Topic outline
UNIT 1: PROFESSIONALISM IN NURSING
Key Unit competence
Demonstrate characteristics of nursing profession while providing care to patient
1.0 Introductory activity
This article illustrates how some aspects of professionalism can have impact
on the patient’s care. An example is the importance of handover among health
professionals. After reading the following text and respond to the questions
accordingly:
A study was conducted using about clinical handover practices. Health
professionals employed in public hospitals and community health centres were
involved. The sample comprised doctors, nurses and allied health professionals,
including physiotherapists, social workers, pharmacists, dieticians and midwives
employed in Australia.
The survey collected information about health professionals’ experiences about
clinical handover. Clinical handover is a way health professionals communicate
patient information for continuity, quality and safety of care for that patient.
Despite widespread measures available to improve clinical handover processes,
participants experienced adverse events relating to clinical handover in seven
areas: delayed prolonged treatment, lack of monitoring information, patient
deterioration, medications errors, patient falls, injuries, and putting infants at risk
of infection.
Innovations are needed in training and education to address the complex barriers
to effective handover existing in health care organisations.
1) What is the importance of handover?
2) What are the consequences of lack of handover?
3) Which health professionals involved in this activity?
4) Which other health professional that you know?5) Which qualities do you expect for a good health professional?
1.1. Concept of professionalism and profession
Learning activity 1.1
Mr. G. is admitted in the emergency ward after sustaining a serious road traffic
accident. The healthcare team receive him with empathy and determination.
The nurse performed a rapid assessment and immediately called the doctor
for intervention she uses her time effectively to avoid any complication. She
puts on an IV fluid to prevent shock due to much bleeding and collect blood
sample for lab investigation and send them to laboratory and the lab technician
examined them. The radiologist comes immediately and performed an X-ray of
the fractured bone of the lower limb, the surgeon decided that the patient will be
operated. The anaesthesiologist comes in to evaluate the patient condition to
prepare him for an operation. The surgeon performed operation, the 2nd day after
the operation the patient’s relative received instructions from dietician about the
meal which is accepted after operation. On the 3rd day, the physiotherapist came
to evaluate the level of mobility of the leg for any intervention to facilitate the
patient to move without any complication.
1) Which professionals are involved in treating MR.G?
2) Which activities they performed to save the life of Mr. G?3) What qualities do you expect those professionals to display for Mr. G?
Definition of concepts
A Profession is a group (vocational or occupational) that requires specialized
education and intellectual knowledge.
Professionalism is an awareness of the conduct, aims, and qualities defining a
given profession, familiarity with professional code of ethics, and understanding
of ethical schools of thought, patient-professional interaction models and patient
rights.
Values are qualities or standards desirable or worthy of esteem in themselves, they
are expressed in behaviours, language and standards of conduct.
Professional values are general attributes sized by a professional group. Nurses
may learn about their profession’s values, standards and motivations trough code
of ethics, formal instruction, and role modelling.
Personal values are the beliefs and attitudes held by an individual that provide a
foundation for behaviour and the way the individual experiences life.
Cultural values that are specific to a people or culture are known as cultural values.
Critical thinking is a purposeful, self-regulatory judgment, resulting in interpretation,
analysis, evaluation and inference.
Quality of practice is an evidence-based professional standards balanced againstservice user needs, satisfaction and organisational efficiency
Self-assessment 1.1
1. Define those concepts:
– Professionalism,
– Quality of practice2. Differentiate professional values from personal values
1.2. Common professions
Learning activity 1.2
Observe the following images and match each number of the image to theappropriate profession inside the table below:



Match each number to the suitable profession
1.2.1. Different functions of health care professionals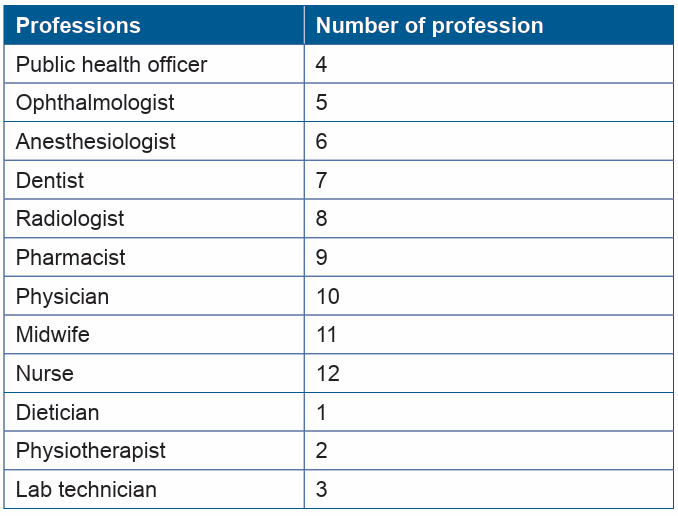
Nurses are the largest healthcare occupation, the specific duties of individual nurses
are dependent on the role, practice setting, population served, and specialty area
of the healthcare practice in which they are employed. All nurses assess patient’s
health, provide clinical treatment, and educate patients and families.
Medical doctor (MD) is licensed health care professional who has the role or
function of assessing the patient, make the diagnosis and can provide medical
treatment and services in any medical specialty, ranging from psychiatry to surgery.
They work in a variety of settings, which include hospitals; outpatient clinics;
academic institutions.
Pharmacists are the medication-use experts in the healthcare system. They
provide medication therapy management, coordinate systems of medication
distribution and dispensing, interface with patients and prescribers, and engage in
the provision of clinical and community-based preventive services.
Dentists perform
the evaluation, diagnosis, prevention and/or treatment
(nonsurgical, surgical or related procedures) of diseases, disorders and/or
conditions of the oral cavity, maxillofacial area and/or the adjacent and associated
structures and their impact on the human body; provided by a dentist within the
scope of his/her education, training and experience, and in accordance with the
ethics of the profession and applicable law.
Physiotherapist can be involved in providing valuable guidance in the inpatient
setting and that adherence to recommendations may lower the risk of readmission.
This observation highlights the role that structured assessments and sharing of
patient information in the inpatient setting have in promoting favourable patient
outcomes after discharge.
They also provide expertise related to exercise prescriptions and training, physical
activity recommendations, patient education, and exercise equipment. Those
working in the inpatient setting are likely to have regular contact with inpatients
either through formal educational sessions or by meeting one-on one with inpatients.
Midwife takes care to the mothers and their babies by providing perinatal care
during pregnancy and delivery with promoting healthy practices like family planning.
Anaesthesiologist works within the operating team by giving anaesthetic drugs
and cardiopulmonary intervention for operated patients.
Lab technician is responsible for testing, analysing, blood test and other body
fluids of patients to confirm the diagnosis.
Radiologist is responsible for performing medical diagnosis for patients usingimaging devices like X-rays, ultrasound, CT scan, MRI etc.
A dietician as a person with legally recognized qualifications in nutrition and
dietetics who applies the science of nutrition to the feeding and education of groups
and individuals in health and diseases.
Public health officer is in charge of policy making and decision making for the
health of populations.
Ophthalmologists diagnose and give treatment to patients with eye diseases or
unhealthy condition. Assess symptoms, diagnose conditions, prescribe medication,
provide follow-up care of patients.Notice: all health professionals, stay current on medical technology and research
Self-assessment 1.2
Explain the functions of the following health professionals:
Nurse
Doctor
Dentist
Ophthalmologist,
Physiotherapist
DieticianLab technician, Radiologist
1.3. Characteristics of a model associate nurse
Learning activity 1.3
Mr. N., 70 years of age, is a male patient who is admitted to the medical-surgical
unit with pneumonia. The patient complains of fatigue, shortness of breath and
cannot finish a short sentence before the respiratory rate increases above the
normal, and presents blue colour on his body extremities. The patient is using
accessory muscles, weak cough reflex.
Vital signs: blood pressure 90/50 mm Hg, heart rate 101 bpm, respiratory rate 28
breaths/min, and temperature 39.5°C.
The nurse Mr.G. performs an assessment to establish a nursing care plan for
Mr. N. : monitoring of vital signs, filling the patient file, entering patient data
in computer system, bed bath and bed making, administration of analgesics,
antimicrobial drugs, and, drug for respiratory system using a proper device;
observation of the patient and record any change, put the patient in suitable
position, administer oxygen, provide health education to the patient’s relative,
evaluate the results and discuss with the doctor about modalities of treatment,
communicate with other health workers about the patient’s condition.
1) Which nursing procedures that will be performed by an associate nurse
to help this patient?
2) Which nursing procedures that will not be done by an associate nurse tohelp this patient?
1.3.1. Definition of terms
A nurse is a person educated and trained to care for sick or disabled. She/he has
completed a program of basic, general nursing education and is authorized by the
appropriate regulatory body to practice nursing in his/her country.
A nurse is a licensed person who is registered with the Rwandan Nursing and
midwifery council based on completion of a recognized education and training
program to take care of, assist and treat the client, who can be an individual, family
or group, sick or well.
Nursing is the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and abilities,
prevention of illness and injury, facilitation of healing, alleviation of suffering through
the diagnosis and treatment of human response, and advocacy in the care of
individuals, families, groups, communities, and populations’’ (ANA, 2017).
Nursing: a profession focusing on assisting individuals, families, and communities
who are healthy or sick to attain, recover, and maintain optimum health and function
from birth to old age (Taylor et al 2011). The use of conducive environment (fresh
air, pure water, cleanness, light) for the patient to assist him/her recovery (Florence
Nightingale 1860). Nursing consists in assisting the individual sick or well, in the
performance of those activities contributing to health or its recovery or a peaceful
death (Virginia Henderson, 1966).
