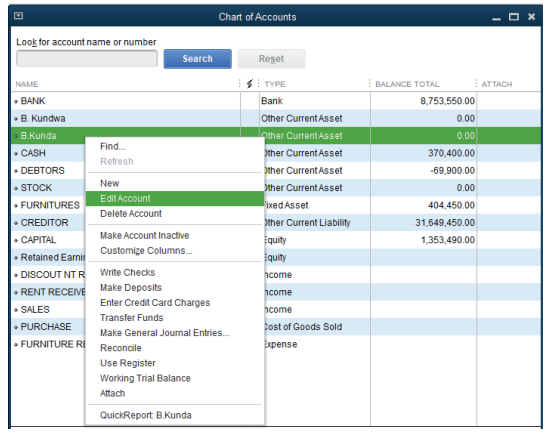
appears as here below with an option to fill the other names, account type, subaccount if any and opening balance.
In the window above B.Kunda is changed and it is replaced by Rukundo, the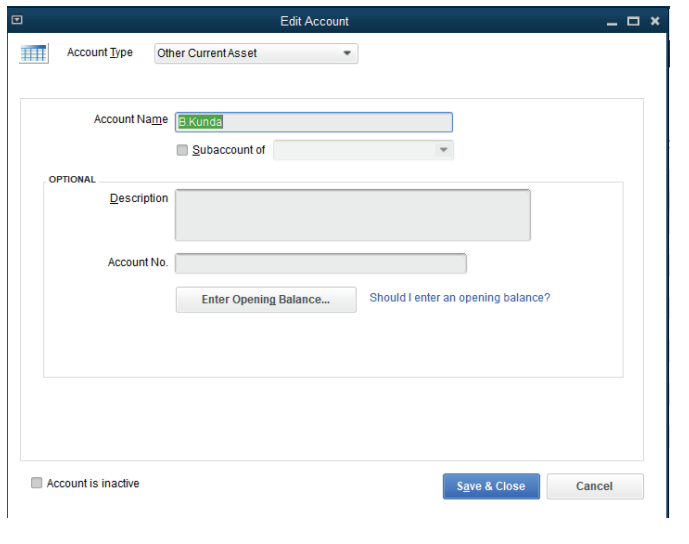
sub account and opening balance is added. It finally appears as in the followingwindow:
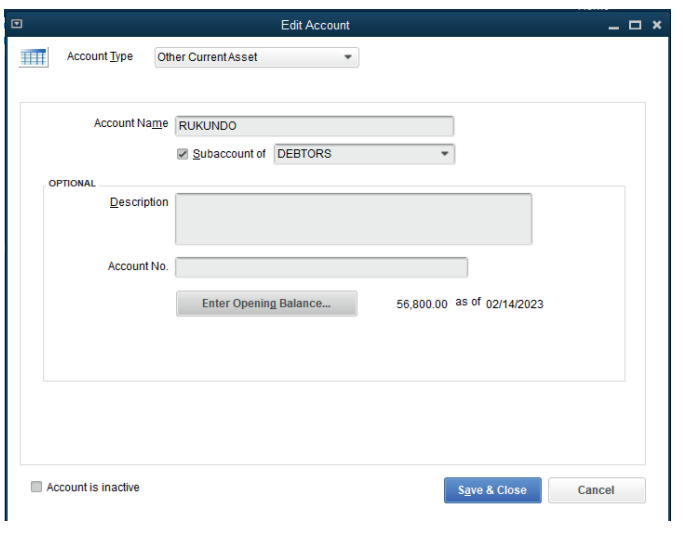
• Click on Save & Close.
Application activity 2.2.
MUKAMURIGO, the accountant of MARANATHA CHURCH uses QuickBooks
in her daily activities. In the beginning, she created the following charts of
accounts: Cash, Bank, Sales< Capital, Purchase<, CUSTOMERS, Rent,
Purchase2, Stock and William. She finally finds that some of the accounts
are duplicated and William account is not necessary.
Replace the duplicated accounts by salary account and change Williamaccount in to Willy Account
2.3. Deleting and making inactive unnecessary accounts
Learning activity 2.3.
The following transactions have been extracted from the file of MUGEMANA
TRADING Ltd
a) Capital: cash and bank
b) Purchase of goods on credit from supplier
c) Sales of goods by cash
d) Returning defective goods to Martin
e) Payment to martin the remaining amount by cheque. 2.5 % Cash
discount received
Below are the charts of accounts prepared by the former accountant:
– Cash
– Bank
– Purchase salary expenses
– Bank overdraft
– Drawings account
– Payables
You are hired as a new accountant. Do you agree that all of these accountsare necessary? If not, remove the unnecessary accounts.
To delete an account, the following steps have to be done:
1. Click on Accountant on menu bar2. Click on Charts of Account
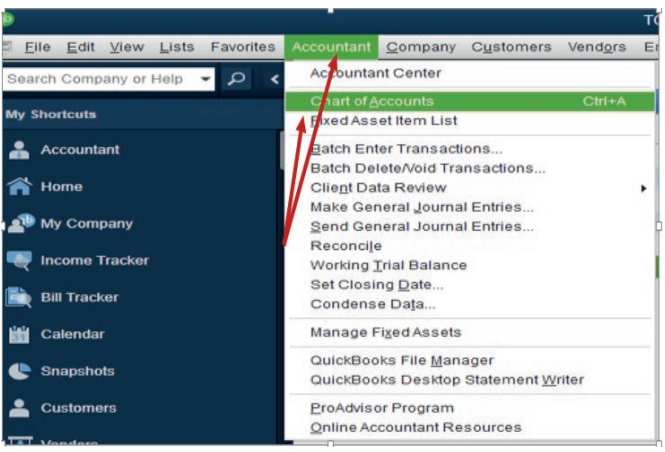
Figure 2.9. Search for an account
3. Find the account to be deleted
4. Here, opening balance Equity account is not necessary. Right click onthe account to delete or to make it inactive
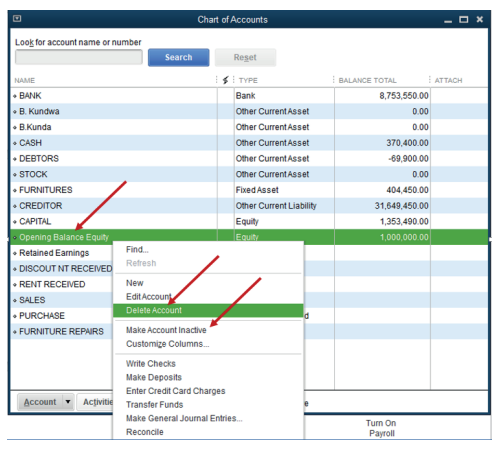
Figure 2.9 Deleting or making Account Inactive unnecessary account.
Delete an account or Click on Make Account Inactive
Once an account is made inactive. It will no longer appear in list of charts of
account.
• Click OK when asked if the user wants to delete or to make an account
inactive.
Once you delete an account, it will be removed in the Chart of Accounts.
The good thing is, you can filter the COA page to include inactive or deletedaccounts.
Application Activity 2.3.
1. What are two reasons for deleting or making an account inactive?
2. Illustrate the process through which an account is deleted.
3. The following transactions have been extracted from the books of
Ganza Ltd:
a. 1/6/2020: Starting the business cash in hand
b. 4/6/2020: purchase of goods on credit from Kundwa
c. 6/6/2020: Sales of goods by cheque
The list of accounts below has been found in charts of account:
– Discount received
– Sales
– Account receivable
– Capital
– Bank
– Cash
– PurchaseRequired: Delete the unnecessary accounts if any.
2.4. Adjustment of account
Learning Activity 2.4.
The accountant of FRESH JUICE Ltd prepared the end of the year final
accounts before adjusting company accounts. During the next period,
the auditors advised her to deal with some accruals and prepayments for
reporting true and fair information.
What are the business account to be adjusted before preparing end ofperiod reports?
At the end of the accounting period, business account has to be adjusted
before preparing the financial statements. Account adjustments, also known
as adjusting entries, are entries that are made in the general journal at the end
of an accounting period to bring account balances up-to-date. Unlike entries
made to the general journal that are a result of business transactions, accountadjustments are a result of internal events.
2.4.1. Assets
Due to various reasons, the business fixed assets loose value through the years.
It is called depreciation. Before preparing the statement of financial position of
any business entity, the accumulated depreciation of any fixed asset must be
subtracted from its original cost so that the net value to report in balance sheet
will be true and fair.
The debtors are also business current asset that are adjusted in case of bad and
doubtful debts. Therefore, the business/firm should write the debtors account
off from the accounts and thus it becomes an expense that should be charged
in the profit & loss account. In practice a firm may also be unable to collect all
the amounts due from debtors. This is because a section of the debtors will nothonor their obligations.
2.4.2. Expenses A.
Accrued Expenses
An accrued expense is an expense that is payable or due for payment but has
not yet been paid during that period. An accrued expense should be charged in
the P&L account and shown in the balance sheet as a current liability. In quick
books, it is a liability account and it is recorded as follow:
Debit: expense account or P&L account
Credit: accrued expenseExample: Accrued salary: 10000Rwf

Figure 2.10 Record of accrued expense
It means that the accrued salary is added on the current salary of the period.
Therefore, it is charger on P&L account and it will appear in balance sheet under
a current liability
B. Prepaid Expenses
A prepaid expense is an expense that is not payable but cash has already been
paid. A prepaid expense should not be charged in the P&L a/c but should be
carried forward to the next financial period and should be shown in the balance
sheet as a current asset. In QuickBooks, prepaid expense is another current
asset account and recorded as follow:
Debit a prepaid expense account
Credit the expense for decreasing its valueExample: Prepaid rent: FRW 10,000
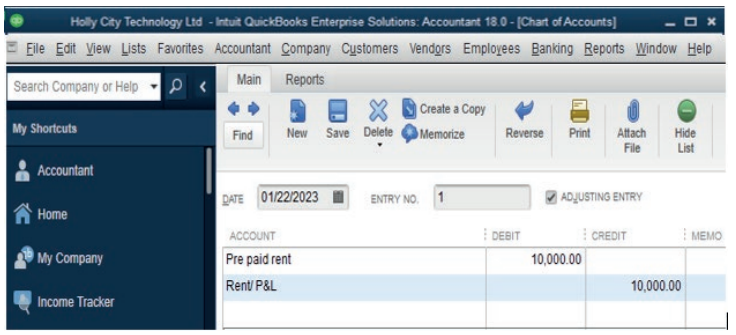
Figure 2.11. Record of prepaid expenses
2.4.3. Income
A. Prepaid Income
This is income that is not yet due but cash has been received for it. This happen
when an income is payable in advance it can be called also the Unearned
revenue. e.g. Rent payable 3 months in advance. A prepaid income should not
be reported in the current financial period but should be carried forward and
reported in the period it relates to as a current liability. In quick books, prepaid
income is another current liability account and it is recorded as follow:
Debit the other income in P&L accountCredit the prepaid income account
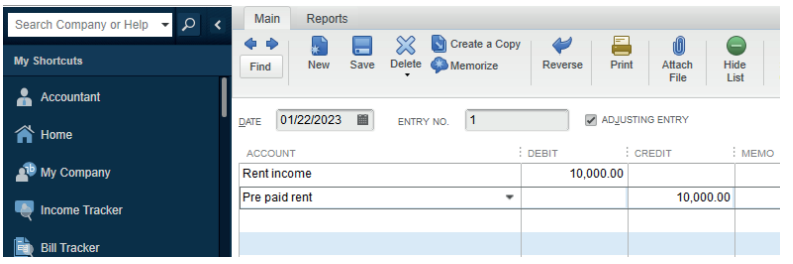
Figure 2.13. Record of prepaid Income
B. Accrued Income
This is income that relates to the current year but cash has not yet been received.
An accrued income should be reported in the profit & loss account and the
same income will be shown in the balance sheet as a current asset. In quick
books, it is another current asset account and it is recorded as follows:
Debit accrued income
Credit the P&L account on that income accountExample: Accrued rent income of FRW 10,000
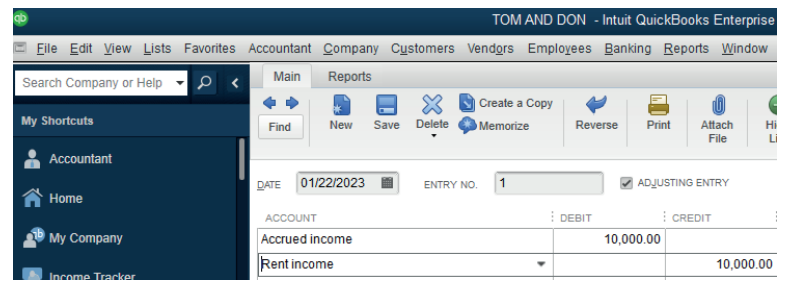
Figure 2.14 Record of accrued income
The assets (fixed and current) and liabilities are the quick books accounts that
have to be adjusted depending on business transactions that are taking placeduring the period.
Application Activity 2.4.
1. True or false
a) Prepaid expense is a current liability account
b) Accrued income should be shown in the balance sheet as a current
liability.
c) A prepaid income should reported in the period it relates to as a
current liability.
2. The adjusting entry that reduces the balance in prepaid insurance will
also include which of the following:
a) A credit to cash
b) A credit to insurance expense
c) A debit to insurance expense
3. KALISA owns and operates a dry cleaner. The following occurred
during the period of January:
a) Prepaid rent for January and February
b) Purchase of insurance in January that will six months
c) Paid salary of his assistant for the last two monthsRequired: Prepare the chart accounts for the above information.
2.5. Owner withdrawals and investments
Activity 2.5
Mrs. Agatha is a sole trader in GAKENKE District. She invested her money in
auditing and consultancy activities. For getting the capital she used to save
for 5 years and finally she got FRW 6,000,000 which she deposited at
bank. During the first month of activities, she withdrawn FRW 120,000 from
business bank account for private use.
• You are to advise her on the chart of account she can create for
recording the transactions in quick books
• Show her the process she will pass through to keep the transactionin the system.
2.5.1 Owners investments
Owner investment, also called contributed capital, is the amount of assets that
the owner puts into the company. In other words, this is the amount of money
or other assets that the owner contributes to the business either to start it or to
keep it running.
In quick books, an owner’s capital account is the equity account listed in
the balance sheet of a business. It represents the net ownership interests of
investors in a business
How to Record an owner’s investment in Quick books?
For recording owner’s initial investments (capital),
Capital account is debited
Cash /Bank account is credited
In case of re-investment for keeping the business running, the same entry will
be done or
Debit the Capital accountCredit any source of re-investment
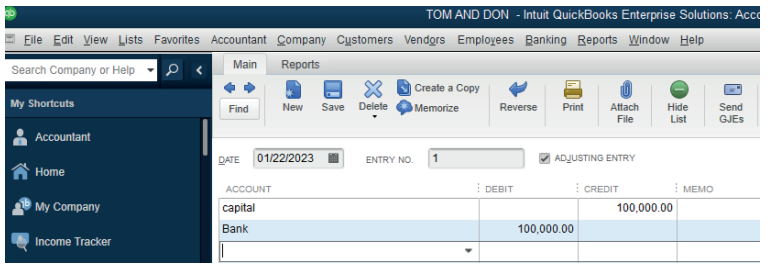
Figure 2. 15 owner’s investment record
2.5.2. Owners’ withdrawals
“Owner Withdrawals,” or “Owner Draws,” in quick books is a contra-equity
account. This means that it is reported in the equity section of the balance sheet,
but its normal balance is the opposite of a regular equity account. Because a
normal equity account has a credit balance, the withdrawal account has a debitbalance.
Withdrawal of any amount in cash or kind from the enterprise for personal use
by the proprietor is termed as Drawings. The Drawings account will be debited
and the cash or goods withdrawn will be credited.Example: Cash withdrawn from bank for personal use: 10,000Rwf
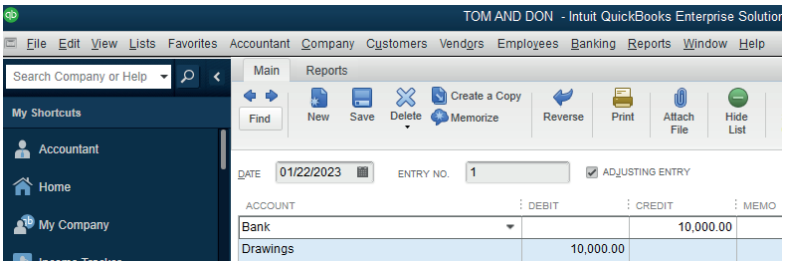
Figure 2.16 Drawings record
Application Activity 2.5.
1. Define the following concepts:
• Investment
• Owners’ equity
• Drawings
2. How can this transaction be recorded using quick books:Drawings of goods valued at 10,000RFW
2.6. Transfer of net income to the owner’s capital account.
Learning Activity 2.6.
BIGIRIMANA is the owner of BEST ELECTRONIC TRADING Ltd. He started
this company with the capital acquired from his saving with the loan got from
BANK OF KIGALI. During the year of business operations, he concluded
some transactions including drawings. At the end of the year, he prepared the
statement of profit or loss which shown that the business has a net income of
7,500,000Rwf.
Required:
• What do you thing is the drawings?
• Assume that you are BIGIRIMANA, what can you do with this netincome for the year?
2.6.1. Net income
Net income refers to the amount an individual or business makes after deducting
costs, allowances and taxes. In commerce, net income is what the business has
left over after all expenses, including salary and wages, cost of goods or raw
material and taxes. Net income shows how much money a company is making
after subtracting all expenses. It can also be referred to as “net profit” or “the
bottom line.”
As part of the closing entry process, the net income is moved into retained
earnings on the balance sheet. The assumption is that all income from the
company in one year is held onto for future use. Any funds that are not heldonto incur an expense that reduces net income.
2.6.2. Owners’ capital account
A capital account is used in accounting to record individual ownership rights
of the owners of a company. The capital account is recorded on the balance
sheet and is composed of the following items: Owner’s capital contributions
made when creating the company or following the creation, as required by the
business.
Basically, the owner’s capital account represents the net assets of the company.
It’s the amount of money left over after the company sells all of its assets and
pays off all of its creditors. This remaining amount of money is what the owner
actually owns or networth.
Owner’s capital account is one of the accounts of equity type of account
which consists of:
Capital
Less: Drawings
Add: Profit in case of positive net income of business or
Less Loss in case of negative net income of the business
Quick books software will transfer the net income (profit or loss) of the business
for the period from the trading, profit or loss account to the statement of financial
position (balance sheet) automatically in its equity section.
Example:
Here under, TOM AND DON business Net Income of the period is FRW30,781,500.
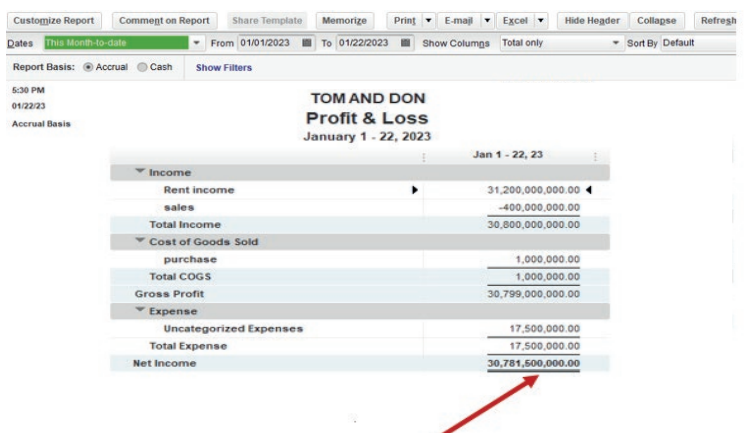
Figure 2.17 Net income to be transferred in balance sheet
This Net Income is transferred to the equity section of TOM AND DON Balancesheet as shown here under:
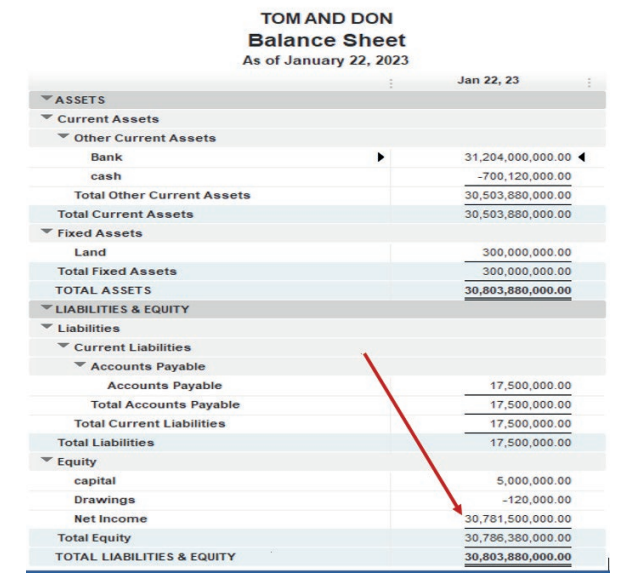
Figure 2.18 use Net Income in Balance sheet
Application Activity 2.6.
1. Define the following concepts:
a) Net income
b) Owners’ capital
2. BLESSED WORK LTD is a small sole trade business of purchasing
and selling of electronics items. It is located in MUHIMA sector,
NYARUGENGE District in KIGALI CITY (Tel +2507884324 -234712;
P.O Box 1213 Kigali. The owner decides to hire you knowing that you are
skilled in computerized accounting for preparing financial statements on
time.
The following past information is provided:
a. On 1st February, 2020: Starting business with RWF 10,000,000cash
and RWF 50,000,000 at bank.
b. 2nd February, 2020: Receiving a loan from Bk of RWF 70,000,000
8th February, 2020: Bought furniture for RWF 12,000,000 and paying
by cheque
c. 10th February, 2020: Purchasing goods on credit from TU` for RWF
4,000,000, cash purchase of FRW 2,500,000 and FRW 1,500,000 by
cheque.
d. 11th February, 2020: credit sales to KANYENGOGA for RWF 3,600,000,
cash sales of FRW 4,350,000 and sales by cheque of FRW 8,500,000.
e. Returns to TUBYIHERERANE FRW 500,000
f. Cash drawings: FRW100,000
g. 12th February, 2020: Paid rent of FRW 450,000 by cheque
12th February, 2020: FRW 1,750,000 Paid
to TUBYIHERERANE by cash. A discount of 7.5% is received.
h. 12th February, KANYENGOGA paid FRW 723,500 by cheque. A
discount of FWR 27,500 is allowed to him.
i. KANYENGOGA retuned goods valued at FRW245,000
j. 15th February, the following transactions took place:
a) Paid wages by cash of 250,500 FRW
b) The insurance is paid by cheque 740,000 FRW
c) Rent received by cheque is 90,450FRWShow the income statement transferred in the balance sheet.
End of Unit Assessment
1. MUGENI has the following items in her balance sheet as on 30 June
2021. Capital FRW 41,800, Creditors FRW 3,200, Fixtures FRW
7,000, Motor Vehicles FRW 8,400, Stock of goods FRW 9,900,
Debtors FRW 6,560, Cash at bank FRW 12,900 and Cash in hand
FRW 240
During the first week of July 2021 the below transactions took place:
b) He bought extra stock of goods FRW 1,540 on credit.
c) One of the debtors paid him FRW 560 in cash.
d) He bought extra fixture by cheque FRW 2,000.Prepare the charts of account
UNIT3: RECEIVING ITEMS AND ENTERING
Key unit competence: Prepare the bill by entering all goods/
services received on the appropriate dateusing QUICKBOOKS
Introductory Activity
Any business activity is intended to make a profit; this requires the sales of goods
or services. Somme businesses purchase goods and resale them without any
transformation. Other businesses transform raw material into finished goods.
