Topic outline
Managing ICT for Project-Based Learning (PBL)


By the end of this unit you should be able to manage student project-based learning activities in a technology-enhanced environment to support collaboration.
Learning Objectives
- Know and understand how to facilitate project based learning using ICTs;
- Manage project based learning activities in a technology environment;
- Identify and describe ICT Tools that support Project Based Learning;
- Describe how to structure real-world problems into a project design.

4 hours


This unit is to be studied online. Online facilitators will provide support but all resources, activities and communication with peers and the facilitator will take place using the LMS tools.
Introduction

Click on the video below to watch a quick introduction to Unit 11: Managing UCT for Project-Based Learning (PBL).

In a previous unit we looked at how ICT can support traditional pedagogy, that is teacher led instruction, In this unit we will look at how we can make the students responsible for their own learning. We will investigate Project Based Learning (PBL). It's important that teachers know and understand how to prepare PBL lessons based learning activities in a technology-enhanced environment to support collaboration.
In project-based learning (PBL), students work in groups and learn about a subject by addressing a real-world problem or issue. The groups of students then create presentations to share with the rest of the class what they have learned. Unlike conventional teaching approaches, which rely on the teacher to direct learning and control information flows, project-based learning gives students the freedom to explore a subject in a way that suits their learning needs. Teachers and advocates of project-based learning believe that this form of learning enables students to:
- Develop greater knowledge about a subject;
- Become more motivated to learn;
- Improve their research and problem-solving skills;
- See how what they are learning at school can be used in real life.
Overview of the PBL methodology
 45 minutes
45 minutes

How do we make our students engaged learners? What about challenging them to resolve a real world problem? Let them be active learners rather than passive. Admittedly this takes some time and lots of planning to ensure that they do make some progress. Project-based learning also means that you need to have a different role. No longer the 'authority' in terms of content and information but rather a 'facilitator' of learning. Let's investigate further.

Study the resources below that provide an overview of the PBL methodology. Ensure that you are aware of the the 5 different phases within PBL. Also differentiate between project-based approaches and conventional classroom teaching.
Click on the links below to read more about PBL:
Edutopia. (2015). Project-based Learning URL
Coffey, H. (2013). Project-based Learning. Learn NCURL
In light of what you have seen and read in the resources above consider the diagram below. Does it encapsulate the PBL approach to learning?.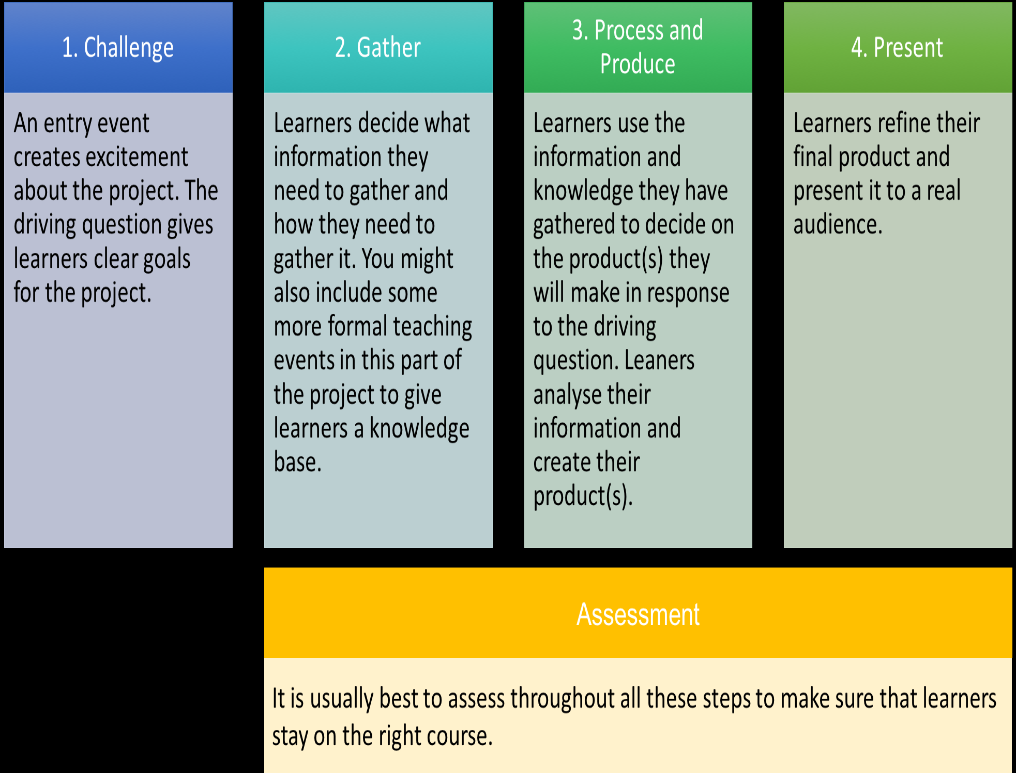
PBL lesson planning
 90 minutes
90 minutes

Don't lose focus on the curriculum. PBL lessons still need to address the specific objectives as stated in the curriculum. Its your job to balance the student's desire to investigate on their own and the need to address the needs of the curriculum. Let's have a go at getting this balance right.