An associate nurse is a member of the nursing team that helps bridge the gap
between health and care assistants and registered nurses. Associate nurses work
with people of all ages, in a variety of settings in health and social care. Their role
contributes to the core work of nursing, freeing up registered nurses to focus on more
complex clinical care. It’s a stand-alone role that also provides a progression route into
graduate level nursing. Some personal qualities that make a good associate nurse are :
1.3.2. Qualities of a good associate nurse
a. Observantion: It’s extremely important for nursing assistants to have
the ability to pay attention to small details. The smallest changes
could be a major health problem for their patient, especially with the
elderly. Minor changes like new bruises and a loss of appetite must
be reported to the patient’s physician. Sometimes, paying attention to
small details like this could be the difference between life and death.
b. Emotional Stability: It takes a strong-willed, compassionate and caring
person for this type of career. Caring for patients can be stressful, especially
those who are struggling with their health or nearing the end of their life.Being supportive and strong for them and their families is crucial.
c. Patience: You will need to have an encouraging and calm manner
while caring for someone who may have just had a stroke and is
learning how to dress again or helping patients walk after surgery.
d. Communication Skills: Nursing assistants or CNAs have to communicate
with doctors, nurses, caseworkers, families, patients and other healthcare
team members daily. It’s important to be clear and detailed as much
as possible with what you’ve observed while caring for your patient.
You will need to listen well, offer support and give clear instructions.
e. Compassion and Empathy: These are qualities that can’t be taught as a
nursing assistant. To have the ability to show compassion and put yourself in
someone else’s shoes and understand how they’re feeling is a much-needed
trait to have while in this career.
1.3.3. The functions of an associate nurse
According to the ministerial order, the associate nurses usually take care of patients
basing on their physical and psychological needs.
1. Provide basic patient care by maintaining patient hygiene, nutrition and
comfort.
E.g.: bed making, bed-bath, position changing, feeding …
2. Monitor the patient’s condition and reports as necessary.
E.g.: taking vital signs, carrying samples taken by the nurse, to the laboratory
for exam
3. Perform sterile and clean procedures with specific focus on prevention and
control of infection in the health facility environment according to established
standards and protocols.
E.g.: simple wound dressing
4. Administer diligently medication within his/her scope of practice according
to prescription and monitor the patient response.
E.g.: provide oral drugs under supervision of registered nurse
5. 5° Carry out pre and post-operative nursing care within his/her scope of
practice.
E.g.: wound dressing
6. Educate and advise the client and other people on continued care and
prevention of recurrence of the health problem.E.g.: provide educational session on hygiene
7. Facilitate patient discharge and where necessary refers him/her to other
health care providers.
E.g.: register discharged patients
8. Transmit verbal and written report and shares information with colleagues
and the direct supervisor on the patient and care provided.
E.g.: fill the vital signs chart
9. Contribute to physical and nutritional rehabilitation in preparation for patient
discharge.
E.g.: Facilitate in patient feeding
10. Provide comprehensive care according to his/her scope of practice to
chronically and terminally ill patients who are referred back.
E.g.: provide support to patient living with HIV or NCDs (hypertension,
diabetes…) reminding or encouraging them to take oral drugs
1.3.4. Comparison of roles between associate nurse and
registered nurses
The respective roles of both associate nurses and registered nurses are to deliver
quality healthcare services to their clients. Although clients benefit from the care
given by associate nurses in a range of settings, associate nurses will contribute
to most aspects of care, including health care delivery and monitoring. Registered
Nurses will take the lead to assessment, planning and evaluation. Registered
Nurses will also lead to managing and coordinating health care with full contribution
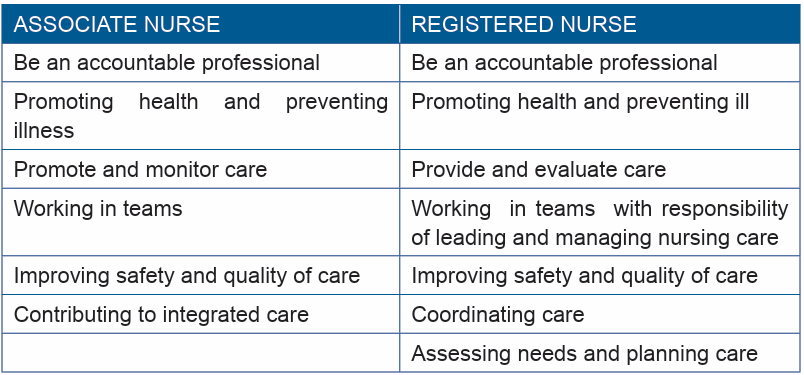
from the associate nurses within the integrated care team.Table3: Comparison between roles of associate nurse vs registered nurse
Self-assessment 1.3
Mr N., a 70 years male patient, is admitted to the medical-surgical unit with
pneumonia. The patient complains of fatigue and shortness of breath and cannot
finish a short sentence before the respiratory rate increases above the normal,
and presents blue colour on his body extremities. The patient is using accessory
muscles, coughs weakly, without any sputum.
The vital signs are: blood pressure 90/50 mm Hg, heart rate 101 bpm, respiratoryrate 28 breaths/ minute, and temperature 39.5°F.
The nurse do an assessment to establish a care plan with the following nursing
care to give for Mr. G. : monitoring of vital signs, filling the patient file, entering
patient data in computer system, bed bath and bed making, administration
of analgesics, antimicrobial drugs, and, drug for respiratory system using a
proper device, observation of the patient and record any change occurring to
the patient, put the patient in suitable position, provide oxygen, provide health
education to the patient relative, evaluate the results and discuss with the doctor
about modalities of treatment, communicate with other health workers about thepatient condition.
1. Describe the activities that will be performed by an associate nurse torespond to the patient’s need?
2. Give three activities that will be performed by a registered nurse to providenursing care to this patient?
1.4. Professionalism
Learning activity 1.4
Mrs D. is working in the surgical ward, she comes to her duty on time, she
organizes her ward , always assess the patient’s needs and make sure the ward
is clean and ventilated she talk to patients’ family and give health education she
communicates timely every abnormal finding to the doctor and always document
the care provided she does follow up of patient lab results and call in the lab if the
results are not available in due time. She encourages her colleagues and always
reminds them that they should take responsibility of their tasks.
On the other side, Mrs Z. is coming late to her duties and ask for permissions
several times and she always find reasons not to come to her duties, she evenfalsifies the medical leave to be able to go and do her business.
When she is in ward, there is a lot of mess, patient’s bed is not clean, the lab
results are not documented on patient’s file and the charts are not well filled. She
talks badly to the patients and their relatives she despises the colleagues and
does not listen to the advises. The unit manager write her the explanation letter
and does not give explanation of her conduct instead she goes to the medical
director and says that every people hates her and despises her and she claims
for not being sent to the training for HIV management because she saw the nurse
in charge of HIV in maternity was trained and when she called meeting to share
the knowledge, Mrs Z refuses to attend and claimed that all nurses should go to
the training while the manager suggested that three nurses will be trained each
trimester so that the patients are not abandoned. she always calls her friends on
the phone in working hours and complain that nobody ever cares for her while
she is always caring for patients alone and go home late due to many patients.
She claims that the hospital is poor and does not provide enough materials for
patient care however, never give report to the unit manager on the drugs and
consumables that is reported every week. She even calls to her cousin who is a
manager of a big company to asks that he would give her another job because
she is not happy to be a nurse.
Compare the behaviour of Mrs. D. and Mrs. Z regarding their nursing profession.
Professionalism is an idea relating to the word “profession” which is almost
synonymous with “occupation” (Downie, 990, pp. 148–157), the same author
indicated the following six characteristics of professionals:
1. The professional has skills or expertise proceeding from a broad knowledge
base.
2. The professional provides a service based on a special relationship with
those whom he or she serves. This relationship involves a special attitude of
beneficence tempered with integrity. To the extent that the public recognises
the authority of the professional, he or she has the social function of speaking
out on broad matters of public policy and justice, going beyond duties to
specific clients.
3. Professionals must be independent of the influence of the state or commerce.
4. The professional should be educated rather than trained and should continue
to develop her or his knowledge and skills within a framework of values.
5. A professional should have legitimised authority and credibility in the eyes
of the general public.
6. A good understanding of bioethics and the ability to apply ethics principles
and skills in the healthcare context is vitally important for all healthcarepractitioners.
i. Responsibility: is an obligation or duty. Condition, quality, fact, or instance of
being responsible; obligation, accountability, dependability, …
ii. Self-determination is defined as the personal decision to do something or
think a certain way, without outside influence.
iii. Accountability is the quality or state of being accountable, especially :
an obligation or willingness to accept responsibility or to account for one’s
actions, it is taking or being assigned responsibility for something that you
have done or something you are supposed to do.
iv. Integrity should be regarded as the primary virtue in the healthcare context.
Healthcare practitioners often support their actions to act or not, on the base
that it would undermine or violate their integrity and/or core beliefs if acting
otherwise.
v. Trust involves an assurance that another will act with the right intentions and
in agreement with fitting moral norms.
vi. Confidentiality the ethical principle or legal right that a physician or other
health professional will hold secret all information relating to a patient, unless
the patient gives consent permitting disclosure.
vii. Adherence to high standards of quality providing evidence-based
healthcare services to those who need them;
viii. Collaboration with others and communicative a working practice whereby
individuals work together for a defined and common purpose, and enables
individuals to achieve that purpose.
Such understanding and application should be fostered during the formal training
of healthcare practitioners and it should continue as part of each practitioner’s
continuous professional development for as long as they practise their profession.
Self-assessment 1.4
1. Explain the authority of a professional in public2. Describe the importance of communication in nursing profession
1.5. Characteristics of nursing profession
Learning activity 1.5
Mr. G. a 60 years old male patient is admitted in the emergency is on the 3rd
day after surgical intervention. The patient complains of dizziness, his body
extremities are cold and pale, vital signs are as follows: blood pressure 80/45
mm Hg, heart rate 131 bpm, respiratory rate 28 breaths/min, and temperature
36.1 °C. The saturation on room air is decreasing to 82% and Hb 10 g/dL.
Mrs. T. a Registered Nurse who is on duty that night, she is a committed nurse
who works with empathy, diligence, and discernment. She is able to manage time
and communicate effectively to her colleague nurses and other health a care
professionals in the surgical unit. She is a hard working with close observation
and use critical thinking to resolve patient’s problems.