For any business, goods or items received from different vendors have to be
recorded with reference to the vendor bills for payment process.
On the other side, other goods or services are sold to customers. For correcting
payment, the invoices are issued and sent to the customers. Payment in all
means are allowed and always recorded in appropriate books of account.
Required:
1) Discuss the purchase and sales of business goods and services2) Enter the business items, vendors and customers in the QuickBooks
3.1. Receiving items
Learning Activity 3.1.
NEW LIFE restaurant started it activities in January 2022. It provides services to
a number of customers in the village. Its owner explained to the new accountant
that the business record includes both services and products especially in
case of recording items received and entering the bills.
Assume that you are the new accountant of NEW LIFE restaurant,
• How will differentiate services from products
• Suggest the characteristics of list of items that will be recoded in yoursystem
3.1.1. Enter the vendor’s name
In the context of accounts payable, a vendor is a person or business that supplies
goods or services to the company. Another term for vendor is supplier. The term
vendor can also be used to mean any seller of goods.
To create a vender name in QuickBooks, Follow these steps:
Click on vendor icon on QuickBooks Home page for finding and clicking onVENDOR.
A click on VENDOR will give the following window and the user click automatically
on New Vendor
A click on New vendor will allow to the user to get a field to fill the new vendor
names address and all other identification and OK

3.1.2. Enter the item list
In QuickBooks, items are the products and services a business buys and sells.
Users enter and track items in QuickBooks so they can quickly add them toinvoices and other sales forms. Items appear as lines on sales forms.
Each unique item gets a line with its name, description, quantity, and cost per
item. Items allow you to use Quantity, to track cost and/or price and even for
that same one thing as both.
When the user chooses to use Items in QuickBooks, the items entered will be
linked to specific accounts. These accounts are visible by looking at the “Chart
of Accounts” in QuickBooks interface. If you have multiple items that need to
be attached to a single job, it is possible to do so with QuickBooks. Simply link
the item to the appropriate account when you enter it in. Then all of the items for
that job will be visible when you run a report.
Example
Cooperative DUTERIMBERE is operating in NYAMIRAMA market. It uses to
buy and sell agricultural products including rice, beans, maize, and sorghum.
To make the list of these items in QuickBooks will be done through the processbelow:
Click on item list &services at the right side of home page of QuickBooks
Figure 3.1 Items and Services icon usage
The items list appears as follow with an option to add new item by clicking onitem menu at the left bottom command of items list window and New.
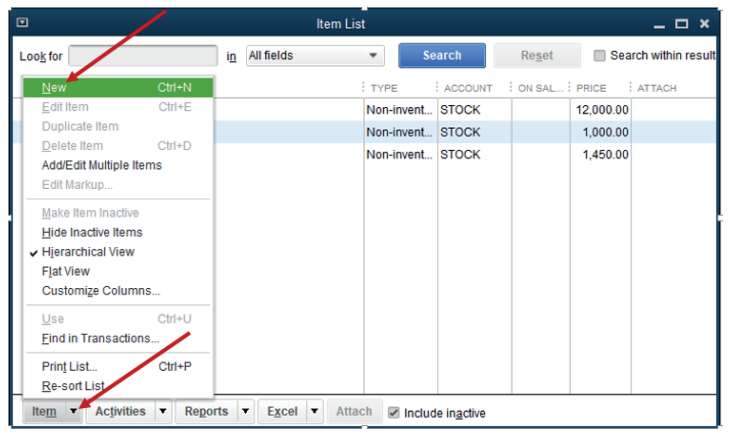
Figure 3.2 Creation of new Item on the list
Choose whether it is an item list of products or services. Here under, it is a list
of products (Non inventory part), item number, there is also an option to add the
item name in description field and the price per unit, then the account related tothe item. Before clicking Ok, make sure the item is active.
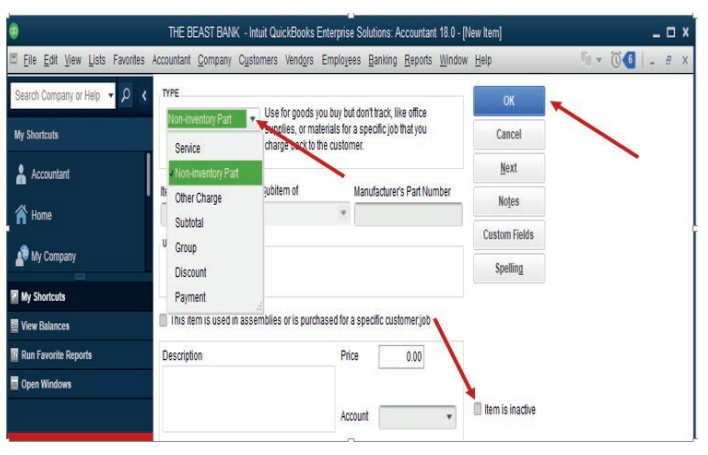
Figure 3.3 Type of products or Services activation
The item list is created and the QuickBooks displays it as here under:
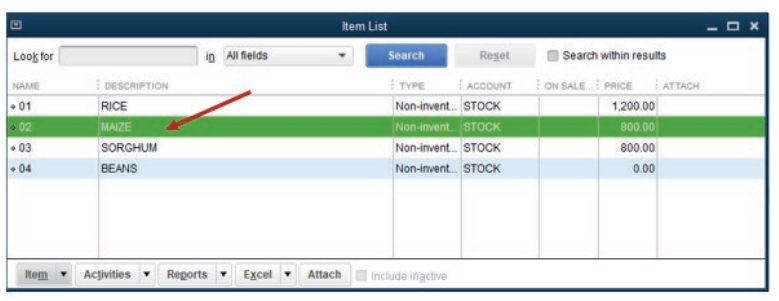
Figure 3.4 List of created items
These items should be either linked to the vendors or the customers as the
cooperative buy and sell them. If some items are linked to the customers, it
means that the cooperative sells the by cash or cheques and on credit basis.
The credit sales are always associated with the debtors (Account receivable),and it is necessary to enter the bill for payment.
Application Activity 3.1.
The following transactions have been extracted from the books of
DUKUNDANE Ltd:
1/6/2015: Starting the business with 5,000,000 FRW cash and 10,000,000
FRW at bank
4/6/2015: purchase of tables and Chairs on credit valued at 12,000,000
FRW, from TUYISENGE
6/6/2015: Sales of goods by cash valued at 7,000,000 FRW
8/6/2016: Remaining goods returned to TUYISENGE
10/6/2016: Payment to TUYISENGE by cheque
• Enter the vendor name• Record the received items
3.2. Enter bill
Learning Activity 3.2.
If purchase transaction is concluded on credit basis, both the seller and the
keep the invoice that details goods or services purchased and sold so that
the transaction should be recorded in business system. How do you thingQuickBooks is used to enter the bill?
Learning Activity 3.2.
The word “bill” designates an accounting document that outlines the amount
a customer has to pay for a product or service that is purchased. It is also
considered as a payment reminder. A bill is issued before the payment is sent,
and it is used one-time and immediately
A bill is an invoice that one of business suppliers will give to the business,
and which, sooner or later, business will have to pay. It might also hear as a‘purchase invoice’ or a ‘supplier invoice.
3.2.1. The steps of entering the bills
For interring the bill, follow the process below:Start by clicking on Enter Bills tool on the QuickBooks home page.
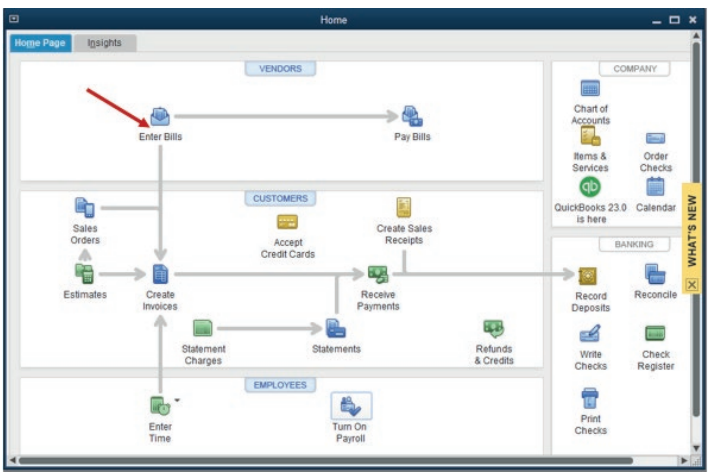
Figure 3.5 Start entering the bill
The bill menu that will give the option to select the vendor to whom the bill is
from. In case there is no vendor list or a there is a need to record a bill from a
new vendor, the user can add new.
3.2.2. Choose the Vendor and the Items relating to the vendorto be paid

Figure 3.6 Add the vendor name
Assume that the bill is from vendor Annet. Annet is selected. It is time to additems supplied by Annet.
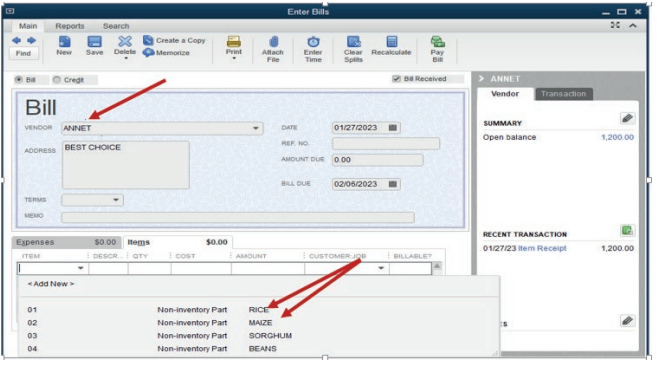
Figure 3.7 selection of items relating to the vendor
Select the item. If there is a missing item on the list, add it through
Add new then Save&Close or Save &New in case Annet’s bill consists of more
than one item. For our case, Annet’s bill consists of rice and maize.
3.2.3. Pay the bill for received items
The business uses to purchase goods or services from different vendors. Being
either credit purchase or cash, the transaction is concluded when the paymentis over. For the above-mentioned case, the bill as paid as follow:
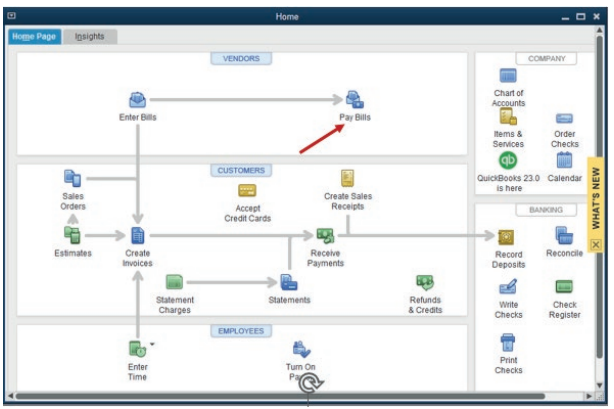
Figure 3.8. Starting Bill Payment process
Annet’s bill will automatically appear, but any total amount will be available on
the bill until all bills are selected. Here under, bills are no selected and Payselected bill is inactive.
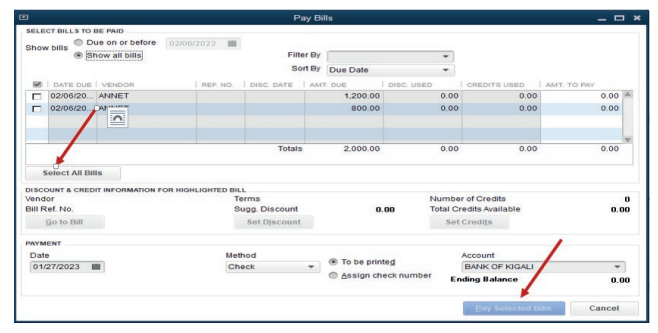
Figure 3.9. Selection of items to be paid
This is Annet’s bill after selecting all bills:
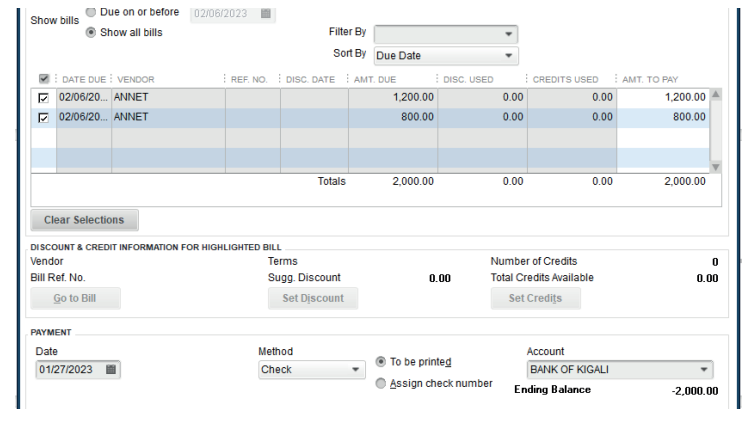
Figure 3.10 Selection of all Bill to be paid
The total amount to pay is 2,000 FRW. There is no discount and the payment
mode is by cheque. It is time to click on Pay selected Bills. A proof of paymentappears as follow:
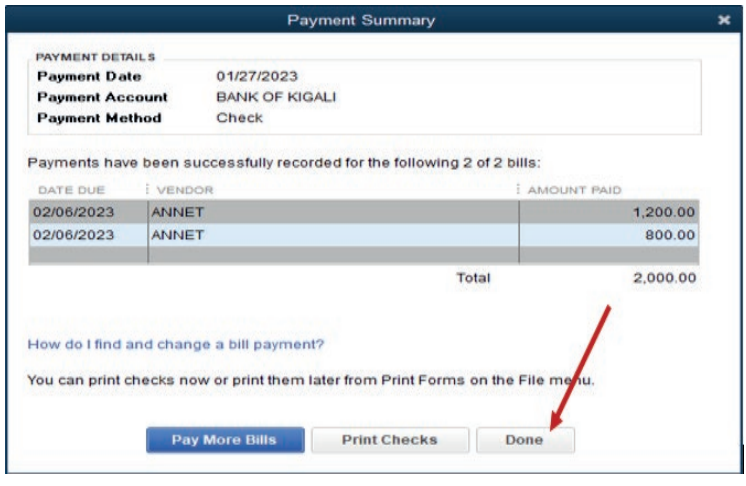
Figure 3.11. Proof of Payment
Click on Print checks if it is necessary to give a hard copy cheque to payee orClick on done for ending the process.
3.2.4. Recording the bills payment
If the payment to the vendor should be done either by cash, bank or cards.
To record the payment, the general journal is used by debiting the vendor’saccount and crediting the source of payment. (Cash, card or bank account.)
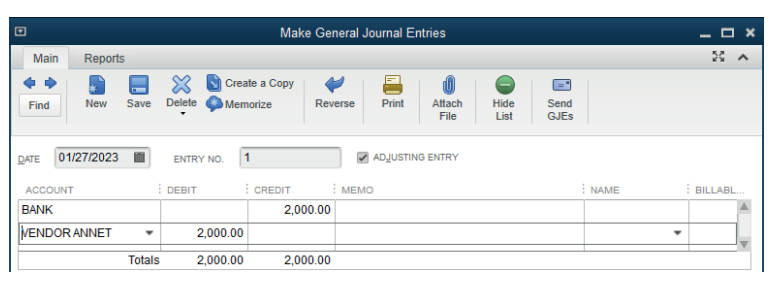
3.2.4. Recording the bills payment
If the payment to the vendor should be done either by cash, bank or cards.
To record the payment, the general journal is used by debiting the vendor’saccount and crediting the source of payment. (Cash, card or bank account.)

End of Unit Assessment
1. Differentiate:
a) Vendor from a customer
b) Order from invoice
2. Mrs. Alex, the owner of BEST ELECTRONIC Ltd stated the business inJanuary 2020. He purchases the items bellow:
SAMSUNG 250 is Alexis’ supplier of computer and telephones while RWIZA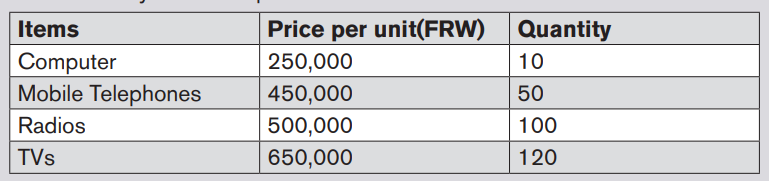
Ltd supplies Computers and TVs. Vision 2050 is a customer of both Radios
and TVs. You are hired as an accountant of BEST ALECTRONCS and the
company uses QuickBooks in preparation of its reports.
Required:
1) Create the list of items
2) Enter the vendors
3) Prepare the bills for received items4) Record the payments to the vendors
UNIT4: SALES AND RECEIVABLES
Key unit competence: Apply the rules of cash, cheques, credit
sales and account receivable transactionsin QUICKBOOKS
Introductory Activity
The management committee of MUTARA ENTERPRISE is experiencing a
low level of return on its investment. It decided to use QuickBooks software
especially while dealing with sales of its products. MUTARA ENTERPRISE
customers are allowed to pay by all means (Cash, cheque and cards). Some
other customers use to pay after a certain period as they buy on credit.
NTAGANDA is the accountant and wants you to assist him in recording both
(credit and cash/bank), sale transactions.
Show him the way appropriate record of credit and cash/bank transaction in
QuickBooks to improve the company current situation and start to get a highlevel of return on investment.
4.1 Credit sales transactions
Learning Activity 3.2.
DUFATANYE SOTRE is engaged in sales of fruit and vegetables in KIMISAGARA
market. The customers in the morning purchase on credit for paying in the
evening after selling.
• Advise the DUFATANYE SOTRE on the ways of recording its daily
sales
• If they DUFATANYE SOTRE needs to use QuickBooks in recording,explain to its accountant the steps of creating a sales invoice
The term “credit sales” refers to a transfer of ownership of goods and services
to a customer in which the amount owed will be paid at a later date. In other
words, credit sales are those purchases made by the customers who do notrender payment in full at the time of purchase.
Credit sales are a type of sales in which companies sell goods to the customer
on credit based on the credibility of customers. It gives the customer time to
make the payment after selling the purchased goods and does not require them
to invest their own money into a business. It helps small businesses, especially
those that do not have enough capital. At the same, it helps big companies also
because it attracts customers.
A credit sales transaction affects two accounts: Debtor (account receivables)
which is debited as it is a current asset and the sales account which is creditedas it is an income.
4.1.1. Record a credit sale
In QuickBooks, a credit sales transaction is recorded as here under:
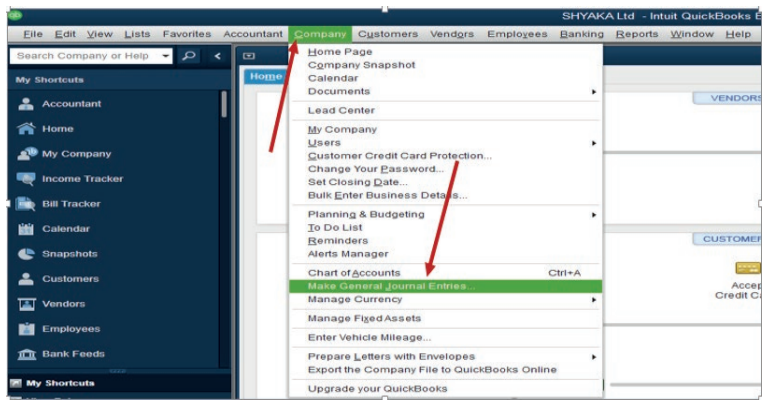
Step 1. Click on company menu on QuickBooks home page, then select MakeGeneral Journal Entries
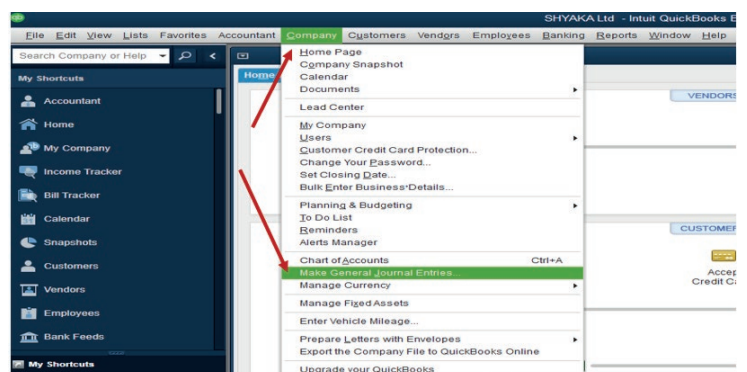
Figure 4.1 General Journal Entries selection
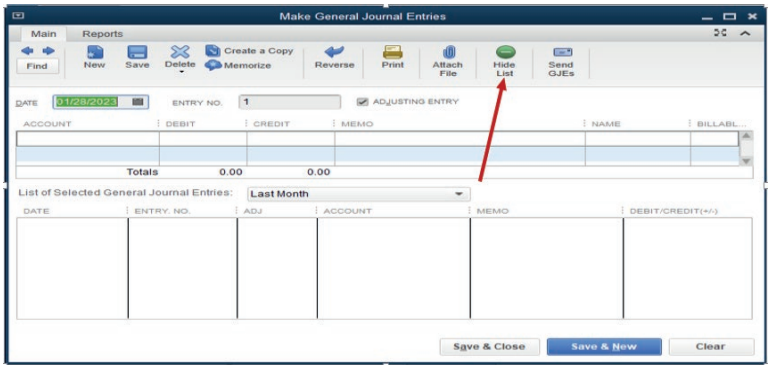
Step2. Complete the general journal
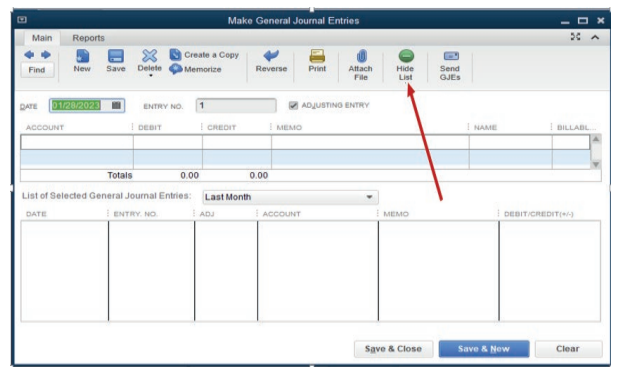
Figure 4.2 Option of hiding list of selected General Journal Entries
The first part of the window is for double entry and the bottom part shows the
number of transactions concluded. For having a clear space for recording, the
bottom part should be hidden by clicking Hide List
Example: SHYAKA Ltd started its business activities in January 2022. During
January the sales transactions concluded with all of its debtors is valued at
FRW 125,000. To record this transaction in the general journal, of course the
debtors and sales account are already created in the chart of account. If not
QuickBooks gives an option to add new account while recording.
Debit debtors: 125,000Credit sales: 125,000
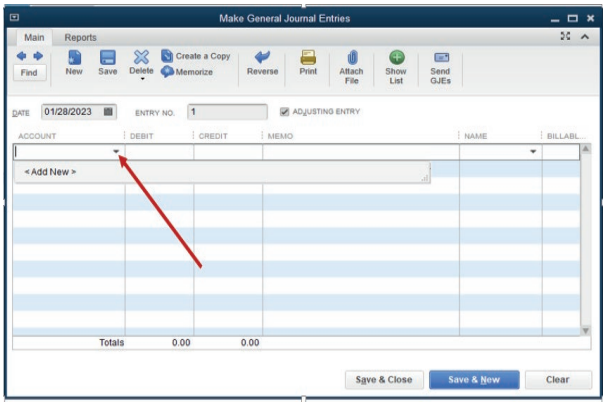
Figure 4.3 Empty General Journal Entries
As there is no debtors and sales accounts created in chart of account, we
can add them by the normal way of account creation, account type, continue,
account name then Save&Close or Save&New. Through this, a debtor
account is created and debited with FRW 125,000. Sales account is createdand credited with the equivalent amount.