- What aspect of your syllabus lends itself to a PBL approach to learning? Study the curriculum and identify a suitable area.
- Use the forum below to discuss your ideas for a PBL lesson with your peers. Provide support by endorsing and querying their posts too.
- Produce a Project Based Learning PBL lesson plan using the template lesson planner provided. There is a section on ICT components so make sure you also identify what digital tools you will employ to support the PBL lesson.
- Save the document as we will come back to it in future activities.
PBL ideas Forum
Constructive feedback
 60 minutes
60 minutes

The theoretical foundation of peer feedback is the social constructivist view of learning. This view emphasizes learning as a social activity and asserts that learners’ interactions with people in the environment stimulate their cognitive growth (Schunk, 2008).
During the peer feedback process, learners present their ideas to peers, receive and provide constructive feedback, and revise and advance their thinking for solving complex problems. Through this interactive process, learners collaboratively construct knowledge when they clarify their own thinking and gain multiple perspectives on a given issue, which enables the creation of more comprehensive and deeper understanding toward learning.
Click on the link below to read more about Peer Assessment.
- Access the reading below and consider its approach to PBL
- Look at the lesson plan you developed in the previous activity. Can you incorporate peer communication as a component of the plan?
Facilitating a PBL project
 15 minutes
15 minutes

Consider the teacher’s role in facilitating a Project Based Learning (PBL) project.
Project-based learning is only possible in classrooms where teachers support students by giving sufficient guidance and feedback. The teacher must thoroughly explain all tasks that are to be completed, provide detailed directions for how to develop the project, and circulate within the classroom in order to answer questions and encourage student motivation.
In order to create successful units focused on project-based learning, teachers must plan well and be flexible. In this approach to instruction, teachers often find themselves in the role of learner and peer with the students. Teachers can assess project-based learning with a combination of objective tests, checklists, and rubrics; however, these often only measure task completion. The inclusion of a reflective writing component provides for self-evaluation of student learning.


Click on the link below to read more about the teacher's role in PBL.
Tips for Teachers- Becoming a Facilitator URL
Teacher's role as a facilitator in a Project-Based Learning File
 30 minutes
30 minutes
 Read the instructions below in order to complete your portfolio activity.It is time to pull your PBL lesson plan together.
Read the instructions below in order to complete your portfolio activity.It is time to pull your PBL lesson plan together.We have done our initial planning so let us review the plan and start to build this lesson.
Your first consideration is to reassess the effectiveness of your questions. Remember that PBL is investigative by nature and the questions you pose must engage and galvanise the class into action. In some respects the question(s) is the engine behind the PBL strategy but questioning is essential to the teaching process whether you are using PBL or not.
Note: This assignment is a recommended Portfolio Task and should be submitted on completion of this course.1. Reflect on the quality of the questions you have posed for the project. - Are they real world questions?
- Do they tie your subject or teaching area to the students’ experiences? Research has shown that if you link your curriculum content to the local context, students are more likely to see the relevance in your subject and be more engaged in the activities you set for them.
- Another consideration is, have you posed an open or closed question?
2. Now consider your role as facilitator. Can you construct the structure of the lesson? For example what resources will you need to help the students investigate your questions? - Are there sufficient books in the library?
- If so, which ones are worthwhile? Identify them.
- Can you book time in the library for the students?
- Will the children have access to the Internet? Do you need to book the computer lab?
- If so, can you focus the students on a number of quality sites? Which ones?
- Are you going to encourage them to look for information at home?
- If so, should you alert the parents to their needs?
- Are you going to encourage them to create their own evidence using digital cameras, video or cell phones to document their environment?
- Again are you going to alert parents to this requirement?
3. Once they have collected data you will need to facilitate the reporting of their findings and helping them draw conclusions. - Do the students have a range of tools to help them organize their data?
- Do they have a range of choices on how to report to the class? What is acceptable?
- How will you organize them so that they have opportunities to work together to organize their reports?
- Are the students required to present their findings?
4. In light of all the arrangements required above don’t forget that the assessment strategy you designed must also be satisfied. - Were the students made aware of the assessment strategy early in the process?
- Were there opportunities for formative assessment so that they could feed what they had learned back into the learning process?
- Does the final reporting and summative assessment work cohesively?
Using the PBL planning template provided below, or alternatively adjust the version you have been working on in previous activities, finalise a PBL lesson plan and upload the document using the assignment submission tool below as part of your portfolio
PBL Planning TemplateFile42.5KB
Portfolio Assignment #11

The following Open Education Resources (OER) have been adapted to create this unit on Manage ICT for Project Based Learning Goals
- Great School Partnership. (2013). Project-based Learning. CC BY NC SA. Available online at http://edglossary.org/project-based-learning/
- Coffey, H. (2013). Project-based Learning. LearnNC. CC BY NC SA. Available online at http://www.learnnc.org/lp/pages/4753
- COL/CCTI. (2017). Module 6: Project Approaches to Learning with ICT. CC BY SA. Available online at: http://schoolnet.org.za/CoL/ACE/course/pbl/activities/pbl.index.htm
- OER4schools. (2013). Unit 5: Enquiry-based learning and project work. CC BY SA. Available online at: http://oer.educ.cam.ac.uk/wiki/OER4Schools/Enquiry-based_learning_and_project_work
- Study Guides & Strategies. (no date). Problem Based Learning. Available online at: www.studygs.net/pbl.htm
- COL/Guyana KD. (no date). Module 3, Unit 3: PBL Cooperative and Collaborative Strategies. CC BY. Available online at http://colccti.colfinder.org/sites/default/files/guyana/pages/KD/Module03/Unit01/01.html
- MoE Kenya. (2016). ICT Tools to Support PBL. Kenyan ICT CFT Course. Available online at: http://kictcft.nba.co.za/course/view.php?id=6
Open License
All materials in this ICT Essentials for Teachers Course unit is licensed by the Ministry of Education, Rwanda under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License
- Know and understand how to facilitate project based learning using ICTs;