When she enters in the room of Mr. G. she remarks that the patient’s operative
wound is bleeding. She takes vital signs, blood sample for lab test and the result
of haemoglobin was 6.5 g/dl. She calls the doctor immediately, and explained
the patient situation the doctor responded that Mr. G. should be transfused, then
the nurse filled a request for the blood transfusion to bring the blood for Mr. G
with the blood Group of A+. However, the lab technician responds that the blood
available is group O+. Mrs.T. never forgets to crosscheck the blood with the
colleague to make sure the patient will not be harmed.
1) What are the qualities that Mrs.T. is using to save the life of Mr.G?
2) If the nurse doesn’t intervene what consequences could result from herinaction?
The following qualities should also characterise a professional nurse.
a. Responsibility: is an obligation or duty. Condition, quality, fact, or instance
of being responsible; obligation, accountability, dependability, …For example,
a nurse should take responsibility to give drug appropriate dose if the doctor
commits an error in prescription.
b. Self-determination is defined as the personal decision to do something
or think a certain way, without outside influence. e.g.: a nurse working with
determination should not wait the unit manager to remind her the care to be
given to the patient
c. Accountability is the quality or state of being accountable, especially: an
obligation or willingness to accept responsibility or to account for one’s actions,
it is taking or being assigned responsibility for something that you have done
or something you are supposed to do. e.g.: if a nurse does not provide care
to the patient according to the quality required, she is accountable.
d. Integrity should be regarded as the primary virtue in the healthcare context.
Healthcare practitioners often support their actions to act or not, on the
base that it would undermine or violate their integrity and/or core beliefs if
acting otherwise. e.g.: the nurse who does not respect patient’s privacy and
confidentiality
e. Effective Communication
In the workplace, nurses must be able to communicate clearly with their
co-workers and with patients and their families. They must be able to take
instructions from co-workers and supervisors, especially in high-pressure
situations.
They must also communicate effectively with patients and their families to
meet their needs and provide quality care. The ability to receive information
effectively and efficiently is essential for nurses. They must be able to read
charts and understand a treatment plan without in-depth instruction. After they
collect data about a patient’s vital signs, they must record that information
immediately and accurately for other nurses, doctors and medical staff to
interpret. Proactive communication with patients and families can set nurses
apart from their peers.
e.g.: the nurse must document on patient file and provide information
necessary like change of vital signs or lab results. If he/she does not report
timely, the patient can get in severe condition and miss necessary interventionat the right time.
f. Optimism While this career may be emotionally challenging at times,
outstanding nurses know how to remain positive and focus on serving others.
Further, nurses who have a positive attitude can act as leaders in their
practice, inspiring optimism in others as well. e.g. :if the patient is in critical
condition, she will not give up to him, she continues to provide care even for
the chronic disease there is a way to improve life condition.
g. Compassion In their career, nurses will see patients suffer. Beyond simply
offering a solution, they must be able to express compassion for patients and
their families. E.g.: a nurse should always consider the pain of the patient and
listen to his/her concerns
h. Even-Temperedness: nurses must be able to manage their responses to
difficult situations in order to solve problems and concentrate on their patients’
health and safety. Not getting visibly angry or upset with patients is important
no matter how difficult the day has been.e.g.: if a nurse is angry to the patient
that one would lose trust
i. Flexibility: Remaining calm under pressure also helps nurses stay flexible
in their work since shifts are typically long. Nurses may have to work nights,
weekends and holidays. On the job, flexibility is a must for nurses. They
cannot predict what the day will bring and what illnesses or injuries they will
have to treat. e.g.: like if the nurse is called during his/ her day off or obligedto go home late due to patient’s condition
Self-assessment 1.5
Mr. G. is admitted in the emergency is on the 3rd day after surgical intervention,
The patient complains of dizziness, and his body extremities are cold and pale.
The vital signs are as follows: blood pressure 80/45 mm Hg, heart rate 131 bpm,
respiratory rate 28 breaths/min, and temperature 36.1 °C. The pulse oximeter on
room air is decreasing to 82%. and Hgb 10 g/dL.
Mrs. T. a registered nurse remarks that the patient’s operative wound is bleeding.
She took blood sample for lab test and the result of haemoglobin was 6.5 g/dl.
She calls the doctor immediately, and explained the patient situation the doctor
responded that Mr. G. should be transfused, then the nurse filled a request for
the transfusion unit to bring the blood for Mr. G with the blood Group of A+
. However, the lab technician responds that the blood available is group O+;
although Mrs.T. knows that the blood with group O+ can help the patient, she
never forgets to check patient identification to make sure the patient will not be
harmed.
1) Explain at least five characteristics of a professional nurse2) What are the qualities of nurses in patient care?
1.6. End unit assessment
End unit assessment
1) Define those concepts: Profession, value
2) Explain the functions of the following health professionals:
Nurse
Radiologist
Lab technicianDentist
3) What is the role of an associate nurse in healthcare team?
4) Compare and contrast the roles of nurse and associate nurse
5) Explain why the health professionals should have the virtue of discernment
6) Using practical examples in patient care, explain the five qualities of
health professionals
7) Explain at least five characteristics of a professional nurse
8) Enumerate the five qualities of health professionals
9) Describe how a nurse can apply the qualities of health professionals in
health care
10) Mr J. is a RN in surgical unit, he has patients with different needs:
The patient A., who was operated for abdominal disease and have to be given a
timely and appropriate food intake according to his condition. Another patient B
was operated for fracture of the left lower limb, and need to be mobilized on the
day provided by the surgeon
The following activities will be required for the nursing management of patients
A and B: monitor the patient vital signs, pain, rehydration/feeding, elimination,
ensure the hygiene, comfort and proper position for the patient, take the samples
for lab examination, document abnormal changes and complete the charts in the
patient’s file, administering drugs according to the prescription, provide health
education, call the dietician for prescription of diet, call the physiotherapist for the
exercise, take the patient to the radiologist for the x-ray
1. What is the task he will do himself as a registered nurse?
2. What are the tasks that will delegate to the associate nurse working in the
same service?
3. Who are the other health professionals who will work with him to assurethe treatment of those patients?
UNIT 2 :NURSES’ CODE OF CONDUCT
Key Unit CompetenceApply the nursing code of conduct
2.0 Introductory activity
Observe the above picture and discuss about the following:
M.E is an enrolled nurse working in district hospital for 3 years. Colleagues and
Unit manager had noticed that the clients assigned to M.E, were not cared for,
wet bed sheets were unchanged and urine bottles not emptied, vital signs not
monitored. M arrived always late also spending a lot of time at the nurses’ station
and on phone while her clients were left without assistance. Her unit manager
and his /her colleagues and care givers raised complaint.
After receiving advice form colleagues and manger, she attends the unit on
time, collaborates with clients and gives care to each client and advocates for
clients’ needs. She becomes a respectful nurse for the clients, improves the
communication and collaboration with unit manager and colleagues and all
assigned clients were cared as required. After reading the above scenario,
analyze the nurse general attitude in the work place and answer to the following
question.
a. Who are the people in the above picture?
b. Show bad behavior of a nurse that are displayed in this scenario?
c. List 3 qualities of a good professional nurse displayed in the scenario
2.1. Introduction to the code of conduct
Learning activity 2.1
Mrs. K. is a registered nurse working in the unit where admitted patient are after
surgical operations. She attends the work always on time, when she arrived in
the morning, she puts on her clear uniform, greets clients and observe overall
situation of t them to identify if there is no emergent situation. She is respectful for
colleagues and clients of all ages. She is kind to everybody in the work even out
of the work, she provides care to all assigned client in safe and timely manner.
Before accomplishing any nursing tasks, she firstly obtains the client consent
and treat them with kindness and respect.
Read the above scenario and answer to the following question
1. Identify the 4 positive professional nurse requirements included in the scenario2. List 2 behaviors that should be respected in the nursing code of conduct
Key Concepts of code and conduct
A code: the Code of Professional Conduct for Nurses is a set of expected national
standards of nursing conduct for nurses and midwives to be respect during the
exercise of the profession
The Code is not intended to give detailed professional advice on specific issues
and areas of practice; rather, it identifies the minimum requirements for conduct in
the profession. A breach of the Code may constitute professional misconduct or
unprofessional conduct (ANA, 2021)
The code of profession conduct will help to address many issues and promote
client and nursing satisfaction.
A conduct: the manner in which a person behaves, especially in a particular place
or situation. Professional conduct refers to the manner in which a person behaves
while acting in a professional capacity.
It is generally accepted that when performing their duties and conducting their
affairs professionals will uphold exemplary standards of conduct.
Specific issues concerning professional practice will be considered when they arise
and may be the subject of professional practice guidelines
Ethics: Ethics refers to moral principles, values that governs a person’s behaviour
or a manner of conducting or accomplishing activities. Ethics deals with principles
or morality and what is right or wrong, it is also concerned with motives and attitudes
and relationship of these attitudes to the good of individuals (Basavanthappa, 2006).
Ethics refers to well-founded standards of right and wrong that prescribe what
humans ought to do, usually in terms of rights, obligations, benefits to society,
justice, or specific qualities.
A code of ethics is a set of guiding principles that all members of a profession
accept. It is a collective statement about the group’s expectations and standards of
behavior. Codes serve as guidelines to assist professional groups when questions
arise about correct practice or behavior. (Poter and Perry Fundamentals of Nursing,
8th edition, Elsevier, 2017).
According to the American Nurses Association (ANA), the nursing code of ethics
and profession conduct is a guide for “carrying out nursing responsibilities in a
manner consistent with quality in nursing care and the ethical obligations of the
profession.” Ethics, in general, are the moral principles that dictate how a personwill conduct (ANA, 2021
Self-assessment 2.1
included in the code of conduct used in Rwanda
1. According to the above definition of nursing code of conduct and aspects
Explain 2 roles of the code of conduct in nursing practice2. Using an example, illustrate how you should honor the nursing profession
2.2. The nursing code of conduct
Learning activity 2.2
Mrs. J. is associate nurse in Internal Medicine and the team of this unit is few
as it comprises only 6 persons for days and night duties Her colleague Mrs.T.
was sick and she was not able to attend to accomplish all assigned task as she
was weak and pregnant. The morning medical round have also ordered taking
blood sample for many clients the even other drugs have been prescribed to
be given before noon. She feels stressed but do her best to accomplish the
assigned tasks. Her colleague Mrs.J. passes in the Mrs.T. subunit observe the
state of T and the assigned tasks; she decides to perform some procedures like
withdrawing blood samples as she is well skilled in puncture of the vein. The unit
manager was very happy and congratulates the nurse.