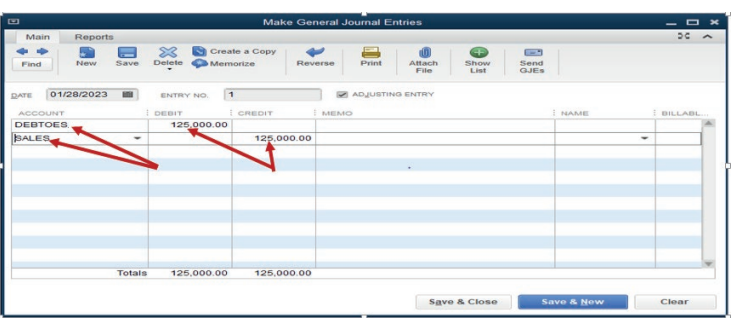
Figure 4.4 .Records of credit sales
In case there is specific customer name, it can be added on the name columnfor clarifying who is the debtor.
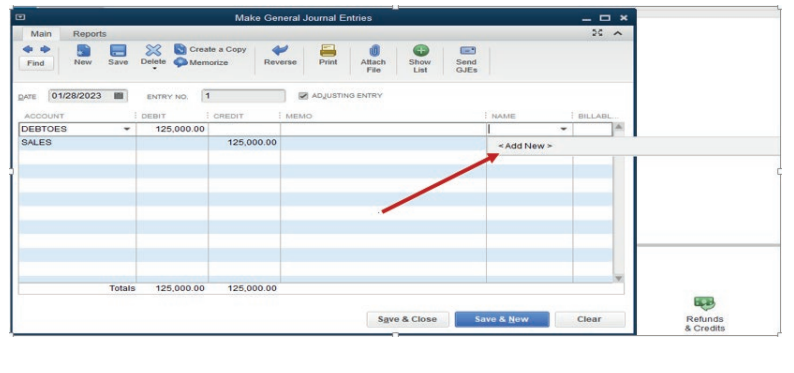
Figure 4.5 created Field for adding customer name
If we click on Add New QuickBooks provides field to add customer name.
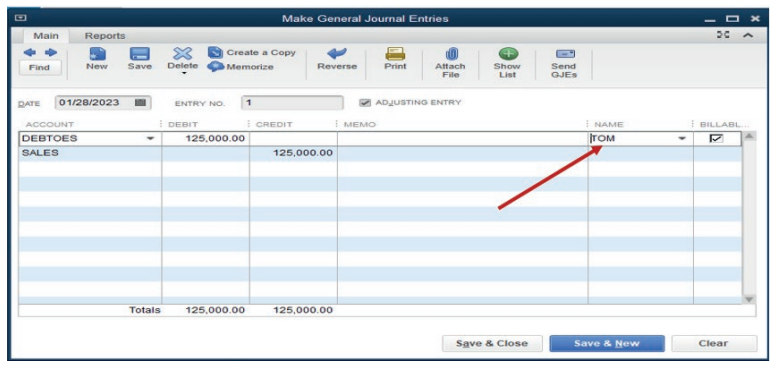
Figure 4.6 recording a sale transaction
A sale transaction is recorded, then Save &Close
4.1.2. Creating a sales (customer) invoice
A Customer invoice is an accounting document sent by seller of goods/services
to a buyer. It records services rendered, items provided, the amount owed by
the customer, and how they can make payment.
Invoices create legally binding agreements between business and buyers,
especially for larger purchases. This type of customer invoice is created based
on a sales order, which includes order lines and item numbers.
Sales order
This is a document hold by the business from its customer ordering the business
to supply determined goods or services.
For our case, the cooperative has on order from a customer KAMBALE whoordered two items: Beans and sorghum.
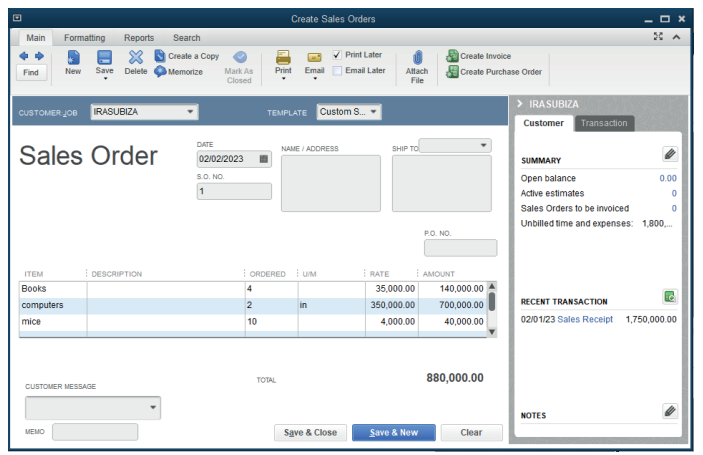
Figure 3.13 Sales order Document
It is a responsibility of the business to create an invoice to its customer for
detailing goods or services that the customer ordered, the business is to deliver
(or delivered) for getting customer know exactly how much she/he owes the
business. The invoice is created through this process by starting on QuickBooks
home page,Click on Create Invoice
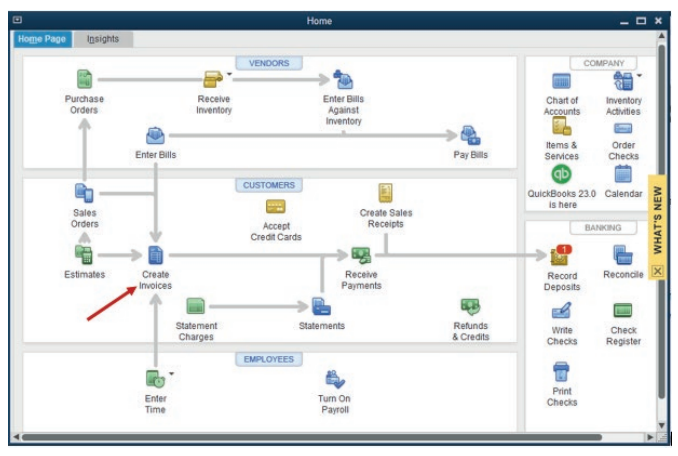
Figure 3.14 icon used in invoice creation
Then a customer invoice window appears as below:
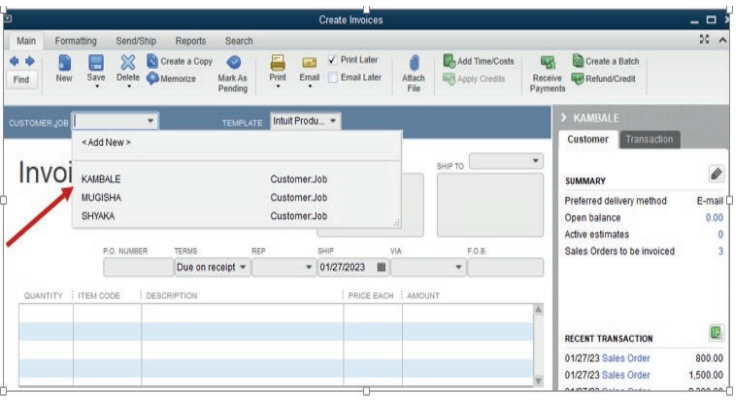
Figure 3.15 list of invoices created
The invoice goes to customer KAMBALE. So, the user selects KAMBALE from
the list of customers. The invoice consists the following:
The invoice number
Terms of payment
Date and details of goods supplied.Click Save &Close.
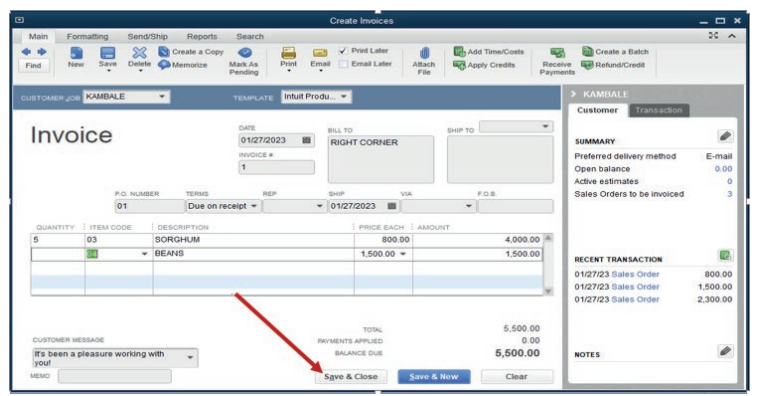
Figure 3.16 Saving an invoice created
Application Activity 4.1.
1. Define a transaction
2. What is a credit sales?
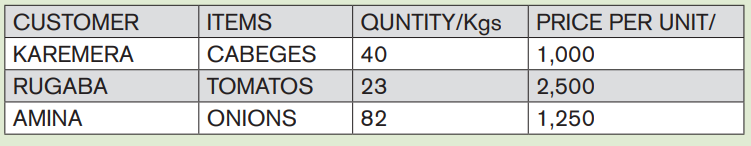
3. Record the transaction below and display the sales invoice to thecustomer KAREMERA
Learning Activity 4.2.
The financial success of a business depends on selling goods or services
to customers, or clients. The more goods or services sold, the more income
the business makes. There are a number of different ways that customers
pay for goods and services sold to them. Sometimes payment is received
immediately and sometimes payment is received later. In the trading
Industry, customers or clients pay for goods and services and the like. These
transactions require the use of cash. Cash means the form of payment the
customer uses such as notes and coins, checks, debit or credit cards and
cheques.
1. Discuss the cash transaction effects on business account2. How this transaction is recorded in QuickBooks?
4.2. Cash/ cheque sales transactions
A cash sale is a business transaction in which the buyer pays for goods or
services at the time of the purchase. In a cash sale, payment is immediate. How
the buyer pays doesn’t matter, as long as there is a transfer of monies. It can
be: Cash: The buyer counts the bills and coins and hands it over to the seller. It
can be the cheque or payment cards for transferring money from the customer
account to the seller’s account.
A cash sales transaction affects two accounts: Cash /bank which is debited asit is a current asset and the sales account which is credited as it is an income.
4.2.1. Record a cash sale
In QuickBooks, a cash sales transaction is recorded as here under:
Step 1. Click on company menu on QuickBooks home page, then select MakeGeneral Journal Entries.
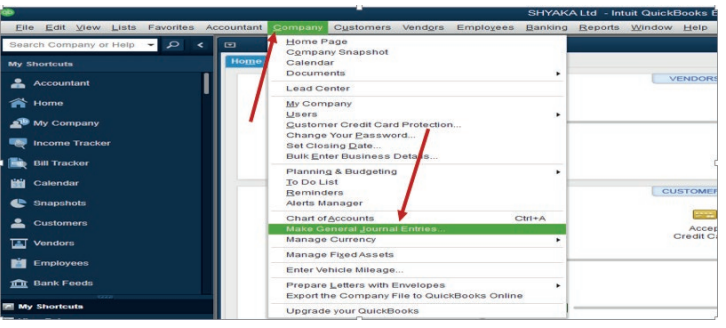
Figure 4.10 Make General Journal Entries
Step2. Complete the general journal
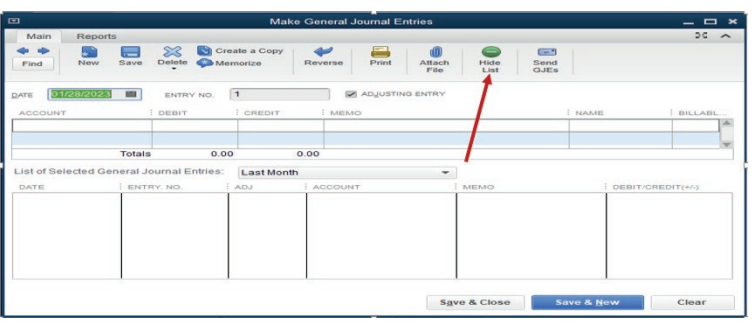
Figure 4.11. General journal to use for recording
The first part of the window is for double entry and the bottom part shows the
number of transactions concluded. For having a clear field for recording, thebottom part should be hidden by clicking Hide List
Example:
SHYAKA Ltd started its business activities in January 2022. During January the
cash and cheques sales transactions concluded with all of its clients are valued
at FRW 521,000 and FRW 755,000 respectively.
To record this transaction in the general journal, of course the cash, bank and
sales account are already created in the chart of account. If not QuickBooks
gives an option to add new account while recording. Here all the accounts arecreated in chart of account.
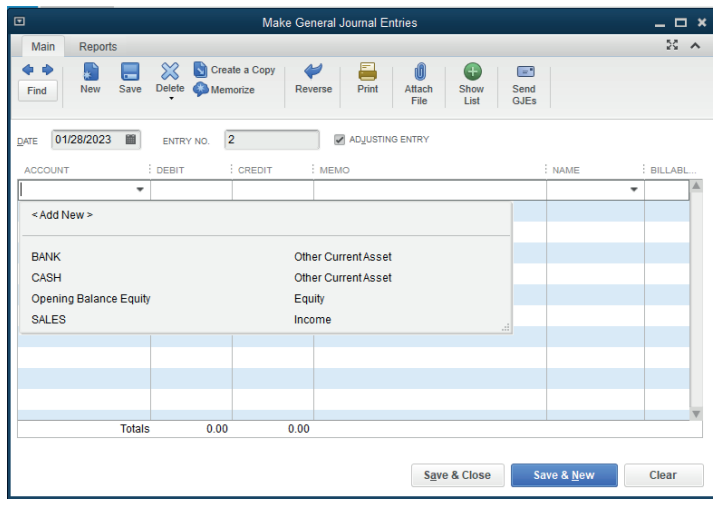
Figure 4.12.Option to record a sales by cheque and by cash
The next step is to debit the account to be debited and credit the account to be
credited respecting the rule of double entry. It means:
Debit Cash account 521,000
Credit Sales account 521000
Debit Bank account 775,000Credit Sales account 755,000
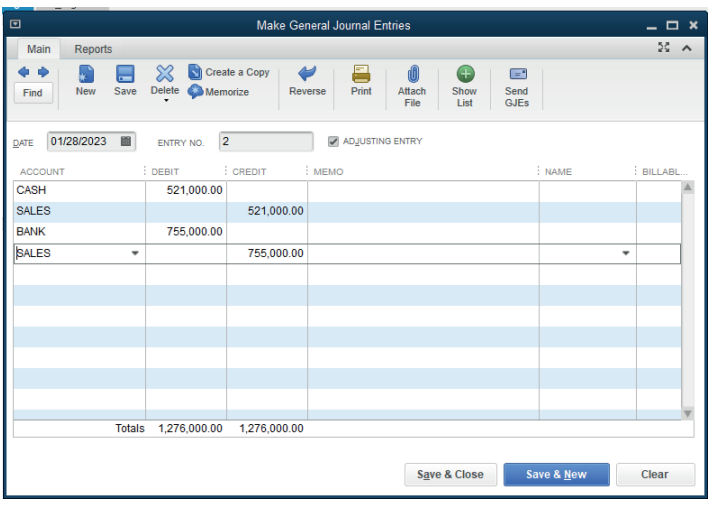
Figure 4.13. Sales by cash and by cheque record
A sale transaction is recorded, then Save &Close
4.2.2. Receiving the payment
This occurs when a payment is received from a customer for goods or services
supplied. The customer who received the invoice has the option to sign a cheque
and send it to the business. He can also deposit cash on business account and
submit the bank deposit slip to the business or pay cash in hand to the business
premises.
For our case, KAMBALE paid by cheque. To process this in QuickBooks, click
on Receiving Payment on QuickBooks home page for getting the followingwindow.
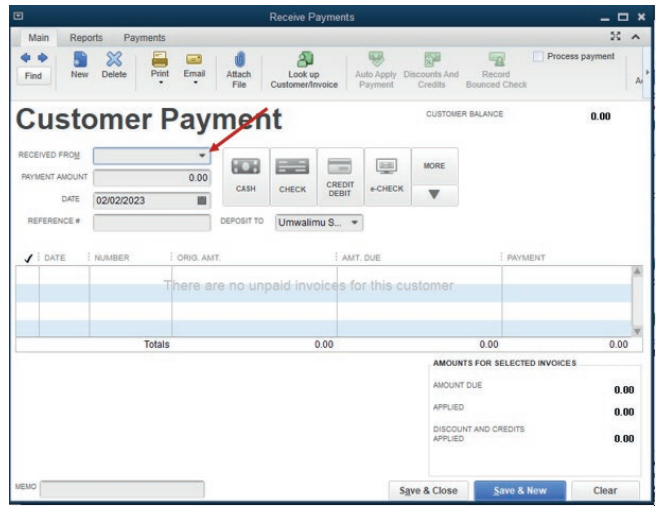
Figure 3.17 Selecting customer paid
This gives the option to enter the customer’s name where the payment is from,
the amount to receive, and after this, check whether the amount is equivalentwith the invoice. If yes, Click on Save & close
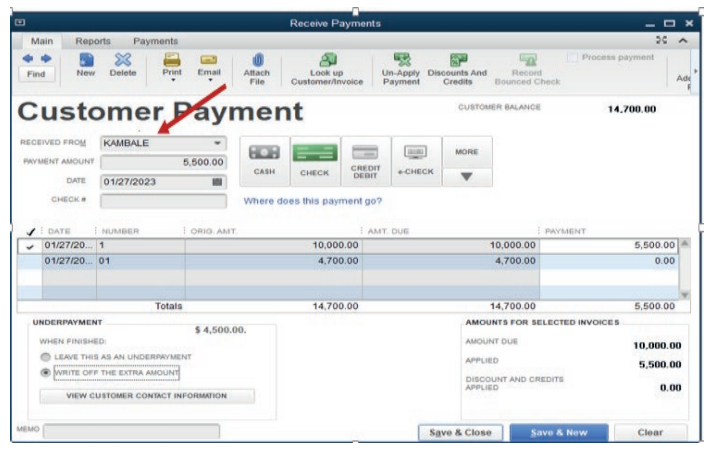
Figure 3.18. save a payment of customers
Save & close leads to the step of confirming the account to which the paymentgoes.
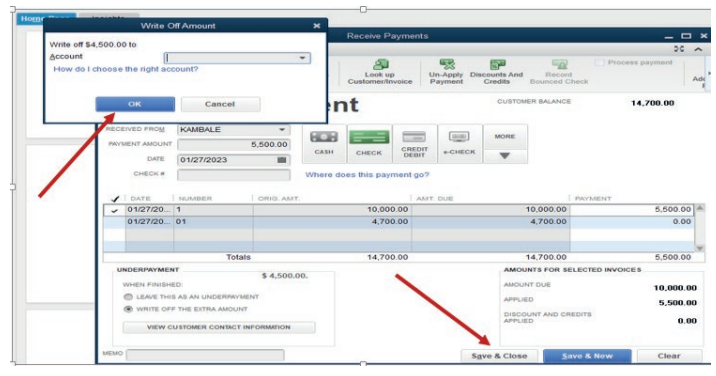
Figure 3.19. Selection of receiving account
Select the account from the list
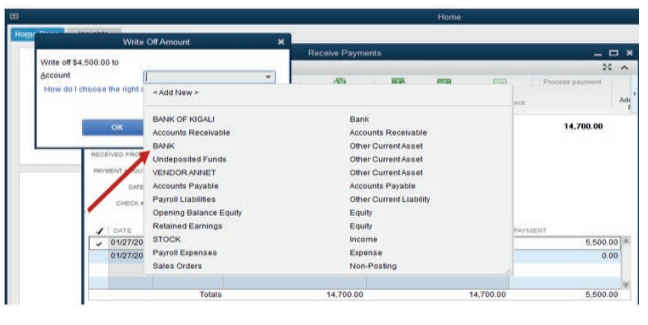
Figure 3.20 Confirmation of receiving Account
Because the payment is done by cheque, the account is Bank. Then OK.
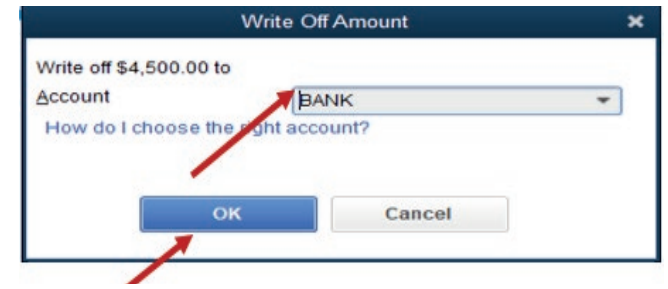
Figure 3.21. The receiving account is Bank
4.2.3. Recording the payment
Cash or cheque payment from customers must be recorded in business books
accounts. QuickBooks recognizes any unrecorded payment and the notificationis shown on its home page as below:
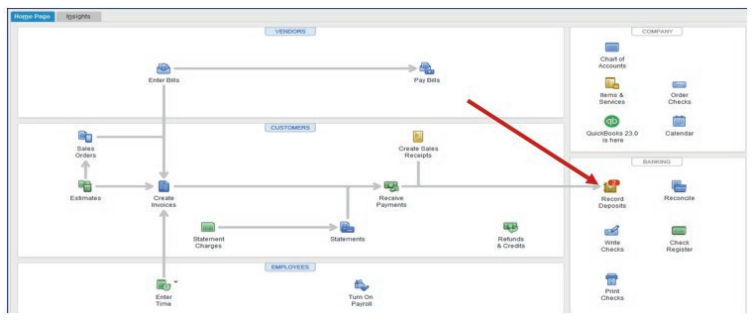
Figure 3.22. QuickBooks Home Page deposit notification
Once we click on notification, the below window showing the date, type of
transaction, payment method, the names of customer who is paying and totalamount paid appears. Click Save & Close
Figure 3.23. Cash Deposit slip
4.2.4. Sales receipt
A sales receipt is a transaction record that the seller issues at the time of sale
to verify the provided product or service and the amount the buyer paid. It is a
proof of payment. It is written by the selling business to its customer when the
payment against goods or services provided is over.
In QuickBooks, a sales receipt is created as following:
Clicking on Create Sales Receipt tool on QuickBooks home page and gettingthe below window:
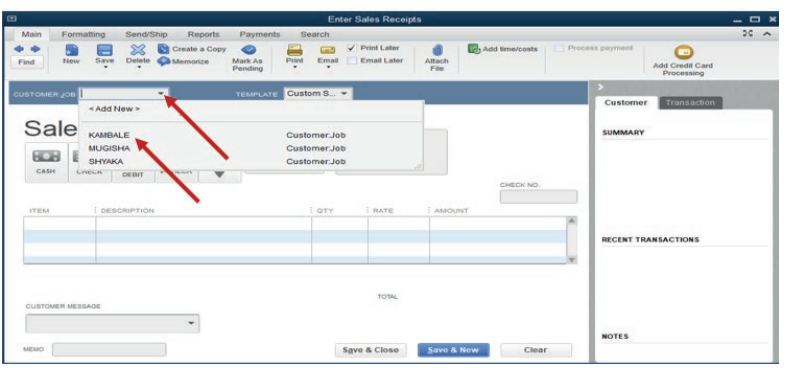
Figure 3.24. creation of sales receipt
From this, KAMBALE is a customer to whom a receipt belongs. So the user
has to add the items and quantity that the customer is paying for, customer
message if necessary, cheque number… Once the below window appears andthere is an exact amount as is per invoice, click save & close
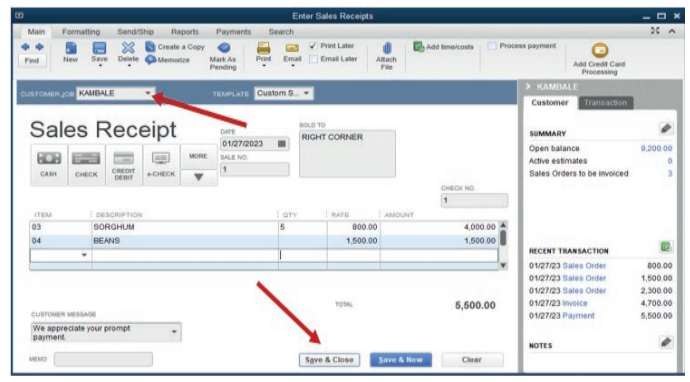
Figure 3.25. selection of the concerned customer
Application Activity 4.2.