According to the above scenario,
1. What do you think about the origin of the stress for the nurse T?
2. Identify the professional behaviors of these nurses?
3. What would be the consequences on the clients if the nurse has a bigburden?
Nurses are currently facing various personal, interpersonal, professional, and in
stitutional even socio- cultural challenges in their professional practice and to deal
with them may not be always clear. The lack of one correct approach or attitude
in addressing different issues may lead to ethical issue or a difficult to choose in
different options to resolve them.
Rwandan regulatory body Nursing Council of Nurses and midwives (NCNM)
adopted by the constitution of the Republic of Rwanda of 04 June, 2003 and
the Law no 25/2008of 25/7/2008 establishing the National Council of Nurses and
Midwives and adopted by the cabinet in its session of 09/07/2010. The Code of
Professional Conduct for Nurses and Midwives is supported by Rwanda National
Council for Nurses and Midwives.
2.2.1. Role of nurse‘s code of conduct:
A code of conduct provides structure and guidance for workplace values and
principles. A respected code is important to the nursing profession to help prevent
inappropriate and incompetent behavior and as a guide for nursing performance.
The Code guides nurses and midwives in their day-to-day practice and helps them
to understand their responsibilities in caring for service users in a safe, ethical and
effective way.
The Code supports ethical and clinical decision-making, on-going reflection and
professional self-development. The code informs the general public about the
professional care they can expect from nurses and midwives.
The code also emphasizes the importance of the obligations of nurses and midwives
to recognize and respond to the needs of service users and families (Georges et
al , 2012).
The code of conduct sets standards for the regulation, monitoring and enforcement
of professional conduct
The code of conduct is used in conjunction with the code of ethics as ethics and
professional conduct can’t be separated.
2.2.2. Standards of professional code of conduct:
According to the code of conduct of Nurses and Midwifes provided by the regulatory
body National Council of Nurses and Midwives (NCNM); the standards of nurse’s
code of conduct is summarized as follow:
a. Conduct of a nurse towards patients
Respect for human rights and values
Without prejudices to provision of particular laws that specify the rights of a patientin Rwanda, the nurse / midwife shall:
Promote the respect of human rights, human dignity, culture and spiritual beliefs of
the individual, family and community
Ensure that the individual receives written and sufficient information on which to
base his/her consent for care and related treatment
Keep confidential any information related to an individual and shall share this
information with colleagues advisedly
Collaboration in promoting health activities
A nurse / midwife shall collaborate with members of the community in initiating and
supporting actions to meet the health and social needs
A nurse / midwife shall also collaborate with others in conserving the environment
Refusal to act for lack of capacity and competence: a nurse or midwife is required
to refuse any instructions to perform any activity that is outside his/ her scope of
competence or one for which he/ she lacks sufficient knowledge. However, in case,
in the case, he/ she shall inform his/her supervisor or the person what gave him/her such instructions.
Example: If a medical doctor asks to the nurse to withdraw excess of fluid in the
peritoneal cavity (Ascites), this is a medical task and is beyond the nurse scope of
competence and he/ she must inform the medical doctor that he/ she is not able toperform that procedure
Quality and continuing professional development: the nurse or midwife shall
be obliged to fulfil his/her duties. He/ she shall regularly demonstrate continual use
of technical knowledge and always be trained on modern techniques: the Nursingacts changes as the Medicine also undergo evolution
Obligation to care her/ his personal health: a nurse or a midwife shall be obliged
to take care of his/her personal health so that his/ her responsibility of providingcare is not compromised
Discretion on duty: a nurse or midwife shall ensure that no action or omission on
his/ her part that may be harmful to health
Safe use of science and technology: a nurse or midwife shall ensure that use of
science and technology on duty is compatible with the safety, dignity and people’srights
E.g., use of suctioning machine if not well used can traumatize upper respiratorytract.
Activities contrary to moral and professional conviction: A nurse shall have
right to refuse to participate in activities contrary to his/ her personal moral and
professional convictions. However, such rights shall not contravene his/herresponsibilities towards patients and those who require his/her services
b. Conduct of a nurse or a midwife in performing his/her duties
• Abide by law and regulation in the country in particular those relevant to
his/her nursing profession
• Maintain professional honor: the nurse shall demonstrate all times a
personal conduct that honors the profession and enhance public confidence
in nursing and midwifery staff. The conduct of a nurse must be integral and
even a model in the society
• Participation in designing and implementation of professional regulations:
a nurse or midwife shall participate in designing and implementing guiding
principles of nursing, midwifery management, research in matters regarding
professional practice or duties of a nurse and a midwife
• Participation in developing professional skills; a nurse or midwife shall be
active in developing a core of research based professional skills
• Role in enhancing better working conditions: a nurse or a midwife, acting
through professional federation or association in which he/she is a member,
shall participate in creating and maintaining safe, equitable social and
economic working conditions in nursing or midwifery practice respectively
• Safe management of resources: a nurse or a midwife shall safely manage
and maintain assets under his/her control as well as public resources, use
effectively the available materials
c. Relations between a nurse, a midwife and colleagues
• Interdisciplinary collaboration : a nurse or midwife shall sustain
collaboration with colleagues and workers in the multidisciplinary team inorder to promote the health and well-being of each client.
• Appropriate measures to protect people: a nurse or a midwife shall take
appropriate measures in order to preserve the health of individual. Families
and the public when endangered by a colleague or any other person• An incompetent nurse can lead to harmful nursing care
• Sharing and exchanging expertise/ experience: a nurse or midwife shall
share expertise and knowledge with colleagues and exchange views on
various professional issues that may arise in their profession. They have toshare experience in order to better care the clients and resolve raised issues
• Non evasion of responsibilities: a nurse or a midwife shall avoid to
relinquish his/her duties and to overburden his/her colleagues in order to
evade responsibilities. Each nurse must accomplish his/her responsibilitiesand let the assigned to tasks to colleagues
Self-assessment 2.2
After understanding how the nurse shall behave with collegues and duties
1. Explain briefly the importance of collaboration between nurses in caring
patients
2. Explain briefly 2 standards of nurse’s conduct between a nurse and a
client
2.3. Purpose of the professional code of conductLearning activity 2.3
Look at the following video on;
Look also at this picture below and guess what is happening during the nurseand client interactions during the provision of nursing care
1. Is the client looks like well-prepared before nursing intervention? Is the
client relaxed and ready to collaborate with the nurse?
2. Identify at least 3 attitudes of the nurse that a client may depreciate during
the nurse client relationship3. Explain the importance of nurse conduct/ behavior in front of the client
The code of ethics aims to :
• Sets standards for the regulation, monitoring and enforcement of professional
conduct,
• Inform the public about the minimum standards of profession
• Help them understand professional nursing conduct,
• Outline the major ethical considerations of the profession and guides the
profession in self regulation.
• Acts as a non-negotiable standard and reminder of nurses’ commitment to
society.
• The code requires nurses to continue with their learning and evidence-basedpractice
Example of a professional code of ethics: American nurses’ association.(ANA) professional code of ethics
A nurse, in all professional relationships, practices with compassion and respect
for the inherent dignity, worth, and uniqueness of every individual, without consid
erations of social or economic status, the nature of health problems.
The nurse’s primary commitment is to the patient, whether an individual, family,
group, or community.
• The nurse promotes, advocates for, and strives to protect the health, safety,
and rights of the patient.
• The nurse is responsible and accountable for individual nursing practice
• The nurse respects the same duties to self as to others, including the
responsibility
• The nurse preserves integrity and safety, maintain competence, and continue
personal and professional growth.
• The nurse participates in establishing, maintaining, and improving health care
environments and conditions of employment conducive to the provision of
quality health care and consistent with the values of the profession through
individual and collective action
• The nurse participates in the advancement of the profession through
contributions to practice, education, administration, and knowledge
development.
• The nurse collaborates with other health professionals and the public in
promoting community, national, and international efforts to meet health needs
• The profession of nursing, as represented by associations and their members,
is responsible for articulating nursing values, for maintaining the integrity of
the profession and its practice.
• The nurse personal conduct promotes the image of institution and the nursingprofession
Self-assessment 2.3
Mrs. J. works in Emergency and the team of this unit is few as it comprises only
8 persons for days and night duties. Her colleague Mrs.L. was sick and she was
not able to attend the planned night duty and asks Jo to replace her and promise
to do the same for him when she will get better. The unit manager agreed but Jo
refuses. The evening J. past the night in the dancing club and the morning, he
comes to work drunk and he fails to provide care to assigned clients and blame
them without any reason . He has forced a patient to get up without support and
due to dizziness, the client falls down hitting the head on the bed
1. According to the above code of ethics and conduct, identify the
unprofessional behaviors of this nurse?
2. Explain 2 purposes of code of ethics3. Enumerate 3 standards of code of ethics for a nurse
End unit assessment
After covering this unit, understanding the Ethics and Nurse’s professional code
of conduct and how to behave in order to promote client health and avoid any
action against nursing practice, answer to the following questions:
1. The nursing profession is recognized worldwide for having a big number
of staff in health facilities. Each nurse has the obligation to act in
respecting ethical principles. One of the following ethical principles is
not important in nursing profession:
a. They are basis for nurse’s decisions on consideration of consequences
of their acts
b. They are universal moral principles when making clinical judgments.
c. They are only applied to the clinical settings while caring different clients
d. They are professional values to be used when interpreting ethical issues
2. client right, it means that:
his/her care
Autonomy is one of the ethical principles in nursing profession even a
a. A patient has to request the health care provider for a care plan about
b. A patient has his own schedule for his health care
c. A patient should always accept nursing care plan for himself
d. A patient has independent to choose and participate in his / her health
care provision
3. Read carefully the following statement and answer by T if it is true or by F
it is false
a. Nurses should always maintain health consumers’ trust by providing
safe and competent care.
b. A right to confidentiality means that the patients should restreint to
reveal thei information to the healthcare professionals
c. A professional nurse must acquire expertise in carrying out nursing
actions.
d. The nurse code of conduct must be applied only in health institutions
4. Case Study
Mm K is a registered nurse working in the unit where admitted clients are after
surgical operations. She attends the work always on time, attends attentively
the morning staff and handover. When she arrived in the morning, she puts on
her clear uniform, greets clients and observe overall situation of them to identify
if there is no emergent situation. She is respectful for colleagues and clients of
all ages. She is kind to everybody in the work even out of the working hours
when necessary to fulfill assigned tasks; she provides care to all assigned clients
in safe and timely manner. Before accomplishing any nursing tasks, she firstly
obtains the client consent and treats them with kindness and respect. All client
is confident in the nurse K and don’ hesitate to give her any information needed
and to ask any question they have
Read the above case study and answer to the following question.
1. Identify 4 professional nurse values included in the scenario
2. Use an example to illustrate the professional benefit of the nurse’s K
behavior on the nursing profession3. Is there any the code conduct of nurse violated in this case?
UNIT 3: SCOPE OF PRACTICE IN HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS
Key Unit competence:Demonstrate understanding of scope of practice of healthcare professionals.
3.0 Introductory activity
Mr T. is admitted in the unit for patient with tuberculosis where a registered
nurse receives him for assessment. He is coughing, with chest pain and present
transpiration on his front. The vital signs are temperature of 38.80C, Blood
pressure of 102/64 mmHg, heart rate of 112beats/min and respiration of 20
cycles /min. The oxygen saturation is 92%. The health care professionals in that
service include nurses, physicians, epidemiologists, dieticians, radiologists and
pharmacist.How the nurse will give intervention for Mr T.’s treatment?
3.1. Introduction and definitions of associate nurse
Learning activity 3.1
Referring to the above case, the registered nurse and associate nurse are goingto intervene for patient care. T.
1. How will an associate nurse intervene to care for Mr. T.?
Associate Nurse: A nursing associate is a member of the nursing team in England
that helps bridge the gap between health and care assistants and registered
nurses. Nursing associates work with people of all ages, in a variety of settings in
health and social care. The role contributes to the core work of nursing, freeing up
registered nurses to focus on more complex clinical care. It’s a stand-alone role thatalso provides a progression route into graduate level nursing.
Scope of practice: Scope of practice describes the services that a qualified health
professional is deemed competent to perform, and permitted to undertake in
keeping with the terms of their professional license.is used by national agencies and
regulatory authorities to define the parameters of a professional’s activities, those
include procedures, actions and associated processes that a licenced individual ispermitted to perform.
The rationale for such scope of practice definitions for health care professionals
include protection of the public, a general societal understanding of the role and
functions of the practitioner, and the need for role clarity to ensure that practitioners
can practice to the full extent of their capabilities and thereby optimise their
contribution to the provision of an effective and safe public health service.
A Profession is a range of roles, functions, responsibilities, activities and
professional accountability for which a nurse, or midwife is educated, competent,
and has the authority to perform within limits of a particular sphere of practice.
A competence is the ability of the nurse or midwife to practice safely and effectively
to fulfil her/his professional responsibility within one’s own scope of practice.
Nursing activities
According to the International Council of Nurses (ICN 2010): Nursing encompasses
autonomous and collaborative care of individuals of all ages, families, groups
and communities, sick or well and in all settings. Nursing includes the promotion
of health, prevention of illness, and the care of ill, disabled and dying people.
Advocacy, promotion of a safe environment, research, participation in shaping
health policy and in patient and health systems management, and education arealso key nursing roles.
The key factors in nursing and midwifery profession determining factors that must
be taken into account in deciding on the scope of practice of nursing and midwifery
shall be the following: competence, accountability autonomy, and continuing
professional development. Nursing activities that the nurse shall perform amongothers, will include the following:
• Reception and registration of patients/client
• Health education to the client/patient, family and community;
• Provision of safe client/patient care;
• Follow-up of client/patient ;
• Prompt reporting of client/patient information on condition as necessary
• Management of working environment;
• Leadership and management of resources;
• Collaboration with multidisciplinary teams;• General safety of patients/clients, staff and working environment.
According to the scope of practice for the nurse as defined by ministerial order
of Rwanda, the registered nurse shall plan, lead, supervise and evaluate health
promotional activities, preventative care, curative, rehabilitative and palliative
services, managerial educational, training and research roles,
An associate nurse will
• Carry out home visits for delivery of health services to individuals, families and
community including follow-up, education, monitoring of nutrition, hygiene
and sanitation in conjunction with multidisciplinary teams
• Use communication skills for behavioural change of an individual, family and
community
• Communicates appropriate information for effective behaviour change and
maintenance of sound health. More details on the roles of the associate nurseare described in unit one on characteristics of the associate nurse.
Self-assessment 3.1
Define these concepts
1. Scope of practice
2. Clarify the importance of the scope of practice
3. Mr. H is an associate nurse and is working in health centre to provide
care to mothers who bring their children coming for measurement of
weight, height and brachial perimeter, assessment for nutritional status,
receiving food supplements like vitamin A, therapeutic milk and injections
for vaccination. He works with Mrs J. who is a registered nurse who is
in charge of vaccination service. Administers vaccinations to children,
give health education to their mothers about hygiene, breast feeding, and
proper nutrition, she registers the children vaccinated and their weight,
height and brachial perimeter, she observes the availability and safety of
the vaccines, and she do a weekly report to the health centre manager.
a. What activities will be done by Mr H.?b. What are the activities done by Mrs J. ?
3.2. Roles of associate nurse
Learning activity 3.2
Mr B. is allocated in the health centre where Mrs C. a registered nurse works
with him. There are many clients and today is for immunization and they profit
that occasion to provide health education to the mothers who bring their children
for immunization.
1. What activities you think that will be done by Mr B. and Mrs C.?
2. During health education, what topics may be used by Mr B. and Mrs C.?
Associates Nurses alike nurses and other healthcare professionals, can expand
their knowledge and skills with the right training and governance. However, the
intention is for nursing associates to support, not substitute, registered nurses.
They follow the standards for nursing and nursing associate programs.
1. Being an accountable professional: associates nurses act in the best
interests of people, putting them first and providing nursing care that is
person-centered, safe and compassionate. They act professionally at all
times and use their knowledge and experiences to make evidence based
decisions and solve problems. They recognize and work within the limits of
their competence and are responsible for their actions.
2. Promoting health and preventing ill health: associates nurses play a
role in supporting people to improve and maintain their mental, physical,
behavioural health and wellbeing. They are actively involved in the prevention
of and protection against disease and ill health, and engage in public health,
community development, and in the reduction of health inequalities
3. Provide and monitor care: associates nurses provide compassionate,
safe and effective care and support to people in a range of care settings.
They monitor the condition and health needs of people within their care on
a continual basis in partnership with people, families, and caregivers. They
contribute to ongoing assessment and can recognize when it is necessary
to refer to others for reassessment.
4. Working in teams: associates nurses play an active role as members of
interdisciplinary teams, collaborating and communicating effectively with
nurses, a range of other health and care professionals and lay caregivers.
5. Improving safety and quality of care: associates nurses improve the quality
of care by contributing to the continuous monitoring of people’s experience
of care. They identify risks to safety or experience and take appropriateaction, putting the best interests, needs and preferences of people first.
6. Contributing to integrated care: associates nurses contribute to the
provision of care for people, including those with complex needs. They
understand the roles of a range of professionals and carers from other
organizations and settings who may be participating in the care of a person
and their family, and their responsibilities in relation to communication andcollaboration.
Self-assessment 3.2
1. Use examples to illustrate four roles of an associate nurse
2. How does an associate nurse improve safety and quality of care whileproviding nursing care?
3.3. Scope of nursing associate
Learning activity 3.3
Mr P. a 50 year old patient is admitted in Internal Medicine service for a long
lasting gastritis. Mr U. an associate nurse working in that service receives the
patient and took vital signs. The registered nurse came to assess the patient and
calls the medical doctor. The Doctor came and ordered to take samples for labinvestigations and prescribed oral medications to reduce the pain.
1) Which activity will be carried out by an associate nurse in caring this client?
2) Which activity is not in the competence of an associate nurse?3) What a AN will do ?
Introduction
In order to meet the proficiency outcomes outlined in the main body of this document,
nursing associates must be able to carry out the procedures in health and caresetting.
Procedures to be undertaken by the nursing associate
At the point of registration, the nursing associate will be able to safely demonstratethe following procedures:
1. Procedures to enable effective monitoring of a person’s condition
• Accurately measure weight and height, calculate body mass index and
recognize
• Use manual techniques and devices to take, record and interpret vital
signs including temperature, pulse, respiration (TPR), blood pressure
(BP) and pulse oximetry (SO2)in order to identify signs of improvement,
deterioration or concern
• Measure and interpret blood glucose levels
• Collect and observe sputum, urine, stool and vomit specimens, interpreting
findings and reporting as appropriate
• Recognize emergency situations and administer basic physical first aid,including basic life support.
2. Procedures for provision of person-centered nursing care provide
support in meeting the needs of people in relation to rest, sleep, comfort and
the maintenance of dignity:
• Use appropriate bed-making techniques, including those required for
people who are unconscious or who have limited mobility
• use appropriate positioning and pressure relieving techniques
• Take appropriate action to ensure privacy and dignity at all times
• appropriate action to reduce or minimize pain or discomfort
• Support people to reduce fatigue, minimize insomnia and take appropriate rest.
3. Provide care and support with hygiene and the maintenance of skin integrity:
• Observe and reassess skin and hygiene status using contemporary
approaches to
• Determine the need for support and ongoing intervention.
• Identify the need for and provide appropriate assistance with washing,
bathing, shaving and dressing
• Monitor wounds and undertake simple wound care using appropriate
evidence-based techniques.