1. Make a clear difference between sales and cash transactions
2. During the month of December 2022, B2C Co. Ltd concluded the
following sales transactions:
Sales on credit to; Teddy: FRW45, 740, Moise: FRW 347,600, Allen: FRW
245,000
Required:
• Record the abov e transactions in the journal of B2C Co. Ltd• Prepare the sales receipt.
End of Unit Assessment
1. Differentiate:
a) Vendor from a customer
b) Order from invoice
2. Mrs. Alex, the owner of BEST ELECTRONIC Ltd stated the business inJanuary 2020. He purchases the items below:
SAMSUNG 250 is Alexis’ supplier of computer and telephones while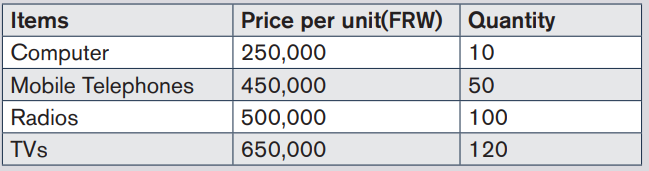
RWIZA Ltd supplies Computers and TVs. Vision 2050 is a customer
of both Radios and TVs. You are hired as an accountant of BEST
ALECTRONCS and the company uses QuickBooks in preparation ofits reports.
Required:
3. Create the list of items
4. Enter the vendors and customers
5. Prepare the bills for received items
6. Record the payments to the vendors
7. Prepare the order on behalf of customer, invoice and receive payment8. Record the payment from the customer
UNIT5: PURCHASES AND PAYABLES
Key unit competence: Apply the rules of cash, cheques, credit
sales and account receivable transactionsin QUICKBOOKS
Introductory Activity
Mr. MUGISHA has a shoes shop. He uses to purchase from different suppliers
on credit basis and then pay after selling.
1. Explain the credit purchase
2. Advise him on process of recording transaction be recorded inQuickBooks?
5.1. Credit purchase transactions
Learning Activity 5.1.
DUFATANYE SOTRE is engaged in sales of fruit and vegetables in
KIMISAGARA market. The customers in the morning purchase on credit for
paying in the evening after selling.
• Advise the DUFATANYE SOTRE on the ways of recording its daily sales
• If DUFATANYE SOTRE needs to use QuickBooks in recording, explainto its accountant the steps of creating a sales invoice
The term “credit purchase” refers to a situation where a buyer or a customer
conclude a purchase of goods or service from the supplier and promises to pay
on future date. It is a purchase transaction on the side of the buying entity but asales transaction on the side of the seller.
When goods or services are bought by a business on account or on credit
for reselling later, we can then say that Credit Purchases have taken place in
accounting. As with purchases, credit purchases can be used to by goods and
services however these are on credit or on the account.
Due to the credit purchase, an account receivable and an account payable are
then created. The account payable is the current liability for the buyer, and they
will pay the supplier at an agreed later date. The buyer should record it as a
Credit Purchase.
From the viewpoint of the supplier, they should record it as an account receivable,
it will be considered a current asset and it should be recorded in AccountsReceivable Subsidiary Ledger.
5.1.1. Record a credit purchase
A credit purchase transaction starts with the purchase order. A purchase order
is a document written buy the buyer to the seller just ordering him/her to supply
ordered good or services. A supplier who receives a order from the buyer try
to deliver goods or services which can be paid either directly or in future date.In QuickBooks, a credit purchase transaction is recorded as here under:
Step 1. Click on company menu on QuickBooks home page, then select MakeGeneral Journal Entries.
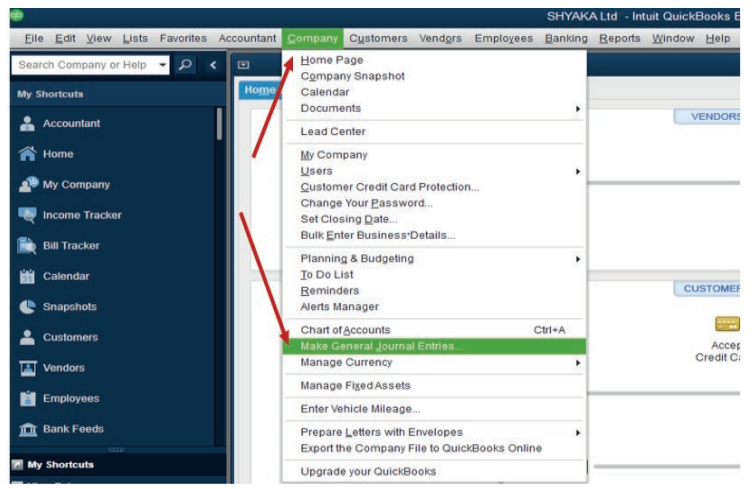
Step2. Complete the general journal
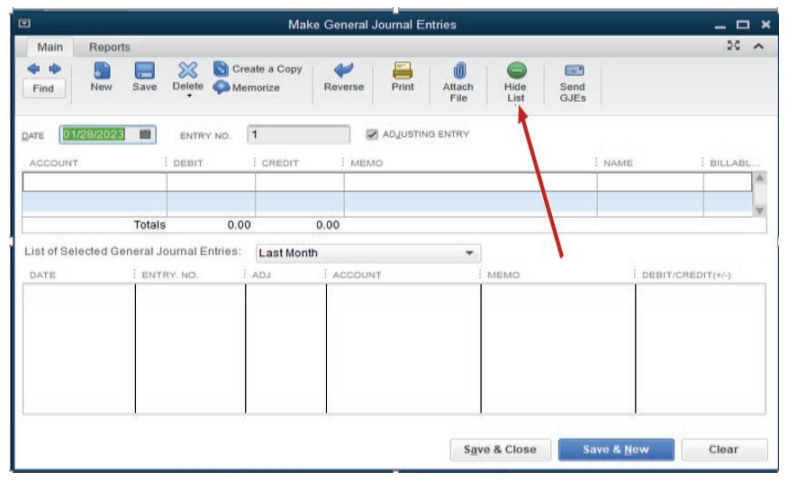
The first part of the window is for double entry and the bottom part shows the
number of transactions concluded. For having a clear space for recording, thebottom part should be hidden by clicking Hide List
Example: SHYAKA Ltd started its business activities in January 2022. During
January the purchase transactions concluded with all of its creditors is valued
at FRW 456,500. To record this transaction in the general journal, of course the
creditors and purchase account are already created in the chart of account. Ifnot QuickBooks gives an option to add new account while recording.
Debit purchase account: 456,500Credit creditors account: 456,500
As there is no debtors and sales accounts created in chart of account, we
can add them by the normal way of account creation, account type, continue,
account name then Save&Close or Save&New. Through this, a debtor
account is created and debited with FRW 125,000. Sales account is createdand credited with the equivalent amount.
A. A debited account (purchase)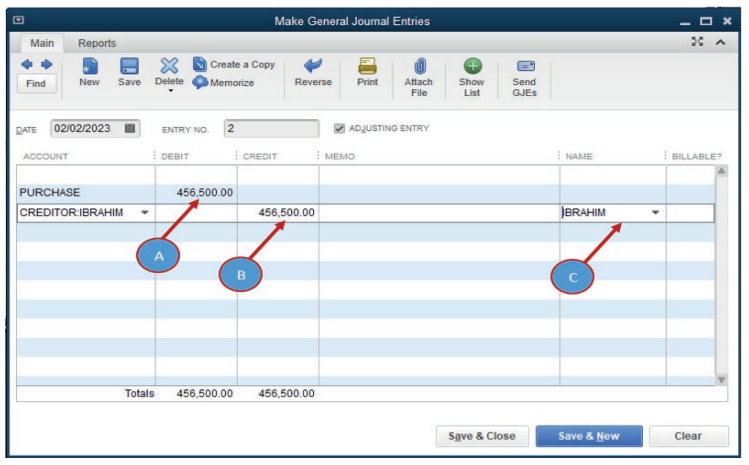
B. A credited account (Creditor)C. Name of supplier
In case there is specific customer name, it can be added on the name column
for clarifying who is the debtor.A purchase transaction is recorded, then Save &Close
5.1.2. Purchase invoice
A purchase invoice is an invoice used to record the purchase of goods or
services by a company. The purchase invoice will include the same information
as a regular invoice, but it will also list the terms of the purchase agreement and
any discounts that were negotiated.
An invoice is issued by the seller (or vendor) upon completion of the terms as
outlined in the purchase order. An invoice includes the previously agreed uponprice that the buyer should pay now that the order has been completed.
In QuickBooks, if goods or services are received by the company from the
vendor, an invoice is checked for ensuring the conformity with order and paid
later. The following is the purchase invoice from vendor that details the itemsreceived for being paid.
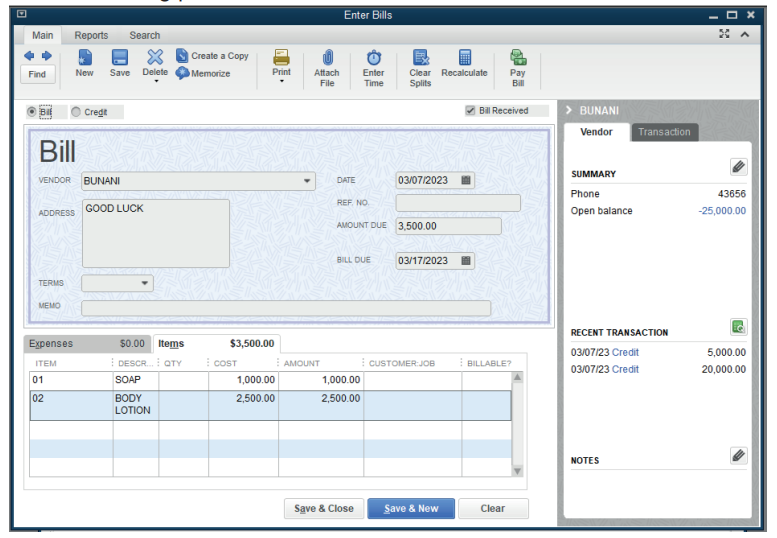
This is a purchase invoice entered in the QuickBooks for being paid.
The company keeps the purchase invoice valued at 25,000FRW to be paid to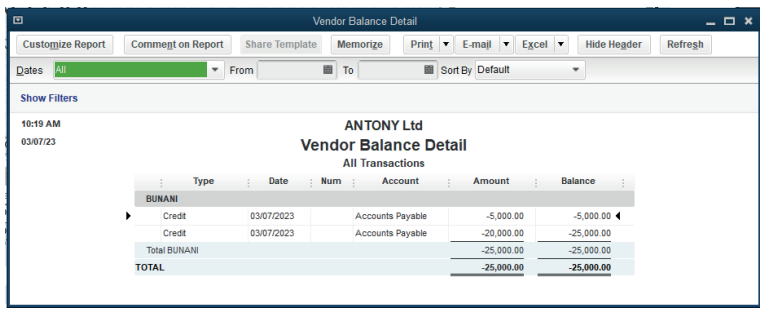
ANTONY Ltd for soaps and body lotion purchased on credit.
Application Activity 5.1.
1. Define a credit purchase transaction
2. What are the account affected by any business credit purchase
transaction?
3. MUGEMANA, a sole trader in Bushenge market purchased goods
valued at 743,980FRW on credit from supplier GATO.Record this transaction in his general journal.
5.2. Cash/ Cheque purchase transactions
Learning Activity 5.2.
JACKY SHOP uses to purchase goods and services and pays directly for
keeping its current assets free from liabilities.
• Is there advantages of purchasing by cash? Explain to Jacky.• Advise her to the recording of cash purchase.
A cash purchase transaction is a transaction where there is an immediate
payment of cash for the purchase of goods or services.
The common definition of a cash transaction is an immediate payment for
the goods or services bought. However, the term can have diverse meanings
because some time cheques or payment cards are used to pay goods orservices and it is always considered as a cash transaction.
5.2.1. Record a cash purchase
A cash purchase transaction affects two accounts: Cash /bank which is debited
as it is an increase in current asset and the sales account which is credited as
it is an income.
In QuickBooks, a cash purchase transaction is recorded as here under:
Step 1. Click on company menu on QuickBooks home page, then select MakeGeneral Journal Entries
Step2. Complete the general journal
The first part of the window is for double entry and the bottom part shows the
number of transactions concluded. For having a clear field for recording, thebottom part should be hidden by clicking. Hide List
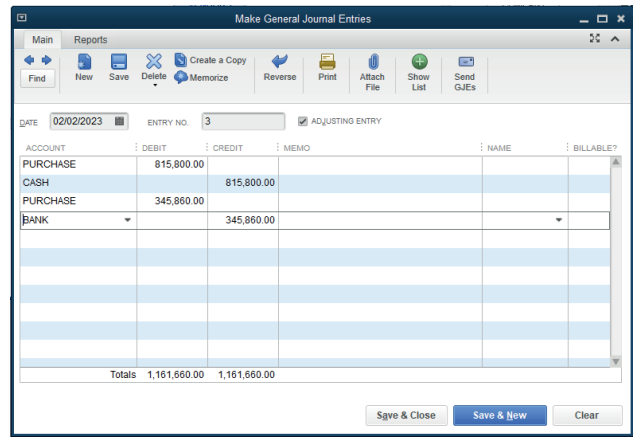
Example: SHYAKA Ltd started its business activities in January 2022. During
January the cash and cheques purchase transactions concluded with all of itssuppliers are valued at FRW 815,800 and FRW 345,860 respectively.
To record this transaction in the general journal, of course the cash, bank and
purchase account are already created in the chart of account. If not QuickBooks
gives an option to add new account while recording. Here all the accounts arecreated in chart of account.
The next step is to debit the account to be debited and credit the account to be
credited respecting the rule of double entry. It means:
Debit Purchase account: 815,800
Credit Cash account: 815,800
Debit Purchase account: 345,860Credit Sales account: 345,860
A purchase transaction is recorded, then Save & Close
5.2.2. Paying the bill
The following steps will be followed for paying vendor bill:
1. Go to the Vendors menu, then select Pay Bills.
2. Select the correct accounts payable account from the dropdown.
3. Select the checkboxes of the bills you want to pay from the table.
Note: To unmark or mark all the bills in the list, select Clear
Selections or Select All Bills.
4. Set any discount or credit that you want to apply to the bills.
• Discount - Select this if your vendor gave you a discount for this
transaction.
• Credit - Select this if you received a credit from your vendor, and you
used it to reduce your total bill amount.
5. Enter the date you paid the bill.
6. Select the payment method:
• Check Select Assign check number if you plan to manually write
the check. Select To be Printed to print the check or add it to the
list of checks to print.
• Credit Card - You can use credit cards to pay bills, then print a
payment stub.
• Online Bill Payment - You can directly pay your vendor bills in
QuickBooks. It also records your payment automatically so your
reports are accurate.
• Online Bank Payment - The payment processor will print and
mail a check to the employee. You can select Include reference
number if you want the bill or credit reference number to be sent
along with your name and account number.
• Cash, Debit or ATM card, Pay pal, or EFT - You can select Check,
then Assign check number even when you’re not paying with an
actual check. Enter the type of payment in the check number field or
leave it blank.
7. Select Pay Selected Bills.
8. Select Done, or select Pay More Bills if you have other bills you needto pay.
Application Activity 5.2.
1. Define a cash purchase
2. List the steps followed in recording a cash purchase
3. Mr. Gashugi purchased goods valued at 2,00,500 FRW by cash.
He also paid 134,550 FRW by cheque for services rendered to him.Record the transaction in QuickBooks and display it.
5.3. Cash/ Cheque purchase transactions and paymentprocesses
Learning Activity 5.3.
Rurangwa is a sole trader who uses to purchase goods and services from
different suppliers. It is his policy to pay directly when goods are deliveredto his company. Discuss the importance of his policy.
A cash transaction refers to a transaction which involves an immediate outflow of
cash towards the purchase of any goods, services, or assets. Cash transaction
can be consumer-oriented or business-oriented. A cash transaction stands
in contrast to other modes of payment, such as credit transactions in
a business involving bills receivable. Similarly, a cash transaction is also differentfrom credit card transactions.
5.3.1. Recording the payment
In QuickBooks, the payment is done either by cheque or credit card. The
accounting entry for this transaction is as follow:
Debit: the vendor (Creditor)Credit: the bank or credit card
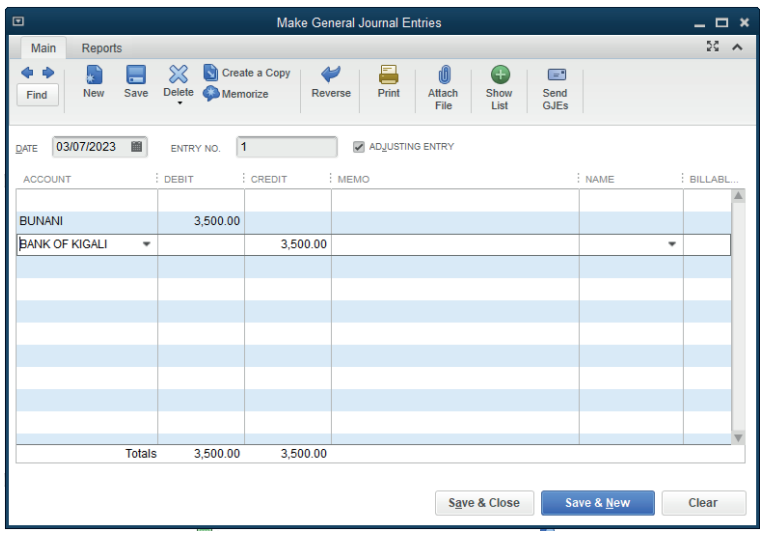
Cash or cheque purchase has the advantages below:
• Convenience for small purchases and tipping
• Lower transaction costs
• Negotiating power
• Buyer anonymity
• Budgeting and debt avoidance
• Preparing for emergencies
5.3.2. Payment receipt
This is a document kept by the company from the vendor as a proof of payment.
A copy of it is kept by the vendor. A payment receipt, also known as a receipt of
payment, is a document issued from a business to its customer when they have
received payment for provided goods or services.
This can apply either to partial or full payments, showing a clear record of how
much money has been received and what is still owed. Cash payment receipts
are useful documents both for the buyer and seller. Buyers can see where they
stand with payment, viewing a clear record of what they have paid for. Sellers
can verify the date and other details of a purchase, using this information to
create more detailed financial statements later. In the case of partial payments,receipts are also helpful as they serve as reminders for outstanding balances.
Application Activity 5.3.
1. What is a cash transaction?2. List the importance of cash os cheque purchase transaction
End of Unit Assessment
1. Make a clear difference between credit purchase and cash purchase
transactions
2. During the month of December 2022, B2C Co. Ltd concluded the
following Purchase transactions:
Purchase on credit to; Meddy: FRW 74,450, Modeste: FRW 645,000,
Arsine: FRW 245,000, Cash purchase: 357,450
Required:
• Record these transactions in the journal of B2C Co. Ltd• Prepare the sales receipt.
UNIT6: FINDING AND CORRECTING OMISSION AND MISSTATEMENTS
Key unit competence: Correct errors in the account balancesusing QUICKBOOKS
Introductory Activity
Mr NGOGA Frank is an accountant in ABC Ltd. During the month of November
2022, he recorded and posted the following transactions:
• Purchase of goods valued at 34,000 Frw by cash and he debited both
purchase and cash account.
• Taking goods worth 12,500 Frw for his own use and no entry has been
made
• The company sold the unused part of its land, the accountant debited
land and credited sales account.
• Cash banked FRw. 390 had been credited to the bank column and
debited to the cash column in the cashbook.
• Cash drawings of FRw. 400 had been credited to the bank column of
the cashbook.
In preparation of final report, some imbalances occurred.
a) For each case, show whether the transaction is posted correctly
b) What do you think is the causes of the imbalance?c) How can this be solved?
Recording transactions, posting to the various accounts and extraction of list of
account balances, it is possible for errors to be committed. Such errors may or
may not affect the totals of the list of account balances. Recall that if the totals
of the list of account balances equal, then this shows arithmetical accuracy in
recording and posting of transactions.
Now it should be said, this does not mean non-existence of errors. It is possible
for some errors not to affect the totals being equal for the list of account
balances. Some errors can affect too the total of list of account balances. For
those errors that affect the trial balance, quick books detect them before endingthe recording process.
6.1. The errors that do not affect the trial balance: Error ofomission, Error of Commission, Error of principle
Learning Activity 6.1.
After all transactions have been posted from the journal to the ledger, it is a
good practice to prepare a trial balance. A trial balance is simply a listing of the
ledger accounts along with their respective debit or credit balances for self check to determine that debits equal credits.
Do you agree with the statement that if the debit side of trial balance is equal
to the credit side of trial balance, there is no error committed in postingtransactions? Discuss your answer.
In Accounting, errors refer to the common mistakes made while recording
or posting accounting entries. These discrepancies are not fraudulent and
generally unintentional. Errors that do not affect the List of account balances
(trial balance) are the ones that totals of the list of account balances equal each
other.
However, on taking a close check on the balances and transactions posted,
errors may have been made and therefore the balances shown on the list of
account balances may be incorrect. Quick books cannot detect such errors.The following errors will not affect the totals of list of account balances
6.1.1. Error of omission
Here, a transaction is completely omitted from the accounts and therefore the
double entry is not made.
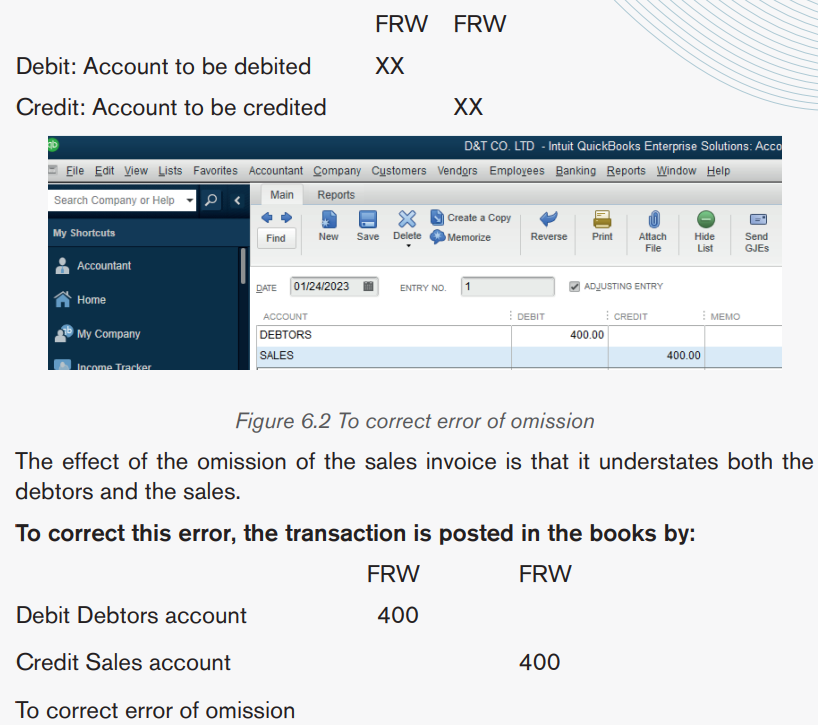
For example, a sales invoice of Frw 400 is not posted in the sales journal
therefore no entry is made in the debtor’s account and the sales account. That
is both debit of Frw 400 in debtor’s account and credit of Frw 400 in the salesaccount.