4. Provide support with nutrition and hydration:
• Assist with feeding and drinking and use appropriate feeding and drinking aids
• Record fluid intake and output to identify signs of dehydration or fluid
retention and escalate as necessary• Support the delivery of artificial nutrition using NGT
5. Provide support with maintaining bladder and bowel health:
• Observe and monitor the level of urinary and bowel continence to
determine the
• Need for ongoing support and intervention
• Assist with toileting, maintaining dignity and privacy and use appropriate
continence products• Care for and manage catheters for all genders
6. Provide support with mobility and safety:
• Use appropriate assessment tools to determine, manage and escalate
the ongoing risk of falls
• Use a range of contemporary moving and handling techniques and
mobility aids
• Use appropriate moving and handling equipment to support people with• Impaired mobility.
7. Provide support with respiratory care: take and be able to identify normalSO2 and oximetry measurements
8. Preventing and managing infection:
• Observe and respond rapidly to potential infection risks using best
practice guidelines
• Use standard precautions protocols
• Use aseptic, non-touch techniques
• Use appropriate personal protection equipment
• Implement isolation procedures
• Use hand hygiene techniques
• Safely decontaminate equipment and environment• Safely handle waste, laundry and sharps.
9. Meeting needs for care and support at the end of life:
• Recognise and take immediate steps to respond appropriately to
uncontrolled symptoms and signs of distress including pain, nausea,
thirst, constipation, restlessness, agitation, anxiety and depression
• Review preferences and care priorities of the dying person and their
family and carers, and ensure changes are communicated as appropriate
• Provide care for the deceased person and the bereaved, respectingcultural requirements and protocols.
10. Procedural competencies required for administering medicines safely:
• Continually assess people receiving care and their ongoing ability to self
administer
• Their own medications. Know when and how to escalate any concerns
• Undertake accurate drug calculations for a range of medications
• Exercise professional accountability in ensuring the safe administration of
• Medicines to those receiving care
• Administer medication via oral, topical routes
• Administer injections using subcutaneous and intramuscular routes and
manage injection equipment
• Administer and monitor medications using enteral equipment
• Administer enemas and suppositories
• Manage and monitor effectiveness of symptom relief medication
• Recognize and respond to adverse or abnormal reactions to medications,
and when and how to escalate any concerns
• Undertake safe storage, transportation and disposal of medicinalproducts.
Self-assessment 3.3
1. Describe five procedures in the scope of practice of an associate nurse2. Which procedures included in preventing and managing infection?
3.4. End Unit Assessment
End unit assessment
Section 1 : Multiple choice questions
Read the following options and choose the right answer
1) Among the following activities which one is not performed by an associate nurse?
a. Vaccination
b. Health education on breast feeding is a health promotional activity
c. Provide oral analgesic drugsd. Provide oxygen therapy
2) Among the following activities which one is in competence of an associate nurse?
a. Give drug for malaria
b. Perform urinary catheter
c. Plan care for the patient in post-operative cared. Evaluate performance of the staff
3) Among the following activities which one is managerial activity?
a. Vaccination
b. Give drug for malaria
c. Give report on numbers of patientd. Evaluate performance of the staff
4) Among the following activities which one is an educational activity?
a. Evaluate performance of the staff
b. Teach nursing student during internship
c. Give drug for diabetesd. Give supplement food to children
Section 2: Read the following statement and answer by T if the
statement is true or F if the statement is False
1. The associate nurse in the unit is not responsible of good utilization of
materials in allocated services
2. The associate nurse carries out home visits for delivery of health services
to individuals, families and community
3. The scope of practice describes the services that a qualified healthprofessional is allowed and competent to perform
Section 3: Case study
Each health institution offers many services to the public and among these
services we have admission of the client in hospitalization unit, or being
cared in outpatient consultation and each client. Receive required care. To
ensure the promotion of the client health and well-being a collaboration of the
multidisciplinary team is very important in caring the client. A client suffering
for a long-lasting gastritis was admitted after road accident and has left an arm
fracture which needs surgical intervention for better management. The client
needs medication to reduce pain, a picture of the fracture and to be prepared forsurgical intervention
According to the scope practice and activities to be carried out in caring this
1. Enumerate activities to be carried out by an associate nurse
2. Clarify how the scope of practice protects the patient as well as thenurse?
SECTION 4. ADDITIONAL ACTIVITIES
4. 1 . Remedial activities
All of you have already been in health institution and observe different activities
carried out by the nurse
a) Identify any 5 activities to be carried out by an associate nurse without
supervision
b) If as an associate nurse you are assigned a task that is not in yourcompetences what are you going to do?
4. 2. Consolidation activities
1) Identify any 4 roles of associate nurse2) By using 4 examples, explain scope of an associate nurse
4. 3. Extended activities
A 20 years old female have been in the health centre as he has headache ,
fever and loss of appetite. The nurse starts by taking vital signs as the client
was looking tired, the client has temperature of 400 Celsius. The nurse decides
to withdraw a blood sample for laboratory investigation then give medication to
reduce body temperature while waiting the result of blood examination . After
having blood results, the client was suffering for Malaria
According to the scope of practice of a nurse:
1. Is the nurse the competence to give treatment to this client? Why?
2. If the client receives appropriate treatment against malaria, what the
nurse should do to prevent the complication and relapse of Malaria?
3. If the client has manifested signs of anemia (insufficient blood in the
body), which health professional is competent to treat adequately thisclient?
UNIT 4 : ETHICAL ISSUES IN HEALTH CARE
Key Unit competence:
To demonstrate good descision making when facing an ethical issue in nursingpractice
4.0 Introductory activity
1. Ms.K. a 12-year-old, has been admitted to an acute care hospital for an
emergency appendectomy. Her parents have been given information about
the surgery and what to expect in the immediate postoperative period. Three
members of the nursing staff have also assured these anxious parents that
they will be notified as soon as K. is admitted to the post anaesthetic area
or sooner if there are complications with the procedure.
After the surgical intervention and while the client was in the recovery room,
the intravenous catheter was leaking fluid and blood out of the vein and the
client bed was dirty and wet . The care giver informs the nurse in charge
of the recovery room but the nurse doesn’t react. Thirty minutes after, the
client was agitated, sweeting and the monitor shows a low blood pressure.
While the nurse come later, she starts by blaming the mother to careless
about the child, she starts to insert a new catheter in the vein, the phone
rings and takes it, the catheter drains the blood in bed and when he resumes
the procedure , the catheter was obstructed . The client and her mother
refuse to be punctured again and complain to the in charge of surgical Unitabout being not being well cared.
In the following examples, identify the ethical principles that would be appropriate
for the nursing staff to employ:
1. Identify the ethical issues that may arise in the above scenario
2. Identify the ethical principles respected in this case3. Explain the ethical principles of nursing care violated
4.1. Ethical principles in nursing practice
Learning activity 4.1
Miss.J. is 16 and she comes in to the community health centre to ask for abortive
method. The nurse asks her about her sexual life and Joan admits that she is
having sexual relations with her father and her mother is not informed. The
nurse is a family friend of Joan’s family and is quite close to Joan’s mother.
Joan’s father is a policeman and is not easy to communicate with him. The
nurse is quite confused by this news and is not sure how to help Joan who is
very anxious and promise to do unsafe abortion before being discovered by her
mother or prefer to die
1. Explain how the nurse is going to apply ethical principles of autonomy,beneficence and non-maleficence for this client
4.1.1. Definition of Ethics
World Health Organization: “ethics is concerned with moral principles, values and
standards of conduct” (WHO, 2016). Ethical issues are event which occur when a
given decision, scenario or activity creates a conflict with a society moral principles.
This may arise with individuals or institution since any of their activities might be
put to question from an ethical point view, Ethics, is one of the cross-cutting themes
relevant and crucial component to all health care professionals (both in pre-service
& in-service).
The principles of ethics included respect for persons autonomy, beneficence, non
maleficence and justice.
The concept of autonomy is an important extension of this principle; acting
autonomously means that the actions are the result of the person’s own deliberation
and choices. The principle of beneficence is often simply stated as an obligation
to act in ways that promote good. The principle of non-maleficence states that we
should act in ways that do not inflict evil or cause harm to others. While a generalprinciple of justice requires that we act in ways that treat people equitably and fairly
4.1.2. Autonomy and Beneficence
Moral principles are useful in ethical decisions about which action is right or wrong
in a situation especially in health care
a) Autonomy: in health care, respect for autonomy refers to the commitment to
include patients in decisions about all aspects of care as a way of acknowledging
and protecting a patient’s independence. the promotion of independent choice,
self determination and freedom of action, the independence and ability to be
self-directed or Self-governance and self-determination in health care provision.
This means that clients are entitled to make decision about what will happen totheir body
Autonomy is a principle and notion of moral decision making which hold that
a rational person (defined by age and mental ability) has the capacity to make
informed and voluntary decisions. Such a person would need to duly consider and
comprehend the risks and benefits of each choice, based on clear informationand without any controlling influences (e.g., fear, coercion, bribery).
Autonomy is also the capability to have input into determining your own well
being (Purtilo & Doherty, 2016), or self-rule that is free from both controlling
interference by others and limitations that prevent meaningful choice’ (Beauchamp
& Childress p.101)
For example, when a patient faces surgery, the surgeon has an obligation to
review the surgical procedure, including risks and benefits, out of respect for
the patient’s autonomy. The consent that patients read and sign before surgery
documents this respect for client autonomy.
Upholding autonomy - Supporting self-determination in others and their
freedom to choose what constitutes a good quality of life for them (Sasson,2000)
b) Beneficence: Beneficence is doing or active promotion of good, refers to taking
positive actions to help others. The principle of beneficence is fundamental to
the practice of nursing and medicine and refer to all forms of action intended to
benefit others. This is done by providing health benefits to the clients, balancingthe benefits and risks of harm, considering how a client can be best helped.
Example: a child
who has fever has a risk of developing seizures. And
respiratory arrest, if you reduce fever you prevent seizures and promote childhealth (doing good).
In the line of beneficence, Fundamental responsibilities of nurses are
1. To promote health
2. To prevent illness
3. To restore health
4. To alleviate suffering(ICN, 2012; Sezibera & Karugarama, 2011)
4.1.3. Non-maleficence and Justice
a) Non-maleficence: Maleficence refers to harm or hurt; thus no maleficence is
the avoidance of harm or hurt. In health care, ethical practice involves not only
the will to do good, but the equal commitment to do no harm to the client. The
health care professional tries to balance the risks and benefits of care while
striving at the same time to do the least harm possible. The nurse must weigh
the harm against the expected benefit and avoiding deliberated , risk of harm
that occurs during the performance of nursing actions.
Non-maleficence is a principle which holds that no intentional or predictable harm
or injury should be charged against a person, either through acts of commission
or omission. The concept of intention is important in an understanding of non
maleficence. It holds that if a person intended to not harm first, but the end result
was harmful, he/she did not act immoral. Non-maleficence is also intentionally
refraining from actions that contribute to harm (Beauchamp & Childress, 2013;
Purtilo & Doherty, 2016)
b) Justice: justice refers to fairness. Most often used in discussions about access
to health care resources, including the just distribution of resources. Justice is
the promotion of equity or fairness in every situation a nurse encounters. Care
must be fairly, justly, and equitably distributed among a group of patients as itcan be compared to fair distribution of goods in the society
Self-assessment 4.1
Mr.K. is a senior nurse working in Internal Medicine unit for more than 15 years.
He has acquired experience in caring different clients suffering for different
pathologies. A client suffering for hemiplegia (paralysis of one side of the body)
was admitted for further investigations and better management of hemiplegia.
The blood sample for laboratory investigations must be withdrawn, the client
gives consent for procedures but don’t consents for urinary catheter as she has
urinary incontinence. While the nurse has inserted a catheter in the vein, the
phone rings and takes it, the catheter drains the blood in bed and when he
resumes the procedure, the catheter was no longer draining out blood. The client
refuse to be punctured again and complain to the in charge of Unit about beingnot being well cared by the nurse
1. Enumerate the ethical principles what were not respected
2. How can we qualify the behaviour of the nurse in the above scenario
3. Was the urinary catheter necessary for the client? If yes, how can weproceed to convince the client?
4.2. Ethical issues in nursing profession
Learning activity 4.2
Mrs N. a 50 years old male patient is admitted in surgical ward for post operative
care, he has a body temperature of 37.4 Celsius degrees, a heart rate of 96beats
per minute, SO2 of 98% and blood pressure of 102/62 mmHg. He undergone an
operation for removal of appendix which was infected and the surgical procedure
was successful. However, this patient has no health insurance, he was treated
due to the emergency situation and currently, the social agent discovered that
he is not able to pay for the surgical intervention as well as for other medicines
and procedures required after the operation.
1) What principle is challenged for that patient?
2) How can a nurse will intervene to respond to the needs of that patient
without compromising to the financial policy of the health care institution?
Ethics are essential to the integrity of the nursing profession as it helps ensure better
patient care. Nursing is a highly fast-paced job with new challenges arising daily
and nurse managers across the country all dealing with similar ethical dilemmas.
Many of these situations are rooted in protecting patients’ rights, adequate staffing,
advanced decision-making, and quality patient care.
• Informed Consent
Informed consent can sometimes be an ethical battle for nurses. There is a concern
as sometimes patients do not feel comfortable asking questions and giving consent
without fully realizing the implications of their treatment. If patients feel supported
and trust their doctors and nurses, they are more likely to follow a treatment plan and
experience better outcomes. Nurses should ensure that patients fully understand
all the facets of their treatment plans. The details include knowing all the risks
and the layout of how a procedure will take place or how certain medications
and treatments will affect them. Therefore, healthcare workers should take every
measure to assure their patients understand the treatment plan to obtain informedconsent securely.
• Protecting Patient Privacy and Confidentiality
Patient privacy and confidentiality are significant ethical issues faced by nurses. If not
done correctly, this can have legal ramifications and result in severe consequences
for healthcare professionals. Although nurses must protect their patient’s rights
and act in their best interest, they are still obligated to respect patient autonomy.
Patient autonomy, the right of patients to independently make decisions about their
care based on personal or cultural belief systems, is a prime principle of nursing
and should be respected by all healthcare professionals. With patient autonomy,
patients have the right to refuse medications, treatments, or procedures. Although
this may conflict with suggestions made by nurses and doctors, nurses will still
have to respect this decision and operate accordingly.
• Shared Patient Decision-Making
Shared decision-making is a far more ethical approach to patient care than years
ago when healthcare professionals fully controlled patient treatment. Share
patient decision-making extends patient autonomy where patients and healthcare
professionals work together to make the best decision possible regarding patient
care. With shared decision-making, patients and healthcare professionals have
open conversations about a patient’s background, values, beliefs, and culture,
building a trusting relationship between patient and doctor. A good relationship will
facilitate nurses and healthcare professionals to get patients to communicate and
cooperate properly. When patients are actively involved in decision-making, they
are more likely to be satisfied with their care and trust the doctor’s treatment plans.
• Addressing Advanced Care Planning
Advanced care planning is always a difficult conversation for healthcare professionals
to have, predominately when end-of-life care conversations surround it. These
conversations are between patients and doctors when they need to make plans
for their future health care if they pass away or are left too ill to make their own
decisions. Patients will explore, discuss, and document their personal preferences
regarding their healthcare. This process helps them identify their personal goals
and values about future medical treatment. They also will share who they would like
to make decisions on their health care if they can’t make decisions for themselves.
For example, an issue might be if a patient has asked not to be on a ventilator, but
their immediate family demands. Despite the problematic scenario, nurses mustput the needs and wants of patients first, especially in end-of-life care.
• Inadequate resources and staffing
When medical facilities have scarce resources, patients are at risk of not receiving
proper care leaving nurses to make difficult decisions. Hard decisions may also need
to be made when facilities are faced with inadequate staffing levels. When there is
not enough staff for patients, nurses do not have the time to do everything needed
for each patient. Patient needs can include recovery times or even addressing the
patient’s emotional and physical needs. A nurses’ moral obligations to patients are
compromised due to work restraints and stress overload. They are left with mentalstruggles trying to decipher where they should focus their priorities.
Self-assessment 4.2
1. What are the 5 common ethical issues in nursing practice?
2. Explain any possible 4 factors that may originate a conflict of interest may
occur in nursing practice.3. What should nurse do in case conflicts are occurring in healthcare?
4.3. Health System and Ethical Challenges
Learning activity 4.3
Mrs.T. aged 68 years old is admitted in Accident and Emergency unit ward for
pulmonary oedema and presents respiratory distress with dyspnoea SO2 65 %
and is in unconscious status. Mr C. the nurse on the shift has no enough bed and
is obliged to put the patient near the other patient who was treated from Covid 19
and tested negative with rapid test but yet the final result from a confirming test
is not yet found and is waited in two hours.
1) What are the ethical issues presented in this situation G.?2) Relate the ethical issue with the ethical principle challenged in this case?
a) Health system challenges
Health system policies or challenges can sometimes contribute to situations of
ethical challenges
Examples:
• Shortage of healthcare professionals
• Large number of patients
• Health insurance payment structure: patients’ lack of health insurance or
money, delays in payments to hospital
• Inequity in distribution of equipment and materials, etc.
b) Challenges and Emerging Health Systems Issues in Rwanda
• Insufficiency of trained health care providers
• Lack of integration and accessibility of NCDs services at all levels of the
healthcare system,
• Specialized NCDs services,
• High NCDs costs and lack of funds mobilization frameworks at global, regional
and national levels,
• Lack of basic equipment and specialized infrastructure for NCDs,
• Essential drugs and advanced NCDs treatment, and
• Lack of proper NCDs data management
All of them they can indirectly contribute to ethical challenges (Yiika Sejdiu, 2018)
c) Dealing with Ethical Issues in Nursing
Every nurse should become familiar with the Code of Ethics for Nurses. The
hospital’s ethics committee, the hospital code of conduct or a variety of educational
resources. Some organizations have an ethics consultation service whose members
assist staff to discuss about any ethical issue that occurs.” Also, having a diverse
group of nurses allows an environment where conversations on ethical issues occur
within their units. These open dialogues will benefit the patients as they feel more
welcomed and recognized by their hospital staff. Example: Another ethical dilemma
for nurses is the refusal of medication and vaccinations from patients and their family
members. Vaccinations often become a high debate, especially when addressing
childhood vaccinations. Although it is a parent’s right to refuse immunization for
their child, healthcare professionals must share the health risks this poses for the
future of their child’s health. Nurses must provide them with accurate information
while also respecting boundaries.
MORAL model to address ethical issues
Usually, the MORAL model is used likely the easiest model to use in everyday
clinical practice site, consisting of similar constructs as the nursing process, the
MORAL model has five steps:
1) Massage the ethical issue: develop a full understanding of the ethical conflict
and gather information about the situation
2) Outline the options
3) Resolve the ethical issue
4) Act by applying the chosen option,
5) Look back and evaluate.
Health policy concerns the choices that a society or a part of society makes in
regard to the health and welfare of its citizens. Nurses are frequently involved in
health policy issues in everyday clinical settings.
E.g.: Insufficiency of nursing staff, limited prescription authority legalized abortion
Moral distress, defined as a painful state of imbalance seen when nurses make
a moral decision but are unable to implement the decision because of real or
perceived institutional constraints, can be positively addressed in the workplace.E.g.: patient who missed the oxygen due to high demands in period of COVID -19.