Figure 6.1. Error of omission. No entry is made.
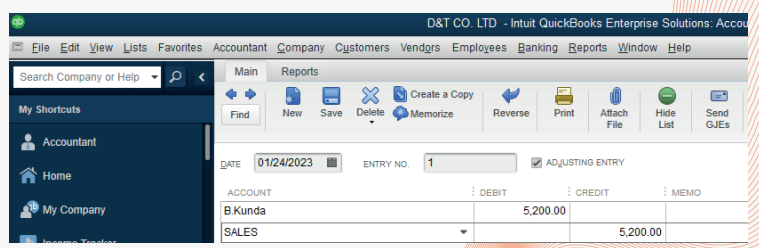
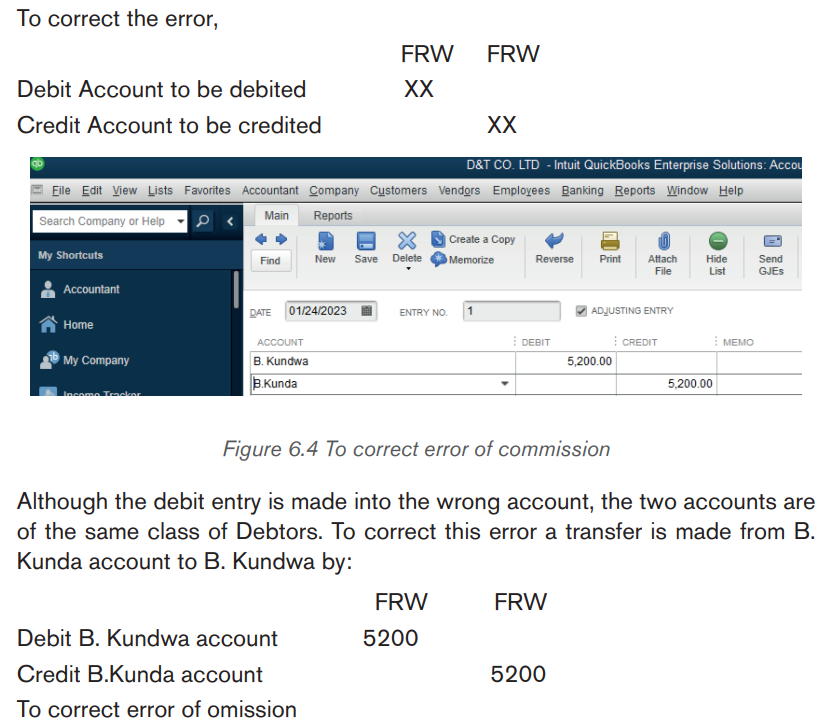
6.1.2. Error of Commission
This error occurs when a transaction is posted to a wrong account but the
account is of the correct class of account. Example: A credit sale to B. Kundwa
is posted to B. Kunda’s account for an amount of Frw 5200. Instead of a debit
to B. Kundwa account it is made to B. Kunda’s account and the corresponding
credit in the sales account is correct.
6.1.3. Error of principle
This type of error occurs when a transaction is posted to the wrong class of
account. For example, Furniture purchased for FRw 423,000 cash is debited
to the Furniture repairs account instead of debiting Furniture account, and thecredit entry in the cashbook is correct.
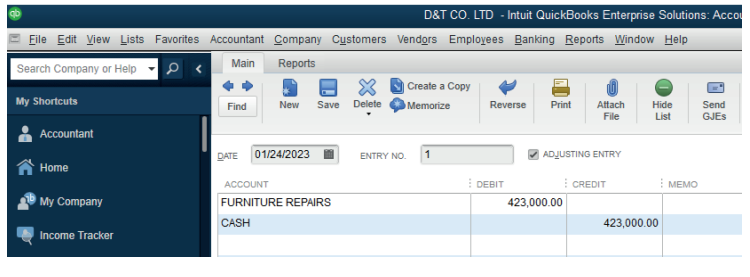
Figure 6.5: Error of principle
The furniture is a non-current asset, and a furniture repair is an expense.
Therefore a capital expenditure has been posted as revenue expenditure.
To correct such an error, the amount in the wrong class of account has to beremoved and transferred to the right class of account.

Figure 6.6 To correct the error of principle
Application Activity 6.1.
1. Explain;
a) Error of omission
b) Error of commission
c) Error of principle
2. The information bellow is from the books of Nelly. You are required to
record them in the journal of Nelly by correcting the errors committed.
a) Cash sales worth 29,000 FRW has never been recorded
b) Cash Payment of stationary has been recorded correcting in cash
and debited in salary account: 10,000 Frw
c) Furniture purchased for FRw 423,000 cash is debited to the
Furniture repairs account instead of debiting Furniture account, andthe credit entry in the cashbook is correct.
6.2.The errors that do not affect the trial balance: Completereversal, Error of Original entry, Compensating Errors
Learning Activity 6.2.
It is human nature to commit some errors especially in recording financial
transactions. This causes the imbalance in some list of account and requiresadjustment. Suggest some of such errors
6.2.1. Complete reversal
A transaction is posted to the correct accounts but to the wrong sides of the
accounts. That is a debit posted as a credit and a credit is posted as a debit in
the right accounts. For example, discount received of FRw 7,120 is debited inthe Discount received account and credited in the Creditor’s account.
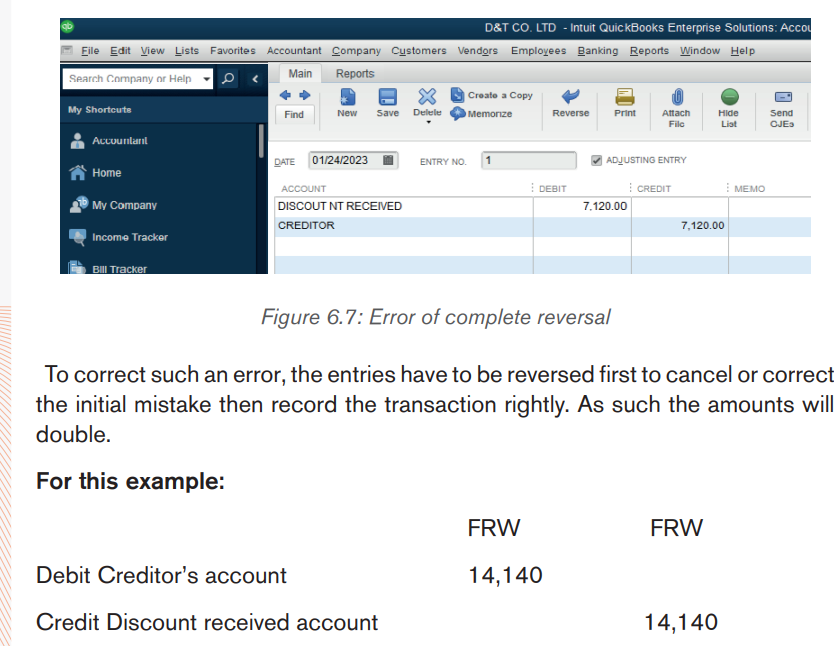
Figure 6.8 To correct error of complete reversal.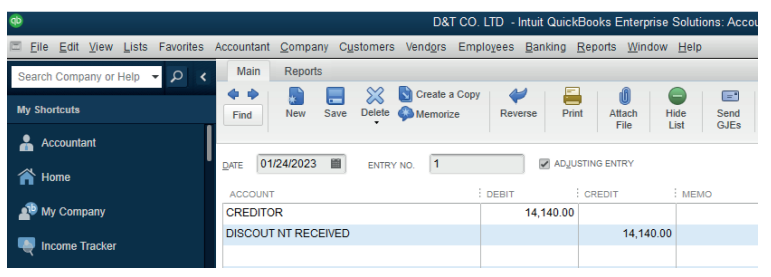
Notice: The account to be debited is debited twice and account to be creditedis credited twice too.
6.2.2. Error of Original entry
Here a transaction is posted to the correct accounts but the amount posted is
not correct. That is, it is either under/over stated. It is possible that the figure in
the amount might be interchanged. Such is a transposition error.
For example, cash received from a debtor of Frw 10,980 is posted to both
debtor and cash account as Frw 10,890. The amounts were understated byFrw 90
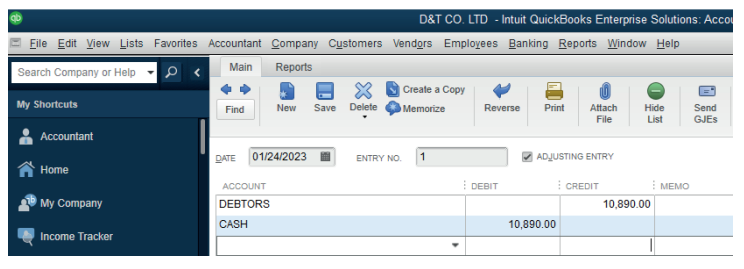
Figure 6.9 error of original entry
To correct this error, the amount understated or overstated is posted to these
accounts so as to increase or reduce the amounts in the accounts to get theright amount.
For this example:
FRw FRw
Debit Cash account 90Credit Debtors’ account 90
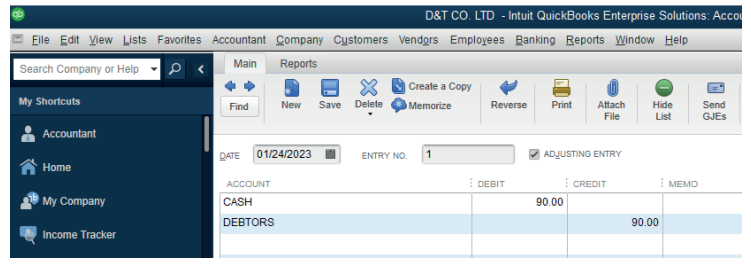
Figure 6.10 To correct the error of original entry
6.2.3. Compensating Errors
These are errors that have the effect that tend to cancel out each other in
amounts. That is, if the effect of one error is to understate the debits or credits
then another error may take place to overstate the debits or credits by the same
amount, hence canceling out each other.
For example, if the balance of bank account is Frw 435,000 but shown in thetrial balance as FRw 345,500.
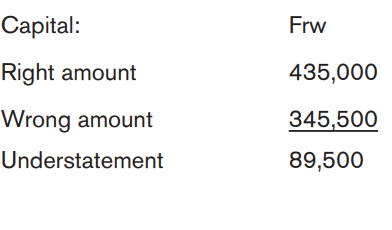
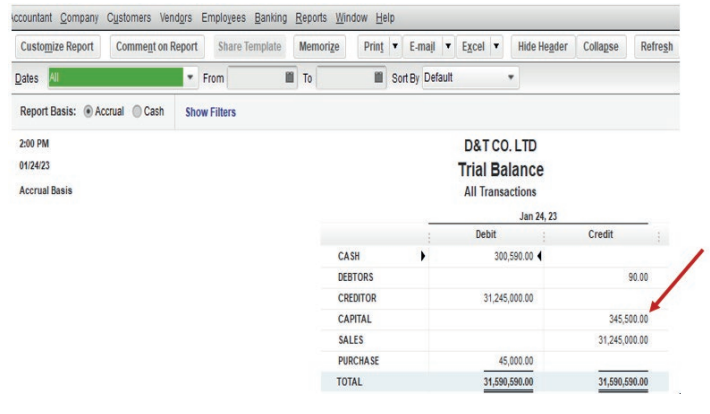
Figure 6.11 Company trial balance capital account overstated.
The balance C/D of capital is Frw 435,000 but it is recorded in the general
journal as Frw 345,000. It has been under casted by Frw 89,500. This undercast
affected both the capital account on its credit side and the debit side of cash
account with the same amount.
Another error carried to the trial balance of furniture account amounting to FRw493,950 instead of Frw 404,450
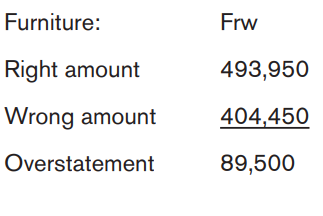
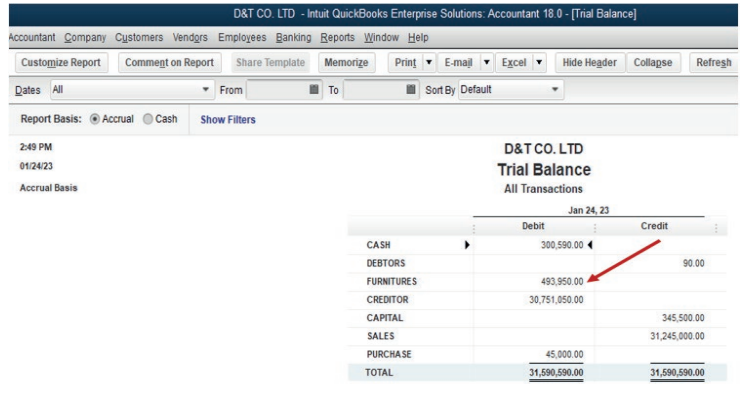
Company trial balance. Furniture account overstated.
The balance of furniture account is Frw 404,450 but it is recorded in the
general journal as Frw 493,950. It has been overstated by Frw 89,500. This
overstatement affected both the furniture account on its debit side and the
credit side of creditors account with the same amount.
The overall effect is nil on the debit side. Notice that the two accounts involved
have debit balances. It is possible to have canceling effect even accounts with
credit balances or even a mixture. The main thing is that, the effect on totals is
nil.
To correct such errors, the accounts involved have to be corrected to take careof the amounts overstated.
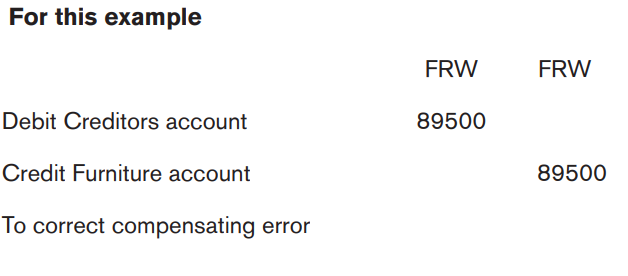
The corrected trial balance will look like the following:
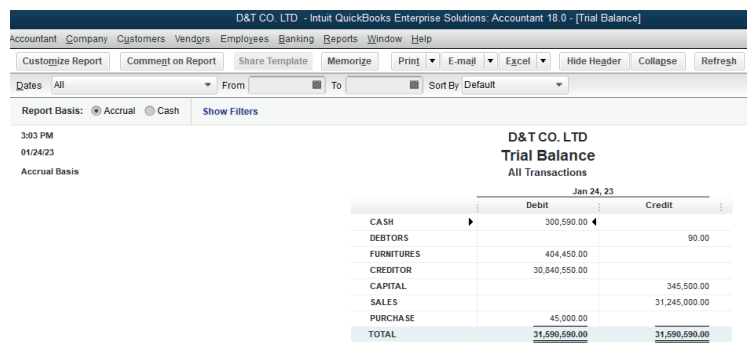
Figure 6.12 Corrected trial balance
Application Activity 6.2.
Give the journal entries needed to record the corrections of the following.
i) Extra capital of FRw. 10,000 paid into the bank had been credited to
Sales account.
ii) Goods taken for own use FRw. 700 had been debited to General
Expenses.
iii) Private insurance FRw. 89 had been debited to Insurance account.
iv) A purchase of goods from C Kelly FRw. 857 had been entered in the
books as FRw. 587.
v) Returns inwards FRw. 168 from M McCarthy had been entered in error
in J Charlton’s account.vi) A sale of a motor van FRw. 1,000 had been credited to Motor Expenses.
6.3. Errors that affect the trial balance
Learning Activity 6.3.
After all transactions have been posted from the journal to the ledger, it is a
good practice to prepare a trial balance. A trial balance is simply a listing of the
ledger accounts along with their respective debit or credit balances for self
check to determine that debits equal credits.
What can you do in case the credit side of trial balance totals does not matchwith the debit side total of credit balance?
6.3.1. Understanding the errors that do not affect the trial balance
These errors will affect the totals of the list of account balances. That means
that the arithmetical accuracy of accounts will be in doubt. The totals of debit
balances will not equal the totals of credit balances
The likely causes may be as follows:
Transaction amount is posted only on one side of the accounts.
A transaction is posted only on one side of both accounts.
A transaction is posted correctly following double entry but different amounts
Error on balances of accounts.
Balance on an account is shown on the wrong side of the account when opening
the ledger accounts or when taken up to the trial balance.
A balance is omitted from the trial balance.
6.3.2 Correction of errors that affect trial balance
To correct such errors, only one account will be needed. The other account to
fulfill double entry will be the suspense account.
Suspense account is a temporary account that is opened to take care of
differences between the total in the list of account balances. This account can
also be used in case a bookkeeper does not know the other account to debit or
credit. Once the other account is known then it is debited or credited and the
corresponding entry to be in the suspense account.
While correcting the error, the difference in the totals of the list of account
balances is placed in the suspense account pending correction. During
correction, one account to be corrected is debited or credited then the suspense
account is credited or debited respectively.
The balance to be shown on the suspense accounts depends on which side of
the list of account balances has the lower total.
If the debits totals exceed total credits, then an amount is included on the credit
side of the list of account balances so that the debits equal credits and is called
Suspense account. This is a credit balance and will be taken to the suspense
account on the credit side.
If the credits totals exceed total debits, then an amount is included on the debit
side of the list of account balances so that the debits equal credits. This is a
debit balance and will be taken to the suspense account on the debit side.
The errors that affect trial balance are automatically detected in quick booksoftware and it cannot allow the next step.
Example of recording the transaction with error
Purchase of furniture valued at Frw 12,500 by cash.
A transaction is posted correctly following double entry but different amounts.
It means:
Debit Furniture account by 12,500
Credit cash account by 15200
Click on save & close or Sane & new,
There is a difference of Frw 2,700 which the software requires to handle beforenext step.
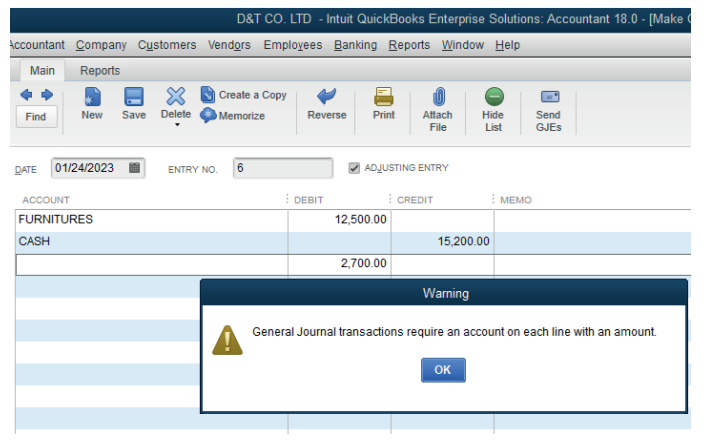
Figure 6.13 Error affecting Trial Balance
Application Activity 6.3.
1. What is an error?
2. Give two examples of errors that do not affect trial balance.3. How do we handle the error that do not affect trial balance?
End of Unit Assessment
1. When posting an invoice for car repairs, FRW 870,000 was entered
on the correct side of the motor expenses account. The invoice was
for FRW 780,000. What correction should be made to the motor
expenses account?
i) Debit FRW 90,000
ii) Credit FRW 90,000
iii) Debit FRW 1,650,000
iv) Credit FRW 1,650,000
2. The following transactions have been extracted from the books of TBB
Ltd on 31 December 2020 that failed to agree.
In January 2021 the following errors made in 2020 were found:
a) Cash banked FRw. 390 had been credited to the bank column and
debited to the cash column in the cashbook.
b) Sales of Frw 2,500 to J Church had been debited in error to J Chane
account.
c) Returns inwards FRw. 168 from M McCarthy had been entered in
error in J Charlton’s account.
d) Discounts received account had been under cast by Frw 3,000.
e) The sale of a motor vehicle at book value had been credited in error
to Sales account Frw 3,600.You are required to show the journal entries necessary to correct the errors.
UNIT7: ACCOUNTING METHODS
Key unit competence: Operate using either cash or accrualmethods of accounting in QUICKBOOKS
Introductory Activity
MAHORO, a young entrepreneur in MUSANZE district is willing to prepare the
financial reports through QuickBooks and the issue is that he does not know
exactly which accounting method to use and why to use such method.
He always deal with a number of suppliers and customers, paid and unpaid
expense, income paid, unpaid and accrued.
Help him to understand the accounting methods so that he can choose one ofthem to use in his business.
Cash-basis or accrual-basis accounting are the most common methods for
keeping track of revenue and expenses. Yet, depending on your business
model, one approach may be preferable. You will need to determine the bestbookkeeping methods and ensure your business model meets requirements.
7.1. Accrual basis accounting
Learning Activity 7.1.
MUGWANEZA, a sole trader in GATSIBO uses to record the financial
transactions using accrual accounting method. He records every transaction
even the ones which do not flow cash out and in. This affects its final statements
in one way or another. What do you thing is the importance and disadvantagesof this system of recording?
Businesses that use accrual accounting recognize income as soon as they
raise an invoice for a customer. And when a bill comes in, it’s recognized as an
expense even if payment won’t be made for another 30 days.
7.1.1. Benefits of accrual accounting method
The accrual accounting method helps the users in the following ways:
• You have a much more accurate picture of business performance and
finances
• You can make financial decisions with far more confidence
• It can sometimes be easier to pitch for long-term finance
7.1.2. Downsides of accrual accounting
In the other ways, the accrual method should have the disadvantages to
the users:
• It’s more work because you have to watch invoices, not just your bank
account
• You may have to pay tax on income before the customer has actually
paid you
• If the customer reneges on the invoice, you can claim the tax back onyour next return
Application Activity 7.1.
1. Explain the accounting accrual method.
2. List down the advantages and disadvantages of accrual accountingmethod.
7.2. Use accrual methods to Display statements
Learning Activity 7.2.
It is necessary that the accountant prepares the final statements and present
them to the different users. The company should choose the accounting
method to use while presenting such report. Advise to the company manageron the accrual method of accounting.
In quick books software, the reports are prepared and when are to be presented,
the user will select which accounting method to use depending on the business
policy.
Example: TOM AND DON Ltd, RWAMAGANA DISTRICT, PO BOX 1245
RWAMAGANA, and Tel; 0788393737, had the transactions below:
The company started the business with 5,000,000 Frw on bank of Kigali
Purchase of 200 kgs of rice by cheque of 1,000,000 Frw
Credit purchase from creditor Tom 4,000,000Frw
Sales: cash: 1,200,000 Frw, Cheque: 345,000 and credit sales to BUNANI:
2,387,500
Bought land by cash 1,800,000 Frw
Returning goods of 1,000,000 Frw to Tom
Paid 10, 000 Frw of salaries by cheque
Cash drawings Frw120,000
Received rent income by cheque: Frw 31,200,000
Required: Present the income statement and balance sheet using Accrual
method.
For Income statement presentation, Click on Reports, Company & Financials
then Profit & Loss Standard. From these transactions, quick books reports are
presented as here under: (Accrual method).Accrual method, TOM AND DON Trading, profit and loss account.