Self-assessment 4.3
1) What are the challenges occurring in health system that may lead to
ethical challenges in nursing?2) Provide 5 examples of issues in health system occurring in Rwanda
4.4. End unit assessment
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. The essence of doing justice refers to One among the following
a. Giving money to poor patients for buying drugs
b. Provide appropriate care without discrimination
c. Identify particular cases for social support
d. Bring to court the nurses who are unethical
2.The no maleficence principle is applied in One among the following actions
a. Avoid to give injection for not harming the patient
b. Check and verify the correct drug and dose before injection
c. Avoid to report a nurse who is unethical to the patient
d. Hiding the patient who is vulnerable to the drug abuse
3.The ethical issues are raised due to which among the following situations
a. Insufficient staff in nursing
b. Lack of support for professional development
c. Difficulties in Health system policy
d. All of the above
4. Ethical dilemma refers to one among the following
a. Informed consent
b. Disclosure of medical conditions
c. Incompetence among peers
d. All of the above
5. The principle of beneficence refers to One among the following nursing
activities
a. Communicate effectively and friendly to the colleagues
b. Performs the nursing care to the assigned patients
c. Provide support when the number of nursing staff is not sufficient
d. All of the above
6. The following actions are not respecting the principle of No maleficence Except
a. Absenteeism
b. Reporting to the doctor when there is error on the drug prescription of the
patient
c. Injecting the wrong dose to the patientd. Not documenting the data examined on the patient’s file
7. The principle of autonomy is applied in which One of the following situations?
a. Provide health education
b. Ensure patient privacy
c. Explain the informed consent formd. Provide the drug prescribed
8. Among the following reasons, One is Most appropriate to justify why nurses
should respect clients
a. Respect the culture
b. Religious customs
c. Inspire trust from the client and the publicd. Practice citizenship
B. SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
1. Define ethical issue in nursing?
2. Illustrate with an example an ethical issue
3. The challenges occurring in health system that may lead to ethicalchallenges in nursing?
C. Additional activities
1. Remedial activities
1. Explain briefly the meaning of ethics in health care
2. Enumerate 4 qualities / traits of good health professional that you would
like to see on the nurse who is caring a friend of yours
3. What are the primary moral principles of nursing practice?
2. Consolidation activities
a. According to what you have observed in health institution in which you
have been or what you have heard in discussing with your colleagues,
What must be the causes of unethical behaviour?
b. As a student in the program of associate nurse, after learning the ethical
issues which may arise during provision of nursing care, identify at least 4common ethical issues which may occur in working place.
3. Extended activity: You are working in health centre receiving clients I
suffering for different health problems which you have adults, middle ages
clients and under 15 years clients and you haven’t sufficient desk to give a
seat to everyone
a) Which clients are you going to select and according more respect?
b) What can you do to improve the working environment and the wellbeing
of clients?c) Which nurse’s value are you going to promote
References
• Elizabeth Manias, Fiona Geddes, Bernadette Watson, Dorothy Jones and Phillip
Della Perspectives of clinical handover processes: a multi-site survey across
different health professionals Journal of clinical nursing 2015 25, 80–91, Doi:
10.1111/jocn.12986
• Doreen M. Towsley-Cook Terese and A. Young 2007 Ethical and legal issues for
imaging professionals Mosby Elsevier Philadelphia US p.2-8
• Barbara Cherry Susan R. Jacob Contemporary nursing issues, trends, and
management pp.411
• Nico Nortjé Willem A. Ho mann Jo-Celene De Jongh Editors 2018 African
Perspectives on Ethics for Healthcare Professionals SPRINGER
• Sue West, Senior Nursing Education Adviser, 2019 Blog: https://www.nmc.org.
uk/news/news-and-updates/blog-whats-a-nursing-associate/
• https://www.google.com/
• https://pmi.edu/blog/march-2021/what-5-qualities-make-a-good-nursing
assistant
• Bandman Elsie L , ( 2004 ) Nursing Ethics Through the life span , 3rd edition ,
Stamford Connecticut
• Zane Wolf ( 2012) , Measure nursing: official journal of the Academy of Medical
Surgical Nurses, 21(1):16-22,6
• Doreen M.Towsley-Cook, Therese A. Young ( 2007 ) Ethical and Legal issues for
Imaging Professionals , Mosby, Inc affiliate Elsevier Inc.
• Ian E Thompson ; Kath M Melia et al (2006 ), Nursing Ethics, 5th Edition ,
Churchill, Livingstone Elsevier
• Rwandan regulatory body Nursing Council of Nurses and midwives (NCNM)
adopted by the constitution of the Republic of Rwanda of 04 June, 2003 and
the Law no 25/2008of 25/7/2008 establishing the National Council of Nurses and
Midwives and adopted by the cabinet in its session of 09/07/2010
• International Council of Nurses (ICN) in Sao Paulo (Brazil) in July 1953 and
revised by the same council in Frankfurt (West Germany) in June 1965.
• The NMBI (2014) Code of Professional Conduct and Ethics
• Bord Altranais agus(2007) Code of Professional conduct for Registered Nurses
and Registered Midwives , Nursing and Midwifery Board of Ireland13. Legal
Principles and the Limits of Law Joseph Raz in https://core.ac.uk/download/
pdf/160248327.pdf
• BASAVANTHAPPA , BT ( 2006) , Fundamentals of nursing, 2nd edition , pages
99- 121, JAYPEE BROTHERS MEDICAL PUBLISHERS, SAINT LOUIS USA
• Margaret Keatings, O’ Neil B. Smith ( 2000), Ethical and Legal Issues in
Canadian Nursing, 2 nd Edition, Saunders Elsevier
• Universal Declaration of Human Rights (United Nations, 1948) which proclaims
that the basis for freedom, justice and peace is founded on the recognition of
the inherent dignity and of the equal and of the absolute rights of human beings.
• The European Convention on Human Rights (Council of Europe, 1998), the
Irish Constitution (Government of Ireland,1937) and the Equal Status Acts
(Government of Ireland, 2000-2008)
• Bord Altranais agus(2007) Code of Professional conduct for Registered Nurses
and Registered Midwives , Nursing and Midwifery Board of Ireland
• ANA’s Principles for Nursing Documentation Guidance for Registered Nurses
2010
• The NMBI (2014) Code of Professional Conduct and Ethics in the Irish health
care context
• Code of Professional Conduct and Ethics for Registered Nurses and Registered
Midwives Draft October 2013
• Potter and Perry (2017) , Fundamentals of nursing , 8th edition, Elsevier, pages
287 -29
• American Nurses Association. (2015b). Nursing: Scope and standards of
practice (3rd ed.). Silver Spring.
• THOMSON Reuters (2021).Nursing and Midwifery Council: sanctions: https://
uk.practicallaw.thomsonreuters.com/w-003-7294?transitiontype=default&conte
xtdata=(sc.default)&firstpage=true
• STEFEN P.O Keef (2021), https://www.gomedmalohio.com/practice-areas/
medical-malpractice/hospital-or-nursing-negligence/
• http://www.nmbi.ie/Standards-Guidance/Code)
• http://www.nmbi.ie/Standards-Guidance/Code
• https://www.google.com/search?q=Role+of+the+regulatory+bodies+in
+nursing+profession+according+to+ICN&sxsrf=AOaemvLte5VkNKKS1_
3IH22boDuUpnKCeg%3A1631195576019&ei=uBE6YfBX1NSBBtWSpSA&oq
=Role+of+the+regulatory+bodies+in+nursing+profession+according
• https://www.slideshare.net/lindadevi1/legal-issues-in-nursing-ppt-11889901 ;
• https://www.google.com/search?q=meaning+of+bad+nursing+practice&biw=
1120&bih
• https://www.medleague.com/same-day-surgery-nursing-malpractice/
https://rnspeak.com/nursing-negligence
• https://www.google.com/search?q=what+is+the+meaning+of+nursing+practice
&oq=whait+is+the+meaning+of+nursing+practice&aqs=ch
&oq=
• https://www.google.com/search?q=what+is+the+meaning+of+nursing+practice
&oq=whait+is+the+meaning+of+nursing+practice&aqs=ch
• https://www.google.com/search?q=what+is+the+meaning+of+nursing+practice
• https://www.google.com/search?q=Role+of+the+regulatory+bodies+in+nursing+
profession+according+to+ICN&sxsrf=AOaemvLte5VkNKKS1_3IH22boDuUpnK
Ceg%3A1631195576019&ei=uBE6YfBX1NSBBtWSpSA&oq=Role+of+the+
regulatory+bodies+in+nursing+profession+according+to+ICN&gs_lcp=Cgdnd3
Mtd2l6EAw6BwgjELADECc6BwgAEEcQsAM6BwgjELACECc6BAgAEA06C
AghEBYQHRAeOgcIIRAKEKABOgQIIRAVSgQIQRgAUJBjWI_zAWDOjAJoA
XACeAGAAZIGiAH0iAGSAQozLTMuNi4xNy40mAEAoAEByAEJwAEB&
sclient=gws-wiz&ved=0ahUKEwjwk_iGhfLyAhVUasAKHVVJCQQQ4dUDCA4
• http://www.nmbi.ie/Standards-Guidance/Code ;
• https://www.google.com/search?q=RNMU&oq=RNMU&aqs=chrome..69i57.
6640j0j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8
• https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/019394599101300407?journalC
ode=wjna
• UK NMC We regulate nursing associate 2020 https://www.nmc.org.uk/about-us
/our-role/who-we-regulate/nursing-associates/
• Standards of proficiency for nursing associates 2018 http://www.nmc.org.uk/ ;
• International Journal of Caring Sciences September-December 2015 Volume 8
| Issue 3| Page 830 www.internationaljournalofcaringsciences.org Review
Article Ethical Issues and Dilemmas Encountered in Nursing Practice in
Turkey Nevin Utkualp, PhD Lecturer Uludağ University.
• Basso-Musso L. Nursing and the resolution of ethical dilemmas. Invest Educ
Enferm. 2012;30(2):260-268
• Abeer M. Zakaria , Wafaa F. Sleem and Abeer Mohamed Seada, 2016.
Effectiveness of ethical issues teaching program on knowledge,
ethical behaviour and ethical stress among nurses, Journal of Nursing
Education and Practice 2016, Vol. 6, No. 7doi: 10.5430/jnep.v6n7p125http://
jnep.sciedupress.com
• American Nurses Association, 2010.Code of ethics for Nurses with interpretive
statement,
• https://www.princetonhcs.org//media/princeton/documentrepository/
documentrepository/nurses/code-of-ethics.pdf
• Saima Hamid, Rabia Kanwal, Mohammad Hamza Bajwa, Sadaf Khalid and
Henna Mubarak 2016. Ethical Issues Faced by Nurses during Nursing Practice
in District Layyah, Pakistan. Diversity and Equality in Health and Care 13(4)doi:10.21767/2049-5471.100068