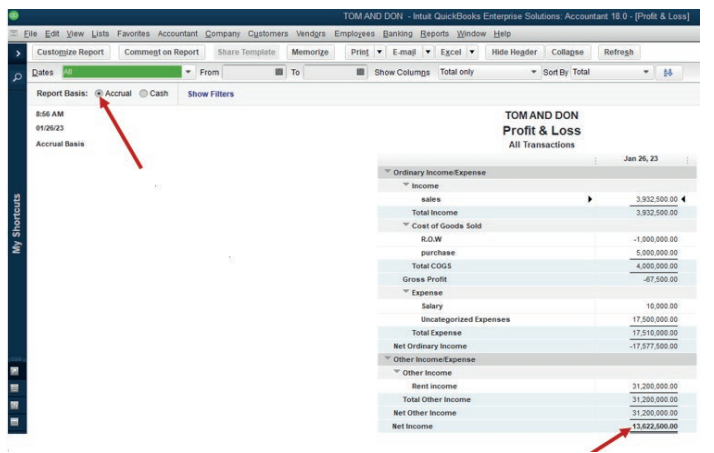
Figure 7.1 Income statement
The statement of profit and loss account shows the net income of 13,622,500
as revenues and expenses are recognized once they occur.
This income statement is prepared with consideration of paid and unpaid
expenses, received and not yet received income.
Under the same method, the net income is transferred to the balance sheet in
equity section. It may appear as here under:TOM AND DON, Accrual method balance sheet
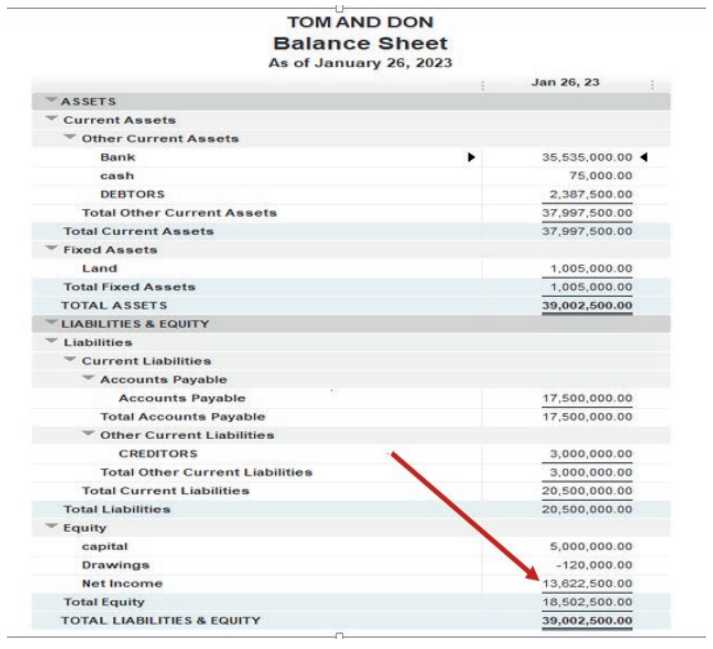
Figure 7.2 Accrual method balance sheet
Application Activity 7.2.
The following transactions are for BERWA LTD for the month of October
2021.
Oct. 1: Started business with FRW 20,000,000 cash
Oct. 2: Purchase land for the business at FRW 3,000,000 by cash
Oct.4: Purchased office equipment on credit from Equipment Suppliers
Ltd at FRW 2,000,000
Oct. 5: Obtained bank loan of FRW 8,000,000 it was deposited to a
bank A/C
Oct.15: Made part payment of FRW 1,500,000 to Equipment Suppliers
Ltd by cheque.
Oct. 17: Bought motor vehicle from TOYOTA RWANDA at a cost of FRW
15,000,000
Present BERWA LTD Balance sheet and income statement displayed usingaccrual method.
7.3. Cash method
Learning Activity 7.3
In accounting, sometimes business owner decides to use cash method in
recording business financial transactions.Businesses that use cash basis accounting recognize income and expenses• Discuss the reason behind this decision.
only when money changes hands. They don’t count sent invoices (debtors) as
income, or bills not yet paid as expenses until they’ve been settled.
Despite the name, cash basis accounting has nothing to do with the form of
payment you receive. You can be paid electronically (cheques or debit and
credit cards) and still do cash accounting. The cash method is most-commonly
used by sole proprietors and businesses with no inventory.The cash accounting method helps the users in the following ways:7.3.1. Benefits of cash accounting
It’s simple and shows how much money you have on hand
You only have to pay tax on money you’ve received, rather than on invoices
you’ve issued, which can help cash flowIn the other ways, the accrual method should have the disadvantages to the7.3.2. Downsides of cash accounting
users
It’s not accurate: it could show you as profitable just because you haven’t paidyour bills
It doesn’t help when you’re making management decisions, as you only have a
day-to-day view of finances
The accounting repots are always prepared through one of these methods. The
results of the reports prepared from the same transactions but the different
methods are different due to the income and expenses considered once accrual
accounting method is used, which may not appear in the reports prepared using
cash accounting method. Let’s use the same transactions, but cash accounting
method to prepare income statement and balance sheet of TOM AND DON Ltd.
Example: TOM AND DON Ltd, RWAMAGANA DISTRITC, PO BOX 1245
RWAMAGANA, Tel; 078304050, had the transactions below:
The company started the business with 5,000,000 Frw on bank of Kigali
Purchase of 200 kgs of rice by cheque of 1,000,000 Frw
Credit purchase from creditor Tom 4,000,000Frw
Sales: cash: 1,200,000 Frw, Cheque: 345,000 and credit sales to BUNANI:
2,387,500
Bought land by cash 1,800,000 Frw
Returning goods of 1,000,000 Frw to Tom
Paid 10, 000 Frw of salaries by cheque
Cash drawings Frw120,000
Received rent income: Frw 31,200,000
Required: Present the income statement and balance sheet using Cash methodTOM AND DON, Trading, profit and loss account cash method
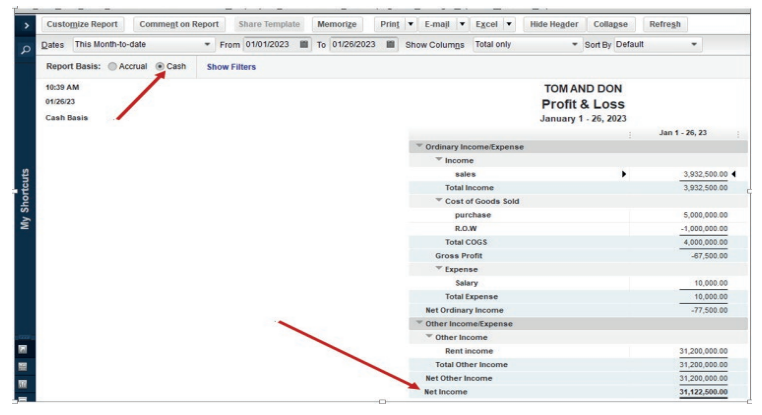
Figure 7.3 Income statement with Cash method
The statement of profit and loss account shows the net income of 31,200,000
as revenues and expenses are recorded once received or paid.
This income statement is prepared with consideration of paid expenses, and
received income. There is an increase in net income, from FRW 13, 6322,500
to FRW 31,122,500 due to the fact that there is an unpaid cash as long as the
method considers to record cash out once it is transferred to the payee.
Under the same method, the net income is transferred to the balance sheet in
equity section. It may appear as here under:Cash method, TOM AND DON Trading, Balance sheet
Figure 7.4 Balance sheet with cash method
Completing reconciliations is a critical monthly task that ensures that QuickBooks
company records match the banking records. This gives the confidence that
business books are accurate so that the user can trust the reports created forthe business and others.
Application Activity 7.3.
HOPE SHOP started with its operations with 100,000 Frw on bank of Kigali.
During the month, the following transactions took place.
• Purchase of goods by cheque of 70,000 Frw and purchase on credit
of 60,000 FRW from MUNYABARAME
• Credit sales to Peter of 50,000 FRW
• Cash sales of 55,000 FRW
• Sales by cheque of 65,000 FRW
• Returning goods of 25,000 FRW to MUNYABARAME and at the same
date, Peter returned goods of 15,000 FRW to us.
• Paid 1, 000 FRW of salaries by cheque
Required:
Present HOPE SHOP Balance sheet and income statement prepared
using cash method.
Present the general journal, trial balance, income statement andbalance sheet.
End of Unit Assessment
1. Differentiate between cash and accrual method of accounting2. Complete the table below:
3. The following transactions have been extracted from the book of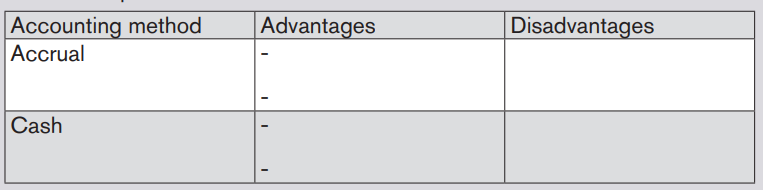
MANEMATALE Ltd
a) Starting the business with
i. Cash: 12,000,000
ii. Bank: 8,000,000
b) Getting a loan from BK 4,000,000
c) Bought goods on credit from Anna valued at 8,000,000
d) Sales of goods on credit to worth 2,000,000 to Ruth
e) Returning goods of 2,000,000 to Anna
f) Payment of the total amount due to Anna by cheque
g) Ruth returned goods to us valued at 1,000,000
h) Cash payment from Ruth for the total amount due from her.
• Present the income statement and balance sheet using cash
method of accounting
• Present the income statement and balance sheet using accrual
method of accountingUNIT8: BANK RECONCILIATION
Key unit competence: Prepare the bank reconciliation usingQUICKBOOKS
Introductory Activity
KANYANA is hired as an account clerk at IGIHOZO super market. At the end
of the month she finds that there is disagreement between the bank account
balance in cash book and the bank account balance on the bank statement.
a) What do you thing are the reasons behind those discrepancies?
b) What do you suggest as an answer for those discrepancies to
ensure that the balance to be reported in financial statement istrue and fair?
8.1. Meaning of Bank reconciliation
Reconciling a bank statement is an important step to ensuring the accuracy of
financial data. To reconcile bank statements, carefully match transactions on the
bank statement to the transactions in accounting records. With QuickBooks,
the user can easily reconcile bank accounts to ensure that the amount record isconsistent with the amount reported by the bank.
Learning Activity 8.1.
The businesses prepare the cash book to record all receipts and payments
concluded either by cheque or by cash. At the end of and financial period,
this record is compared to the statement of the account by checking the bank
column.What is the document that the business uses to match the two documents?
The cashbook for cash at bank records all the transactions taking place at
the bank i.e. the movements of the account held with the bank. The bank will
send information relating to this account using a bank statement for the firm to
compare.
Ideally, the records as per the bank and the cashbook should be the same and
therefore the balance carried down in the cashbook should be the same as the
balance carried down by the bank in the bank statement.
In practice however, this is not the case and the two (balance as per the bank
and firm) are different. A bank reconciliation statement explains the difference
between the balance at the bank as per the cashbook and balance at bank asper the bank statement.
8.2. The Purposes and causes of a bank reconciliation
statement
1. What is the meaning of bank statement?8.2.1. Purposes
Application Activity 8.1.
2. List the two document involved in preparation of bank reconciliationstatement.
The bank reconciliation statement is prepared for the reasons below:To update the cashbook with some of the items appearing in the bank statement
Learning Activity 8.2.
The accountant of any business has to ensure that the additions and
deductions on the bank statement are compared (or reconciled) with the items
that are entered in company's general ledger, if there are differences, such
as outstanding payments or deposits in transit, they can be noted as timing
differences.
1. How do you think the accountants can deal with this situation?2. Who do you think is committing the errors that cause the differences?
e.g. bank charges, interest charges and dishonored cheques and make
adjustments for any errors reflected in the cashbook.
To detect and prevent errors or frauds relating to the cashbook.
To detect and prevent errors or frauds relating to the bank.
8.2.2. Causes of the differences
The causes of differences are the following:
Items appearing in the cashbook and not reflected in the bank statement.
The following are the causes of imbalance between cash books and bank
statement
Unpresented Cheques: Cheques issued by the firm for payment to the
creditors or to other supplies but have not been presented to the firm’s bank for
payment.
Uncredited deposits/cheques: These are cheques received from customers
and other sources for which the firm has banked but the bank has not yet availed
the funds by crediting the firm’s account. Errors made in the cashbook. These
include:
Payments over/understated
Deposits over/understated
Deposits and payments miss posted
Overcasting and under casting the Bal c/d in the cashbook.
Items appearing in the bank statement and not reflected in the
cashbook.
The items that appear in bank statement but not reflected in cash book ere:
Bank charges: These charges include service, commission or cheques.
Interest charges on overdrafts.
Direct Debits (standing orders)
Dishonored cheques
Direct credits
Interest Income/Dividend incomes
Errors of the Bank Statement (Made By the Bank).
Such errors include:
– Overstating/understating.
– Deposits– Withdrawals
8.3. Steps of reconciliation in QuickBooks
8.3.1. Import transactionsQuickBooks has to be connected to the bank, for importing transactions relating
Application Activity 8.2.
1. What is Bank reconciliation?
2. Complete the following sentences:
a) ……………………………… are cheques issued by the firm for
payment to the creditors or to other supplies but have not been
presented to the firm’s bank for payment.
b) The cheques received from customers and other sources for which
the firm has banked but the bank has not yet availed the funds by
crediting the firm’s account are called ………………………………….
3. In which cases the bank can dishonor a cheque? Mention at least 4
cases.
4. It is normal that the bank makes some mistakes that leads to the differencebetween cash book and bank statement. List three of these mistakes.
to the bank. When the user receives the bank statement or account statement
at the end of the month, he can start reconciling the accounts. QuickBooksorganizes all data for making bank reconciliation easily.
Learning Activity 8.3.
To reconcile the bank balance as shown in the bank statement (pass book)
with the balance shown by the cash book, Bank Reconciliation Statement is
prepared. After identifying the reasons of difference, the Bank Reconciliation
statement is prepared without making change in the cash book balance.
You are required to discuss the process in which the bank reconciliationstatement should be prepared.
8.3.2. Reconcile accounts
To reconcile the accounts, the user clicks on Reconcile icon on QuickBooksHome Page. It gives the following window.

Through this window, the user selects the account to be reconciled by clicking
on the account field. A list of account appears.
In QuickBooks, choose the account to reconcile.

The bank account is selected to be reconciled, the window below appears:
From this window, the user fills the required field including selection of date
at which the reconciliation is taking place, Beginning and Ending balance,
Service charge and the Account which is charged, Interest earned if anyand the Account that receives the interest.
After filling these fields, the user can click on Continue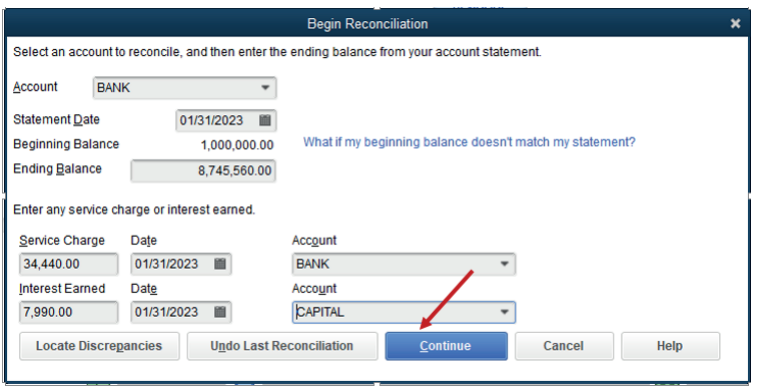
QuickBooks will let the user check data on his bank account and asks to
reconcile.
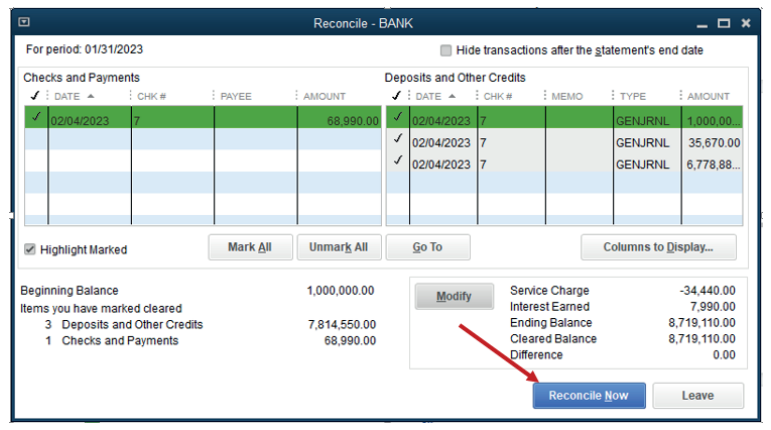
Before reconciliation, the user will make sure that all transactions are selectedby clicking on Mark All.
With bank statement in-hand, the user can systematically check off matching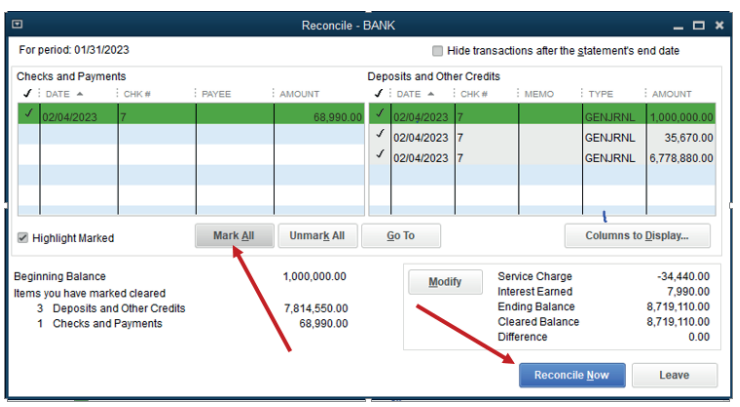
transactions one-by-one by clicking their boxes.
The bottom of the screen contains a running total of items checked off, and
thus have been reconciled. This is useful for comparing the totals in books to
the totals on bank statement. To complete the reconciliation, make sure thedifference shown is zero.
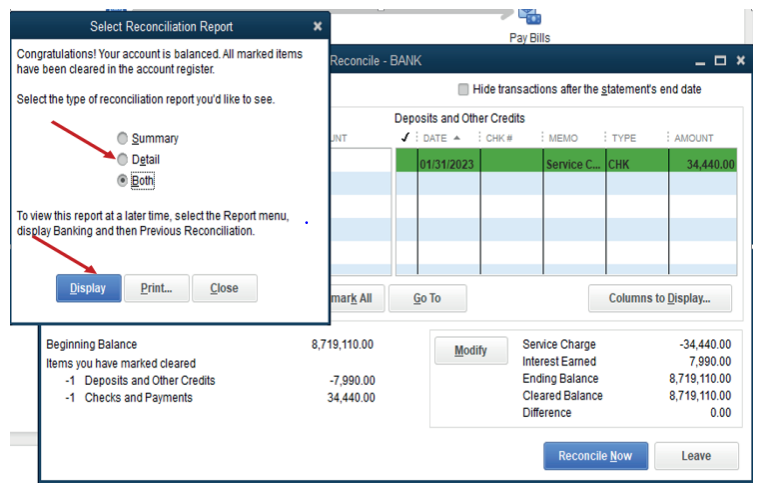 Here, a click on reconcile Now, QuickBooks gives to the user an option to
Here, a click on reconcile Now, QuickBooks gives to the user an option to
Display the reconciliation report. The user can also choose the type of reportto display being either Summary, Details or Both.
Let’s display a Details report here under:
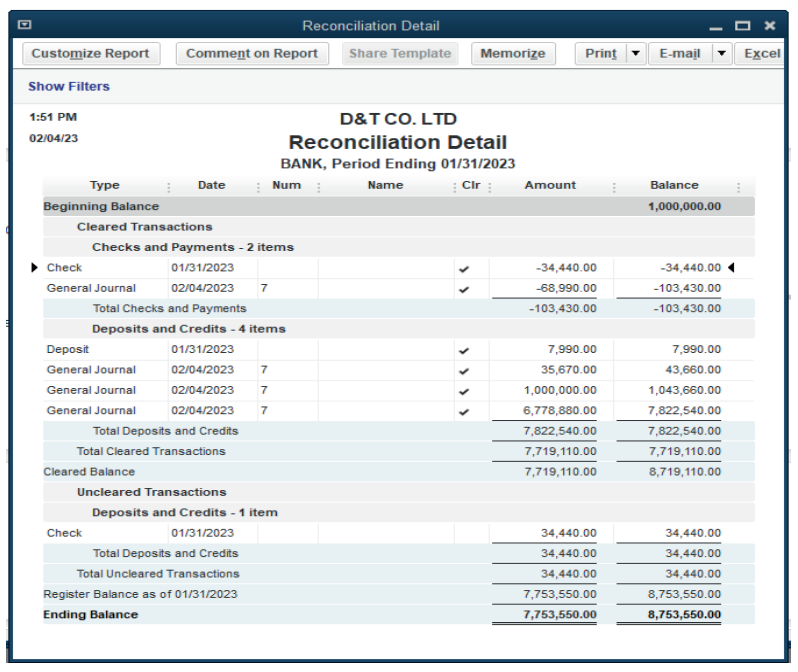
If the user selects to display the summary reconciliation, it appears as follow:
Sometime the user can reconcile and there is a remaining difference which is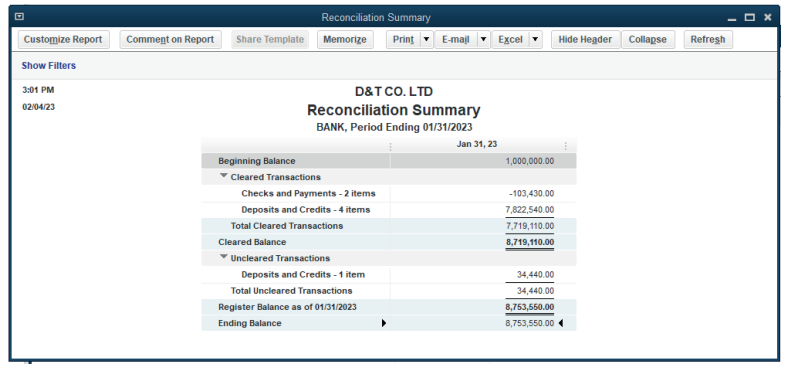
not zero.Application Activity 8.3.
Form the information below, prepare and display the bank reconciliationDetails period ending at 31/01/2023
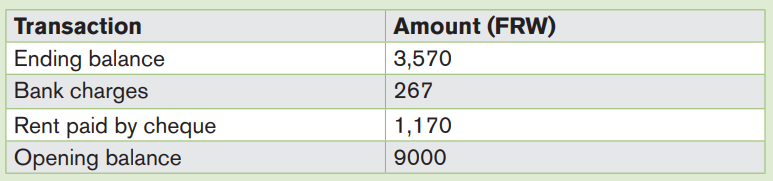
End of Unit Assessment
1. What is meant by a Bank Reconciliation statement?
2. What is the need of preparing Bank Reconciliation statement?
3. Enumerate the causes of difference in the balance of cash book and
bank statement.
4. From the following particulars, prepare Bank Reconciliation statement
as on December 31, 2022.
Opening bank balance: FRW 42,000
Ending balance:
The ending balance is a result of the transactions below:
i) Starting business with FRW 1,000,000 at bank
ii) Purchase of goods by cheque: FRW 550,000 FRW
iii) Sales by cheque: FRW 765,000
iv) Interest earned: FRW 90,150
v) Commission paid: FRW 12,490vi) Interest charges: FRW 4,215
UNIT9: FINAL REPORTS
Key unit competence: Prepare the final reports after making therequired adjustments using QUICKBOOK
Introductory Activity
Mrs. INEZA, The new accountant of MUSANZE INVESTMENT GROUP (MIG)
is wondering what is expected from her exactly, especially at the end of financial
period. She is used to record company transactions in different journals and
prepare the ledger accounts through QuickBooks accounting software.
Finally, the reports are to be submitted to the different users for coming up with
rational decisions. These decision are based on final financial reports prepared
by INEZA. It means that the bright future of MIG depends on these report.
1. Assist to Mrs. INEZA to understand the process of documenting and
communicating financial report of MIG performance over a time period.
2. Suggest the important reports that should be prepared and
communicated to the users3. List the further importance of final reports to the company.
Final reports are a set of documents that show the financial situation of
a company at the end of a particular period of time. They are compilations
of financial information that are derived from the accounting records of abusiness. There are different types of final reports:
9.1. Statement of Cash Flows
Learning Activity 9.1.
The business day to day activities are concerned with purchasing and selling,
receiving and paying, investing and financing the operations of the business. It
means that there is a kind of flow of business cash in and out.
1. Suggest the financial report in which business cash in and out can be
shown.
2. Enumerate the purpose of this report3. Explain the different parts of this report
The cash flow statement is a financial statement that show the business cash
inflow and cash outflow for a certain period.
Purpose of a statement of cash flows:
To provide information about the cash inflows and outflows of an entity during
a period.
To summarize the operating, investing, and financing activities of the business.
The cash flow statement helps users to assess a company’s liquidity, financial
flexibility, operating capabilities, and risk.
The statement of cash flows is useful because it provides answers to the
following important questions:
– Where did cash come from?
– What was cash used for?
– What was the change in the cash balance?
Specifically, the information in a statement of cash flows, if used with information
in the other financial statements, helps external users to assess:
– A company’s ability to generate positive future net cash flows,
– A company’s ability to meet its obligations and pay dividends,
– A company’s need for external financing,
The reasons for differences between a company’s net income and associatedcash receipts and payments.
Both the cash and noncash aspects of a company’s financing and investing
transactions.
In cash flow, Cash inflows, cash outflows and finally the deficit or surplus are
discussed as follow:
9.1.1. Cash inflows
Cash inflow refers to the revenue generated or income received by the
business. In simple terms, it is the cash that comes into the organisation due to
its operating, financial or investing activities. Cash Inflow includes the following:
Cash Inflows from operating activities
Operating activities are all the things a company does to bring its products and
services to market on an ongoing basis. Cash inflow from operating activities
indicates the amount of money a company brings in from its ongoing, regular
business activities, such as:
– Cash receipts from sale of goods,
– Cash receipts from the rendering of services,
– Cash receipts from royalties,
– Cash receipts from fees,
– Cash receipts from commissions,
– Cash receipts customers;
– Cash receipts from recovery of trade debts;
– Covered insurance claims;
– Cash receipts from sales of non-current assets;
Cash Inflows from Investing Activities
Cash inflows from investing activities is a section of the cash flow statement that
shows the cash generated relating to investment activities. Investing activities
include:
– Cash receipt from disposal of fixed assets including intangibles.
– Cash receipt from the repayment of advances or loans made to third
parties (except in case of financial enterprise).
– Cash receipt from disposal of shares.
– Interest received in cash from loans and advances. Dividend received
from investments in other enterprises.– Cash receipts from sales of non-current assets (except for held-for resale);
Cash Inflows from financing activities
It is the net amount of funding a company generates in a given time period. It
includes the followings:
– Cash proceeds from issuing shares (equity or/and preference).
– Cash proceeds from loans, bonds and other short/long-term borrowings.
– Cash receipts from borrowing (irrespective of maturity) from third
parties (including credit institutions).
QuickBooks itself identifies the activities following the recording command and
produces the statement.
9.1.2. Cash outflows
Cash Outflow refers to the amount that a business disburses or the expenditure
incurred by a company during the financial year, which means that it is the
amount which goes out of the business.
Cash Outflows from operating activities:
Cash payments to acquire materials for providing services and manufacturing
goods for resale. It includes:
– Cash payments to suppliers for goods and services.
– Cash payments to and on behalf of the employees.
– Cash payments to an insurance enterprise for premiums
– Taxes paid;
– Cash payments to purchase current investments;
Cash Outflows from investing activities
Cash out flows from investing activities is a section of the cash flow statement
that shows the cash.
It includes:
– Cash payments to acquire fixed assets including intangibles and
capitalized research and development.
– Cash payments to acquire shares, warrants or debt instruments of other
enterprises other than the instruments those held for trading purposes.
– Cash advances and loans made to third party
– Cash payments to build, reconstruct or repair non-current tangible
assets– Cash payments to acquire securities.
Cash Outflows from financing activities
Cash outflow from financing activity measures the movement of cash between
a firm and its owners, investors, and creditors. It includes:
– Cash repayments of amounts borrowed (long term loan)
– Interest paid on debentures
– Dividends paid on equity and preference capital.
– Cash payments to acquire own shares;
Example
Mrs. APENDEKI, started her shop with a balance carried down of FRw
12,500,000.
She also got a bank loan from VISION FUND worth FRW 2,000,000 for
increasing the business capital.
She bought a building of FRW 12,000,000
One of her old customer paid the amount due of FRW 345,650.
Payment of loan in full with an interest of FRW 350,000
She sold some of her old furniture on FRW 500,000 and received commission
or FRW 45,000.
She paid FRW 940,650 to acquire her own shares in I&M Bank Rwanda
FRW 150,000 paid to suppliersThe Mrs. APENDEKI TRIAL BALANCE will be displayed as below:
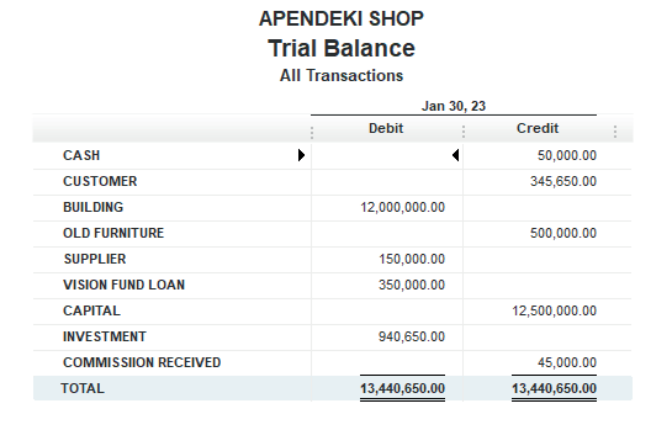
Figure 9.1 Trial Balance
Steps to present the cash flow statement
Company file is created
Charts of accounts are created
Transactions are recorded in the journal
Click on Report on QuickBooks Home page, Company& Financial, thenStatement of Cash Flow.
Figure 9.2 Selection of Cash Flows Statement
In preparation of cash flow statement, QuickBooks considers the credit side
of trial balance as income (Cash Receipts or cash in). While the debit side
of the trial balance is considered as expenses (Payment or cash out). In cash
flow statement, receipt or income amount are positive figures while payments
or expenses amount have negative figures. The difference between the total
receipt and total payment is NET INCOME. So, the net income for the periodis FRW 45,000.
The Mrs. APENDEKI cash flow statement on 30th January 2023 will be displayed as below:
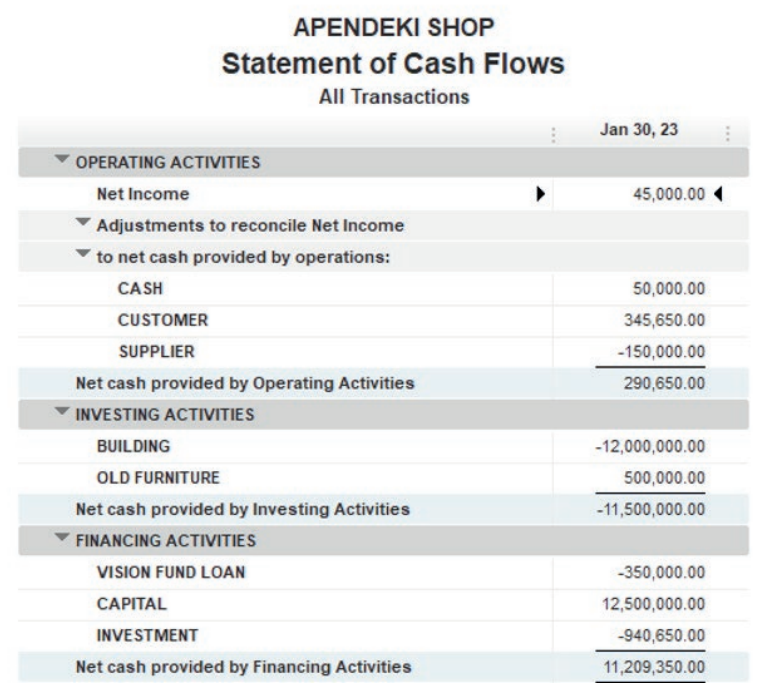
Figure 9.3 Cash flow statement on 30th January
9.1.3. Surplus and deficit
Surplus: A surplus in cash flow statement is the cash that exceeds the cash
required for day-to-day operations. If cash received by the business during a
certain period is greater than cash paid for the same period, the difference is
positive (positive balance), it is called “surplus”
Deficit: This is a negative cash flow. It is when the business has more outgoing
than incoming money. It indicates that a company has more money moving outof it than into it.
a) How to deal with surplus
Positive cash flow indicates that a company has more money flowing into the
business than out of it over a specified period. This is an ideal situation to be in
because having an excess of cash allows the company to:
– Expand business activities
– Settle debt payments
– Reinvest in itself and its shareholders
– Acquire new fixed assets
– Increase credit sales and decrease cash sales
– Increase cash purchases and decrease credit purchases
Positive cash flow does not necessarily translate to profit, however the business
can be profitable without being cash flow-positive, and you can have positive
cash flow without actually making a profit.
b) How to deal with deficit?
• Increase cash sales and decrease credit sales.• Increase credit purchases and decrease cash purchase
Application Activity 9.1.
1. Define a cash flow statement
2. Differentiate:
a) Surplus from deficit
b) Operating activities from Investing activities
3. Nadine had the following transactions during the year 2020
a) Cash received from customers 32,900
b) Cash paid to suppliers 17,950,000
c) Cash paid to employees 11,250
d) Interest paid 2,100
Required: Prepare Nadine’s cash flow statement for the year ended 31December 2020.
9.2. Statement of profit & loss
Learning Activity 9.2.
To start any business activity, the owner has to invest his money and he
expects the returns from this investment within a certain period. To achieve
this, a number of expenses to run day to day business activities is incurred. The
owner can sometime get additional income from other activities out of the mainbusiness. All of these should be well managed for achieving targets.
1. What do you think will be the components of the statement in which the
owner prepares the results of his investment?2. Discus the effects of this results on the owner investment
It is a financial statement that shows the net profit or net loss that the business
that has been made from all the activities during a financial period. The net profit
(or loss) is determined by deducting all the expenses from all the incomes of
the same financial period. In practice, the trading account is combined togetherwith the net profit and loss account into one report the income statement
9.2.1. Purpose of profit and loss account statement
The main reason why people set up businesses is to make profits. Of course, if
the business is not successful, it may well incur losses instead. The calculation
of such profits and losses is probably the most important objective of the
accounting function. The owners will want to know how the actual profits
compare with the profits they had hoped to make.
Knowing what profits are being made helps businesses to do many things,including:
Planning ahead
• Obtaining loans from banks, other businesses, or from private individuals
• Telling prospective business partners how successful the business is
• Telling someone who may be interested in buying the business how
successful the business is
• Calculating the tax due on the profits so that the correct amount of taxcan be paid to the tax authorities.
9.2.2. Trading account
One of the most important uses of trading and profit and loss accounts is
that of comparing the results obtained with the results expected. In a trading
organization, a lot of attention is paid to how much profit is made, before
deducting expenses, for every sales revenue.
This part consists of Net Sales (The difference between total sales and returns
inwards.) and Cost of goods sold.
Net sales
To find a Net sale in Quick Books, follow these steps:
Company file is created
Charts of accounts are created
Transactions are recorded in the journalClick on Company and Make General Journal Entries
Figure 9.4 Selection of General Journal Entries
The QuickBooks general journal recording window appears and the userrecords transactions by respecting the rule of double entry.
Figure 9.5 Empty General Journal
Example:
Mrs. APENDEKI, started her shop with a balance carried down of FRw
12,500,000 cash.
She sold goods as follow:
– Cash: FRW 341,000
– Bank: FRW 457,000
– Credit to Alexis: FRW187,000
– Alexis returned goods valued at FRW 37,000.
Required: Record the transactions above and present the net sales.The records of transactions in the General journal
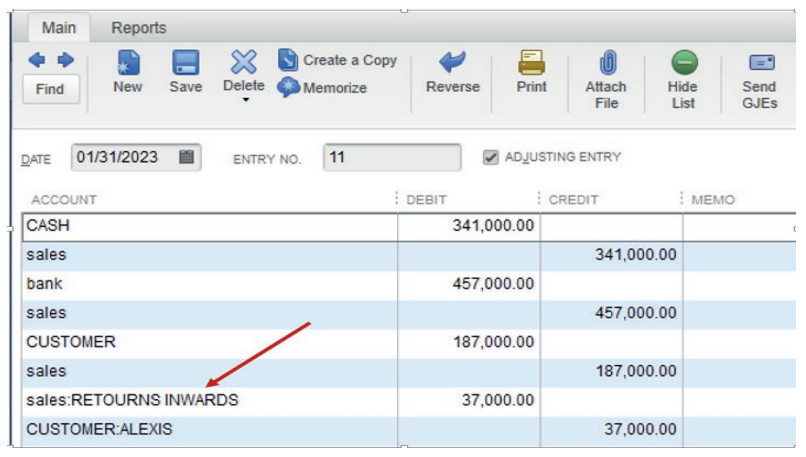
Figure 9.6 Filled general Journal
Note: To insure that returns in wards from customer is deducted from Total
sales of APENDEKI, it requires that the account is created in type of Income,Account Name is Returns inwards of course and Sub account of Sales.
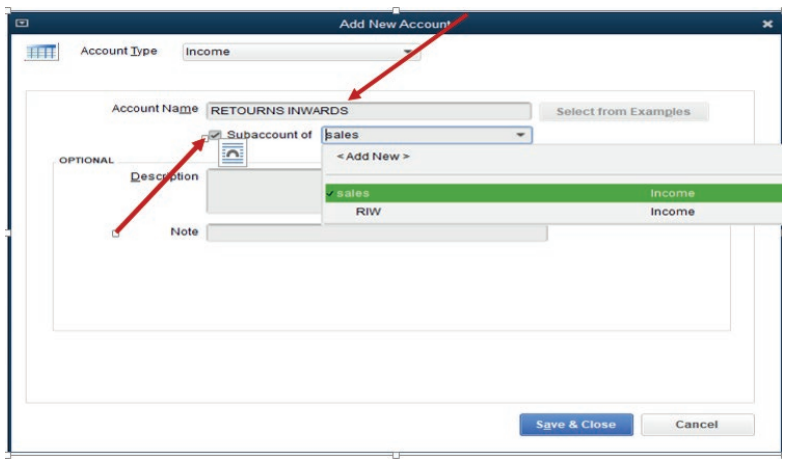
Figure 9.7 Returns inwards and Sub account of sales.
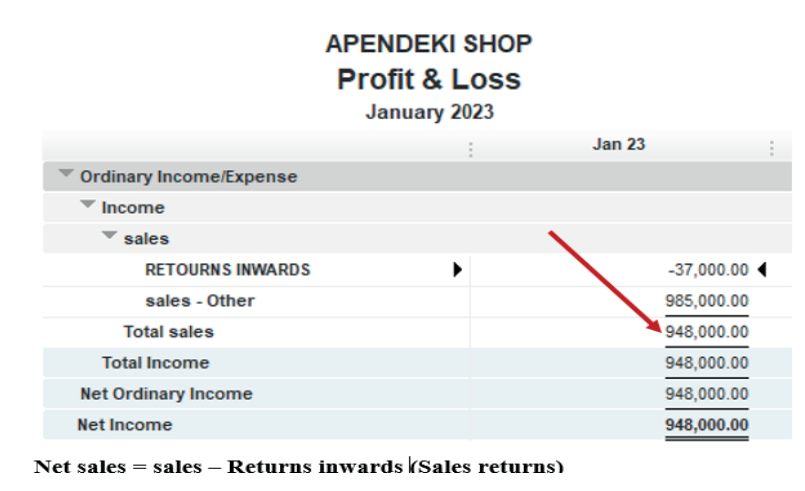
Figure 9.8 Result of Net Sales
Cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold is the total amount the business paid as a cost directly
related to the sale of products. Depending on your business, that may include
products purchased for resale, raw materials, packaging, and direct labor related
to producing or selling the good.
It includes the opening stock, purchase associated with wages and carriage
inwards, minus returns outwards and closing stock. QuickBooks has a type of
account called Cost of Goods sold. The above mentioned are the sub accounts
of Cost of goods sold account.
Example: Let’s add some transactions on the PAENDKI business:
Purchase: By cheque: FRW 25,000, by credit FRW440,000
Purchase return FRW 100,000
Required: Prepare the cost of goods sold and Gross profit
To find the cost of goods sold in Quick Books, follow these steps:
Company file is created
Charts of accounts are createdTransactions are recorded in the journal
Click on Company and Make General Journal Entries
Record the transactions by respecting the rules of double entryClick on Reports, Company and Financials then Profit and Loss Standards

Figure 9.9 Cost of Goods Sold
Gross profit:
The gross profit of a company is the total sales of the firm minus the total cost
of the goods sold. The total sales are all the goods sold by the company. The
total cost of the goods sold is the sum of all the variable costs involved in sales.
Gross profit is the excess of sales revenue over the cost of goods sold. Where
the cost of goods sold is greater than the sales revenue, the result is a gross
loss. By taking the figure of sales revenue less the cost of goods sold to generate
that sales revenue, it can be seen that the accounting custom is to calculatea trader’s profits only on goods that have been sold.
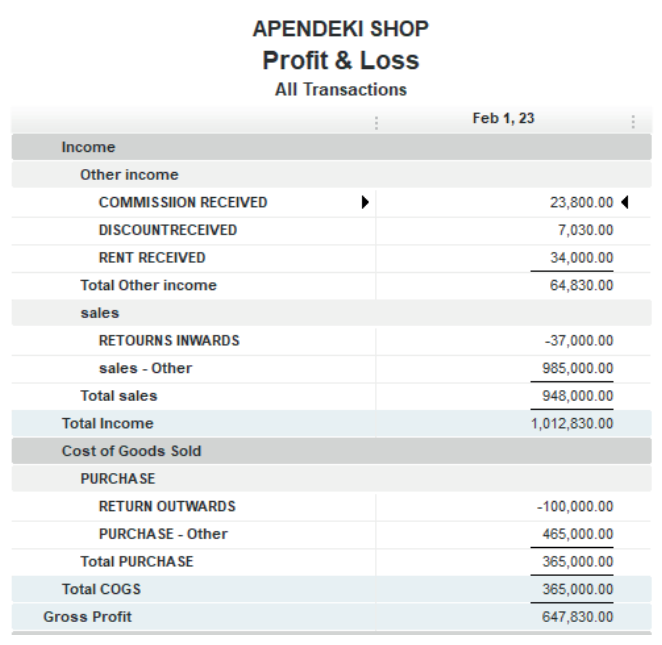
Figure 9.10 Gross Profit
9.2.3. Profit and Loss account
A profit and loss statement (P&L), also known as an income statement, is a
financial report that shows a company’s revenues and expenses over a given
period of time, usually a fiscal quarter or year. It is one of four major statements
in the financial reporting process, and it shows the organization›s net profit or
loss during that time
QuickBooks will provide this financial statement by adding business other income
on the gross profit and subtracting the business total operating expenses.
Business other income
The business can get more additional income which is not from its main activities.
This will be added to the gross profit before subtracting all expenses incurred
during a period. This include:
• Rent received
• Commission received• Discount received…
Let’s add other income on APENDEKI business as follow;
Rent received FRW 34000
Commission received FRW 23800
Discount received FRW 7030
All of other income has been received by cash.
To record the other income in Quick Books, follow these steps:
• Company file is created
• Charts of accounts are created
• Transactions are recorded in the journal
• Click on Company and Make General Journal Entries
• Record the transactions by respecting the rules of double entry
• Click on Reports, Company and Financials then Profit and LossStandards
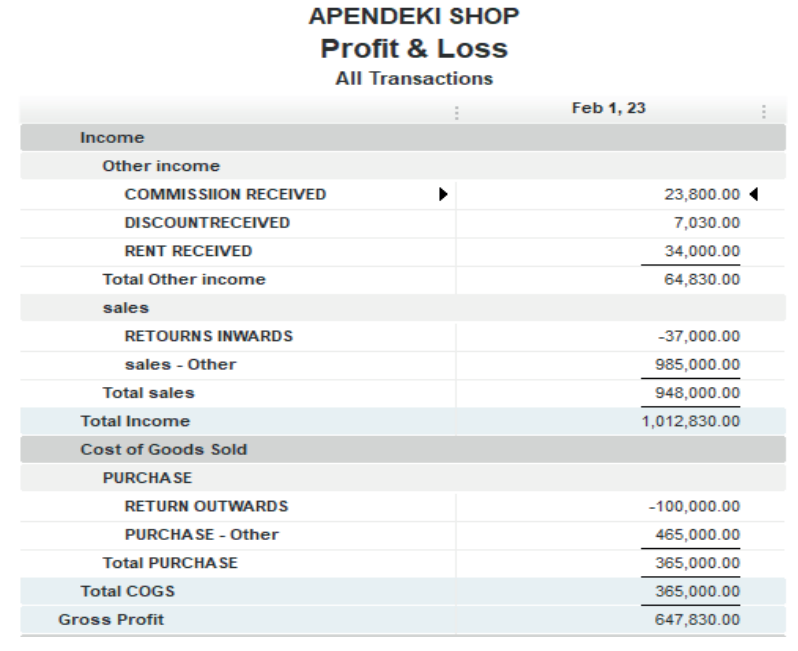
Business operating expenses
Operating expenses, operating expenditures, or refers to the costs incurred
by a business for its operational activities. In other words, operating expenses
are the costs that a company must make to perform its operational activities.
It includes: Salaries, wages, stationeries, bad debts, carriage outwards, rent
expenses, insurance …
Let’s add some expenses on APPENDEKI business
Example: Paid rent of FRW 200,000by cash and salary of her assistant 0f
FRW 50,000 by cheque.
To insert the expenses in Quick Books, follow these steps:
• Company file is created
• Charts of accounts are created
• Transactions are recorded in the journal
Click on Company and Make General Journal Entries
Record the transactions by respecting the rules of double entry (Debiting
expenses and crediting the corresponding account)
Click on Reports, Company and Financials then Profit and LossStandards
The expenses will appear in the income statement as follows:
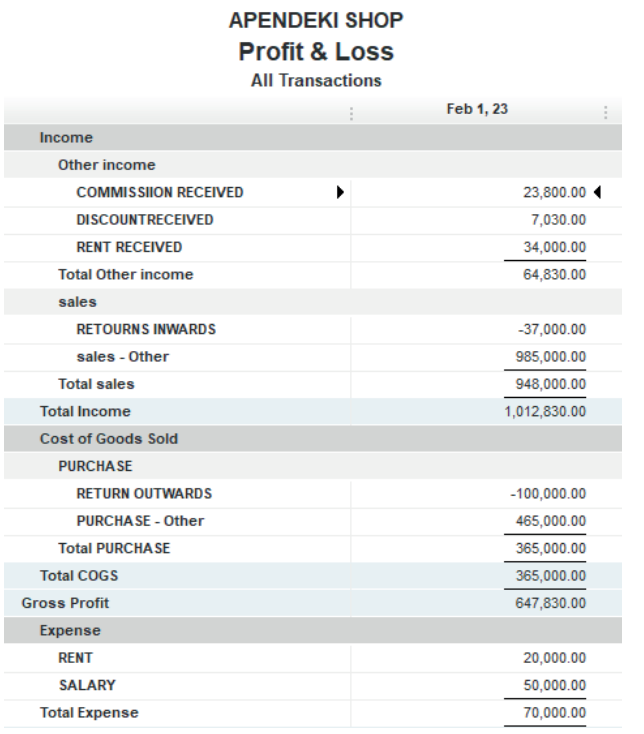
Figure 9.11.Expense in Income Statement
Business Net Income (Profit/Loss)
Net income is gross profit minus all other expenses and costs as well as any
other income and revenue sources that are not included in gross income. Profit
and loss is calculated by taking the total revenue derived from an activity andtaking away the total expenses.
It looks like this: Profit and loss = total revenue – total expenses.
If the resulting figure is negative, the business has made a loss. If it is a positive,
the business has made a profit. Net loss is the excess of expenses overrevenues while Net income is the excess of revenues over expenses.
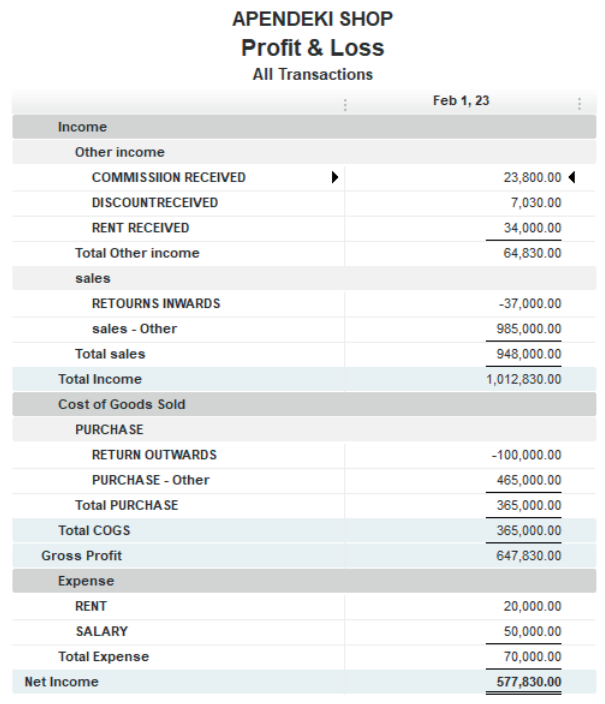
Figure 9.12 Net Income with the excess of revenues over expenses
The business Net Income is transferred to the statement of financial position.
In case of profit, it increases the owner’s equity while the loss decreases the
owner’s equity.
The APENDEKI SHOP made a profit and it will be transferred to the balancesheet in the next lesson.
Application Activity 9.2.
The transactions below have been extracted from the books of MULINDI
Ltd during the month of February 2020
a. Starting the business with 200,000,000 FRW. A half of it at bank, the
remaining amount cash in hand.
b. Receiving 10,000,000 FRW from BK deposited at the account.
c. Purchasing goods valued at 4,500,000frw by cash.
d. Credit purchase worth 7,800,000frw from supplier JEF.
e. Cash sale worth 12,800,000frw
f. Bought furniture of 364,000 FRW and paid by cash. Carriage inward
was 5,000rwf
g. Returning goods valued at 1,398,000FRWto JEF
h. Payment to JEF worth 3,120,000frw. A discount of 2.5 per cent is
received.
i. Sale on credit to KANYAMANZA WORTH 2,387,500 FRW
j. KANYAMANZA returned goods worth 1,000,000 FRW, he also paid
1,000, 000FRWon the remaining amount and he is allowed a discount
of 5 per cent.
k. Paid wages by cash of 250,500 FRW
l. The insurance is paid by cheque 740,000FRW.
m. Rent received by cheque is 90,450 FRWRecord these transactions and prepare the statement of profit and loss.
End of Unit Assessment
1. What is a statement of Profit and loss2. Complete the table below:
3. List the purpose of statement of profit and loss account
4. The transactions below have been extracted from the file of JYAMBERE
Ltd.
i) Starting the business with Cash: FRW 12,000,000
ii) Bought goods on credit from Anna valued at FRW 8,000,000
iii) Sales of goods on credit to worth FRW 2,000,000
iv) Purchase goods of FRW 2,000,000 to Anna
v) Payment of FRW 2,500 for insurance by cheque
vi) Sales return valued at FRW 1,000,000
vii)Rent received in cashPresent the statement of profit and loss
9.3. Statement of financial position
Learning Activity 9.3.
MUKAMANA, a sole trader at NYAGATARE has the file with the following
information
– Land 4,000,000
– Motor vehicle 5,000,000
– Machinery 4,000,000
– Capital 10,000,000– Long term loan 3,000,000
You are asked to:
1. Show the accounting equation from the given information
2. Which financial statement in which the accounting equation isapplied?
A business owns properties. These properties are called assets. The assets
are the business resources that enable it to trade and carry out trading. They arefinanced or funded by the owners of the business who put in funds.
9.3.1. Assets
An asset is a resource controlled by a business entity/firm as a result of past
events for which economic benefits are expected to flow to the firm.
An example is if a business sells goods on credit then it has an asset called a
debtor. The past event is the sale on credit and the resource is a debtor. This
debtor is expected to pay so that economic benefits will flow towards the firm
i.e. in form of cash once the customers pays. Assets are classified into two
main types:
• Fixed (Noncurrent) assets
• Current assets.
Noncurrent assets: are acquired by the business to assist in earning revenues
and not for resale. They are normally expected to be in business for a period of
more than one year.
Major examples include:
– Land
– Buildings
– Plant and machinery
– Fixtures,
– Furniture & fittings
– Equipment
– Vehicles, …
Current assets: They are not expected to last for more than one year. They
are in most cases directly related to the trading activities of the firm. Examples
include:
– Stock of goods (for purpose of selling).
– Trade debtor’s/accounts receivables (owe the business amounts as a
resort of trading).
– Other debtors (owe the firm amounts other than for trading).
– Cash at bank.– Cash in hand.
In QuickBooks, the assets of the business are presented in balance sheet as
long as the records of transaction took place following the rule of double entry.
Once the user needs to check the business assets, he/she must ensure that:
The company profile is created of course
The charts of account and sub accounts relating to the assets
The proper records
Presentation of the report through reports, Company and Financials then
balance sheet standard
Example: Consider the following transactions extracted from the books on XYX
Ltd as they took place during the month of January 2022.
• FRW 1,780,000 cash invested in business
• Receiving a loan from BANK OF KIGALI: FRW 2,000,000
• Bought vehicle for delivery: FRW 1,000,000 paid by cash
• Drawings from bank: FRW 25,000
• Credit purchase of FRW 45,000 from MUTESI
• Sales on credit worth FRW 98,000 to AGNES
Required: Prepare the balance sheet by showing the total assets, equity and
liabilitiesXYZ Ltd TOTAL ASSETS
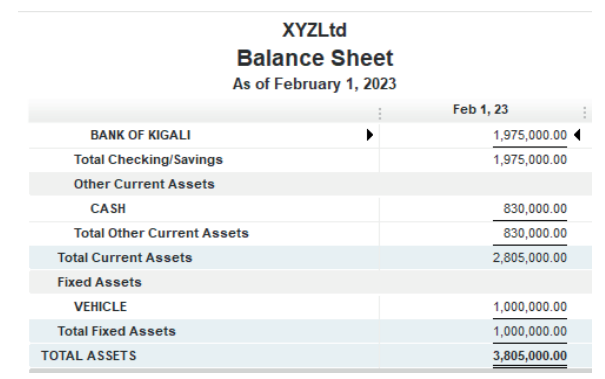
Figure 9.13 current assets and Fixed assets
9.3.2. Equity
Equity is the net amount of funds invested in a business by its owners, plus any
retained earnings (Net profit): Owner’s equity = capital plus net profit minus
drawings.
This is the residual amount on the owner’s interest in the firm after deducting
liabilities from the assets. It includes: Items like introduced capital, profit/loss
and drawings appear under equity.
Owner’s equity= capital +Net profit/- Loss - Drawings.
The XYZ Ltd equity consists of the capital with it the owner started the business,
the net income from statement of profit & loss and the drawings. It appears asfollows:
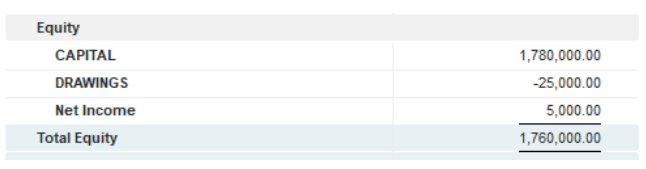
Figure 9.14. Total Equity
9.3.3. Liabilities
These are obligations of a business as a result of past events settlement of
which is expected to result to an economic outflow of amounts from the firm.
An example is when a business buys goods on credit, then the firm has a liability
called creditor. The past event is the credit purchase and the liability being the
creditor the firm will pay cash to the creditor and therefore there is an out flow
of cash from the business.
– Liabilities are also classified into two main classes.
– Non-current liabilities (or long term liabilities)
– Current liabilities (or short term liabilities
Non-current liabilities: are expected to last or be paid after one year. This
includes long-term loans from banks or other financial institutions.
Example: 4 years loan
Current liabilities: last for a period of less than one year and therefore will bepaid within one year. Major examples:
Trade creditors/ or accounts payable: owed amounts as a result of business
buying goods on credit.
Other creditors: owed amounts for services supplied to the firm other than
goods.
Bank overdraft: (Sundry) amounts advanced by the bank for a short-term
period.
Unearned revenues
Prepaid income
According to the transactions above, XYZ Ltd has a LOAN as long term liabilityand CREDITOR AGNES as current liability. The total liability appears as below:
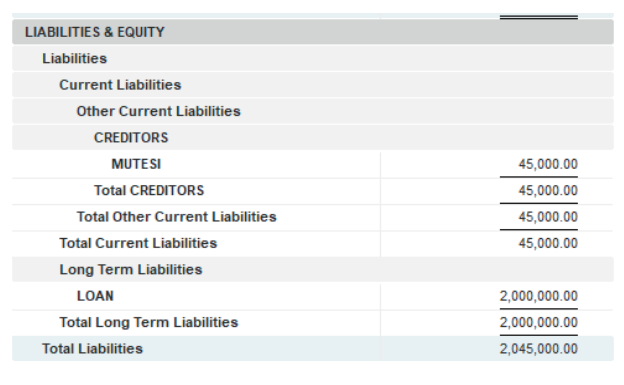
Figure 9.15. Current liabilities and non-current liabilities
Accounting equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity (3,805,000 = (2,045,000 + 1,760,000)
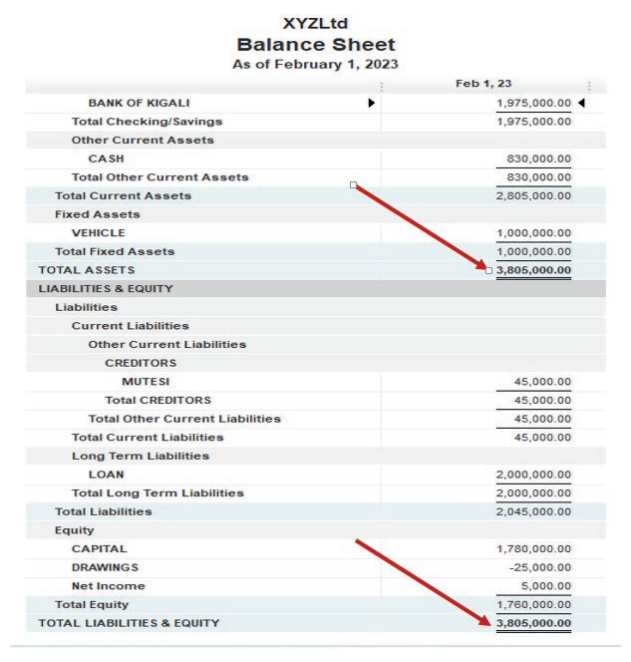
Figure 9.16. Total Liabilities and Equity
Application Activity 9.3.
1. Define the balance sheet
2. Give the main parts of balance sheet3. Explain the effects of Profit or loss on owners’ equity
End of Unit Assessment
1. Define the balance sheet
2. Give the main parts of balance sheet
3. Explain the effects of Profit or loss on owners’ equity
4. The following transactions have been extracted from the books of
ASIFIWE Trading Company:
– On 1st February, 2022 Starting business with RWF 60,000,000 cash
– 2nd February, 2022 Receiving a loan from KCB of RWF 20,000,000
– 8th February, 2022 Buying premises for RWF 1,100,000 by cheque
– 10th February, 2022 Purchasing goods on credit from Peter for
RWF 4,500,000
– 11th February, 2022 Selling goods on credit to KALISA for RWF
6,500,000
– 12th February, 2022 receiving cash from KALISA (full payment
of his debt)Required: Prepare the statement of financial position of the business
UNIT10:IMPORT AND EXPORT DATA TO/FROM
Key unit competence: Import and export data to/from other systemand software.
Introductory Activity
The senior accountant of MGDS Ltd has an urgent meeting with the business
owners. He is required to attend the meeting with well printed financial reports
and list of vendors, customers, charts of account and items so that the owners
will be using them in the decision making process. Because of urgency, the
accountant is wondering how he can get all the required reports and list out of
QuickBooks.
a. If you are acting on behalf of the accountant o MGDS Ltd, What can you
do?b. How can you do this?
Instead of starting from scratch, you can transfer data to and from QuickBooks.
This makes it easy if you need to convert, upgrade, or create a new company file.
The user can import data like bank transactions, accountant’s changes, general
journal entries, and batch transactions. The customers and vendors also can beimported or exported to and from QuickBooks.
10.1. Data import
Learning Activity 10.1.
1. Information is different from Data. True or False.
2. Vendors and customers can’t be imported from external source to
QuickBooks. True or False
3. Read the information in the table below and prepare in excel sheet andimport it in QuickBooks as an accountant of XYZ Ltd.
Data is defined as facts or figures, or information that’s stored in or used by a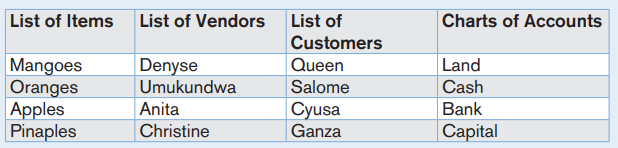
computer. In accounting, data are all (ledgers and journals and spreadsheets)
that support a financial statement.
10.1.1. Meaning
Data Import lets you upload data from external sources and use it in other
system. In Quick books, data can be imported from excel or spread sheet to
be used automatically in QuickBooks. Data can also be exported from other
external software and system.
10.1.2. Transactions to be imported
The user can have a numerous data on his computer but out of QuickBooks.
There is no reasons to take time re-typing. Instead, data like list of vendors,
customers, charts of account and items… can be imported from excel toQuickBooks.
Application Activity 10.1.
1. What is the meaning of data import?
2. Give three examples of data that can be imported from external sourceto QuickBooks
10.2. Process to import and export
Learning Activity 10.2.
The QuickBooks users or accountants in general are always facing the issue
of a huge data to record in system. For not losing time, if data are in other
computer system, the user can import it for processing it as fast as possible.List the steps associated with data import.
Example: HOPE SHOP, a manufacturing company is willing to create a chart
of account, list of items, customers and vendor in its QuickBooks for staring itsday to day business activities.
10.2.1. To import the list of vendors
Start on QuickBooks Home page and click on VENDORS
The vendor window appears as follow and the user has only one vendor called
MUNYABARABE. As longer as there is another file on the user’s computer
containing a number of vendors, the user will not waste his time to record them,contrary, he has to IMPORT
From the above window,
Click on Excel if there is a need to import from an excel sheet document. For
us, we need a list of vendors in excel. A click on Import from Excel gives
the following window in which the user has to select Vendors as he needs toimport the vendors.
A click on Vendor gives an empty excel sheet. A user has to close it for browsing
the appropriate file containing data he needs to import. By closing this emptyexcel sheet, it is better to select: I’ll Add My Data Later. And don’t Save.
Click on I’ll Add My Data Later to find the field of Browser
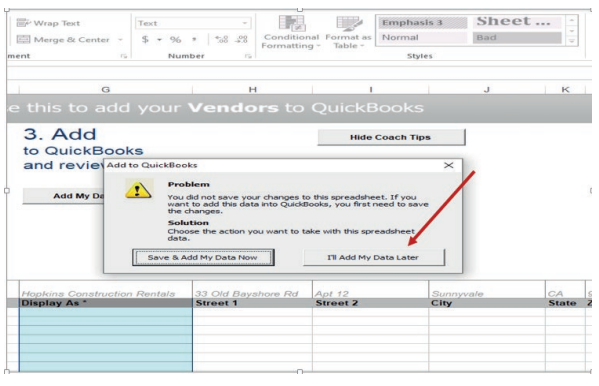
Browse the file containing data to be imported
A click on browser leads to the file location. It is located on desktop and file
Name in MY VENDORS.
A Click on Open gives to the user an option to add data from Excel sheet to
QuickBooks. It means that the list of vendors included in MY VENDORS file are
going to be added on the only one vendor MUNYABARAME in QuickBooks. It
also gives the option to edit the data before being imported.Click on Add My Data Now
From the window below the user gets View vendor list which leads to the final
list of all vendors in QuickBooks.
The user finally gets the long list of all business vendors without losing time to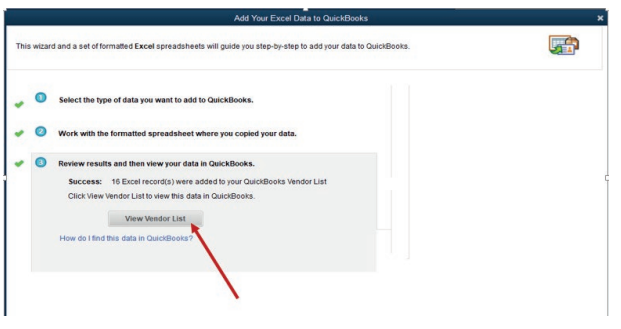
type it but by importing it.
The same process can be used on any other data that the user is willing to
import from Excel file.
Application Activity 10.2.
1. What is data import?2. Enumerate the steps followed to import data from Excel to QuickBooks
10.2.2. Data Export
Learning Activity 10.2.
1. What is data export?
2. Enumerate the steps followed to export data from QuickBooks to Excelfile format
Export means to carry away. To remove, to carry or send (something) to some
other place. Data export is defined as the extraction and conversion of raw data
from their existing place and format into a format required by another.
a. Data to be exported
The user can have a numerous data in his QuickBooks but not on his computer.
There is no reasons to take time for re-typing. Instead, data like list of vendors,
customers, charts of account and items… can be exported from QuickBooks
to excel files.
Apart from this, the financial repot of business can be also exported and be
presented using another format different to the one used in QuickBooks.
b. Process to Export data
If the company profile has been created, list of items, list of vendors, list of
customers, chart of account and business transactions are recorded correctly,
the remaining task is export data from QuickBooks to another file format.
Example:
APENDEKI SHOP, a manufacturing company created a long list of chart of
account, list of items, customers and vendor in its QuickBooks for staring its day
to day business activities. At the end of the day, business transactions have been
recorded and the reports presented in QuickBooks. The user recognizes that
the accounting report should be submitted in excel format not in QuickBooks.
To export the report, (Trial balance, Income statement balance sheet and cash
flow statement) there are the steps to follow:
Start on QuickBooks Home page and click on REPORTS; Company &Financials,
Profit &loss if you are to export the income statement. The next step is to clickon Excel and Create a New Work Sheet. It appears as follows:

Click on Export. The following windows appears:
The same data as the one presented by QuickBooks is exported and displayed
in Excel. As it is in Excel now, it can be well edited and presented to the differentusers better than it was in QuickBooks.
The same process can be used to export data like list of vendors, customers,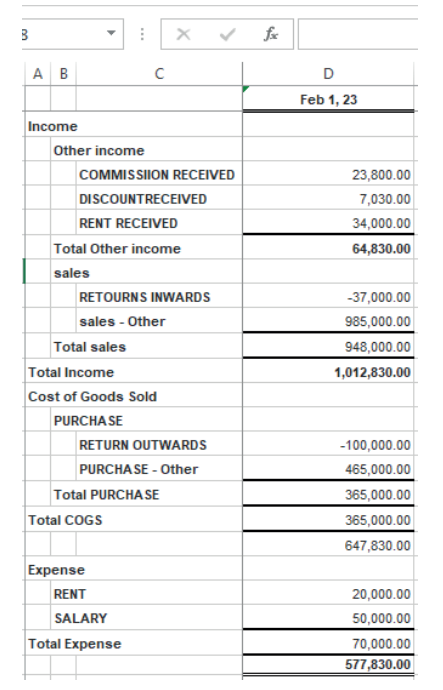
charts of account and items from QuickBooks to Excel or any other possibleexternal files.
Application Activity 10.2.
1. Differentiate Data import from data export
2. Trial balance can’t be exported from QuickBooks to external files. True
or False.
3. Read the information in the table below: record it in QuickBooks and
export it from QuickBooks to an excel format file as an accountant ofXYZ Ltd
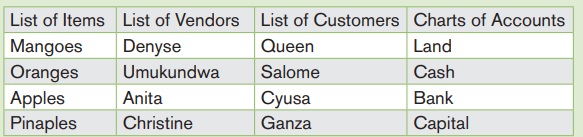
End of Unit Assessment
1. Define the following concepts:
• Data
• Import
• Export
2. Discuss the advantage of importing or exporting data from and to
QuickBooks and excel file.
3. GOOD LUCK Shop is a small sole trade business of purchasing and
selling of Eggplants. It is located in MUGANZA Sector, RUSIZI District
in Western Province (Tel +250788373939
GOOD LUCK Shop is well known for its services in Society and this attracts
clients. Now days GOOD LUCK shop is facing serious problems related to
the use of manual accounting, lack of tool which helps to analyze the financial
prospects in advance, financial projection and the challenge of performing an
effective payroll system.
Therefore the Manager wants to solve the above said problems by using
accounting software QuickBooks to record financial transactions and Ms
Office excel for effectiveness of the business. The decision is made to hireyou knowing that you are skilled and able to help the business to perform well.
Below are transactions occurred during February?
a. On 1st February, 2022 Starting business with RWF 25,000,000 (from
the business owner)
b. 2nd February, 2022 Receiving a loan from KCB of RWF 5,000,000
c. 8th February,2022 Buying premises for RWF 500,000 and paying rent
for RWF 250,000 (both by cheque)
d. 10th February, 2022 Purchasing goods on credit from GASANA for
RWF 2,000,000
Record the information in QuickBooks and export the trial balance and generalledger of GOOD LUCK SHOP in excel file.
BIOGRAPHY
1. SARAH A. DROLLETTE (2009), A Basic Guide for Beginning
QuickBooks Users, Utah State University
2. SaoudJayed MASHKOUR (2019), Accounting in English, Iraq
3. Elizabeth A. MINBIOLE (2000), Accounting principles II, NEW YORK
4. PRU MARRIOTT, J.R EDWARDS AND H.J MELLETT 2002), Introduction
to accounting, 3rd edition, London
5. Kate MOONEY (2008), The essentials of accounting dictionary, Canada
6. Jeffry R. HABER (2004), Accounting demystified, USA
7. BPP Learning media Ltd (2006), Fundamentals of accounting, UK
8. https://quickbooks.intuit.com/global/9. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/QuickBooks
